You are viewing documentation for a release that is no longer maintained. To view the documentation for the most recent version, see the latest RHACS docs.
Architecture
Enter a short description here.
Abstract
Chapter 1. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes architecture
Discover Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes architecture and concepts.
1.1. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes architecture overview
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes(RHACS) uses a distributed architecture that supports high scale deployments and is optimized to minimize the impact on the underlying OpenShift Container Platform or Kubernetes nodes. You install RHACS as a set of containers in your OpenShift Container Platform or Kubernetes cluster. RHACS includes services that you install on each cluster secured by RHACS and centralized services you install on one cluster.
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes version 3.69.1 and newer
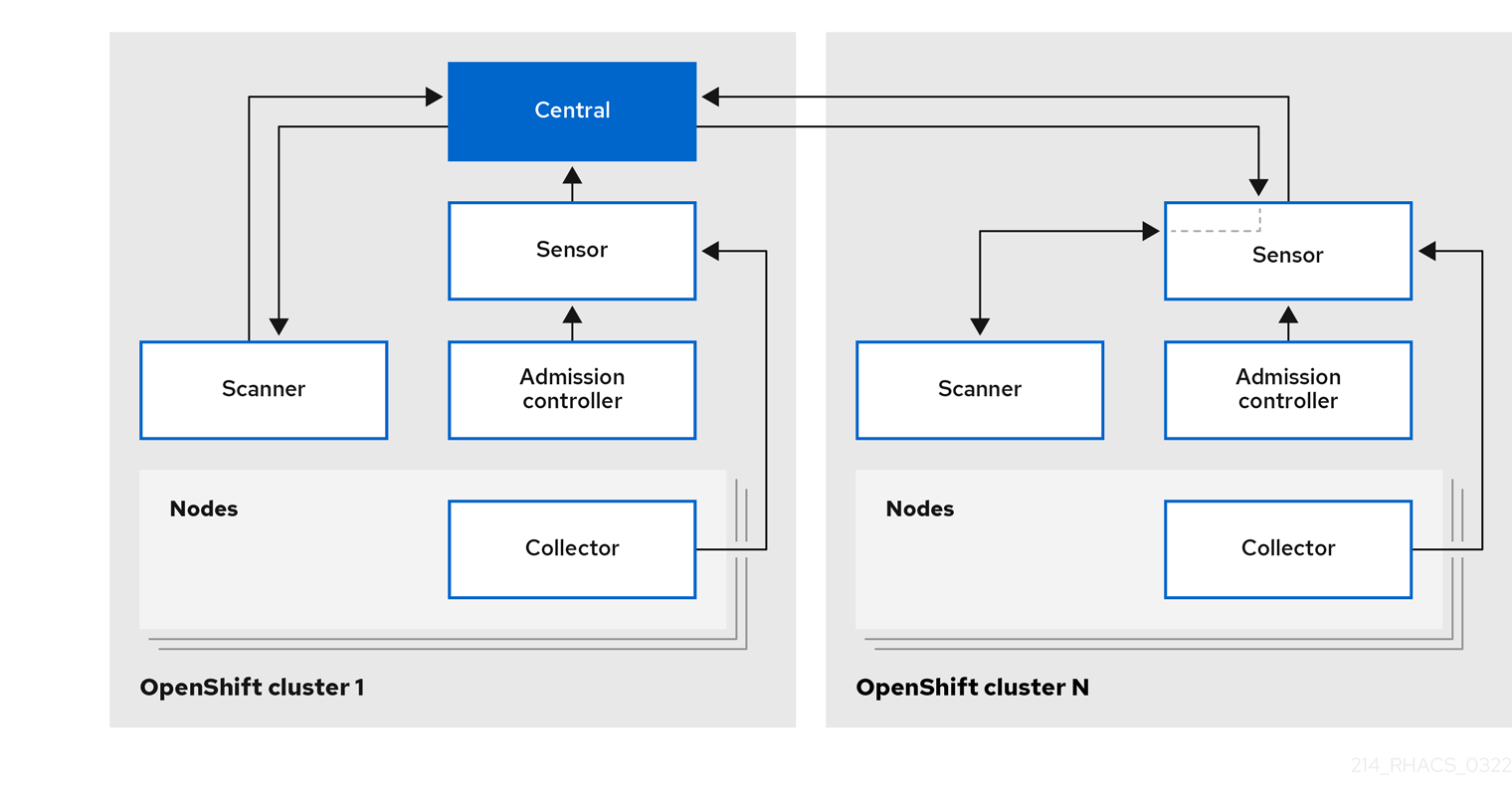
Figure 1.1. High level Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes architecture for OpenShift Container Platform
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes version 3.69 and older
For Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes versions 3.69 and older, Scanner is installed only on the cluster where Central is installed.
Centralized services
You install Centralized services on a single cluster (Cluster 1 in Figure 1 and 2). These services includes two main components, Central and Scanner.
- Central: Central is the RHACS application management interface and services. It handles data persistence, API interactions, and user interface (RHACS Portal) access. You can use the same Central instance to secure multiple OpenShift Container Platform or Kubernetes clusters.
- Scanner: Scanner is a Red Hat-developed and certified vulnerability scanner for scanning container images and their associated databases. It analyzes all image layers to check known vulnerabilities from the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) list. Scanner also identifies vulnerabilities in packages installed by package managers and in dependencies for multiple programming languages.
Scanner Architecture in Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes version 3.69.1 and newer
When you install Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes version 3.69.1 and newer on OpenShift Container Platform, you also install a lightweight version of Scanner on each secured cluster (Figure 1) to enable scanning of images in the integrated OpenShift Container Registry (OCR).
Secured cluster services
You install the secured cluster services on each cluster that you want to secure by using the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes (Cluster N in Figure 1 and 2). The cluster where you install Central is also secured and includes these services.
- Sensor: Sensor is the service responsible for analyzing and monitoring the cluster. It handles interactions with the OpenShift Container Platform or Kubernetes API server for policy detection and enforcement, and it coordinates with Collector.
- Admission controller: The admission controller prevents users from creating workloads that violate security policies in RHACS.
- Collector: Collector analyzes and monitors container activity on cluster nodes. It collects information about container runtime and network activity and sends the collected data to Sensor.
- Scanner (only on OpenShift Container Platform version 3.69.1 and newer): On OpenShift Container Platform, RHACS installs a lightweight version of Scanner on each secured cluster (Figure 1) to enable scanning of images in the integrated OCR.
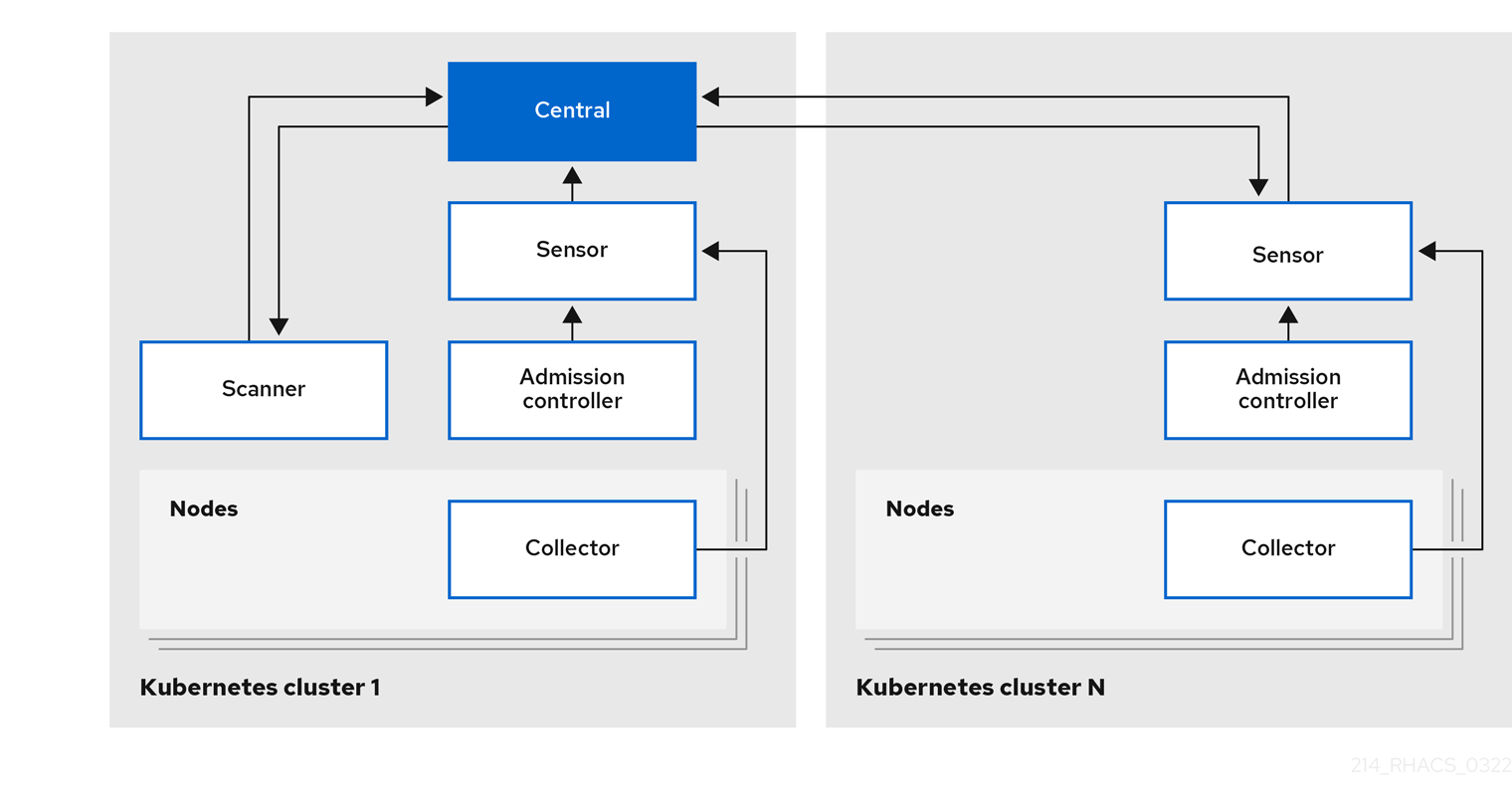
Figure 2 depicts the architecture in a Kubernetes environment, where you install only the Scanner centrally.
Figure 1.2. High level Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes architecture for Kubernetes
1.2. External components
In addition to the primary services, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes also interacts with other entities to provide enhanced security for your clusters.
Figure 3 depicts the RHACS architecture for OpenShift Container Platform, but you should note the following exceptions:
- In RHACS version 3.69 and older, Scanner services are only installed once with the centralized service.
- In other Kubernetes based environments, Scanner services are only installed once with the centralized service.
Figure 1.3. External components
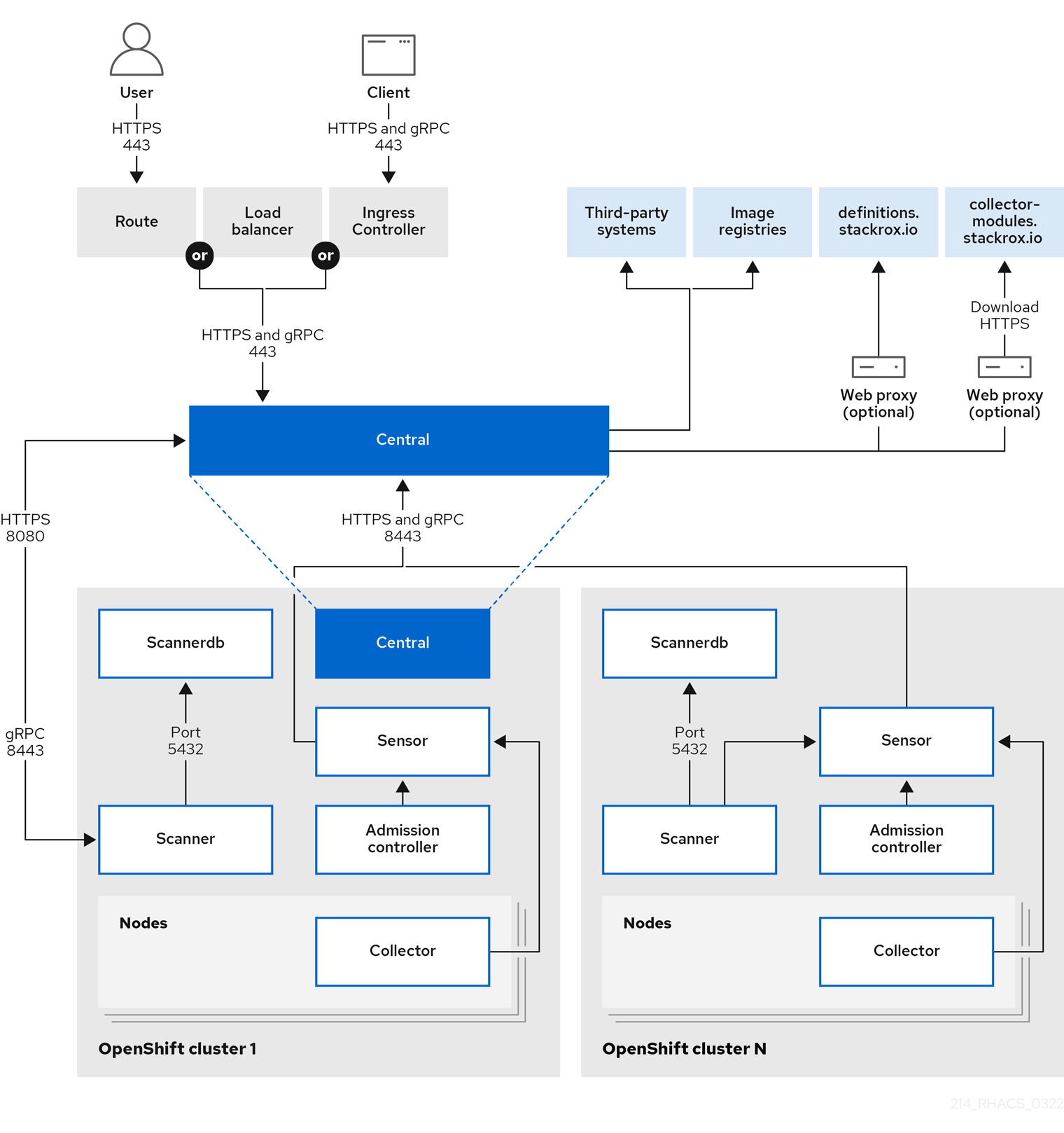
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes uses the following external components:
- Third-party systems: You can integrate RHACS with other systems such as CI/CD pipelines, event management (SIEM) systems, logging, email, and more.
- Image registries: You can integrate RHACS with various image registries and use RHACS to scan and view active images. By using the image pull secrets discovered in secured clusters, RHACS automatically configures these registry integrations.
-
definitions.stackrox.io: RHACS aggregates the data from various vulnerability feeds at the
definitions.stackrox.ioendpoint and then passes this information to Central. The feeds include general, NVD, and distribution-specific, such as Alpine, Debian, and Ubuntu. -
collector-modules.stackrox.io: Central reaches out to
collector-modules.stackrox.ioto obtain supported kernel modules and passes on these modules to Sensor and Collector.

