Chapter 26. Configuring automated unlocking by using a Tang key in the web console
You can configure automated unlocking of a LUKS-encrypted storage device using a key provided by a Tang server.
Prerequisites
- The RHEL 9 web console has been installed. See Installing the web console for details.
-
The
cockpit-storagedandclevis-lukspackages are installed on your system. -
The
cockpit.socketservice is running at port 9090. - A Tang server is available. See Deploying a Tang server with SELinux in enforcing mode for details.
Procedure
Open the RHEL web console by entering the following address in a web browser:
https://<localhost>:9090Replace the <localhost> part by the remote server’s hostname or IP address when you connect to a remote system.
- Provide your credentials and click Storage. In the Storage table, click the disk that contains an encrypted volume you plan to add to unlock automatically.
In the following page with details of the selected disk, click + in the Keys section to add a Tang key:
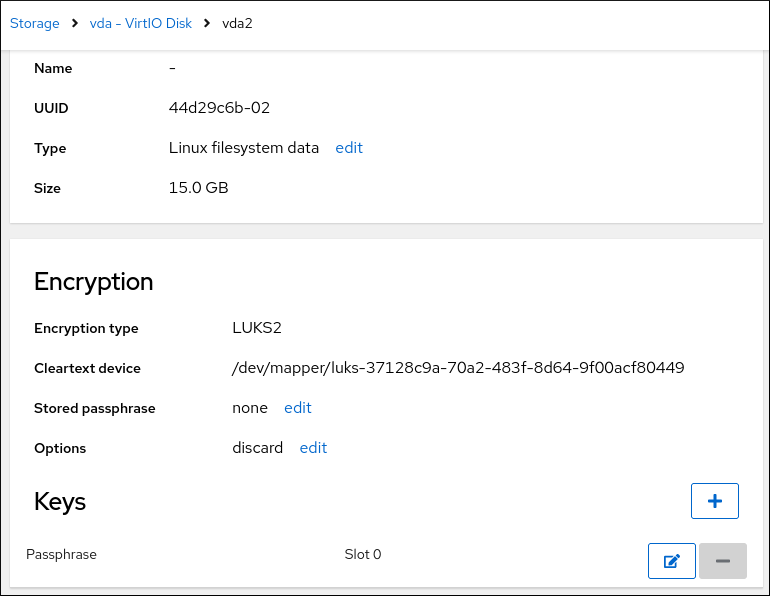
Select
Tang keyserverasKey source, provide the address of your Tang server, and a password that unlocks the LUKS-encrypted device. Click Add to confirm: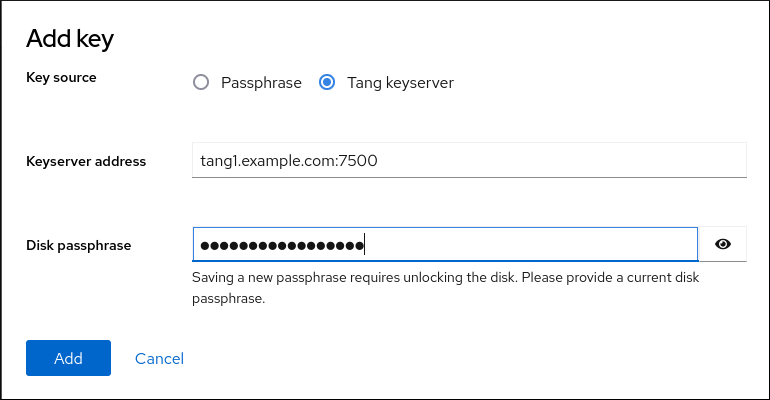
The following dialog window provides a command to verify that the key hash matches.
In a terminal on the Tang server, use the
tang-show-keyscommand to display the key hash for comparison. In this example, the Tang server is running on the port 7500:# tang-show-keys 7500 x100_1k6GPiDOaMlL3WbpCjHOy9ul1bSfdhI3M08wO0Click Trust key when the key hashes in the web console and in the output of previously listed commands are the same:
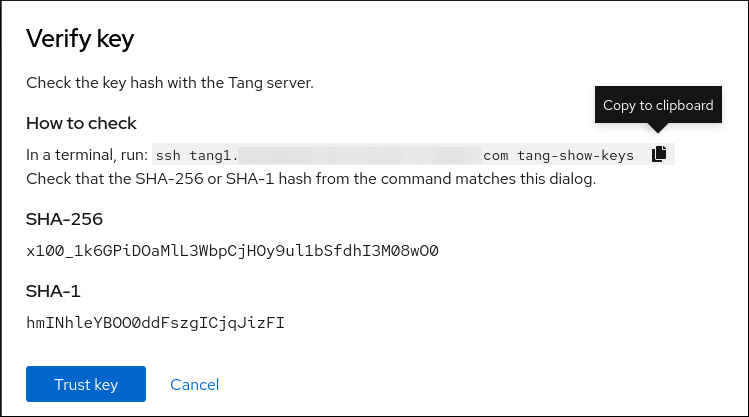
-
In RHEL 9.2 and later, after you select an encrypted root file system and a Tang server, you can skip adding the
rd.neednet=1parameter to the kernel command line, installing theclevis-dracutpackage, and regenerating an initial RAM disk (initrd). For non-root file systems, the web console now enables theremote-cryptsetup.targetandclevis-luks-akspass.pathsystemdunits, installs theclevis-systemdpackage, and adds the_netdevparameter to thefstabandcrypttabconfiguration files.
Verification
Check that the newly added Tang key is now listed in the Keys section with the
Keyservertype: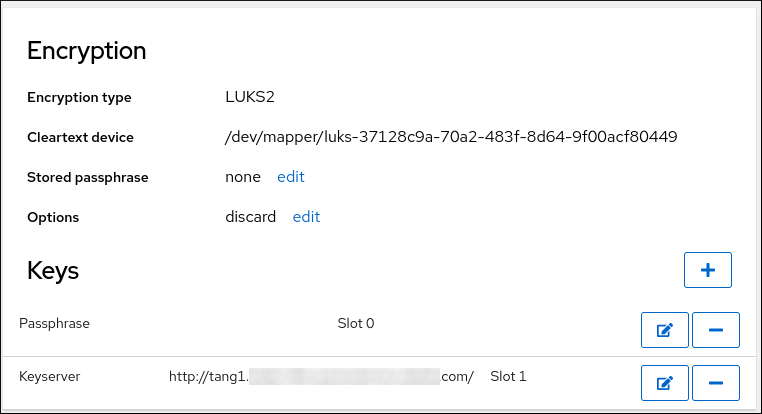
Verify that the bindings are available for the early boot, for example:
# lsinitrd | grep clevis-luks lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 48 Jan 4 02:56 etc/systemd/system/cryptsetup.target.wants/clevis-luks-askpass.path -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/clevis-luks-askpass.path …
Additional resources

