Demonstrate GitOps on Managed OpenShift with ArgoCD
Overview
Get OpenShift GitOps running in your cluster, including deploying a sample application and demonstrating how ArgoCD ensures environment consistency.
This demo assumes you have a Managed OpenShift Cluster available and cluster-admin rights.
GitHub resources referenced in the demo:
- BGD Application: gitops-bgd-app
- OpenShift / ArgoCD configuration: gitops-demo
Required command line (CLI) tools
Environment Set Up
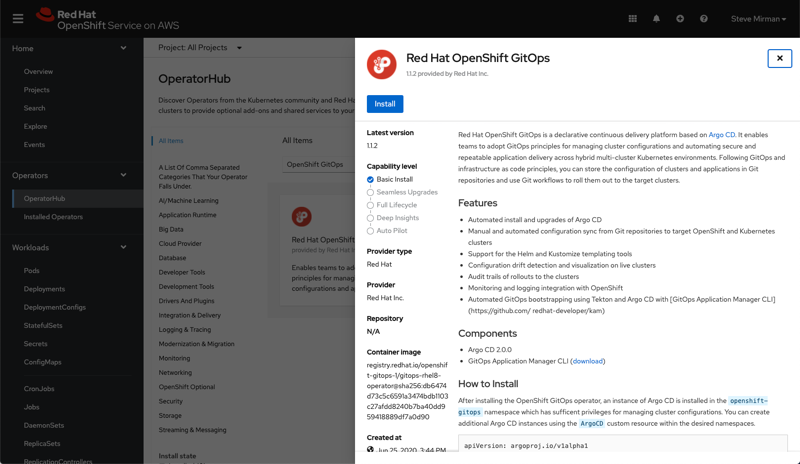
Install the OpenShift GitOps operator
- Install the OpenShift GitOps operator from the Operator Hub
Pull files from GitHub
-
Clone the
gitops-demoGitHub repository to your local machinegit clone https://github.com/rh-mobb/gitops-demo gitops -
Export your local path to the GitHub files
export GITOPS_HOME="$(pwd)/gitops" cd $GITOPS_HOME
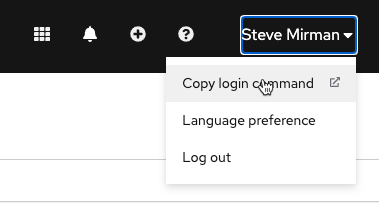
Log in to OpenShift via the CLI
-
Retrieve the login command from the OpenShift console
-
Enter the command in your terminal to authenticate with the OpenShift CLI (oc)
Output should appear similar to:
Logged into "https://<YOUR-INSTANCE>.openshiftapps.com:6443" as "<YOUR-ID>" using the token provided.
Deploy the ArgoCD Project
Create a new OpenShift project
- Create a new OpenShift project called gitops
oc new-project gitops
Edit service account permissions
- Add cluster-admin rights to the
openshift-gitops-argocd-application-controllerservice account in the openshift-gitops namespace
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin -z openshift-gitops-argocd-application-controller -n openshift-gitops
Log in to ArgoCD
-
Retrieve ArgoCD URL:
argoURL=$(oc get route openshift-gitops-server -n openshift-gitops -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}{"\n"}') echo $argoURL -
Retrieve ArgoCD Password:
argoPass=$(oc get secret/openshift-gitops-cluster -n openshift-gitops -o jsonpath='{.data.admin\.password}' | base64 -d) echo $argoPass -
In a browser, navigate to the ArgoCD console using the
$argoURLvalue returned above

-
Log in with the user name admin and the password returned as
$argoPassabove
Optional step if you prefer CLI access
Login to the CLI:argocd login --insecure --grpc-web $argoURL --username admin --password $argoPass
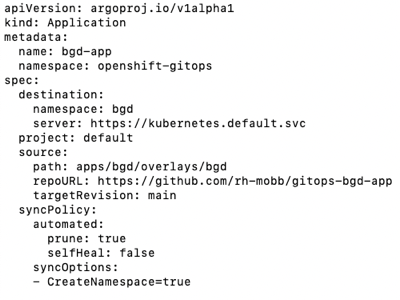
Deploy the ArgoCD project
-
Use
kubectlto apply thebgd-app.yamlfilekubectl apply -f documentation/modules/ROOT/examples/bgd-app/bgd-app.yamlThe bgd-app.yaml file defines several things, including the repo location for the
gitops-bgd-appapplication
-
Check the rollout running the following command:
kubectl rollout status deploy/bgd -n bgd -
Once the rollout is complete get the route to the application
oc get route bgd -n bgd -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}{"\n"}' -
In your browser, paste the route to open the application
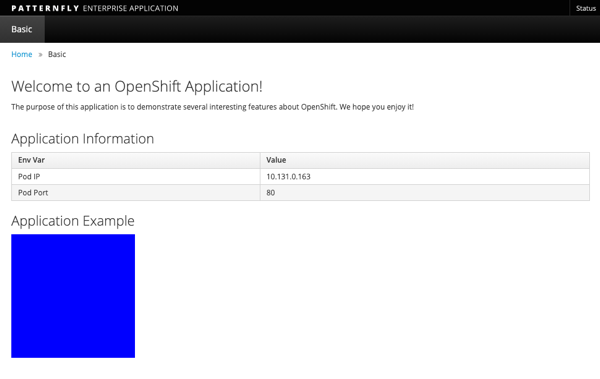
-
Go back to your ArgoCD window and verify the configuration shows there as well
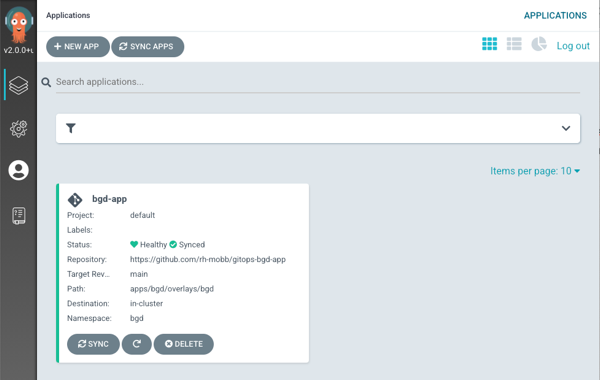
-
Exploring the application in ArgoCD, you can see all the components are green (synchronized)
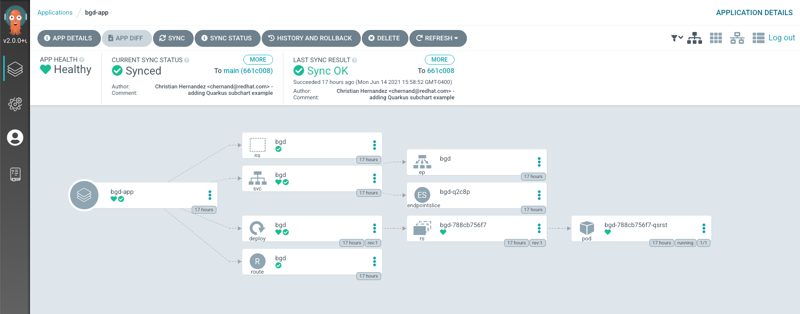
Deploy a change to the application
-
In the terminal, enter the following command which will introduce a chance into the bgd application
kubectl -n bgd patch deploy/bgd --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/env/0/value", "value":"green"}]' -
Go back to your ArgoCD window. The application should no longer be synchronized
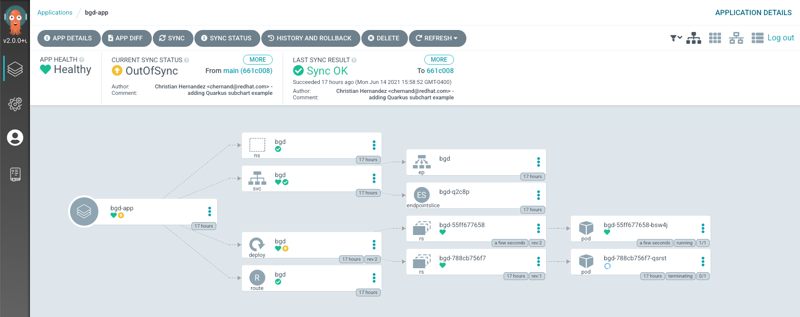
-
Refresh the bgd application window and notice the change in box color
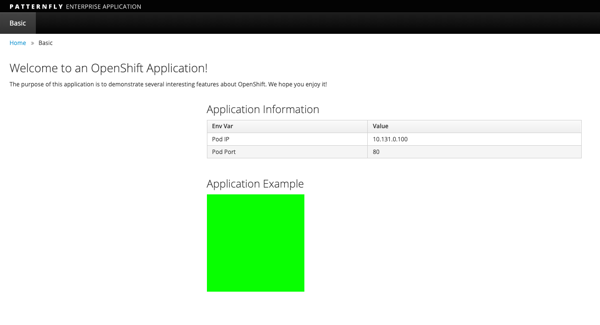
The new deployment changed the box from blue to green, but only within OpenShift, not in the source code repository
Synchronize the application
-
In the ArgoCD console, click the
SYNCbutton to re-synchronize the bgd application with the approved configuration in the source code repository

-
Refresh the bgd application window and notice the change in box color

Video Walkthrough
If you prefer a more visual medium, you can watch Steve Mirman walk through this quickstart on YouTube.


Comments