JBoss AS7 Security on OpenShift
By Arun Neelicattu and David Jorm, Red Hat Security Response Team
OpenShift is Red Hat's new Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering. It is a next generation platform for deploying applications, offering developers the capability to leverage many of the promises of cloud computing. OpenShift has been designed to minimize the security concerns surrounding cloud, paving the way for safe adoption of the technology.
Multi-tenanted security
The core concern is security in a multi-tenanted environment. Typically, applications run within an organisation's own computing infrastructure. In the cloud, they can be sharing physical and virtual computing resources with other applications in a number of different configurations. Strict logical separation of workloads is necessary to make multi-tenanted environments secure. OpenShift achieves this using SELinux and Linux Containers to separate workloads and users.
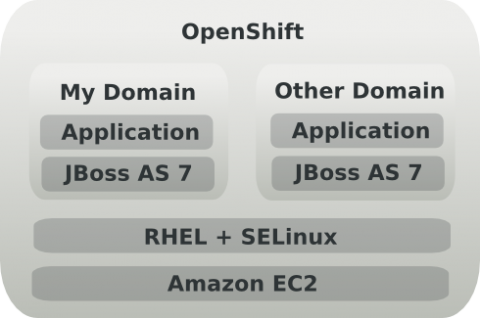
In addition to traditional file permissions and ACLs, OpenShift uses custom SELinux policies to provide tight controls on each workload, and ensure it is sandboxed from accessing computing resources associated with other workloads. The SELinux sandboxing is applied on a per-process and per-user basis.
The video, Red Hat OpenShift's Technology Foundations, provides an overview of how OpenShift is built and the role SELinux plays in it.
JBoss Security
Each JBoss application on OpenShift runs in a dedicated instance of JBoss AS 7, which itself runs on a dedicated JVM instance. This means no local JVM bytecode manipulation attacks are possible. Furthermore, if a user were able to exploit a local JVM flaw, the SELinux sandboxing will prevent them from using this to attack other workloads. By default, JBoss applications are only accessible on port 80. JBoss management consoles are not available, significantly reducing the attack surface of the application.
Security Patches
OpenShift is built using Red Hat's supported products. It consumes updates from the Red Hat Network, meaning all the latest security patches are automatically applied, without user intervention.
Secure PaaS
With robust separation of workloads, sandboxing, attack surface reduction and automated updates, OpenShift offers a PaaS environment with security features that match a well-configured in-house environment. Security is seen as one of the key challenges of cloud computing - OpenShift is stepping up to the challenge.
If you'd like to try OpenShift, the Getting Started page and the User Guide are good starting points.





Comments