Web console
Read more to learn how to use console components.
Abstract
Chapter 1. Web console
Learn how to access and use components of the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console from the following documentation:
1.1. Accessing your console
The Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes web console is integrated with the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform web console as a console plug-in. You can access Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management within the OpenShift Container Platform console from the cluster switcher by selecting All Clusters. The cluster switcher is a drop-down menu that initially displays local-cluster.
Select local-cluster when you want to use OpenShift Container Platform console features on the cluster where you installed Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management. Select All Clusters when you want to use Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management features to manage your fleet of clusters.
If the cluster switcher is not present, the required console plug-ins might not be enabled. For new installations, the console plug-ins are enabled by default. If you upgraded from a previous version of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management and want to enable the plug-ins, or if you want to disable the plug-ins, complete the following steps:
- To disable the plug-in, be sure you are in the Administrator perspective in the OpenShift Container Platform console.
- Find Administration in the navigation and click Cluster Settings, then click the Configuration tab.
-
From the list of Configuration resources, click the Console resource with the
operator.openshift.ioAPI group, which contains cluster-wide configuration for the web console. -
Select the Console plug-ins tab. Both the
acmandmceplug-ins are listed. - Modify plug-in status from the table. In a few moments, you are prompted to refresh the console.
Note: If you are using OpenShift Container Platform 4.12, you can enable and disable the console. See MultiClusterHub advanced for information.
To learn more about the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console, see Console overview.
1.2. Console overview
Learn more about console components that you can use to view, manage, or customize your console.
See the following image of the Navigation from the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console, which is described in more detail later in each section. See that the navigation represents major production function.
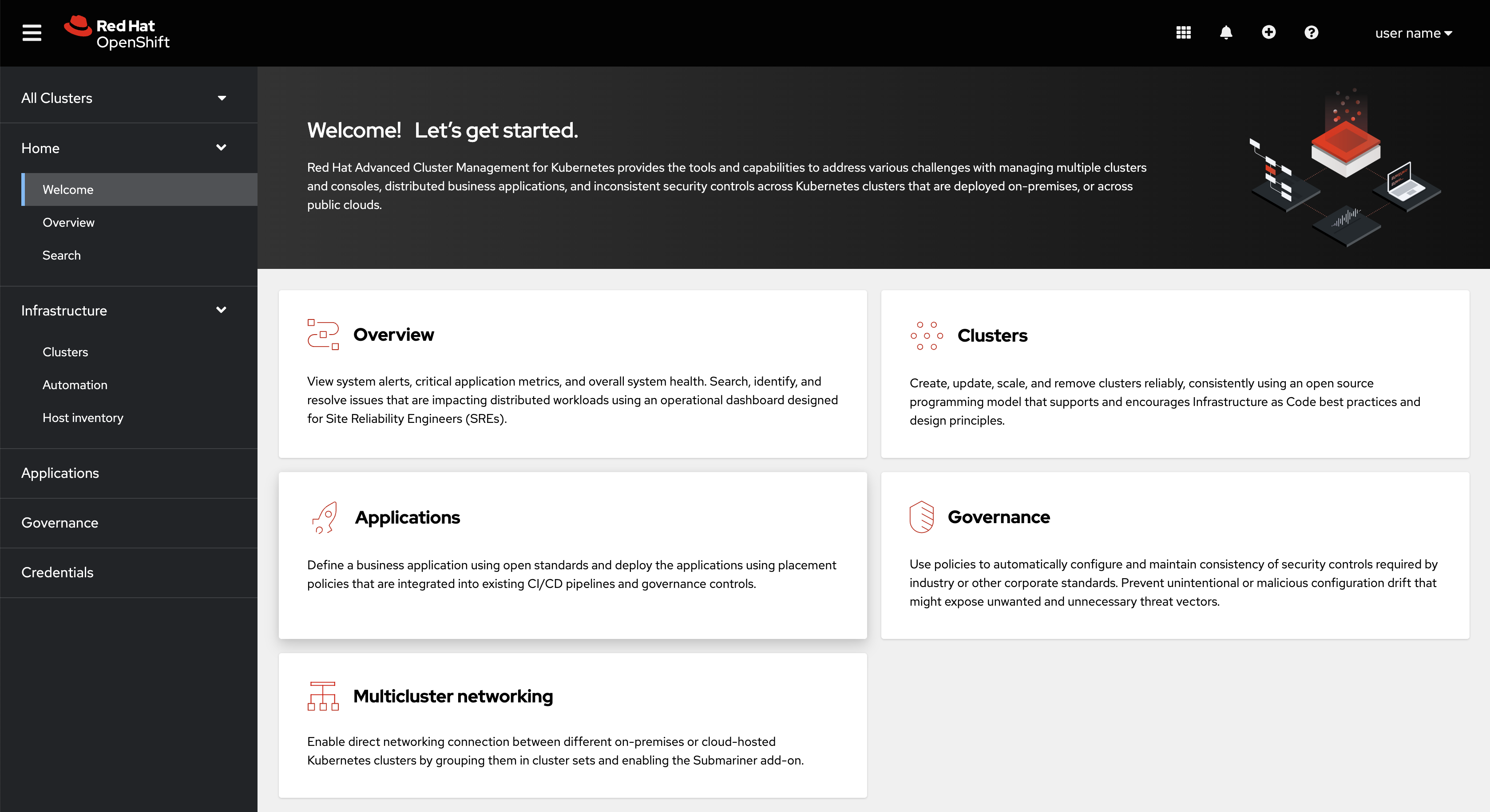
1.2.1. Console components
1.2.2. Home
From the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes Home page, you get more information about the product and you can access header features, as well as the pages for the major components of the product.
Access the Welcome page and the Overview, which gives you visibility into your clusters.
You can view the following information about your clusters on the Overview dashboard:
- Metric data from your managed clusters by selecting the Grafana link
- Cluster and node counts across all clusters and for each provider
- Cluster status
- Cluster compliance
- Pod status
- Select Grafana to access the Grafana dashboard.
- Click Add provider connections to access the Clusters page.
Search is also available from the Home tab. To learn about Search, see Searching in the console introduction.
1.2.3. Infrastructure
From Clusters, you can create new clusters or import existing clusters. From Automation, you can create an Ansible template.
For more information about managing clusters, see The multicluster engine operator cluster lifecycle overview.
Additionally, see specific information on these cluster types at Configuring Ansible Automation Platform tasks to run on managed clusters.
1.2.4. Applications
Create an application and edit a .yaml file. Access an overview or more advanced information about each application. For more information about application resources, see Managing applications.
1.2.5. Governance
Create and edit a .yaml file to create a policy. Use the Governance dashboard to manage policies and policy controllers.
For more information, see Governance.
1.2.6. Credentials
The credential stores the access information for a cloud provider. Each provider account requires its own credential, as does each domain on a single provider.
Review your credentials or add a credential.
See Managing credentials overview for more specific information about providers and credentials.

