How the OpenStack instance process to launch in OVN integrated enviroment?
Environment
- Red Hat OpenStack Director v.13
- Red Hat OpenStack Director v.14
Issue
- In OVN integrated environment how the OpenStack instance has schedule and launch?
Resolution
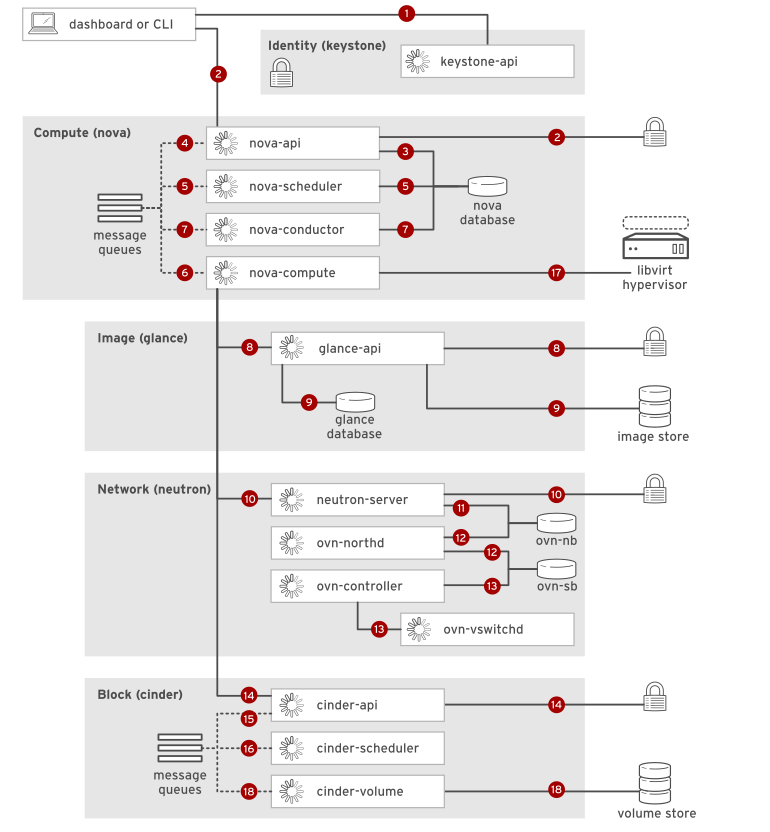
- The launch process uses a combination of REST API calls to OpenStack services, and message broker RPC calls for coordination between service components.
Instance Launch Process
-
Using the dashboard or the command-line client, the user's account credentials are sent as a
REST APIcall to the identity service endpoint. After successful authentication, the identity service generates and returns an authentication token (auth token) to the user. The auth token is included with subsequent REST calls to other services, to permit those services to perform actions on behalf of this user. -
The instance launch request and the auth token are sent as a
REST APIcall to the compute service endpoint.nova_apirelays the request to the identity service, which validates the auth token and returns allowed roles and permissions in the updated token header. -
nova_apicreates a persistent database entry for the new instance, including the launch parameters in the original request. Other processes can obtain data from this entry, and update the current state to this persistent entry. -
nova_apipublishes arpc.callto a named message queue, requestingnova_schedulerto locate an acceptable compute node to host the new instance. -
nova_schedulersubscribes to the new instance request, reads filtering and weighing parameters from the instance database entry, reads cluster compute node data from the database, and updates the instance record with the selected compute host ID.nova_schedulersubmits arpc.callto a message queue, requesting thatnova_computeinitiate an instance launch. -
nova_computesubscribes to the new instance request, then publishes arpc.callfornova_conductorto prepare for an instance launch. -
nova_conductorsubscribes to the new instance request, reads the database entry to obtain the compute host ID and instance flavor with requested RAM, vCPUs, and disk configuration, and then publishes the new instance state to the message queue. -
nova_computesubscribes to the new instance request to retrieve the instance information. Using the image ID from the instance request,nova_computesends aREST APIcall to the image service to obtain the requested image's URL. Theglance_apiservice forwards the request to the identity service, which again validates the auth token and returns allowed roles and permissions in the updated token header. -
Using the image ID,
glance_apiretrieves image metadata from the image service database and returns the image URL tonova_compute.nova_computeloads the image from the image store using the URL. -
nova_computesends aREST APIcall to the networking service, requesting allocation and configuration of network resources for the new instance.neutron_serverforwards the request to the identity service, which again validates the auth token and returns allowed roles and permissions in the updated token header. -
neutron_server, as a cloud management system plug-in, reads and writes logical network resource definitions to theovn-nbdatabase.neutron_serverchecks for the existing network and creates new resources for needed ports, connections, and network parameters. -
The
ovn-northddaemon reads fromovn-nband translates the logical network configuration into logical data-path flows in the ovn-sb database. The additional physical network and port bindings are populated by theovn-controlleron the selected compute host. -
The
ovn-controllerreads the configuration from ovn-sb and updates the compute host's status in the physical network and the binding tables.ovn-controllerconnects toovs-vswitchdas an OpenFlow controller to dynamically configure control over network traffic through OpenFlow rules on OVS bridges.neutron_serverreturns the L2 configuration obtained from the compute hostlibvirtdriver, and the requested DHCP address, to the message queue.nova_computewrites this instance network state to the instance database entry. -
nova_computesends aREST APIcall to the block storage service, requesting volume data for the new instance disks.cinder_apiforwards the request to the identity service, which again validates the auth token and returns allowed roles and permissions in the updated token header. -
cinder_apipublishes arpc.callto a named message queue, requesting thatcinder_schedulercreate a volume of the requested size, or to locate the volume metadata for a volume that already exists. -
cinder_schedulersubscribes to the new instance request, creates or locates the volume, and then returns the requested metadata tonova_scheduler. -
nova_computegenerates data for the compute node driver and executes the request usinglibvirtto create a VM on the compute host. The VM appears in the dashboard and in commands that list servers.nova_computepasses the volume information tolibvirt. -
cinder_volumesubscribes to the new instance request and retrieves the cluster map.libvirtthen mounts the volume on the new instance.
This solution is part of Red Hat’s fast-track publication program, providing a huge library of solutions that Red Hat engineers have created while supporting our customers. To give you the knowledge you need the instant it becomes available, these articles may be presented in a raw and unedited form.


Comments