The declarative authentication provider persists in RHACS despite the configuration stanza being removed from the Central CR
Environment
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes
- 4.x
Issue
In Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes, an auth provider created via a declarativeConfiguration is not deleted when it's stanza is simply removed from the Central CR.
-
For example, consider an auth provider defined via the following
auth.yaml:name: OCP uiEndpoint: central_endpoint:443 groups: - key: group value: ocp-admin role: Admin openshift: enable: true -
Then used to create the ConfigMap
declarative-configs:$ oc create cm declarative-configs --from-file=auth.yaml -
And finally implemented in the Central CR:
$ oc get centrals.platform.stackrox.io/stackrox-central-services -o yaml | yq .spec.central adminPasswordSecret: name: acs-password declarativeConfiguration: configMaps: - name: declarative-configs exposure: loadBalancer: enabled: false port: 443 nodePort: enabled: false route: enabled: true persistence: persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: stackrox-db -
After Central restarts, the auth provider is visible in the RHACS UI:
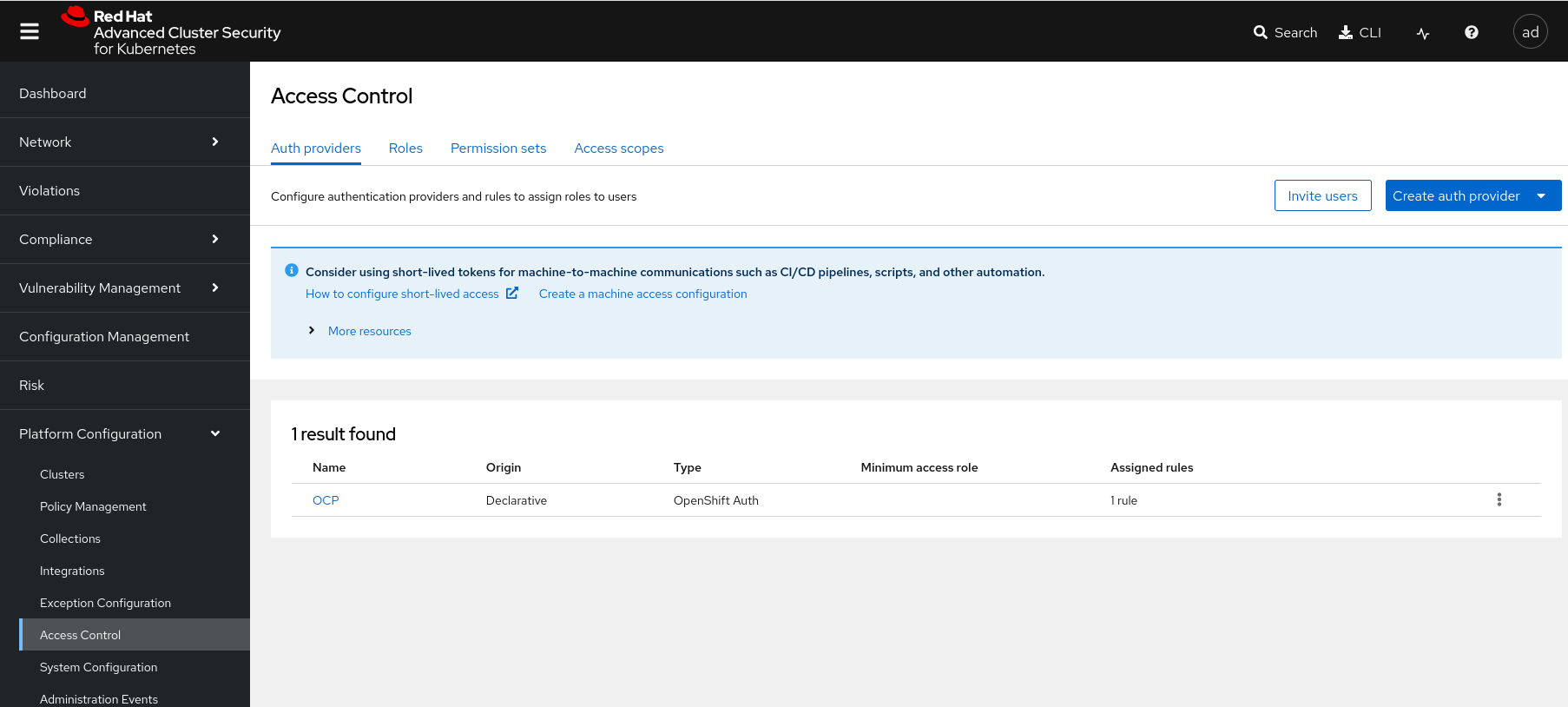
-
Later, an attempt is made to remove that particular auth provider by simply removing the declarativeConfiguration stanza from the Central CR:
$ oc get centrals.platform.stackrox.io/stackrox-central-services -o yaml | yq .spec.central adminPasswordSecret: name: acs-password exposure: loadBalancer: enabled: false port: 443 nodePort: enabled: false route: enabled: true persistence: persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: stackrox-db -
After Central restarts, the auth provider still exists:

Resolution
This issue has been reported to Red Hat engineering. It is being tracked in Bug ROX-29812. For more information, please open a new support case with Red Hat Support.
One particular workaround is to directly remove the auth provider from the central-active database.
-
Get the database password from the
central-db-passwordsecret:$ oc get secrets -n stackrox central-db-password --template={{.data.password}} | base64 -df` -
Exec into the
central-dbpod:$ oc exec -it -n stackrox <central-db-pod> sh -
Log into the
central-activedatabase with the password obtained in the first step:sh-4.4$ psql -h localhost -p 5432 -d central_active -
List the auth providers (in this example there is only one):
central_active=# select * from public.auth_providers; id | name | serialized --------------------------------------+------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8c6b3201-484e-54c3-a624-1d30ab78d6e3 | OCP | \x0a2438633662333230312d343834652d353463332d613632342d31643330616237386436653312034f43501a096f70656e7368696674221463656e7472616c5f656e64706f696e743a34343328013a2f2f73736f2f6c6f67696e2f38633662333230312d343834652d353463332d613632342d316433306162373864366533500162021802720c08f79baec10610fbe0fadb03 (1 row) -
Delete the row associated with the unwanted auth provider:
central_active=# delete from public.auth_providers where name = 'OCP'; DELETE 1 -
Exit out of the
central-dbpod and then delete thecentralpod;$ oc delete pod -l app=central -n stackrox pod "central-XXXXXXXXXX-XXXXX" deleted -
After the
centralpod is redeployed, the auth provider no longer exists in Central.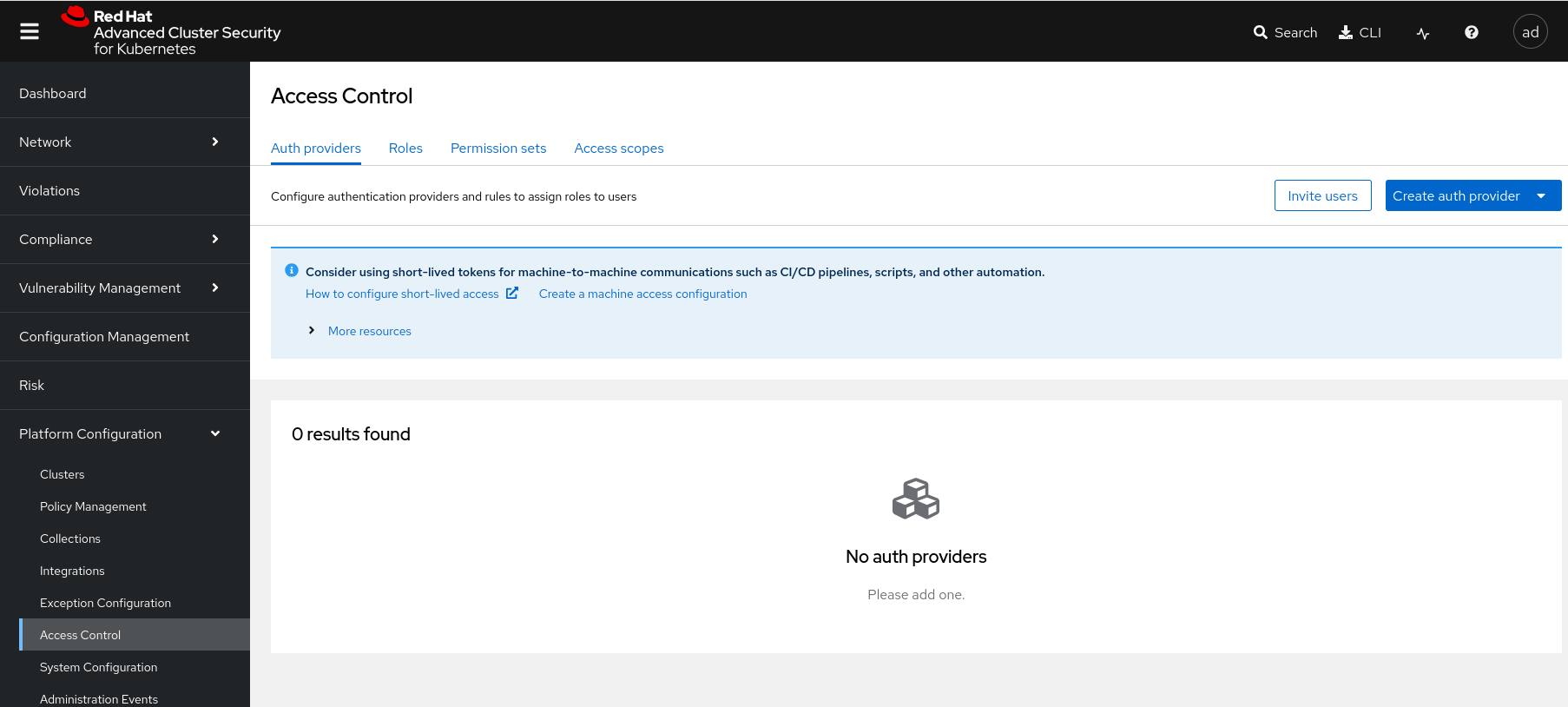
Root Cause
Central appears to completely skip evaluation of declarative resources if no config map is defined and specified in the declarativeConfiguration stanza of the Central CR.
This solution is part of Red Hat’s fast-track publication program, providing a huge library of solutions that Red Hat engineers have created while supporting our customers. To give you the knowledge you need the instant it becomes available, these articles may be presented in a raw and unedited form.


Comments