Chapter 2. Getting started with AMQ Streams
AMQ Streams is designed to work on all types of OpenShift cluster regardless of distribution, from public and private clouds to local deployments intended for development. AMQ Streams supports a few features which are specific to OpenShift, where such integration benefits OpenShift users and cannot be implemented equivalently using standard OpenShift.
This guide assumes that an OpenShift cluster is available and the oc command-line tool is installed and configured to connect to the running cluster.
AMQ Streams is based on Strimzi 0.17.x. This chapter describes the procedures to deploy AMQ Streams on OpenShift 3.11 and later.
To run the commands in this guide, your cluster user must have the rights to manage role-based access control (RBAC) and CRDs.
2.1. Installing AMQ Streams and deploying components
To install AMQ Streams, download and extract the amq-streams-x.y.z-ocp-install-examples.zip file from the AMQ Streams download site.
The folder contains several YAML files to help you deploy the components of AMQ Streams to OpenShift, perform common operations, and configure your Kafka cluster. The YAML files are referenced throughout this documentation.
The remainder of this chapter provides an overview of each component and instructions for deploying the components to OpenShift using the YAML files provided.
Although container images for AMQ Streams are available in the Red Hat Container Catalog, we recommend that you use the YAML files provided instead.
2.2. Custom resources
Custom resources allow you to configure and introduce changes to a default AMQ Streams deployment. In order to use custom resources, custom resource definitions must first be defined.
Custom resource definitions (CRDs) extend the Kubernetes API, providing definitions to add custom resources to an OpenShift cluster. Custom resources are created as instances of the APIs added by CRDs.
In AMQ Streams, CRDs introduce custom resources specific to AMQ Streams to an OpenShift cluster, such as Kafka, Kafka Connect, Kafka MirrorMaker, and users and topics custom resources. CRDs provide configuration instructions, defining the schemas used to instantiate and manage the AMQ Streams-specific resources. CRDs also allow AMQ Streams resources to benefit from native OpenShift features like CLI accessibility and configuration validation.
CRDs require a one-time installation in a cluster. Depending on the cluster setup, installation typically requires cluster admin privileges.
Access to manage custom resources is limited to AMQ Streams administrators.
CRDs and custom resources are defined as YAML files.
A CRD defines a new kind of resource, such as kind:Kafka, within an OpenShift cluster.
The Kubernetes API server allows custom resources to be created based on the kind and understands from the CRD how to validate and store the custom resource when it is added to the OpenShift cluster.
When CRDs are deleted, custom resources of that type are also deleted. Additionally, the resources created by the custom resource, such as pods and statefulsets are also deleted.
Additional resources
2.2.1. AMQ Streams custom resource example
Each AMQ Streams-specific custom resource conforms to the schema defined by the CRD for the resource’s kind.
To understand the relationship between a CRD and a custom resource, let’s look at a sample of the CRD for a Kafka topic.
Kafka topic CRD
apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta1 kind: CustomResourceDefinition metadata: 1 name: kafkatopics.kafka.strimzi.io labels: app: strimzi spec: 2 group: kafka.strimzi.io versions: v1beta1 scope: Namespaced names: # ... singular: kafkatopic plural: kafkatopics shortNames: - kt 3 additionalPrinterColumns: 4 # ... subresources: status: {} 5 validation: 6 openAPIV3Schema: properties: spec: type: object properties: partitions: type: integer minimum: 1 replicas: type: integer minimum: 1 maximum: 32767 # ...
- 1
- The metadata for the topic CRD, its name and a label to identify the CRD.
- 2
- The specification for this CRD, including the group (domain) name, the plural name and the supported schema version, which are used in the URL to access the API of the topic. The other names are used to identify instance resources in the CLI. For example,
oc get kafkatopic my-topicoroc get kafkatopics. - 3
- The shortname can be used in CLI commands. For example,
oc get ktcan be used as an abbreviation instead ofoc get kafkatopic. - 4
- The information presented when using a
getcommand on the custom resource. - 5
- The current status of the CRD as described in the schema reference for the resource.
- 6
- openAPIV3Schema validation provides validation for the creation of topic custom resources. For example, a topic requires at least one partition and one replica.
You can identify the CRD YAML files supplied with the AMQ Streams installation files, because the file names contain an index number followed by ‘Crd’.
Here is a corresponding example of a KafkaTopic custom resource.
Kafka topic custom resource
apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta1 kind: KafkaTopic 1 metadata: name: my-topic labels: strimzi.io/cluster: my-cluster 2 spec: 3 partitions: 1 replicas: 1 config: retention.ms: 7200000 segment.bytes: 1073741824 status: conditions: 4 lastTransitionTime: "2019-08-20T11:37:00.706Z" status: "True" type: Ready observedGeneration: 1 / ...
- 1
- The
kindandapiVersionidentify the CRD of which the custom resource is an instance. - 2
- A label, applicable only to
KafkaTopicandKafkaUserresources, that defines the name of the Kafka cluster (which is same as the name of theKafkaresource) to which a topic or user belongs.The name is used by the Topic Operator and User Operator to identify the Kafka cluster when creating a topic or user.
- 3
- The spec shows the number of partitions and replicas for the topic as well as the configuration parameters for the topic itself. In this example, the retention period for a message to remain in the topic and the segment file size for the log are specified.
- 4
- Status conditions for the
KafkaTopicresource. Thetypecondition changed toReadyat thelastTransitionTime.
Custom resources can be applied to a cluster through the platform CLI. When the custom resource is created, it uses the same validation as the built-in resources of the Kubernetes API.
After a KafkaTopic custom resource is created, the Topic Operator is notified and corresponding Kafka topics are created in AMQ Streams.
2.2.2. AMQ Streams custom resource status
The status property of a AMQ Streams custom resource publishes information about the resource to users and tools that need it.
Several resources have a status property, as described in the following table.
| AMQ Streams resource | Schema reference | Publishes status information on… |
|---|---|---|
|
| The Kafka cluster. | |
|
| The Kafka Connect cluster, if deployed. | |
|
| The Kafka Connect cluster with Source-to-Image support, if deployed. | |
|
|
| |
|
| The Kafka MirrorMaker tool, if deployed. | |
|
| Kafka topics in your Kafka cluster. | |
|
| Kafka users in your Kafka cluster. | |
|
| The AMQ Streams Kafka Bridge, if deployed. |
The status property of a resource provides information on the resource’s:
-
Current state, in the
status.conditionsproperty -
Last observed generation, in the
status.observedGenerationproperty
The status property also provides resource-specific information. For example:
-
KafkaConnectStatusprovides the REST API endpoint for Kafka Connect connectors. -
KafkaUserStatusprovides the user name of the Kafka user and theSecretin which their credentials are stored. -
KafkaBridgeStatusprovides the HTTP address at which external client applications can access the Bridge service.
A resource’s current state is useful for tracking progress related to the resource achieving its desired state, as defined by the spec property. The status conditions provide the time and reason the state of the resource changed and details of events preventing or delaying the operator from realizing the resource’s desired state.
The last observed generation is the generation of the resource that was last reconciled by the Cluster Operator. If the value of observedGeneration is different from the value of metadata.generation, the operator has not yet processed the latest update to the resource. If these values are the same, the status information reflects the most recent changes to the resource.
AMQ Streams creates and maintains the status of custom resources, periodically evaluating the current state of the custom resource and updating its status accordingly. When performing an update on a custom resource using oc edit, for example, its status is not editable. Moreover, changing the status would not affect the configuration of the Kafka cluster.
Here we see the status property specified for a Kafka custom resource.
Kafka custom resource with status
apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta1 kind: Kafka metadata: spec: # ... status: conditions: 1 - lastTransitionTime: 2019-07-23T23:46:57+0000 status: "True" type: Ready 2 observedGeneration: 4 3 listeners: 4 - addresses: - host: my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.myproject.svc port: 9092 type: plain - addresses: - host: my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.myproject.svc port: 9093 certificates: - | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- type: tls - addresses: - host: 172.29.49.180 port: 9094 certificates: - | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- type: external # ...
- 1
- Status
conditionsdescribe criteria related to the status that cannot be deduced from the existing resource information, or are specific to the instance of a resource. - 2
- The
Readycondition indicates whether the Cluster Operator currently considers the Kafka cluster able to handle traffic. - 3
- The
observedGenerationindicates the generation of theKafkacustom resource that was last reconciled by the Cluster Operator. - 4
- The
listenersdescribe the current Kafka bootstrap addresses by type.ImportantThe address in the custom resource status for external listeners with type
nodeportis currently not supported.
The Kafka bootstrap addresses listed in the status do not signify that those endpoints or the Kafka cluster is in a ready state.
Accessing status information
You can access status information for a resource from the command line. For more information, see Section 16.1, “Checking the status of a custom resource”.
2.3. Cluster Operator
The Cluster Operator is responsible for deploying and managing Apache Kafka clusters within an OpenShift cluster.
2.3.1. Cluster Operator
AMQ Streams uses the Cluster Operator to deploy and manage clusters for:
- Kafka (including ZooKeeper, Entity Operator and Kafka Exporter)
- Kafka Connect
- Kafka MirrorMaker
- Kafka Bridge
Custom resources are used to deploy the clusters.
For example, to deploy a Kafka cluster:
-
A
Kafkaresource with the cluster configuration is created within the OpenShift cluster. -
The Cluster Operator deploys a corresponding Kafka cluster, based on what is declared in the
Kafkaresource.
The Cluster Operator can also deploy (through configuration of the Kafka resource):
-
A Topic Operator to provide operator-style topic management through
KafkaTopiccustom resources -
A User Operator to provide operator-style user management through
KafkaUsercustom resources
The Topic Operator and User Operator function within the Entity Operator on deployment.
Example architecture for the Cluster Operator

2.3.2. Watch options for a Cluster Operator deployment
When the Cluster Operator is running, it starts to watch for updates of Kafka resources.
Depending on the deployment, the Cluster Operator can watch Kafka resources from:
AMQ Streams provides example YAML files to make the deployment process easier.
The Cluster Operator watches for changes to the following resources:
-
Kafkafor the Kafka cluster. -
KafkaConnectfor the Kafka Connect cluster. -
KafkaConnectS2Ifor the Kafka Connect cluster with Source2Image support. -
KafkaConnectorfor creating and managing connectors in a Kafka Connect cluster. -
KafkaMirrorMakerfor the Kafka MirrorMaker instance. -
KafkaBridgefor the Kafka Bridge instance
When one of these resources is created in the OpenShift cluster, the operator gets the cluster description from the resource and starts creating a new cluster for the resource by creating the necessary OpenShift resources, such as StatefulSets, Services and ConfigMaps.
Each time a Kafka resource is updated, the operator performs corresponding updates on the OpenShift resources that make up the cluster for the resource.
Resources are either patched or deleted, and then recreated in order to make the cluster for the resource reflect the desired state of the cluster. This operation might cause a rolling update that might lead to service disruption.
When a resource is deleted, the operator undeploys the cluster and deletes all related OpenShift resources.
2.3.3. Deploying the Cluster Operator to watch a single namespace
Prerequisites
-
This procedure requires use of an OpenShift user account which is able to create
CustomResourceDefinitions,ClusterRolesandClusterRoleBindings. Use of Role Base Access Control (RBAC) in the OpenShift cluster usually means that permission to create, edit, and delete these resources is limited to OpenShift cluster administrators, such assystem:admin. Modify the installation files according to the namespace the Cluster Operator is going to be installed in.
On Linux, use:
sed -i 's/namespace: .*/namespace: my-namespace/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yamlOn MacOS, use:
sed -i '' 's/namespace: .*/namespace: my-namespace/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yaml
Procedure
Deploy the Cluster Operator:
oc apply -f install/cluster-operator -n my-namespace
2.3.4. Deploying the Cluster Operator to watch multiple namespaces
Prerequisites
-
This procedure requires use of an OpenShift user account which is able to create
CustomResourceDefinitions,ClusterRolesandClusterRoleBindings. Use of Role Base Access Control (RBAC) in the OpenShift cluster usually means that permission to create, edit, and delete these resources is limited to OpenShift cluster administrators, such assystem:admin. Edit the installation files according to the namespace the Cluster Operator is going to be installed in.
On Linux, use:
sed -i 's/namespace: .*/namespace: my-namespace/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yamlOn MacOS, use:
sed -i '' 's/namespace: .*/namespace: my-namespace/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yaml
Procedure
Edit the file
install/cluster-operator/050-Deployment-strimzi-cluster-operator.yamland in the environment variableSTRIMZI_NAMESPACElist all the namespaces where Cluster Operator should watch for resources. For example:apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment spec: # ... template: spec: serviceAccountName: strimzi-cluster-operator containers: - name: strimzi-cluster-operator image: registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-rhel7-operator:1.4.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: STRIMZI_NAMESPACE value: watched-namespace-1,watched-namespace-2,watched-namespace-3For all namespaces which should be watched by the Cluster Operator (
watched-namespace-1,watched-namespace-2,watched-namespace-3in the above example), install theRoleBindings. Replace thewatched-namespacewith the namespace used in the previous step.This can be done using
oc apply:oc apply -f install/cluster-operator/020-RoleBinding-strimzi-cluster-operator.yaml -n watched-namespace oc apply -f install/cluster-operator/031-RoleBinding-strimzi-cluster-operator-entity-operator-delegation.yaml -n watched-namespace oc apply -f install/cluster-operator/032-RoleBinding-strimzi-cluster-operator-topic-operator-delegation.yaml -n watched-namespace
Deploy the Cluster Operator
This can be done using
oc apply:oc apply -f install/cluster-operator -n my-namespace
2.3.5. Deploying the Cluster Operator to watch all namespaces
You can configure the Cluster Operator to watch AMQ Streams resources across all namespaces in your OpenShift cluster. When running in this mode, the Cluster Operator automatically manages clusters in any new namespaces that are created.
Prerequisites
-
This procedure requires use of an OpenShift user account which is able to create
CustomResourceDefinitions,ClusterRolesandClusterRoleBindings. Use of Role Base Access Control (RBAC) in the OpenShift cluster usually means that permission to create, edit, and delete these resources is limited to OpenShift cluster administrators, such assystem:admin. - Your OpenShift cluster is running.
Procedure
Configure the Cluster Operator to watch all namespaces:
-
Edit the
050-Deployment-strimzi-cluster-operator.yamlfile. Set the value of the
STRIMZI_NAMESPACEenvironment variable to*.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment spec: # ... template: spec: # ... serviceAccountName: strimzi-cluster-operator containers: - name: strimzi-cluster-operator image: registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-rhel7-operator:1.4.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: STRIMZI_NAMESPACE value: "*" # ...
-
Edit the
Create
ClusterRoleBindingsthat grant cluster-wide access to all namespaces to the Cluster Operator.Use the
oc create clusterrolebindingcommand:oc create clusterrolebinding strimzi-cluster-operator-namespaced --clusterrole=strimzi-cluster-operator-namespaced --serviceaccount my-namespace:strimzi-cluster-operator oc create clusterrolebinding strimzi-cluster-operator-entity-operator-delegation --clusterrole=strimzi-entity-operator --serviceaccount my-namespace:strimzi-cluster-operator oc create clusterrolebinding strimzi-cluster-operator-topic-operator-delegation --clusterrole=strimzi-topic-operator --serviceaccount my-namespace:strimzi-cluster-operator
Replace
my-namespacewith the namespace in which you want to install the Cluster Operator.Deploy the Cluster Operator to your OpenShift cluster.
Use the
oc applycommand:oc apply -f install/cluster-operator -n my-namespace
2.3.6. Deploying the Cluster Operator from the OperatorHub
You can deploy the Cluster Operator to your OpenShift cluster by installing the AMQ Streams Operator from the OperatorHub. The OperatorHub is available in OpenShift 4 only.
Prerequisites
-
The Red Hat Operators
OperatorSourceis enabled in your OpenShift cluster. If you can see Red Hat Operators in the OperatorHub, the correctOperatorSourceis enabled. For more information, see the Operators guide. - Installation requires a user with sufficient privileges to install Operators from the OperatorHub.
Procedure
- In the OpenShift 4 web console, click Operators > OperatorHub.
Search or browse for the AMQ Streams Operator, in the Streaming & Messaging category.

- Click the AMQ Streams tile and then, in the sidebar on the right, click Install.
On the Create Operator Subscription screen, choose from the following installation and update options:
- Installation Mode: Choose to install the AMQ Streams Operator to all (projects) namespaces in the cluster (the default option) or a specific (project) namespace. It is good practice to use namespaces to separate functions. We recommend that you install the Operator to its own namespace, separate from the namespace that will contain the Kafka cluster and other AMQ Streams components.
- Approval Strategy: By default, the AMQ Streams Operator is automatically upgraded to the latest AMQ Streams version by the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM). Optionally, select Manual if you want to manually approve future upgrades. For more information, see the Operators guide in the OpenShift documentation.
Click Subscribe; the AMQ Streams Operator is installed to your OpenShift cluster.
The AMQ Streams Operator deploys the Cluster Operator, CRDs, and role-based access control (RBAC) resources to the selected namespace, or to all namespaces.
On the Installed Operators screen, check the progress of the installation. The AMQ Streams Operator is ready to use when its status changes to InstallSucceeded.

Next, you can deploy the other components of AMQ Streams, starting with a Kafka cluster, using the YAML example files.
2.4. Kafka cluster
You can use AMQ Streams to deploy an ephemeral or persistent Kafka cluster to OpenShift. When installing Kafka, AMQ Streams also installs a ZooKeeper cluster and adds the necessary configuration to connect Kafka with ZooKeeper.
You can also use it to deploy Kafka Exporter.
- Ephemeral cluster
-
In general, an ephemeral (that is, temporary) Kafka cluster is suitable for development and testing purposes, not for production. This deployment uses
emptyDirvolumes for storing broker information (for ZooKeeper) and topics or partitions (for Kafka). Using anemptyDirvolume means that its content is strictly related to the pod life cycle and is deleted when the pod goes down. - Persistent cluster
-
A persistent Kafka cluster uses
PersistentVolumesto store ZooKeeper and Kafka data. ThePersistentVolumeis acquired using aPersistentVolumeClaimto make it independent of the actual type of thePersistentVolume. For example, it can use Amazon EBS volumes in Amazon AWS deployments without any changes in the YAML files. ThePersistentVolumeClaimcan use aStorageClassto trigger automatic volume provisioning.
AMQ Streams includes several examples for deploying a Kafka cluster.
-
kafka-persistent.yamldeploys a persistent cluster with three ZooKeeper and three Kafka nodes. -
kafka-jbod.yamldeploys a persistent cluster with three ZooKeeper and three Kafka nodes (each using multiple persistent volumes). -
kafka-persistent-single.yamldeploys a persistent cluster with a single ZooKeeper node and a single Kafka node. -
kafka-ephemeral.yamldeploys an ephemeral cluster with three ZooKeeper and three Kafka nodes. -
kafka-ephemeral-single.yamldeploys an ephemeral cluster with three ZooKeeper nodes and a single Kafka node.
The example clusters are named my-cluster by default. The cluster name is defined by the name of the resource and cannot be changed after the cluster has been deployed. To change the cluster name before you deploy the cluster, edit the Kafka.metadata.name property of the resource in the relevant YAML file.
apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta1 kind: Kafka metadata: name: my-cluster # ...
2.4.1. Deploying the Kafka cluster
You can deploy an ephemeral or persistent Kafka cluster to OpenShift on the command line.
Prerequisites
- The Cluster Operator is deployed.
Procedure
If you plan to use the cluster for development or testing purposes, you can create and deploy an ephemeral cluster using
oc apply.oc apply -f examples/kafka/kafka-ephemeral.yaml
If you plan to use the cluster in production, create and deploy a persistent cluster using
oc apply.oc apply -f examples/kafka/kafka-persistent.yaml
Additional resources
- For more information on deploying the Cluster Operator, see Section 2.3, “Cluster Operator”.
-
For more information on the different configuration options supported by the
Kafkaresource, see Section 3.1, “Kafka cluster configuration”.
2.5. Kafka Connect
Kafka Connect is a tool for streaming data between Apache Kafka and external systems. It provides a framework for moving large amounts of data into and out of your Kafka cluster while maintaining scalability and reliability. Kafka Connect is typically used to integrate Kafka with external databases and storage and messaging systems.
In Kafka Connect, a source connector is a runtime entity that fetches data from an external system and feeds it to Kafka as messages. A sink connector is a runtime entity that fetches messages from Kafka topics and feeds them to an external system. The workload of connectors is divided into tasks. Tasks are distributed among nodes (also called workers), which form a Connect cluster. This allows the message flow to be highly scalable and reliable.
Each connector is an instance of a particular connector class that knows how to communicate with the relevant external system in terms of messages. Connectors are available for many external systems, or you can develop your own.
The term connector is used interchangably to mean a connector instance running within a Kafka Connect cluster, or a connector class. This guide uses the term connector when the meaning is clear from the context.
AMQ Streams allows you to:
- Create a Kafka Connect image containing the connectors you want
-
Deploy and manage a Kafka Connect cluster running within OpenShift using a
KafkaConnectresource -
Run connectors within your Kafka Connect cluster, optionally managed using
KafkaConnectorresources
Kafka Connect includes the following built-in connectors for moving file-based data into and out of your Kafka cluster.
| File Connector | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Transfers data to your Kafka cluster from a file (the source). |
|
| Transfers data from your Kafka cluster to a file (the sink). |
To use other connector classes, you need to prepare connector images by following one of these procedures:
The Cluster Operator can use images that you create to deploy a Kafka Connect cluster to your OpenShift cluster.
A Kafka Connect cluster is implemented as a Deployment with a configurable number of workers.
You can create and manage connectors using KafkaConnector resources or manually using the Kafka Connect REST API, which is available on port 8083 as the <connect-cluster-name>-connect-api service. The operations supported by the REST API are described in the Apache Kafka documentation.
2.5.1. Deploying Kafka Connect to your cluster
You can deploy a Kafka Connect cluster to your OpenShift cluster by using the Cluster Operator.
Prerequisites
Procedure
Use the
oc applycommand to create aKafkaConnectresource based on thekafka-connect.yamlfile:oc apply -f examples/kafka-connect/kafka-connect.yaml
Additional resources
2.5.2. Extending Kafka Connect with connector plug-ins
The AMQ Streams container images for Kafka Connect include the two built-in file connectors: FileStreamSourceConnector and FileStreamSinkConnector. You can add your own connectors by:
- Creating a container image from the Kafka Connect base image (manually or using your CI (continuous integration), for example).
- Creating a container image using OpenShift builds and Source-to-Image (S2I) - available only on OpenShift.
2.5.2.1. Creating a Docker image from the Kafka Connect base image
You can use the Kafka container image on Red Hat Container Catalog as a base image for creating your own custom image with additional connector plug-ins.
The following procedure explains how to create your custom image and add it to the /opt/kafka/plugins directory. At startup, the AMQ Streams version of Kafka Connect loads any third-party connector plug-ins contained in the /opt/kafka/plugins directory.
Prerequisites
Procedure
Create a new
Dockerfileusingregistry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-kafka-24-rhel7:1.4.0as the base image:FROM registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-kafka-24-rhel7:1.4.0 USER root:root COPY ./my-plugins/ /opt/kafka/plugins/ USER 1001- Build the container image.
- Push your custom image to your container registry.
Point to the new container image.
You can either:
Edit the
KafkaConnect.spec.imageproperty of theKafkaConnectcustom resource.If set, this property overrides the
STRIMZI_KAFKA_CONNECT_IMAGESvariable in the Cluster Operator.apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta1 kind: KafkaConnect metadata: name: my-connect-cluster spec: #... image: my-new-container-image
or
-
In the
install/cluster-operator/050-Deployment-strimzi-cluster-operator.yamlfile, edit theSTRIMZI_KAFKA_CONNECT_IMAGESvariable to point to the new container image, and then reinstall the Cluster Operator.
Additional resources
-
For more information on the
KafkaConnect.spec.image property, see Section 3.2.11, “Container images”. -
For more information on the
STRIMZI_KAFKA_CONNECT_IMAGESvariable, see Section 4.1.7, “Cluster Operator Configuration”.
2.5.2.2. Creating a container image using OpenShift builds and Source-to-Image
You can use OpenShift builds and the Source-to-Image (S2I) framework to create new container images. An OpenShift build takes a builder image with S2I support, together with source code and binaries provided by the user, and uses them to build a new container image. Once built, container images are stored in OpenShift’s local container image repository and are available for use in deployments.
A Kafka Connect builder image with S2I support is provided on the Red Hat Container Catalog as part of the registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-kafka-24-rhel7:1.4.0 image. This S2I image takes your binaries (with plug-ins and connectors) and stores them in the /tmp/kafka-plugins/s2i directory. It creates a new Kafka Connect image from this directory, which can then be used with the Kafka Connect deployment. When started using the enhanced image, Kafka Connect loads any third-party plug-ins from the /tmp/kafka-plugins/s2i directory.
Procedure
On the command line, use the
oc applycommand to create and deploy a Kafka Connect S2I cluster:oc apply -f examples/kafka-connect/kafka-connect-s2i.yaml
Create a directory with Kafka Connect plug-ins:
$ tree ./my-plugins/ ./my-plugins/ ├── debezium-connector-mongodb │ ├── bson-3.4.2.jar │ ├── CHANGELOG.md │ ├── CONTRIBUTE.md │ ├── COPYRIGHT.txt │ ├── debezium-connector-mongodb-0.7.1.jar │ ├── debezium-core-0.7.1.jar │ ├── LICENSE.txt │ ├── mongodb-driver-3.4.2.jar │ ├── mongodb-driver-core-3.4.2.jar │ └── README.md ├── debezium-connector-mysql │ ├── CHANGELOG.md │ ├── CONTRIBUTE.md │ ├── COPYRIGHT.txt │ ├── debezium-connector-mysql-0.7.1.jar │ ├── debezium-core-0.7.1.jar │ ├── LICENSE.txt │ ├── mysql-binlog-connector-java-0.13.0.jar │ ├── mysql-connector-java-5.1.40.jar │ ├── README.md │ └── wkb-1.0.2.jar └── debezium-connector-postgres ├── CHANGELOG.md ├── CONTRIBUTE.md ├── COPYRIGHT.txt ├── debezium-connector-postgres-0.7.1.jar ├── debezium-core-0.7.1.jar ├── LICENSE.txt ├── postgresql-42.0.0.jar ├── protobuf-java-2.6.1.jar └── README.md
Use the
oc start-buildcommand to start a new build of the image using the prepared directory:oc start-build my-connect-cluster-connect --from-dir ./my-plugins/
NoteThe name of the build is the same as the name of the deployed Kafka Connect cluster.
- Once the build has finished, the new image is used automatically by the Kafka Connect deployment.
2.5.3. Creating and managing connectors
When you have created a container image for your connector plug-in, you need to create a connector instance in your Kafka Connect cluster. You can then configure, monitor, and manage a running connector instance.
AMQ Streams provides two APIs for creating and managing connectors:
-
KafkaConnectorresources (referred to asKafkaConnectors) - Kafka Connect REST API
Using the APIs, you can:
- Check the status of a connector instance
- Reconfigure a running connector
- Increase or decrease the number of tasks for a connector instance
-
Restart failed tasks (not supported by
KafkaConnectorresource) - Pause a connector instance
- Resume a previously paused connector instance
- Delete a connector instance
2.5.3.1. KafkaConnector resources
KafkaConnectors allow you to create and manage connector instances for Kafka Connect in an OpenShift-native way, so an HTTP client such as cURL is not required. Like other Kafka resources, you declare a connector’s desired state in a KafkaConnector YAML file that is deployed to your OpenShift cluster to create the connector instance.
You manage a running connector instance by updating its corresponding KafkaConnector, and then applying the updates. You remove a connector by deleting its corresponding KafkaConnector.
To ensure compatibility with earlier versions of AMQ Streams, KafkaConnectors are disabled by default. To enable them for a Kafka Connect cluster, you must use annotations on the KafkaConnect resource. For instructions, see Section 3.2.14, “Enabling KafkaConnector resources”.
When KafkaConnectors are enabled, the Cluster Operator begins to watch for them. It updates the configurations of running connector instances to match the configurations defined in their KafkaConnectors.
AMQ Streams includes an example KafkaConnector, named examples/connector/source-connector.yaml. You can use this example to create and manage a FileStreamSourceConnector.
2.5.3.2. Availability of the Kafka Connect REST API
The Kafka Connect REST API is available on port 8083 as the <connect-cluster-name>-connect-api service.
If KafkaConnectors are enabled, manual changes made directly using the Kafka Connect REST API are reverted by the Cluster Operator.
2.5.4. Deploying a KafkaConnector resource to Kafka Connect
Deploy the example KafkaConnector to a Kafka Connect cluster. The example YAML will create a FileStreamSourceConnector to send each line of the license file to Kafka as a message in a topic named my-topic.
Prerequisites
-
A Kafka Connect deployment in which
KafkaConnectorsare enabled - A running Cluster Operator
Procedure
Edit the
examples/connector/source-connector.yamlfile:apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1alpha1 kind: KafkaConnector metadata: name: my-source-connector 1 labels: strimzi.io/cluster: my-connect-cluster 2 spec: class: org.apache.kafka.connect.file.FileStreamSourceConnector 3 tasksMax: 2 4 config: 5 file: "/opt/kafka/LICENSE" topic: my-topic # ...
- 1
- Enter a name for the
KafkaConnectorresource. This will be used as the name of the connector within Kafka Connect. You can choose any name that is valid for an OpenShift resource. - 2
- Enter the name of the Kafka Connect cluster in which to create the connector.
- 3
- The name or alias of the connector class. This should be present in the image being used by the Kafka Connect cluster.
- 4
- The maximum number of tasks that the connector can create.
- 5
- Configuration settings for the connector. Available configuration options depend on the connector class.
Create the
KafkaConnectorin your OpenShift cluster:oc apply -f examples/connector/source-connector.yaml
Check that the resource was created:
oc get kctr --selector strimzi.io/cluster=my-connect-cluster -o name
2.6. Kafka MirrorMaker
The Cluster Operator deploys one or more Kafka MirrorMaker replicas to replicate data between Kafka clusters. This process is called mirroring to avoid confusion with the Kafka partitions replication concept. The MirrorMaker consumes messages from the source cluster and republishes those messages to the target cluster.
For information about example resources and the format for deploying Kafka MirrorMaker, see Kafka MirrorMaker configuration.
2.6.1. Deploying Kafka MirrorMaker
Prerequisites
- Before deploying Kafka MirrorMaker, the Cluster Operator must be deployed.
Procedure
Create a Kafka MirrorMaker cluster from the command-line:
oc apply -f examples/kafka-mirror-maker/kafka-mirror-maker.yaml
Additional resources
- For more information about deploying the Cluster Operator, see Section 2.3, “Cluster Operator”
2.7. Kafka Bridge
The Cluster Operator deploys one or more Kafka bridge replicas to send data between Kafka clusters and clients via HTTP API.
For information about example resources and the format for deploying Kafka Bridge, see Kafka Bridge configuration.
2.7.1. Deploying Kafka Bridge to your OpenShift cluster
You can deploy a Kafka Bridge cluster to your OpenShift cluster by using the Cluster Operator.
Prerequisites
Procedure
Use the
oc applycommand to create aKafkaBridgeresource based on thekafka-bridge.yamlfile:oc apply -f examples/kafka-bridge/kafka-bridge.yaml
Additional resources
2.8. Deploying example clients
Prerequisites
- An existing Kafka cluster for the client to connect to.
Procedure
Deploy the producer.
Use
oc run:oc run kafka-producer -ti --image=registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-kafka-24-rhel7:1.4.0 --rm=true --restart=Never -- bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list cluster-name-kafka-bootstrap:9092 --topic my-topic
- Type your message into the console where the producer is running.
- Press Enter to send the message.
Deploy the consumer.
Use
oc run:oc run kafka-consumer -ti --image=registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-streams-kafka-24-rhel7:1.4.0 --rm=true --restart=Never -- bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server cluster-name-kafka-bootstrap:9092 --topic my-topic --from-beginning
- Confirm that you see the incoming messages in the consumer console.
2.9. Topic Operator
The Topic Operator is responsible for managing Kafka topics within a Kafka cluster running within an OpenShift cluster.
2.9.1. Topic Operator
The Topic Operator provides a way of managing topics in a Kafka cluster through OpenShift resources.
Example architecture for the Topic Operator
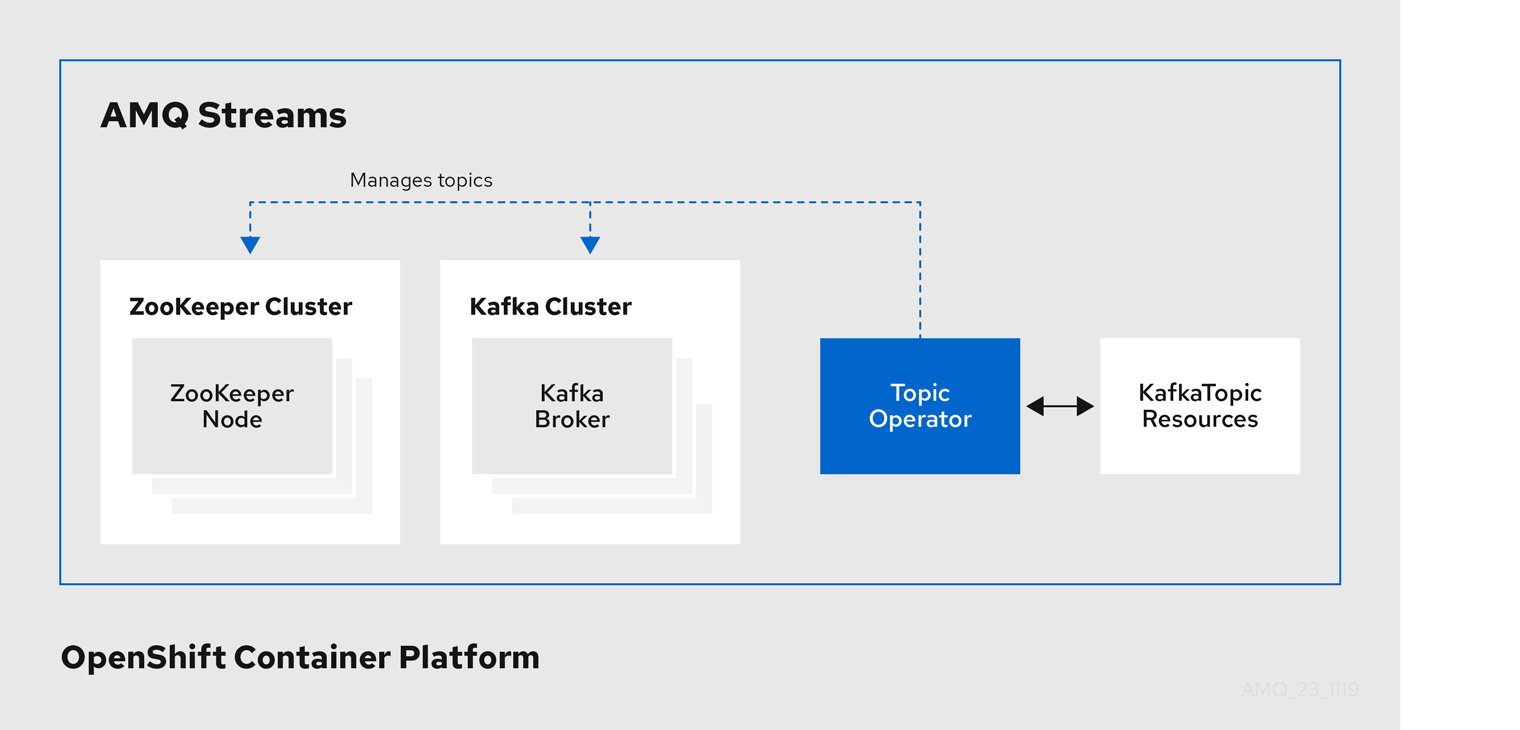
The role of the Topic Operator is to keep a set of KafkaTopic OpenShift resources describing Kafka topics in-sync with corresponding Kafka topics.
Specifically, if a KafkaTopic is:
- Created, the Topic Operator creates the topic
- Deleted, the Topic Operator deletes the topic
- Changed, the Topic Operator updates the topic
Working in the other direction, if a topic is:
-
Created within the Kafka cluster, the Operator creates a
KafkaTopic -
Deleted from the Kafka cluster, the Operator deletes the
KafkaTopic -
Changed in the Kafka cluster, the Operator updates the
KafkaTopic
This allows you to declare a KafkaTopic as part of your application’s deployment and the Topic Operator will take care of creating the topic for you. Your application just needs to deal with producing or consuming from the necessary topics.
If the topic is reconfigured or reassigned to different Kafka nodes, the KafkaTopic will always be up to date.
2.9.2. Deploying the Topic Operator using the Cluster Operator
This procedure describes how to deploy the Topic Operator using the Cluster Operator. If you want to use the Topic Operator with a Kafka cluster that is not managed by AMQ Streams, you must deploy the Topic Operator as a standalone component. For more information, see Section 4.2.6, “Deploying the standalone Topic Operator”.
Prerequisites
- A running Cluster Operator
-
A
Kafkaresource to be created or updated
Procedure
Ensure that the
Kafka.spec.entityOperatorobject exists in theKafkaresource. This configures the Entity Operator.apiVersion: kafka.strimzi.io/v1beta1 kind: Kafka metadata: name: my-cluster spec: #... entityOperator: topicOperator: {} userOperator: {}-
Configure the Topic Operator using the properties described in Section B.62, “
EntityTopicOperatorSpecschema reference”. Create or update the Kafka resource in OpenShift.
Use
oc apply:oc apply -f your-file
Additional resources
- For more information about deploying the Cluster Operator, see Section 2.3, “Cluster Operator”.
- For more information about deploying the Entity Operator, see Section 3.1.11, “Entity Operator”.
-
For more information about the
Kafka.spec.entityOperatorobject used to configure the Topic Operator when deployed by the Cluster Operator, see Section B.61, “EntityOperatorSpecschema reference”.
2.10. User Operator
The User Operator is responsible for managing Kafka users within a Kafka cluster running within an OpenShift cluster.
2.10.1. User Operator
The User Operator manages Kafka users for a Kafka cluster by watching for KafkaUser resources that describe Kafka users, and ensuring that they are configured properly in the Kafka cluster.
For example, if a KafkaUser is:
- Created, the User Operator creates the user it describes
- Deleted, the User Operator deletes the user it describes
- Changed, the User Operator updates the user it describes
Unlike the Topic Operator, the User Operator does not sync any changes from the Kafka cluster with the OpenShift resources. Kafka topics can be created by applications directly in Kafka, but it is not expected that the users will be managed directly in the Kafka cluster in parallel with the User Operator.
The User Operator allows you to declare a KafkaUser resource as part of your application’s deployment. You can specify the authentication and authorization mechanism for the user. You can also configure user quotas that control usage of Kafka resources to ensure, for example, that a user does not monopolize access to a broker.
When the user is created, the user credentials are created in a Secret. Your application needs to use the user and its credentials for authentication and to produce or consume messages.
In addition to managing credentials for authentication, the User Operator also manages authorization rules by including a description of the user’s access rights in the KafkaUser declaration.
2.10.2. Deploying the User Operator using the Cluster Operator
Prerequisites
- A running Cluster Operator
-
A
Kafkaresource to be created or updated.
Procedure
-
Edit the
Kafkaresource ensuring it has aKafka.spec.entityOperator.userOperatorobject that configures the User Operator how you want. Create or update the Kafka resource in OpenShift.
This can be done using
oc apply:oc apply -f your-file
Additional resources
- For more information about deploying the Cluster Operator, see Section 2.3, “Cluster Operator”.
-
For more information about the
Kafka.spec.entityOperatorobject used to configure the User Operator when deployed by the Cluster Operator, seeEntityOperatorSpecschema reference.
2.11. Strimzi Administrators
AMQ Streams includes several custom resources. By default, permission to create, edit, and delete these resources is limited to OpenShift cluster administrators. If you want to allow non-cluster administators to manage AMQ Streams resources, you must assign them the Strimzi Administrator role.
2.11.1. Designating Strimzi Administrators
Prerequisites
-
AMQ Streams
CustomResourceDefinitionsare installed.
Procedure
Create the
strimzi-admincluster role in OpenShift.Use
oc apply:oc apply -f install/strimzi-admin
Assign the
strimzi-adminClusterRoleto one or more existing users in the OpenShift cluster.Use
oc create:oc create clusterrolebinding strimzi-admin --clusterrole=strimzi-admin --user=user1 --user=user2
2.12. Container images
Container images for AMQ Streams are available in the Red Hat Container Catalog. The installation YAML files provided by AMQ Streams will pull the images directly from the Red Hat Container Catalog.
If you do not have access to the Red Hat Container Catalog or want to use your own container repository:
- Pull all container images listed here
- Push them into your own registry
- Update the image names in the installation YAML files
Each Kafka version supported for the release has a separate image.
| Container image | Namespace/Repository | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Kafka |
| AMQ Streams image for running Kafka, including:
|
| Operator |
| AMQ Streams image for running the operators:
|
| Kafka Bridge |
| AMQ Streams image for running the AMQ Streams kafka Bridge |

