-
Language:
English
-
Language:
English
Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Gluster Storage
Console Developer Guide
Red Hat Storage Console Developer Guide
Abstract
Part I. Introduction
Chapter 1. Introduction
- Broad client support - Any programming language, framework, or system with support for HTTP protocol can use the API;
- Self descriptive - Client applications require minimal knowledge of the storage infrastructure as many details are discovered at runtime;
- Resource-based model - The resource-based REST model provides a natural way to manage a storage platform.
- Integrate with enterprise IT systems.
- Integrate with third-party software.
- Perform automated maintenance or error checking tasks.
- Automate repetitive tasks in a Red Hat Storage environment with scripts.
1.1. Representational State Transfer
GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. This provides a stateless communication between the client and server where each request acts independent of any other request and contains all necessary information to complete the request.
1.2. Prerequisites
- An installation of Red Hat Storage Console, which includes the REST API;
- A client or programming library that initiates and receives HTTP requests from the REST API. As an example, this guide includes basic instructions on use with cURL in Appendix B, API Usage with cURL;
- Knowledge of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which is the protocol used for REST API interactions. The Internet Engineering Task Force provides a Request for Comments (RFC) explaining the Hypertext Transfer Protocol at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt; and,
- Knowledge of Extensible Markup Language (XML), which the API uses to construct resource representations. The W3C provides a full specification on XML at http://www.w3.org/TR/xml/.
Chapter 2. Authentication and Security
2.1. TLS/SSL Certification
Procedure 2.1. Attain a certificate
- Method 1 - Use a command line tool to download the certificate from the server. Examples of command line tools include cURL and Wget; both are available for multiple platforms.
- If using cURL:
curl -o rhsc.cer http://[rhsc-server]/ca.crt
- If using Wget:
wget -O rhsc.cer http://[rhsc-server]/ca.crt
- Method 2 - Use a web browser to navigate to the certificate located at:
http://[rhsc-server]/ca.crt
Depending on the chosen browser, the certificate either downloads or imports into the browser's keystore.- If the browser downloads the certificate: save the file as
rhsc.cer.If the browser imports the certificate: export it from the browser's certification options and save it asrhsc.cer.
rhsc.cer on your client machine. An API user imports this file into the client's certificate store.
Procedure 2.2. Import a certificate to your client
- A certificate import for your client relies on how the client itself stores and interprets certificates. This guide contains an example on importing to a Java keystore in Appendix D, Java Keystores. For clients not using Network Security Services (NSS) or Java KeyStore (JKS), please refer to your client documentation for more information on importing a certificate.
2.2. HTTP Authentication
Authorization header, the API sends a 401 Authorization Required as a result:
Example 2.1. Access to the REST API without appropriate credentials
HEAD [base] HTTP/1.1 Host: [host] HTTP/1.1 401 Authorization Required
Authorization header for the specified realm. An API user encodes an appropriate Red Hat Storage Console domain and user in the supplied credentials with the username@domain:password convention.
Table 2.1. Encoding credentials for access to the API
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| username | rhscadmin |
| domain | domain.example.com |
| password | 123456 |
| unencoded credentials | rhscadmin@domain.example.com:123456 |
| base64 encoded credentials | cmhzY2FkbWluQGRvbWFpbi5leGFtcGxlLmNvbToxMjM0NTYK |
Example 2.2. Access to the REST API with appropriate credentials
HEAD [base] HTTP/1.1 Host: [host] Authorization: Basic cmhzY2FkbWluQGRvbWFpbi5leGFtcGxlLmNvbToxMjM0NTYK HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...
Important
Important
2.3. Authentication Sessions
- Send a request with the
AuthorizationandPrefer:persistent-auth.HEAD [base] HTTP/1.1 Host: [host] Authorization: Basic cmhzY2FkbWluQGRvbWFpbi5leGFtcGxlLmNvbToxMjM0NTYK Prefer: persistent-auth HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...
This returns a response with the following header:Set-Cookie: JSESSIONID=5dQja5ubr4yvI2MM2z+LZxrK; Path=/api; Secure
Note theJSESSIONID=value. In this example the value isJSESSIONID=5dQja5ubr4yvI2MM2z+LZxrK. - Send all subsequent requests with the
Prefer:persistent-authand cookie header with theJSESSIONID=value. TheAuthorizationis no longer needed when using an authenticated session.HEAD [base] HTTP/1.1 Host: [host] Prefer: persistent-auth cookie: JSESSIONID=5dQja5ubr4yvI2MM2z+LZxrK HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...
- When the session is no longer required, perform a request to the sever without the
Prefer: persistent-authheader.HEAD [base] HTTP/1.1 Host: [host] Authorization: Basic cmhzY2FkbWluQGRvbWFpbi5leGFtcGxlLmNvbToxMjM0NTYK HTTP/1.1 200 OK ...
Chapter 3. REST API Quick Start Examples
Important
Host: and Authorization: fields. However, these fields are mandatory and require data specific to your installation of Red Hat Storage Console.
Important
USER:PASS) and certificate location (CERT). Ensure all requests performed with cURL fulfil certification and authentication requirements. See Chapter 2, Authentication and Security and Appendix B, API Usage with cURL for more information.
Note
id attribute for each resource. Identifier codes in this example might appear different to the identifier codes in your Red Hat Storage Console environment.
3.1. Example: Access API Entry Point
Example 3.1. Access the API entry point
GET /api HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC Host]/api
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<api>
<link href="/api/capabilities" rel="capabilities"/>
<link href="/api/clusters" rel="clusters"/>
<link href="/api/clusters?search={query}" rel="clusters/search"/>
<link href="/api/events" rel="events"/>
<link href="/api/events;from={event_id}?search={query}" rel="events/search"/>
<link href="/api/hosts" rel="hosts"/>
<link href="/api/hosts?search={query}" rel="hosts/search"/>
<link href="/api/networks" rel="networks"/>
<link href="/api/networks?search={query}" rel="networks/search"/>
<link href="/api/roles" rel="roles"/>
<link href="/api/tags" rel="tags"/>
<link href="/api/users" rel="users"/>
<link href="/api/users?search={query}" rel="users/search"/>
<link href="/api/groups" rel="groups"/>
<link href="/api/groups?search={query}" rel="groups/search"/>
<link href="/api/domains" rel="domains"/>
<special_objects>
<link href="/api/tags/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" rel="tags/root"/>
</special_objects>
<product_info>
<name>Red Hat Storage Console</name>
<vendor>Red Hat</vendor>
<version major="3" minor="0" build="0" revision="0"/>
<full_version>3.0.0-0.10.el6_5</full_version>
</product_info>
<summary>
<hosts>
<total>0</total>
<active>0</active>
</hosts>
<users>
<total>1</total>
<active>1</active>
</users>
</summary>
<time>2014-06-23T06:47:18.567+05:30</time>
</api>
<total>1</total>
<active>1</active>
</users>
</summary>
</api>rel= attribute of each collection link provides a reference point for each link. The next step in this example examines the cluster collection, which is available through the rel="cluster" link.
product_info and summary. This data is covered in chapters outside this example.
3.2. Example: List Cluster Collection
Default cluster on installation. This example uses the Default cluster to group resources in your Red Hat Storage environment.
Example 3.2. List clusters collection
GET /api/clusters HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<clusters>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95" id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95">
<name>Default</name>
<description>The default server cluster</description>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks" rel="networks"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/permissions" rel="permissions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes" rel="glustervolumes"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glusterhooks" rel="glusterhooks"/>
<data_center href="/api/datacenters/5849b030-626e-47cb-ad90-3ce782d831b3" id="5849b030-626e-47cb-ad90-3ce782d831b3"/>
<memory_policy>
<overcommit percent="100"/>
<transparent_hugepages>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</transparent_hugepages>
</memory_policy>
<scheduling_policy>
<policy>none</policy>
</scheduling_policy>
<version major="3" minor="3"/>
<error_handling>
<on_error>migrate</on_error>
</error_handling>
<virt_service>false</virt_service>
<gluster_service>true</gluster_service>
<threads_as_cores>false</threads_as_cores>
<tunnel_migration>false</tunnel_migration>
<trusted_service>false</trusted_service>
<ballooning_enabled>false</ballooning_enabled>
</cluster>
</clusters>id code of your Default cluster. This code identifies this cluster in relation to other resources of your storage environment.
3.3. Example: List Host Collection
host1 registered with the default cluster.
Example 3.3. List hosts collection
GET /api/hosts HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC Host]/api/hosts
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept: application/xml
<hosts>
<host href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6" id="411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6">
<actions>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/approve" rel="approve"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/forceselectspm" rel="forceselectspm"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/iscsilogin" rel="iscsilogin"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/iscsidiscover" rel="iscsidiscover"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/commitnetconfig" rel="commitnetconfig"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/fence" rel="fence"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/deactivate" rel="deactivate"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/install" rel="install"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/activate" rel="activate"/>
</actions>
<name>host1</name>
<comment></comment>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/nics" rel="nics"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/tags" rel="tags"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/permissions" rel="permissions"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6/hooks" rel="hooks"/>
<address>10.70.42.154</address>
<certificate>
<organization>TestOrg</organization>
<subject>O=TestOrg,CN=10.70.42.154</subject>
</certificate>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32" id="02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32"/>
<port>54321</port>
<type>rhel</type>
<storage_manager priority="5">false</storage_manager>
<version major="4" minor="14" build="7" revision="2" full_version="vdsm-4.14.7.2-1.el6rhs"/>
<hardware_information>
<manufacturer>Red Hat</manufacturer>
<version>6Server-6.4.0.4.el6</version>
<serial_number>00000000-0000-0000-0000-00259078DB32</serial_number>
<product_name>RHEV Hypervisor</product_name>
<uuid>504dd302-0c14-4153-ae48-a0b2fa9484ce</uuid>
<family>Red Hat Enterprise Linux</family>
</hardware_information>
<power_management type="apc">
<enabled>false</enabled>
<options/>
</power_management>
<ksm>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</ksm>
<transparent_hugepages>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</transparent_hugepages>
<iscsi>
<initiator>iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:6f8b848932c9</initiator>
</iscsi>
<ssh>
<port>22</port>
<fingerprint>e7:02:ba:01:72:35:1c:5b:5a:ac:ba:b6:da:5d:23:8e</fingerprint>
</ssh>
<cpu>
<topology sockets="1" cores="1" threads="1"/>
<name>Intel Xeon E312xx (Sandy Bridge)</name>
<speed>2200</speed>
</cpu>
<memory>2103443456</memory> <max_scheduling_memory>1698693120</max_scheduling_memory>
<summary>
<active>0</active>
<migrating>0</migrating>
<total>0</total>
</summary>
<os type="RHEL">
<version full_version="6Server - 6.5.0.1.el6"/>
</os>
<libvirt_version major="0" minor="10" build="2" revision="0" full_version="libvirt-0.10.2-29.el6_5.9"/>
</host>
</hosts>id code of your Default server. This code identifies this host in relation to other resources of your virtual environment.
3.4. Example: Add Host to Cluster
Example 3.4. Add Server to Cluster
POST /api/hosts HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <host> <cluster id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95"/> <name>host1</name> <address>IP_ADDRESS</address> <root_password>ROOT_PASSWORD</root_password> </host>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/hosts -d "<host><cluster id=\"99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95\"/><name>host1</name><address>IP_ADDRESS</address><root_password>ROOT_PASSWORD</root_password></host>"
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<host href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349" id="de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349">
<name>host1</name>
<actions>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/fence" rel="fence"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/install" rel="install"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/activate" rel="activate"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/deactivate" rel="deactivate"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/approve" rel="approve"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/iscsilogin" rel="iscsilogin"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/iscsidiscover" rel="iscsidiscover"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/commitnetconfig" rel="commitnetconfig"/>
</actions>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/storage" rel="storage"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/nics" rel="nics"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/tags" rel="tags"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/permissions" rel="permissions"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<address>10.16.159.64</address>
<status>
<state>unassigned</state>
</status>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95" id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95"/>
<port>54321</port>
<type>rhel</type>
<storage_manager priority="5">false</storage_manager>
<power_management>
<enabled>false</enabled>
<options/>
</power_management>
<ksm>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</ksm>
<transparent_hugepages>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</transparent_hugepages>
<cpu>
<speed>0</speed>
</cpu>
<memory>0</memory>
<summary>
<total>0</total>
</summary>
</host>3.5. Example: Create Volume
data, volume type DISTRIBUTE, and having two bricks in the default cluster.
Example 3.5. Creating a Volume
POST api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<gluster_volume>
<name>data</name>
<volume_type>DISTRIBUTE</volume_type>
<bricks>
<brick>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick1</brick_dir>
</brick>
<brick>
<server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick2</brick_dir>
</brick>
</bricks>
</gluster_volume>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes -d "<gluster_volume><name>data</name><volume_type>DISTRIBUTE</volume_type><bricks><brick><server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick1</brick_dir></brick><brick><server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick2</brick_dir></brick></bricks></gluster_volume>"
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb" id="6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/setoption" rel="setoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/resetoption" rel="resetoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/resetalloptions" rel="resetalloptions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/rebalance" rel="rebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/stoprebalance" rel="stoprebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/start" rel="start"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/stop" rel="stop"/>
</actions>
<name>vol1</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/6c657343-7a9d-46f1-b9f2-209cd1a8aafb/bricks" rel="bricks"/>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32" id="02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32"/>
<volume_type>distribute</volume_type>
<transport_types>
<transport_type>tcp</transport_type>
</transport_types>
<replica_count>0</replica_count>
<stripe_count>0</stripe_count>
<options/>
<status>
<state>down</state>
</status>
</gluster_volume>3.6. Example: List Volume Collection
Default cluster.
Example 3.6. List Volume Collection
GET /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept: application/xml
<gluster_volumes>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa" id="0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/setoption" rel="setoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/resetoption" rel="resetoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/resetalloptions" rel="resetalloptions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/rebalance" rel="rebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/stoprebalance" rel="stoprebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/start" rel="start"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/stop" rel="stop"/>
</actions>
<name>test</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks" rel="bricks"/>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32" id="02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32"/>
<volume_type>distribute</volume_type>
<transport_types>
<transport_type>tcp</transport_type>
</transport_types>
<replica_count>0</replica_count>
<stripe_count>0</stripe_count>
<options>
<option name="auth.allow" value="*"/>
<option name="nfs.disable" value="off"/>
<option name="user.cifs" value="enable"/>
</options>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
</gluster_volume>
</gluster_volumes>3.7. Example: Start Volume
Example 3.7. Start Volume
POST api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/start HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <action/>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/start -d "<action/>"
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept: application/xml
<action>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>
3.8. Example: List Brick Collection
Example 3.8. List Brick Collection
GET /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept: application/xml
<bricks>
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/migrate" rel="migrate"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/stopmigrate" rel="stopmigrate"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/activate" rel="activate"/>
</actions>
<brick href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/f115ae70-2ff6-43c7-aa36-26631df82bcb" id="f115ae70-2ff6-43c7-aa36-26631df82bcb">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/f115ae70-2ff6-43c7-aa36-26631df82bcb/replace" rel="replace"/>
</actions>
<name>vm12.lab.eng.blr.redhat.com:/home/1</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/f115ae70-2ff6-43c7-aa36-26631df82bcb/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa" id="0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa"/>
<server_id>411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6</server_id>
<brick_dir>/home/1</brick_dir>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
</brick>
<brick href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/b46215cd-785e-41aa-b424-5783955d43ee" id="b46215cd-785e-41aa-b424-5783955d43ee">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/b46215cd-785e-41aa-b424-5783955d43ee/replace" rel="replace"/>
</actions>
<name>vm12.lab.eng.blr.redhat.com:/home/2</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/b46215cd-785e-41aa-b424-5783955d43ee/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa" id="0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa"/>
<server_id>411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6</server_id>
<brick_dir>/home/2</brick_dir>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
</brick>
</bricks>3.9. Example: Add Bricks to Volume
Example 3.9. Add Bricks to Volume
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<bricks>
<brick>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick3</brick_dir>
</brick>
</bricks>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks -d "<bricks><brick><server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick3</brick_dir></brick></bricks>"
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<bricks>
<brick href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/5241646b-f7aa-4484-9c4a-be33ebf4f51d" id="5241646b-f7aa-4484-9c4a-be33ebf4f51d">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/5241646b-f7aa-4484-9c4a-be33ebf4f51d/replace" rel="replace"/>
</actions>
<name>vm12.lab.eng.blr.redhat.com:/home/3</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa/bricks/5241646b-f7aa-4484-9c4a-be33ebf4f51d/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<port>49154</port>
<pid>26691</pid>
<device>/dev/mapper/vg_vm12-lv_root</device>
<mnt_options>rw</mnt_options>
<fs_name>ext4</fs_name>
<gluster_clients>
<gluster_client>
<host_name>10.70.36.84</host_name>
<client_port>1019</client_port>
<bytes_read>1260</bytes_read>
<bytes_written>900</bytes_written>
</gluster_client>
</gluster_clients>
<memory_pools>
<memory_pool>
<name>test-server:fd_t</name>
<hot_count>0</hot_count>
<cold_count>1024</cold_count>
<padded_size>108</padded_size>
<alloc_count>0</alloc_count>
<max_alloc>0</max_alloc>
<pool_misses>0</pool_misses>
<max_stdalloc>0</max_stdalloc>
</memory_pool>
...
</memory_pools>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/02b2bd03-5e54-45f9-9302-33a4ba96eb32/glustervolumes/0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa" id="0635fb7e-0da8-48ca-ae9c-72be85c36afa"/>
<server_id>411fd862-1469-4dff-ad5a-a7be364d83a6</server_id>
<brick_dir>/home/3</brick_dir>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
</brick>
</bricks>3.10. Example: Check System Events
login action for admin creates entries in the events collection. This example lists the events collection and identifies events specific to log in of the admin.
Example 3.10. List the events collection
GET /api/events HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC Host]/api/events
<events>
<event href="/api/events/54" id="54">
<description>User admin@internal logged in.</description>
<code>30</code>
<severity>normal</severity>
<time>2013-11-27T17:48:01.264+05:30</time>
<user href="/api/users/fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc" id="fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc"/>
<origin>oVirt</origin>
<custom_id>-1</custom_id>
<flood_rate>30</flood_rate>
</event>
</events>id="54"- The API authenticates with theadminuser's username and password.id="192"- The API, acting as theadminuser, startsVolume Dataon theDefaultclusterid="193"- The API logs out of theadminuser account.
Chapter 4. Python Quick Start Example
4.1. Python Quick Start Introduction
ovirtsdk Python library provided by the rhsc-sdk package. This package is available to systems subscribed to a Red Hat Storage pool if you use the certificate-based Red Hat Network, or the Red Hat Storage channel if you use the Red Hat Network classic. See the Red Hat Storage Console Installation Guide for more information on subscribing systems to download software from these locations.
Note
- A networked installation of Red Hat Storage Console.
- A networked and configured Red Hat Storage Server.
- A working understanding of both the logical and physical objects that make up a Red Hat Storage environment.
- A working understanding of the Python programming language.
Important
Note
Note
ovirtsdk.infrastructure.errors module.
4.2. Example: Accessing the API Entry Point using Python
ovirtsdk Python library provides the API class, which acts as the entry point for the API.
Example 4.1. Accessing the API entry point using Python
API class. If connection is established successfully, a message is printed. Lastly, the disconnect() method of the API class is called to close the connection.
- The
urlof the Console with which to connect. - The
usernameof the user to authenticate. - The
passwordof the user to authenticate. - The
ca_filethat is the path to a certificate. The certificate is expected to be a copy of the Console's Certificate Authority. It can be obtained fromhttps://[HOST]/ca.crt.
API class supports other parameters. Only mandatory parameters are specified in this example.
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
print "Connected to %s successfully!" % api.get_product_info().name
api.disconnect()
except ConnectionError, err:
print "Connection failed: %s" % errConnected to Red Hat Storage Console successfully!
Example 4.2. Listing the Cluster Collection using Python
API class provides a cluster collection named default cluster. This collection contains all the clusters in the environment.
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
c_list = api.clusters.list()
for c in c_list:
print "%s (%s)" % (c.get_name(), c.get_id())
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % exDefault cluster exists, the example outputs:
Default (99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95)
Example 4.3. Listing the Networks Collection using Python
API class provides access to a networks collection named Management Networks. This collection contains all the networks in the environment.
networks collection. It also outputs some basic information about each network in the collection.
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@domain",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
n_list = api.networks.list()
for n in n_list:
print n.get_description()
print n.get_id()
print n.get_name()
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % exManagement Network 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000009 ovirtmgmt
Example 4.4. Listing the Host Collection using Python
API class provides access to a host collection. This collection contains all the hosts in the storage cluster.
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@domain",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
s_list = api.hosts.list()
for s in s_list:
print "host name: %s (host ID: %s)" % (s.get_name(), s.get_id())
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
host name: 10.70.37.49 (host ID: 5be18d62-e7b0-4407-8ff6-68290a92338f) host name: 10.70.37.50 (host ID: 3b202041-6e14-43df-a844-92a141bed1ed)
Example 4.5. Listing the Volume Collection using Python
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@domain",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
clusterName= "CLUSTERNAME"
for volume in api.clusters.get(
clusterName).glustervolumes.list():
print "volumeName:", volume.get_name(),
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % exExample 4.6. Listing the Brick Collection from a Volume using Python
getGlusterVolumeBrickDetails()lists the bricks of the volume that is assigned to the cluster.
def getGlusterVolumeBrickDetails(clusterName, volumeName):
bricks = []
for brick in API.clusters.get(
clusterName).glustervolumes.get(
volumeName).get_bricks().list():
bricks.append({"Brick": brick.get_name(),
"Status": brick.get_status().state})
return bricksExample 4.7. Listing hooks in a Red Hat Storage Console
getHookList(clusterName) lists the Gluster hooks created in the Console.
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@domain",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
clusterName="Default"
hooks=[]
for hook in api.clusters.get(clusterName).glusterhooks.list():
print "hookName:", hook.name
print "glusterCommand:", hook.get_gluster_command()
print "Stage:", hook.get_stage()
print "Hook ID:", hook.get_id()
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
hookName: add-brick-PRE-28Quota-enable-root-xattr-heal.sh glusterCommand: add-brick Stage: PRE Hook ID: b368f9dc-02a5-4e86-b96e-ea5393e73dc7 hookName: gsync-create-POST-56glusterd-geo-rep-create-post.sh glusterCommand: gsync-create Stage: POST
Part II. REST Application Programming Interface
Chapter 5. Entry Point
GET request on the entry point URI consisting of a host and base.
Example 5.1. Accessing the API Entry Point
www.example.com and the base is /api, the entry point appears with the following request:
GET /api HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Host: www.example.com
Authorization: [base64 encoded credentials]
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<api>
<link href="/api/domains" rel="domains" />
...
<product_info>
<name>Red Hat Storage Console</name>
<vendor>Red Hat</vendor>
<version major="3" minor="0" build="0" revision="0"/>
<full_version>3.0.0-0.10.el6_5</full_version>
</product_info>
<summary>
<hosts>
<total>3</total>
<active>2</active>
</hosts>
<users>
<total>1</total>
<active>1</active>
</users>
</summary>
</api>
Note
Host: and Authorization: request headers and assume the base is the default /api path. This base path differs depending on your implementation.
5.1. Product Information
product_info element to help an API user determine the legitimacy of the Red Hat Storage environment. This includes the name of the product, the vendor and the version.
Example 5.2. Verify a genuine Red Hat Storage environment
<api>
...
<product_info>
<name>Red Hat Storage Console</name>
<vendor>Red Hat</vendor>
<version major="3" minor="0" build="0" revision="0"/>
<full_version>3.0.0-0.10.el6_5</full_version>
</product_info>
...
</api>5.2. Link elements
link elements and URIs for all of the resource collections the API exposes. Each collection uses a relation type to identify the URI a client needs.
Table 5.1. Available Relationship Types
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
capabilities | Supported capabilities of the Red Hat Storage Console. |
clusters | Clusters. |
events | Events. |
hosts | Hosts. |
networks | Virtual networks. |
roles | Roles. |
tags | Tags. |
users | Users. |
groups | Imported identity service groups. |
domains | Identity service domains. |
link elements also contain a set of search URIs for certain collections. These URIs use URI templates [2] to integrate search queries. The purpose of the URI template is to accept a search expression using the natural HTTP pattern of a query parameter. The client does not require prior knowledge of the URI structure. Thus clients should treat these templates as being opaque and access them with a URI template library.
"collection/search".
Table 5.2. Relationships associated with search query URIs
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
clusters/search | Query clusters. |
events/search | Query events. |
hosts/search | Query hosts. |
users/search | Query users. |
groups/search | Query groups. |
5.3. Summary element
Table 5.3. Summary Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
hosts | Total number of hosts and total number of active hosts. |
users | Total number of users and total number of active users. |
5.4. RESTful Service Description Language (RSDL)
GET /api?rsdl HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<rsdl href="/api?rsdl" rel="rsdl">
<description>...</description>
<version major="3" minor="0" build="0" revision="0"/>
<schema href="/api?schema" rel="schema">
<name>...</name>
<description>...</description>
</schema>
<links>
<link href="/api/capabilities" rel="get">
...
</link>
...
</links>
</rsdl>Table 5.4. Table 5.5. RSDL Structure Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| description | A plain text description of the RSDL document. |
| version | The API version, including major release, minor release, build and revision. |
| schema | A link to the XML schema (XSD) file. . |
| links | Defines each link in the API. |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<rsdl href="/api?rsdl" rel="rsdl">
...
<links>
<link href="/api/..." rel="...">
<request>
<http_method>...</http_method>
<headers>
<header>
<name>...</name>
<value>...</value>
</header>
...
</headers>
<body>
<type>...</type>
<parameters_set>
<parameter required="..." type="...">
<name>...</name>
</parameter>
...
</parameters_set>
</body>
</request>
<response>
<type>...</type>
</response>
</link>
...
</links>
</rsdl>Table 5.5. RSDL Link Structure Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
link | A URI for API requests. Includes a URI attribute (href) and a relationship type attribute (rel). |
request | Defines the request properties required for the link. |
http_method | The method type to access this link. Includes the standard HTTP methods for REST API access: GET, POST, PUT and DELETE. |
headers | Defines the headers for the HTTP request. Contains a series of header elements, which each contain a header name and value to define the header. |
body | Defines the body for the HTTP request. Contains a resource type and a parameter_set, which contains a sets of parameter elements with attributes to define whether they are required for a request and the data type. The parameter element also includes a name element to define the Red Hat Storage Console property to modify and also a further parameter_set subset if type is set to collection. |
response | Defines the output for the HTTP request. Contains a type element to define the resource structure to output. |
Chapter 6. Capabilities
rel="capabilities" link obtained from the entry point URI.
6.1. Version-Dependent Capabilities
<capabilities>
<version major="3" minor="2">
...
</version>
<version major="3" minor="1">
...
</version>
...
</capabilities>version contains a series of capabilities dependent on the version specified.
6.2. Current Version
true or false.
<capabilities>
<version major="3" minor="4" href="/api/capabilities/332e3433-2e34-332e-3433-2e34332e3433" id="332e3433-2e34-332e-3433-2e34332e3433">
...
<current>true</current>
...
</version>
</capabilities>6.3. Red Hat Storage Volume Types
gluster_volume_types element lists the available type of Red Hat Storage volumes.
<capabilities>
<version major="3" minor="4"href="/api/capabilities/332e3433-2e34-332e-3433-2e34332e3433" id="332e3433-2e34-332e-3433-2e34332e3433">
...
<gluster_volume_types>
<gluster_volume_type>distribute</gluster_volume_type> <gluster_volume_type>replicate</gluster_volume_type> <gluster_volume_type>distributed_replicate</gluster_volume_type>
<gluster_volume_type>stripe</gluster_volume_type> <gluster_volume_type>distributed_stripe</gluster_volume_type> <gluster_volume_type>striped_replicate</gluster_volume_type> <gluster_volume_type>distributed_striped_replicate</gluster_volume_type>
</gluster_volume_types>
...
</version>
</capabilities>6.4. Red Hat Storage Transport Types
transport_types element lists the available transport types for Red Hat Storage volumes.
<capabilities>
<version major="3" minor="4" href="/api/capabilities/332e3433-2e34-332e-3433-2e34332e3433" id="332e3433-2e34-332e-3433-2e34332e3433">
...
<transport_types>
<transport_type>tcp</transport_type>
<transport_type>rdma</transport_type>
</transport_types>
...
</version>
</capabilities>6.5. Step Type
step_type element lists the available type of job steps while monitoring a jobs on Red Hat Storage volumes.
<step_types>
<step_type>validating</step_type>
<step_type>executing</step_type>
<step_type>finalizing</step_type>
<step_type>rebalancing_volume</step_type>
<step_type>removing_bricks</step_type>
<step_type>unknown</step_type>
</step_types>6.6. Gluster Hook Content Type
content_type element lists the Gluster Hook content types.
<content_types>
<content_type>text</content_type>
<content_type>binary</content_type>
</content_types>6.7. Gluster Hook Stage
hook_states element lists the available status of the hooks.
<hook_states>
<hook_state>enabled</hook_state>
<hook_state>disabled</hook_state>
<hook_state>missing</hook_state>
</hook_states>6.8. Resource Status States
creation_states, host_states, host_non_operational_details, gluster_volume_states, and brick_states.
Chapter 7. Common Features
Note
Table 7.1. Element property icons
| Property | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| Required for creation | These elements must be included in the client-provided representation of a resource on creation, but are not mandatory for an update of a resource. | 
|
| Non-updateable | These elements cannot have their value changed when updating a resource. Include these elements in a client-provided representation on update only if their values are not altered by the API user. If altered, the API reports an error. | 
|
| Read-only | These elements are read-only. Values for read-only elements are not created or modified. | 
|
7.1. Representations
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
<name>Resource-Name</name>
...
</resource>
In the context of a volume, the representation appears as follows:
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554" id="83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554">
<name>vol1</name>
...
</gluster_volume>
Table 7.2. Common attributes to resource representations
| Attribute | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
id | GUID | Each resource in the storage infrastructure contains an id, which acts as a globally unique identifier (GUID). The GUID is the primary method of resource identification. | 
|
href | string | The canonical location of the resource as an absolute path. | 
|
7.2. Collections
7.2.1. Listing All Resources in a Collection
GET request on the collection URI obtained from the entry point.
GET /api/[collection] HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<collection>
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
<name>Resource-Name</name>
<description>A description of the resource</description>
...
</resource>
...
</collection>
7.2.2. Listing Extended Resource Sub-Collections
Accept header includes the detail parameter.
GET /api/collection HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml; detail=subcollection
detail parameters:
GET /api/collection HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml; detail=subcollection1; detail=subcollection2
detail parameter that separates the sub-collection with the + operator:
GET /api/collection HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml; detail=subcollection1+subcollection2+subcollection3
Table 7.3. Collections that use extended sub-collections
| Collection | Extended Sub-Collection Support |
|---|---|
hosts | statistics |
bricks | statistics |
step | statistics |
Example 7.1. An request for extended statistics in the servers collection
GET /api/hosts HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml; detail=statistics
7.2.3. Searching Collections with Queries
GET request on a "collection/search" link results in a search query of that collection. The API only returns resources within the collection that satisfy the search query constraints.
GET /api/collection?search={query} HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<collection>
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
...
</resource>
...
</collection>7.2.3.1. Query Syntax
query with a GET request:
GET /api/collection?search={query} HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xmlquery template value refers to the search query the API directs to the collection. This query uses the same format as Red Hat Storage Console search query language:
(criteria) [sortby (element) asc|desc]
sortby clause is optional and only needed when ordering results.
Table 7.4. Example search queries
| Collection | Criteria | Result |
|---|---|---|
volumes | type=REPLICATE | Displays a list of all replicate volumes |
events | severity>normal sortby time | Displays the list of all events with severity higher than normal and sorted by the time element values. |
events | severity>normal sortby time desc | Displays the list of all events with severity higher than normal and sorted by the time element values in descending order. |
query template to be URL-encoded to translate reserved characters, such as operators and spaces.
Example 7.2. URL-encoded search query
GET /api/events?search=severity%3Derror HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
Important
7.2.3.2. Wildcards
Example 7.3. Wildcard search query for name=server*
GET /api/hosts?search=name%3Dserver* HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
server, such as server-1, server-2, or server-data.
Example 7.4. Wildcard search query for name=s*1
GET /api/hosts?search=name%3D*1 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
s and ending with 1, such as server1 or server-1 .
7.2.3.3. Pagination
page command.
Example 7.5. Paginating resources
GET /api/collection?search=page%201 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
page value to view the next page of results.
GET /api/collection?search=page%202 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
page command also in conjunction with other commands in a search query. For example:
GET /api/collection?search=sortby%20element%20asc%20page%202 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
7.2.4. Creating a Resource in a Collection
POST request to the collection URI containing a representation of the new resource.
POST request requires a Content-Type: application/xml header. This informs the API of the XML representation in the body content as part of the request.
fault representation indicating the missing elements.
POST /api/collection HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource>
<name>Resource-Name</name>
</resource>
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
<name>Resource-Name</name>
...
</resource>
Location header in the response gives the URI of the queried resource. The response body contains either a complete representation, partial representation or no representation of the resource. It is recommended that clients rely only on fetching the representation via the URI in the response header.
7.3. Resources
7.3.1. Retrieving a Resource
GET request on a URI obtained from a collection listing.
GET /api/collection/resource_id HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
...
</resource>
7.3.2. Updating a Resource
PUT request containing an updated description from a previous GET request for the resource URI. Details on modifiable properties are found in the individual resource type documentation.
PUT request requires a Content-Type: application/xml header. This informs the API of the XML representation in the body content as part of the request.
PUT /api/collection/resource_id HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource>
<name>New-Resource-Name</name>
</resource>
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
<name>New-Resource-Name</name>
...
</resource>
409 Conflict error with a fault representation in the response body.
7.3.3. Deleting a Resource
DELETE request sent to its URI.
DELETE /api/collection/resource_id HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
DELETE request to specify additional properties. A DELETE request with optional body content requires a Content-Type: application/xml header to inform the API of the XML representation in the body content. If a DELETE request contains no body content, omit the Content-Type: application/xml header.
7.3.4. Sub-Collection Relationships
- 1:N mappings, where mapped resources are dependent on a parent resources. Without the parent resource, the dependent resource cannot exist. For example, the link between a volume and its bricks.
- 1:N mappings, where mapped resources exist independently from parent resources but data is still associated with the relationship. For example, the link between a network and a cluster.
link rel= attribute:
GET /api/collection/resource_id HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id">
...
<link rel="subcollection"
href="/api/collection/resource_id/subcollection"/>
...
</resource>
GET /api/collection/resource_id/subcollection HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<subcollection>
<subresource id="subresource_id"
href="/api/collection/resource_id/subcollection/subresource_id">
...
</subresource>
...
</subcollection>
7.3.5. XML Element Relationships
- Backlinks from a resource in a sub-collection to a parent resource; or
- Links between resources with an arbitrary relationship.
Example 7.6. Backlinking from a sub-collection resource to a resource using an XML element
GET /api/collection/resource_id/subcollection/subresource_id HTTP/1.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<subcollection>
<subresource id="subresource_id"
href="/api/collection/resource_id/subcollection/subresource_id">
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id"/>
...
</subresource>
</subcollection>
7.3.6. Actions
<resource>
...
<actions>
<link rel="start" href="/api/collection/resource_id/start"/>
<link rel="stop" href="/api/collection/resource_id/stop"/>
...
</actions>
...
</resource>
POST request to the supplied URI. The body of the POST requires an action representation encapsulating common and task-specific parameters.
Table 7.5. Common action parameters
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
async | If true, the server responds immediately with 202 Accepted and an action representation contains a href link to be polled for completion. |
grace_period | a grace period in milliseconds, which must expire before the action is initiated. |
fault response.
Content-Type: application/xml header since the POST request requires an XML representation in the body content.
202 Accepted response provides a link to monitor the status of the task:
POST /api/collection/resource_id/action HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/xml
Accept: application/xml
<action>
<async>true</async>
</action>
HTTP/1.1 202 Accepted
Content-Type: application/xml
<action id="action_id"
href="/api/collection/resource_id/action/action_id">
<async>true</async>
...
<action>
GET on the action URI provides an indication of the status of the asynchronous task.
Table 7.6. Action statuses
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
pending | Task has not yet started. |
in_progress | Task is in operation. |
complete | Task completed successfully. |
failed | Task failed. The returned action representation would contain a fault describing the failure. |
GETs are 301 Moved Permanently redirected back to the target resource.
GET /api/collection/resource_id/action/action_id HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<action id="action_id"
href="/api/collection/resource_id/action/action_id">
<status>
<state>pending</state>
</status>
<link rel="parent" /api/collection/resource_id"/>
<link rel="replay" href="/api/collection/resource_id/action"/>
<action>
rel attribute:
Table 7.7. Action relationships
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
parent | A link back to the resource of this action. |
replay | A link back to the original action URI. POSTing to this URI causes the action to be re-initiated. |
7.3.7. Permissions
permissions sub-collection. Each permission contains a user, an assigned role and the specified resource. For example:
GET /api/collection/resource_id/permissions HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<permissions>
<permission id="permission-id"
href="/api/collection/resource_id/permissions/permission_id">
<role id="role_id" href="/api/roles/role_id"/>
<user id="user_id" href="/api/users/user_id"/>
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id"/>
</permission>
...
</permissions>
POST request with a permission representation and a Content-Type: application/xml header to the resource's permissions sub-collection. Each new permission requires a role and a user:
POST /api/collection/resource_id/permissions HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/xml
Accept: application/xml
<permission>
<role id="role_id"/>
<user id="user_id"/>
</permission>
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<permission id="permission_id"
href="/api/resources/resource_id/permissions/permission_id">
<role id="role_id" href="/api/roles/role_id"/>
<user id="user_id" href="/api/users/user_id"/>
<resource id="resource_id" href="/api/collection/resource_id"/>
</permission>
7.3.8. Handling Errors
fault representation in the response entity body. The fault contains a reason and detail strings. Clients must accommodate failed requests via extracting the fault or the expected resource representation depending on the response status code. Such cases are clearly indicated in the individual resource documentation.
PUT /api/collection/resource_id HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<resource>
<id>id-update-test</id>
</resource>
HTTP/1.1 409 Conflict
Content-Type: application/xml
<fault>
<reason>Broken immutability constraint</reason>
<detail>Attempt to set immutable field: id</detail>
</fault>
Chapter 8. Clusters
clusters collection provides information about clusters in a Red Hat Storage environment. An API user accesses this information through the rel="clusters" link obtained from the entry point URI (see Chapter 5, Entry Point).
Table 8.1. Cluster elements
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
link rel="networks" | relationship | A link to the sub-collection for networks associated with this cluster. | |
link rel="permissions" | relationship | A link to the sub-collection for cluster permissions. See Section 7.3.7, “Permissions”. | |
version major= minor= | complex | The compatibility level of the cluster. | 
|
supported_versions | complex | A list of possible version levels for the cluster. | 
|
gluster_service | boolean | defines whether gluster services are enabled on the cluster. Is always true in Red Hat Storage Console | |
virt_service | boolean | defines whether virtualization services are enabled on the cluster. Is always false in Red Hat Storage Console. |
Example 8.1. An XML representation of a cluster
<clusters>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95" id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95">
<name>Default</name>
<description>The default server cluster</description>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks" rel="networks"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/permissions" rel="permissions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes" rel="glustervolumes"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glusterhooks" rel="glusterhooks"/>
<data_center href="/api/datacenters/5849b030-626e-47cb-ad90-3ce782d831b3" id="5849b030-626e-47cb-ad90-3ce782d831b3"/>
<memory_policy>
<overcommit percent="100"/>
<transparent_hugepages>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</transparent_hugepages>
</memory_policy>
<scheduling_policy>
<policy>none</policy>
</scheduling_policy>
<version major="3" minor="4"/>
<error_handling>
<on_error>migrate</on_error>
</error_handling>
<virt_service>false</virt_service>
<gluster_service>true</gluster_service>
<threads_as_cores>false</threads_as_cores>
<tunnel_migration>false</tunnel_migration>
<trusted_service>false</trusted_service>
<ballooning_enabled>false</ballooning_enabled>
<ksm>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</ksm>
</clusters>name and server elements. Identify the server with id attribute and name element. name element is mandatory. See Section 7.2.4, “Creating a Resource in a Collection” for more information.
Example 8.2. Creating a cluster
POST /api/clusters HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<cluster>
<name>cluster1</name>
</cluster>Example 8.3. Updating a cluster
PUT /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95 HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<cluster>
<description>Cluster 1</description>
</cluster>DELETE request.
Example 8.4. Removing a cluster
DELETE /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95 HTTP/1.1 HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
8.1. Networks Sub-Collection
networks sub-collection. Every host within a cluster connects to these associated networks.
network sub-collection is the same as a standard network resource with an additional cluster id= to signify a relationship to the cluster and a display element to represent the display network status in the cluster.
networks sub-collection as described in Chapter 7, Common Features. POSTing a network id or name reference to the networks sub-collection associates the network with the cluster.
Example 8.5. Associating a network resource with a cluster
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<network>
<name>ovirtmgmt</name>
</network>
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Location: https://[host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks/da05ac09-00be-45a1-b0b5-4a6a2438665f
Content-Type: application/xml
<network id="da05ac09-00be-45a1-b0b5-4a6a2438665f"
href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks/
da05ac09-00be-45a1-b0b5-4a6a2438665f">
<name>rhsc</name>
<status>
<state>operational</state>
</status>
<description>Display Network</description>
<cluster id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95"
href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95"/>
<data_center id="d70d5e2d-b8ad-494a-a4d2-c7a5631073c4"
href="/api/datacenters/d70d5e2d-b8ad-494a-a4d2-c7a5631073c4"/>
<display>true</display>
</network>PUT request to specify the Boolean value (true or false) of the display element.
Example 8.6. Setting the display network status
PUT /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks/da05ac09-00be-45a1-b0b5-4a6a2438665f HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<network>
<display>false</display>
</network>
DELETE request to the appropriate element in the collection.
Example 8.7. Removing a network association from a cluster
DELETE /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/networks/da05ac09-00be-45a1-b0b5-4a6a2438665f HTTP/1.1
8.2. Gluster Hooks
glusterhooks collection provides information about Gluster Hooks in a Red Hat Storage environment. An API user accesses this information through the rel="glusterhooks" link obtained from the entry point URI (see Chapter 5, Entry Point).
Note
Table 8.2. Gluster Hooks elements
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
cluster | relationship | A reference to the cluster that includes this hook. | locked |
name | string | The name of the hook script | Read only |
gluster_command | string | gluster volume command for which the hook is executed | read only |
stage | string | stage of the command; PRE or POST | read only |
content_type | string | TEXT or BINARY | read only |
checksum | string | md5 checksum of the hook script | read only |
content | string | content of the hook script | read only |
conflict_status | integer | bit representation of the conflict detected for the hook. First bit is for content, second is for status and third is for missing hooks. | read only |
conflicts | string | comma separated list of conflict | read only |
status | One of enabled or disabled | The status of the hook. | update |
Example 8.8. An XML representation of Gluster Hook Collection
<glusterhooks>
<gluster_hook href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6" id="8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6/resolve" rel="resolve"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6/enable" rel="enable"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6/disable" rel="disable"/>
</actions> <name>add-brick-PRE-28Quota-enable-root-xattr-heal.sh</name> <cluster href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59" id="419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59">
<name>Cluster_3_3</name> ...
</cluster>
<gluster_command>add-brick</gluster_command>
<stage>PRE</stage>
<content_type>TEXT</content_type> <checksum>f08a82c0ac88b2565842d1de7cdb14c0</checksum>
<conflict_status>0</conflict_status>
<conflicts></conflicts>
<status>
<state>enabled</state>
</status>
</gluster_hook>8.2.1. Managing Gluster Hooks
8.2.1.1. Listing Gluster Hooks
GET request on the volume URI.
GET /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glusterhooks HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept: application/xml
<glusterhooks>
<gluster_hook href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6" id="8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6/resolve" rel="resolve"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6/enable" rel="enable"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/8ead05b0-3085-41a3-8693-9a7dfd6761a6/disable" rel="disable"/>
</actions>
<name>add-brick-PRE-28Quota-enable-root-xattr-heal.sh</name>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59" id="419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59">
<name>Cluster_3_3</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/networks" rel="networks"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/permissions" rel="permissions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes" rel="glustervolumes"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks" rel="glusterhooks"/>
<memory_policy>
<overcommit percent="100"/>
<transparent_hugepages>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</transparent_hugepages>
</memory_policy>
<scheduling_policy>
<policy>none</policy>
</scheduling_policy>
<error_handling>
<on_error>migrate</on_error>
</error_handling>
<virt_service>false</virt_service>
<gluster_service>true</gluster_service>
<threads_as_cores>false</threads_as_cores>
<tunnel_migration>false</tunnel_migration>
<trusted_service>false</trusted_service>
<ballooning_enabled>false</ballooning_enabled>
</cluster>
<gluster_command>add-brick</gluster_command>
<stage>PRE</stage>
<content_type>TEXT</content_type>
<checksum>f08a82c0ac88b2565842d1de7cdb14c0</checksum>
<conflict_status>0</conflict_status>
<conflicts></conflicts>
<status>
<state>enabled</state>
</status>
</gluster_hook>8.2.1.2. Enabling Gluster Hooks
POST request to its URI.
POST /api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/747bbb9e-ace6-424b-be31-16b33e02d882/enable HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glusterhooks/747bbb9e-ace6-424b-be31-16b33e02d882/enable -d "<action/>"
<action>
<job href="/api/jobs/58584575-6089-4cef-bdae-a2fc5f406bbd" id="58584575-6089-4cef-bdae-a2fc5f406bbd"/>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>8.2.1.3. Resolving Gluster Hook Conflict
POST request. MISSING_HOOK, CONTENT_CONFLICT, and STATUS_CONFLICT are the types of conflict that can be resolved on a cluster.
- Missing Hook Conflict:
MISSING_HOOKconflict can be resolved either by adding the hook to the host where it is missing or by removing it from all hosts and from the Red Hat Storage Console by issuing aDELETErequest.cURL command to resolve missing hook conflict by adding hook:curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glusterhooks/59ecbacb-1ce3-43f7-82e4-55db8ed74f56/resolve -d "<action><resolution_type>ADD</resolution_type></action>"The API returns the following representation:<action> <resolution_type>ADD</resolution_type> <job href="/api/jobs/46d89857-37a1-492a-9327-78922884a778" id="46d89857-37a1-492a-9327-78922884a778"/> <status> <state>complete</state> </status> </action>cURL command to resolve missing hook conflict by deleting hook:curl -X DELETE -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glusterhooks/18782869-3e62-42a5-a59d-91f896afd5d7<action> <job href="/api/jobs/3dd9800f-a8c6-4f58-a3cf-dff190d2f06f" id="3dd9800f-a8c6-4f58-a3cf-dff190d2f06f"/> <status><state>complete</state> </status> </action>
- Content ConflictThis conflict can be resolved with the
resolution_type = copy. If the version of the hook is incorrect in Red Hat Storage Console, the content is copied from a host by passing the host.name parameter. If the host.name parameter is empty, then the content is copied from Red Hat Storage Console to all host where content is differentcURL command:curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glusterhooks/59ecbacb-1ce3-43f7-82e4-55db8ed74f56/resolve -d "<action><resolution_type>COPY</resolution_type><host><name>host.name</name></host></action>"The API returns the following representation:<action> <host> <name>host.name</name> </host> <resolution_type>COPY</resolution_type> <job href="/api/jobs/75486b97-ee5b-4a61-af6e-960b874985fc" id="75486b97-ee5b-4a61-af6e-960b874985fc"/> <status> <state>complete</state> </status> </action> - Status ConflictThis conflict is resolved by either enabling or disabling a hook in a cluster.
Chapter 9. Hosts
hosts collection provides information about the hosts in a Red Hat Storage environment. An API user accesses this information through the rel="hosts" link obtained from the entry point URI (see Chapter 5, Entry Point).
Table 9.1. Host elements
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
link rel="nics" | relationship | A link to the nics sub-collection for host network interfaces. | |
link rel="tags" | relationship | A link to the tags sub-collection for host tags. | |
link rel="permissions" | relationship | A link to the permissions sub-collection for host permissions. See Chapter 7, Common Features. | |
link rel="statistics" | relationship | A link to the statistics sub-collection for host statistics. | 
|
address | string | The IP address or hostname of the host. | 

|
status | See below | The host status. | 
|
cluster id= | GUID | A reference to the cluster that includes this host. | |
port | integer | The listen port of the VDSM daemon running on this host. | 
|
iscsi | complex | The SCSI initiator for the host. | 
|
cpu | complex | Statistics for the host CPU. Includes sub-elements for the CPU's name, topology cores=, topology sockets= and speed. The topology cores= aggregates the total cores while the topology sockets= aggregates the total physical CPUs. | 
|
version major= minor= | complex | The compatibility level of the host. | 
|
root_password | string | The root password of this host, by convention only included in the client-provided host representation on creation. | 

|
status contains one of the following enumerative values: down, error, initializing, installing, install_failed, maintenance, non_operational, non_responsive, pending_approval, preparing_for_maintenance, connecting, reboot, unassigned and up. These states are listed in host_states under capabilities.
Example 9.1. An XML representation of a host
<hosts>
<host href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56" id="eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56">
<actions>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/forceselectspm" rel="forceselectspm"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/iscsilogin" rel="iscsilogin"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/iscsidiscover" rel="iscsidiscover"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/commitnetconfig" rel="commitnetconfig"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/approve" rel="approve"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/fence" rel="fence"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/install" rel="install"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/activate" rel="activate"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/deactivate" rel="deactivate"/>
</actions>
<name>host1</name>
<comment></comment>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/storage" rel="storage"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics" rel="nics"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/tags" rel="tags"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/permissions" rel="permissions"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/hooks" rel="hooks"/>
<address>10.70.43.145</address>
<certificate>
<organization>Test</organization>
<subject>O=Test,CN=10.70.43.145</subject>
</certificate>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59" id="419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59"/>
<port>54321</port>
<type>rhel</type>
<storage_manager priority="5">false</storage_manager>
<version major="4" minor="14" build="7" revision="2" full_version="vdsm-4.14.7.2-1.el6rhs"/>
<hardware_information>
<manufacturer>Red Hat</manufacturer>
<version>6Server-6.4.0.4.el6</version>
<serial_number>4C4C4544-004E-5A10-8031-B1C04F4E5631_bc:30:5b:f2:bc:60</serial_number>
<product_name>RHEV Hypervisor</product_name>
<uuid>f70d244f-5fd9-4106-965d-a3d1bb1f0b3b</uuid>
<family>Red Hat Enterprise Linux</family>
</hardware_information>
<power_management>
<enabled>false</enabled>
<options/>
</power_management>
<ksm>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</ksm>
<transparent_hugepages>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</transparent_hugepages>
<iscsi>
<initiator>iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:4c5810adce86</initiator>
</iscsi>
<ssh>
<port>22</port>
<fingerprint>7b:e5:04:1f:df:b4:73:ed:4f:c2:7a:97:a7:5a:93:98</fingerprint>
</ssh>
<cpu>
<topology sockets="1" cores="1" threads="1"/>
<name>Intel Xeon E312xx (Sandy Bridge)</name>
<speed>2200</speed>
</cpu>
<memory>2103443456</memory>
<max_scheduling_memory>1698693120</max_scheduling_memory>
<summary>
<active>0</active>
<migrating>0</migrating>
<total>0</total>
</summary>
<os type="RHEL">
<version full_version="6Server - 6.5.0.1.el6"/>
</os>
<libvirt_version major="0" minor="10" build="2" revision="0" full_version="libvirt-0.10.2-18.el6_4.15"/>
</host>
</hosts>name, address and root_password elements. See Section 7.2.4, “Creating a Resource in a Collection” for more information.
Example 9.2. Creating a host
POST /api/hosts HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <host> <name>host2</name> <address>host2.example.com</address> <root_password>p@55w0Rd!</root_password> <cluster>cluster_name</cluster> </host>
root_password element is only included in the client-provided initial representation and is not exposed in the representations returned from subsequent requests.
name and cluster elements are updatable post-creation. See Section 7.3.2, “Updating a Resource” for more information.
Example 9.3. Updating a host
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <host> <name>host3</name> </host>
DELETE request.
Example 9.4. Removing a host
DELETE /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3 HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
9.1. Network Interface Sub-Collection
nics sub-collection represents a host's physical network interfaces. Each host_nic element in the representation acts as a network interface and contains the following elements:
Note
Table 9.2. Elements for a host's network interfaces
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
name | string | The name of the host network interface, e.g. eth0 |  [a]
[a] 
|
link rel="statistics" | relationship | A link to the statistics sub-collection for a host's network interface statistics. | 
|
link rel="master" | relationship | A reference to the master bonded interface, if this is a slave interface. | 
|
host id= | GUID | A reference to the host. | 
|
network id= | GUID | A reference to the network, if any, that the interface is attached. |  [b]
[b] |
mac address= | string | The MAC address of the interface. | 
|
ip address= netmask= gateway= | complex | The IP level configuration of the interface. | |
boot_protocol | enumerated | The protocol for IP address assignment when the host is booting. A list of enumerated values is available in capabilities. | |
speed | integer | The network interface speed in bits per second. | 
|
status | enumerated | The link status for the network interface. These states are listed in host_nic_states under capabilities. | 
|
vlan id | integer | The VLAN which this interface represents. | 
|
bonding | complex | A list of options and slave NICs for bonded interfaces. |  [c]
[c] 
|
[a]
Only required when adding bonded interfaces. Other interfaces are read-only and cannot be added.
[b]
Only required when adding bonded interfaces. Other interfaces are read-only and cannot be added.
[c]
Only required when adding bonded interfaces. Other interfaces are read-only and cannot be added.
| |||
Example 9.5. An XML representation of a network interface on a host
<host_nic href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics/4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a" id="4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a">
<actions>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics/4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a/attach" rel="attach"/>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics/4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a/detach" rel="detach"/>
</actions>
<name>eth0</name>
<link href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics/4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a/statistics" rel="statistics"/>
<host href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56" id="eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56"/>
<network href="/api/networks/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000009" id="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000009"/>
<mac address="00:15:1e:00:9d:4c"/>
<ip address="10.70.43.145" netmask="255.255.252.0" gateway="10.70.43.254"/>
<boot_protocol>dhcp</boot_protocol>
<status>
<state>up</state>
</status>
<mtu>1500</mtu>
<bridged>true</bridged>
<custom_configuration>false</custom_configuration>
</host_nic>network, ip and boot_protocol elements using a PUT request.
name and network elements are required. Identify the network element with the id attribute or name element.
PUT request.
PUT /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/nics/
e8f02fdf-3d7b-4135-86e1-1bf185570cd8 HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<nic>
<ip address="192.168.0.129" netmask="255.255.255.0" gateway="192.168.0.1"/>
</nic>
DELETE request.
DELETE /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/nics/ e8f02fdf-3d7b-4135-86e1-1bf185570cd8 HTTP/1.1 HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
9.1.1. Bonded Interfaces
host_nic resource containing a bonding element.
Table 9.3. Bonded interface properties
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
options | complex | A list of option elements for a bonded interface. Each option contains property name and value attributes. |  [a]
[a] 
|
slaves | complex | A list of slave host_nic id= elements for a bonded interface. |  [b]
[b] 
|
[a]
Only required when adding bonded interfaces. Other interfaces are read-only and cannot be added.
[b]
Only required when adding bonded interfaces. Other interfaces are read-only and cannot be added.
| |||
POSTing to a host_nic with bonding options and slave interfaces. The name, network and bonded elements are required when creating a new bonded interface. Either the id or name elements identify the network and slave host_nics.
Example 9.6. Creating a bonded interface
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/nics HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<host_nic>
<name>bond4</name>
<network id="e657d631-657d-42bb-a536-73501a085d85"/>
<bonding>
<options>
...
</options>
<slaves>
<host_nic id="eb14e154-5e73-4f7f-bf6b-7f52609d94ec"/>
<host_nic id="6aede5ca-4c54-4b37-a81b-c0d6b53558ea"/>
</slaves>
</bonding>
</host_nic>
Important
bond0, bond1, bond2, bond3 and bond4 are the only valid names for a bonded interface.
DELETE request to a bonded interface URI deletes it.
Important
9.1.2. Network Interface Statistics
statistics sub-collection for a host's network interface statistics. Each statistic contains the following elements:
Table 9.4. Elements for a host's network interface statistics
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | string | The unique identifier for the statistic entry. |
description | string | A plain text description of the statistic. |
unit | string | The unit or rate to measure the statistical values. |
type | One of GAUGE or COUNTER | The type of statistic measures. |
values type= | One of INTEGER or DECIMAL | The data type for the statistical values that follow. |
value | complex | A data set that contains datum. |
datum | see values type | An individual piece of data from a value. |
host_nic id= | relationship | A relationship to the containing host_nic resource. |
Table 9.5. Host NIC statistic types
|
Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
data.current.rx |
The rate in bytes per second of data received.
|
data.current.tx |
The rate in bytes per second of data transmitted.
|
errors.total.rx |
Total errors from receiving data.
|
errors.total.tx |
Total errors from transmitting data.
|
Example 9.7. An XML representation of a host's network interface statistics sub-collection
<statistics>
<statistic href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics/4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a/statistics/ecd0559f-e88f-3330-94b4-1f091b0ffdf7" id="ecd0559f-e88f-3330-94b4-1f091b0ffdf7">
<name>data.current.rx</name>
<description>Receive data rate</description>
<values type="DECIMAL">
<value>
<datum>0</datum>
</value>
</values>
<type>GAUGE</type>
<unit>BYTES_PER_SECOND</unit>
<host_nic href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/nics/4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a" id="4800fa31-08f0-40bb-9964-ea6045702b2a"/>
</statistic>
...
</statistics>Note
statistics sub-collection is read-only.
9.1.3. Attach Action
id or name elements identify the network.
Example 9.8. Action to attach a host network interface to a network
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/nics/e8f02fdf-3d7b-4135-86e1-1bf185570cd8/attach HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<action>
<network id="e657d631-657d-42bb-a536-73501a085d85"/>
</action>
Important
9.1.4. Detach Action
id or name elements identify the network.
Example 9.9. Action to detach a host network interface to a network
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/nics/e8f02fdf-3d7b-4135-86e1-1bf185570cd8/detach HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<action>
<network id="e657d631-657d-42bb-a536-73501a085d85"/>
</action>
Important
9.2. Statistics Sub-Collection
statistics sub-collection for host-specific statistics. Each statistic contains the following elements:
Table 9.6. Elements for host statistics
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | string | The unique identifier for the statistic entry. |
description | string | A plain text description of the statistic. |
unit | string | The unit or rate to measure the statistical values. |
type | One of GAUGE or COUNTER | The type of statistic measures. |
values type= | One of INTEGER or DECIMAL | The data type for the statistical values that follow. |
value | complex | A data set that contains datum. |
datum | see values type | An individual piece of data from a value. |
host id= | relationship | A relationship to the containing host resource. |
Table 9.7. Host statistic types
|
Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
memory.total |
Total memory in bytes on the host.
|
memory.used |
Memory in bytes used on the host.
|
memory.free |
Memory in bytes free on the host.
|
memory.buffers |
I/O buffers in bytes.
|
memory.cached |
OS caches in bytes.
|
swap.total |
Total swap memory in bytes on the host.
|
swap.free |
Swap memory in bytes free on the host.
|
swap.used |
Swap memory in bytes used on the host.
|
swap.cached |
Swap memory in bytes also cached in host's memory.
|
ksm.cpu.current |
Percentage of CPU usage for Kernel SamePage Merging.
|
cpu.current.user |
Percentage of CPU usage for users.
|
cpu.current.system |
Percentage of CPU usage for system.
|
cpu.current.idle |
Percentage of idle CPU usage.
|
cpu.load.avg.5m |
CPU load average per five minutes.
|
Example 9.10. An XML representation of the host's statistics sub-collection
<statistics>
<statistic href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56/statistics/7816602b-c05c-3db7-a4da-3769f7ad8896" id="7816602b-c05c-3db7-a4da-3769f7ad8896">
<name>memory.total</name>
<description>Total memory</description>
<values type="INTEGER">
<value>
<datum>2103443456</datum>
</value>
</values>
<type>GAUGE</type>
<unit>BYTES</unit>
<host href="/api/hosts/eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56" id="eaf4af64-e51c-4e72-a2cf-bdb6076a9e56"/>
</statistic>
</statistics>Note
statistics sub-collection is read-only.
9.3. Actions
host resources.
install, activate, fence, deactivate, approve, iscsilogin, iscsidiscover and commitnetconfig.
9.3.1. Install Action
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux host - This host type requires a
root_passwordelement that refers to the password for the host'srootuser.
Example 9.11. Action to install VDSM to a Red Hat Enterprise Linux host
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/install HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<action>
<root_password>p@55w0Rd!</root_password>
</action>9.3.2. Activate Action
Example 9.12. Action to activate a host
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/activate HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <action/>
9.3.3. Fence Action
fence action. The capabilities lists available fence_type options.
Example 9.13. Action to fence a host
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/fence
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<action>
<fence_type>start</fence_type>
</action>9.3.4. Deactivate Action
Example 9.14. Action to deactivate a host
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/deactivate HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <action/>
9.3.5. Commit Network Configuration Action
Example 9.15. Action to commit network configuration
POST /api/hosts/2ab5e1da-b726-4274-bbf7-0a42b16a0fc3/commitnetconfig HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <action/>
Important
Chapter 10. Volumes
volumes collection provides information about volumes in a Red Hat Storage environment.
Table 10.1. Volume elements
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
volumeName | relationship | Name of the volume to be created. | 

|
volumeType | relationship | DISTRIBUTE,REPLICATE, DISTRIBUTED_REPLICATE, STRIPE, DISTRIBUTED_STRIPE. | 
|
replicaCount | complex | replicaCount is mandatory if volumeType is REPLICATE or DISTRIBUTED_REPLICATE | 
|
stripeCount | complex | stripeCount is mandatory if volumeType is STRIPE or DISTRIBUTED_STRIPE | 
|
bricks | complex | list of bricks of a volume. You can add/remove bricks to/from a volume. | 
|
| options | complex | list of options of the volume |
Example 10.1. An XML representation of a volume
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50" id="6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/rebalance" rel="rebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/stoprebalance" rel="stoprebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/resetoption" rel="resetoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/resetalloptions" rel="resetalloptions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/setoption" rel="setoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/start" rel="start"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/stop" rel="stop"/>
</actions>
<name>newVol</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/bricks" rel="bricks"/>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59" id="419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59"/>
<volume_type>distribute</volume_type>
<transport_types>
<transport_type>tcp</transport_type>
</transport_types>
<replica_count>0</replica_count>
<stripe_count>0</stripe_count>
<options/>
<status>
<state>down</state>
</status>
</gluster_volume>10.1. Creating a Volume
volumeName, volumeType,transportType and brick elements. The API creates a new volume with a POST request to the URI containing a representation of the new volume
Example 10.2. Creating a volume
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<gluster_volume>
<name>data</name>
<volume_type>distribute</volume_type>
<bricks>
<brick>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick1</brick_dir>
</brick>
<brick>
<server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick2</brick_dir>
</brick>
</bricks>
</gluster_volume>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes -d "<gluster_volume><name>data</name><volume_type>DISTRIBUTE</volume_type><bricks><brick><server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick1</brick_dir></brick><brick><server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick2</brick_dir></brick></bricks></gluster_volume>"
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554" id="83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554">
<name>data</name>
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/start" rel="start"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/stop" rel="stop"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/setOption" rel="setOption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/rebalance" rel="rebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/resetOption" rel="resetOption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/resetAllOptions" rel="resetAllOptions"/>
</actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks" rel="bricks"/>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95" id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95"/>
<volume_type>distribute</volume_type>
<transport_types>
<transport_type>TCP</transport_type>
</transport_types>
<replica_count>0</replica_count>
<stripe_count>0</stripe_count>
<options/>
<state>DOWN</state>
</gluster_volume>10.2. Listing Volumes
GET request on the cluster URI.
Example 10.3. Listing Volumes
GET /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50" id="6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/rebalance" rel="rebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/stoprebalance" rel="stoprebalance"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/resetoption" rel="resetoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/resetalloptions" rel="resetalloptions"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/setoption" rel="setoption"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/start" rel="start"/>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/stop" rel="stop"/>
</actions>
<name>newVol</name>
<link href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59/glustervolumes/6d4bc7ed-4278-45e1-973e-e9a5e061de50/bricks" rel="bricks"/>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59" id="419590b8-5aa0-473b-9651-aa41f1372c59"/>
<volume_type>distribute</volume_type>
<transport_types>
<transport_type>tcp</transport_type>
</transport_types>
<replica_count>0</replica_count>
<stripe_count>0</stripe_count>
<options/>
<status>
<state>down</state>
</status>
</gluster_volume>10.3. Managing Volumes
POST request to the URI.
10.3.1. Starting a Volume
POST request to the volumes URI.
Example 10.4. Starting a Volume
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/start HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml <action> [ <force>true</force> ] </action>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/start -d "<action/>"
<action>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>10.3.2. Stopping a Volume
POST request.
Example 10.5. Stopping a Volume
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/stop HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<action>
[ <force>true</force> ]
</action>
<action>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/stop -d "<action/>"
<action>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>10.3.3. Removing a Volume
DELETE request.
Example 10.6. Removing a Volume
DELETE /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/ceb59bbb-173d-4a5a-9b92-0189a17eae27 HTTP/1.1 HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
curl -X DELETE -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554"
10.3.4. Setting a Volume Option
POST request to the volume URI.
Example 10.7. Setting a Volume Option
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/setOption HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<action>
<option name="key" value="value" />
</action>curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS]https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/setOption -d "<action><option name="key" value="value" /></action>"
10.3.5. Resetting a Volume Option
POST request.
Example 10.8. Resetting a Volume Option
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/resetOption
HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<action>
<option name="key" value="value"/>
<force>true</force>
</action>
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532- 9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/resetOption -d "<action><option name="key" value="value"/><force>true</force></action>"
<action>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>10.3.6. Resetting all Volume Options
POST request.
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/ceb59bbb-173d-4a5a-9b92-0189a17eae27/resetAllOptions HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/resetAllOptions -d "<action/>"
<action>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>10.3.7. Rebalancing Volume
POST request. The status of rebalance operation can be monitored by job id returned by this API.
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/ceb59bbb-173d-4a5a-9b92-0189a17eae27/rebalance -d "<action/>" HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml Content-type: application/xml
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glustervolumes/380474af-360b-48fa-a210-9c08b913ffa3/rebalance -d "<action/>"
<action>
<job href="/api/jobs/0937afb0-2c21-4834-8fee-70e8982b8a8e" id="0937afb0-2c21-4834-8fee-70e8982b8a8e"/>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>
/api/jobs/<job_id>/steps /api/jobs/<job_id>/steps/<step_id> --for step type rebalance /api/jobs/<job_id>/steps/<step_id>/statistics -- for detail information of rebalance status per node
Example 10.9. Monitoring Rebalance
<statistics>
<statistic href="/api/hosts/93fb8339-3888-44de-8050-e1166714e186/statistics/efca817c-2c70-3c82-b5b4-cff3dc24acbd" id="efca817c-2c70
-3c82-b5b4-cff3dc24acbd">
<name>files.moved</name>
<description>Number of files moved</description>
<values type="INTEGER">
<value>
<datum>0</datum>
</value>
</values>
<type>COUNTER</type>
<unit>NONE</unit>
<host href="/api/hosts/93fb8339-3888-44de-8050-e1166714e186" id="93fb8339-3888-44de-8050-e1166714e186"/>
<step href="/api/jobs/0937afb0-2c21-4834-8fee-70e8982b8a8e/steps/1560867e-7460-49d4-8bdb-6444a6ffef3a" id="1560867e-7460-49d4-8
bdb-6444a6ffef3a"/>
</statistic>
...
</statistics>curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC-Host]/api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glustervolumes/380474af-360b-48fa-a210-9c08b913ffa3/stoprebalance -d "<action/>"
10.4. Managing Bricks
10.4.1. Listing of Bricks
GET request on the volume URI.
GET /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Accept: application/xml
<bricks>
<brick href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks/29311ecf-d8db-4912-902b-b31dba8803d2" id="29311ecf-d8db-4912-902b-b31dba8803d2">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks/29311ecf-d8db-4912-902b-b31dba8803d2/replace" rel="replace"/>
</actions>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554" id="83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554"/>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/tmp/data-brick1</brick_dir>
<state>UP</state>
</brick>
<brick href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks/33f04f44-c78c-4c76-a23c-fe9d750c2fd3" id="33f04f44-c78c-4c76-a23c-fe9d750c2fd3">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks/33f04f44-c78c-4c76-a23c-fe9d750c2fd3/replace" rel="replace"/>
</actions>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554" id="83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554"/>
<server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/tmp/data-brick2</brick_dir>
<state>UP</state>
</brick>
</bricks>10.4.2. Adding a Brick
POST request to its URI.
POST /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<bricks>
<brick>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick3</brick_dir>
</brick>
</bricks> curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks -d "<bricks><brick><server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick3</brick_dir></brick></bricks>"
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<bricks>
<brick href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks/a2a496fc-9df0-446f-b632-da808d65d501" id="a2a496fc-9df0-446f-b632-da808d65d501">
<actions>
<link href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks/a2a496fc-9df0-446f-b632-da808d65d501/replace" rel="replace"/>
</actions>
<gluster_volume href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554" id="83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554"/>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick3</brick_dir>
<state>UP</state>
</brick>
</bricks>
10.4.3. Removing a Brick
DELETE request sent to its URI. Before removing a brick, data must be migrated to ensure there is no data loss with a POST request sent to its URI.
POST /api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glustervolumes/380474af-360b-48fa-a210-9c08b913ffa3/bricks/migrate -d "<action><bricks><brick><name>host:brick_dir</name></brick></bricks></action>"
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/44571c63-a110-4fba-9a8c-7b30446ba8bf/glustervolumes/380474af-360b-48fa-a210-9c08b913ffa3/bricks/migrate -d "<action><bricks><brick><name>host:brick_dir</name></brick></bricks></action>"
<action>
<bricks>
<brick>
<name>host:brick_dir</name>
</brick>
</bricks>
<job href="/api/jobs/5d070f64-2f9b-44d7-8c44-64829355422d" id="5d070f64-2f9b-44d7-8c44-64829355422d"/>
<status>
<state>complete</state>
</status>
</action>/api/jobs/<job_id>/steps /api/jobs/<job_id>/steps/<step_id> --for step type remove brick /api/jobs/<job_id>/steps/<step_id>/statistics -- for detail information of remove brick
DELETE request for a brick(s).
DELETE /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks
curl -X DELETE -u [USER:PASS] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes/83101900-2f12-4855-838e-36b8a9e04554/bricks -d "<bricks><brick><name>host:brick_dir</brick></bricks>"
Chapter 11. Groups
groups collection contains imported groups from directory services.
group resource contains a set of elements.
Table 11.1. Imported group elements
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
link rel="tags" | relationship | A link to the tags sub-collection for tags attached to this group. |
link rel="permissions" | relationship | A link to the permissions sub-collection for permissions attached to this group. |
link rel="roles" | relationship | A link to the roles sub-collection for roles attached to this group. |
Example 11.1. An XML representation of a group resource
<group id="85bf8d97-273c-4a5c-b801-b17d58330dab"
href="/api/groups/85bf8d97-273c-4a5c-b801-b17d58330dab">
<name>Everyone</name>
<link rel="tags"
href="/api/groups/85bf8d97-273c-4a5c-b801-b17d58330dab/tags"/>
<link rel="permissions"
href="/api/groups/85bf8d97-273c-4a5c-b801-b17d58330dab/permissions"/>
<link rel="roles"
href="/api/groups/85bf8d97-273c-4a5c-b801-b17d58330dab/roles"/>
</group>
Chapter 12. Roles
rel="roles" link obtained from the entry point URI (see Chapter 5, Entry Point) provides access to a static set of system roles.
role element contains the following:
Table 12.1. Role elements
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
link="permits" | relationship | A link to the permits sub-collection for role permits. | 
|
mutable | Boolean: true or false | Defines the ability to update or delete the role. Roles with mutable set to false are roles built into the Red Hat Storage Console environment. | 
|
administrative | Boolean: true or false | Defines the role as administrative-only. |
Example 12.1. An XML representation of the roles collection
<roles>
<role id="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001"
href="/api/roles/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001">
<name>SuperUser</name>
<description>Roles management administrator</description>
<link rel="permits"
href="/api/roles/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001/permits"/>
<mutable>false</mutable>
<administrative>true</administrative>
</role>
<role id="00000000-0000-0000-0001-000000000001"
href="/api/roles/00000000-0000-0000-0001-000000000001">
<name>RHSCUser</name>
<description>RHSC user</description>
<link rel="permits"
href="/api/roles/00000000-0000-0000-0001-000000000001/permits"/>
<mutable>false</mutable>
<administrative>false</administrative>
</role>
</roles>
name, administrative and a list of initial permits. See Section 7.2.4, “Creating a Resource in a Collection” for more information.
Example 12.2. Creating a role
POST /api/roles HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<role>
<name>Finance Role</name>
<administrative>true</administrative>
<permits>
<permit id="1"/>
</permits>
</role>name, description and administrative elements are updatable post-creation. See Section 7.3.2, “Updating a Resource” for more information.
Example 12.3. Updating a role
PUT /api/roles/8de42ad7-f307-408b-80e8-9d28b85adfd7 HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<role>
<name>Engineering Role</name>
<description>Standard users in the Engineering Role</description>
<administrative>false</administrative>
</role>DELETE request.
Example 12.4. Removing a role
DELETE /api/roles/8de42ad7-f307-408b-80e8-9d28b85adfd7 HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
12.1. Permits Sub-Collection
permits, which the API lists in capabilities.
permits are listed as a sub-collection:
Example 12.5. Listing a role's permits
GET /api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9/permits HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<permits>
<permit id="1"
href="/api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9/permits/1">
<name>create_vm</name>
<administrative>false</administrative>
<role id="b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9"
href="/api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9"/>
</permit>
...
</permits>permit to a role with a POST request to the permits sub-collection. Use either an id attribute or a name element to specify the permit to assign.
Example 12.6. Assign a permit to a role
POST /api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9/permits HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-Type: application/xml
<permit id="1"/>
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/xml
<permits>
<permit id="1"
href="/api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9/permits/1">
<name>create_vm</name>
<administrative>false</administrative>
<role id="b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9"
href="/api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9"/>
</permit>
</permits>permit from a role with a DELETE request to the permit resource.
Example 12.7. Remove a permit from a role
DELETE /api/roles/b67dfbe2-0dbc-41e4-86d3-a2fbef02cfa9/permits/ HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Chapter 13. Users
rel="users" link. Individual user elements contain the following:
Table 13.1. User elements
| Element | Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
user_name | string | The user principal name (UPN). The UPN is used as a more convenient identifier when adding a new user. | 
|
link rel="tags" | relationship | A link to the tags sub-collection for user resources. | |
link rel="roles" | relationship | A link to the roles sub-collection for user resources. | |
name | string | A free-text name for the user. | 
|
domain | string | The containing directory service domain. | 
|
groups | complex | A list of directory service groups for this user. | 
|
Example 13.1. An XML representation of a user resource
GET /api/users HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
<user id="225f15cd-e891-434d-8262-a66808fcb9b1"
href="/api/users/225f15cd-e891-434d-8262-a66808fcb9b1">
<name>Admin</name>
<actions/>
<link rel="roles"
href="/api/users/225f15cd-e891-434d-8262-a66808fcb9b1/roles"/>
<link rel="tags"
href="/api/users/225f15cd-e891-434d-8262-a66808fcb9b1/tags"/>
<domain>domain.example.com</domain>
<logged_in>false</logged_in>
<user_name>admin@domain.example.com</user_name>
<groups>
<group>Group Policy Creator Owners@domain.example.com/Users</group>
<group>Domain Admins@domain.example.com/Users</group>
<group>Enterprise Admins@domain.example.com/Users</group>
<group>Schema Admins@domain.example.com/Users</group>
<group>Administrators@domain.example.com/Builtin</group>
</groups>
</user>
POST request to the users collection. The client-provided new user representation includes an embedded roles list with at least one initial role to assign to the user. For example, the following request assigns two initial roles to the user joe@domain.example.com:
Example 13.2. Adding a user from directory service and assigning two roles
POST /api/users HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/xml
Accept: application/xml
<user>
<user_name>joe@domain.example.com</user_name>
<roles>
<role>
<name>RHSC User</name>
</role>
<role id="00000000-0000-0000-0001-000000000003"/>
</roles>
</user>
Note
domains collection prior to creation of the user.
POST or DELETE requests to the roles sub-collection of an individual user. The example below illustrates how the API adds the RHSCUser role to the role assignments for a particular user.
Note
user element is only used for the initial creation. All interactions post-creation with the user's role assignments go through the roles sub-collection.
Example 13.3. Adding roles to a user
POST /api/users/225f15cd-e891-434d-8262-a66808fcb9b1/roles HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/xml
Accept: application/xml
<role>
<name>RHSCUser</name>
</role>
Note
PUT verb. The only changes allowed post-creation are in the user's role assignments.
DELETE request on the users collection. The directory service domain remains unchanged after such a deletion.
Chapter 14. Events
rel="events" link obtained from the entry point URI accesses the events collection and lists system events from Red Hat Storage Console.
Table 14.1. Event elements
| Element | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
description | string | A description of the system event. |
code | integer | The integer event code. |
severity | One of normal, warning, error or alert | The level of severity for the event. |
time | xsd:dateTime format: YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss | The timestamp indicating when the event happened. |
user id | GUID | The identification code for the user who triggered the event. |
Example 14.1. An XML representation of the events collection
<events>
<event href="/api/events/767" id="767">
<description>User rhcadmin logged in.</description>
<code>30</code>
<severity>normal</severity>
<time>2014-01-29T14:42:55.041+05:30</time>
<user href="/api/users/fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc" id="fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc"/>
<origin>oVirt</origin>
<custom_id>-1</custom_id>
<flood_rate>30</flood_rate>
</event>
...
</events>
user, an event representation also contains a set of XML element relationships to resources relevant to the event.
Example 14.2. An XML representation of a volume start event
<event href="/api/events/192" id="192">
<description>Gluster Volume data started.</description>
<code>4004</code>
<severity>normal</severity>
<time>2012-09-13T20:59:22.137-04:00</time>
<user href="/api/users/fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc" id="fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc"/>
<cluster href="/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95" id="99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95"/>
</event>
Default cluster .
Note
events collection is read-only.
14.1. Searching Events
events collection provides search queries similar to other resource collections (see Section 7.2.3, “Searching Collections with Queries”). An additional feature when searching the events collection is the ability to search from a certain event. This queries all of events since a specified event.
from argument added to the URI after the query. This from argument references an event id code.
Example 14.3. Searching from an event
GET /api/events?search=type%3D30&from=1012 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
type set to 30 since id="1012"
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/xml
<events>
<event id="1018" href="/api/events/1018">
<description>User admin logged in.</description>
<code>30</code>
<severity>normal</severity>
<time>2011-07-11T14:03:22.485+10:00</time>
<user id="80b71bae-98a1-11e0-8f20-525400866c73"
href="/api/users/80b71bae-98a1-11e0-8f20-525400866c73"/>
</event>
<event id="1016" href="/api/events/1016">
<description>User admin logged in.</description>
<code>30</code>
<severity>normal</severity>
<time>2011-07-11T14:03:07.236+10:00</time>
<user id="80b71bae-98a1-11e0-8f20-525400866c73"
href="/api/users/80b71bae-98a1-11e0-8f20-525400866c73"/>
</event>
<event id="1014" href="/api/events/1014">
<description>User admin logged in.</description>
<code>30</code>
<severity>normal</severity>
<time>2011-07-11T14:02:16.009+10:00</time>
<user id="80b71bae-98a1-11e0-8f20-525400866c73"
href="/api/users/80b71bae-98a1-11e0-8f20-525400866c73"/>
</event>
</events>
14.2. Paginating Events
page command in a search query.
page value in combination with the sortby clause:
sortby time asc page 1
sortby clause defines the base element to order of the results and whether the results are ascending or descending. For search queries of events, set the base element to time and the order to ascending (asc) so the API displays all events from the creation of your storage environment.
page condition defines the page number. One page equals the default number of events to list. Pagination begins at page 1. To view more pages, increase the page value:
sortby time asc page 2
sortby time asc page 3
sortby time asc page 4
Example 14.4. Paginating events
event resources. The URL-encoded request is:
GET /api/events?search=sortby%20time%20asc%20page%201 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
page value to view the next page of results.
GET /api/events?search=sortby%20time%20asc%20page%202 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
from argument to set the starting id.
GET /api/events?search=sortby%20time%20asc%20page%202&from=30 HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
Part III. Python Software Development Kit
Chapter 15. Software Development Kit Overview
15.1. Introduction to the Red Hat Storage Software Development Kit
15.2. Software Development Kit Prerequisites
- A system with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6, or later, installed. Both the Server and Workstation variants are supported.
- A subscription to Red Hat Storage entitlements.
rhsc-sdk package, the Python 2.6 interpreter will be installed if it does not already exist on the system.
Important
rhsc-sdk package must be installed. As a result, the prerequisites listed here must be met both on the systems being used to develop scripts using the software development kit, and on those systems on which the scripts are intended to run.
15.3. Installing the Software Development Kit
The software development kit is provided by the rhsc-sdk package. This package includes all of the Python bindings for the Red Hat Storage Console API. To begin using the software development kit, you must install the rhsc-sdk package on the system that you wish to use for script development. The instructions that appear here are intended for use on a system running Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 or later.
Procedure 15.1. Installing the Python SDK
- Ensure that your system has the required entitlements:
- When using certificate-based Red Hat Network, you must subscribe to the
Red Hat Storageentitlement to install therhsc-sdkpackage. - When using Red Hat Network classic, you must subscribe to the
Red Hat Storage Consolechannel to install therhsc-sdkpackage. Refer to the Red Hat Storage Console Installation Guide for specific channel names current to your system.
- Ensure that you are logged in as the
rootuser. - Install the
rhsc-sdkpackage using theyumcommand.#yum install rhsc-sdkResultTherhsc-sdkpackage is now installed. TheovirtsdkPython library is now available for use on the local system.
Chapter 16. Using the Software Development Kit
16.1. Connecting to the API Using Python
API class from the ovirtsdk.api module. To be able to do this, it is necessary to first import the class at the start of the script:
from ovirtsdk.api import API
API class takes a number of arguments. Supported arguments are:
-
url - Specifies the URL of the Manager to connect to, including the
/apipath. This parameter is mandatory. -
username - Specifies the user name to use when connecting, in the User Principle Name (UPN) format. This parameter is mandatory.
-
password - Specifies the password for the user provided by the
usernameparameter. This parameter is mandatory. -
key_file - Specifies a PEM-formatted key file containing the private key associated with the certificate specified by
cert_file. This parameter is optional. -
cert_file - Specifies a PEM-formatted client certificate to be used for establishing the identity of the client on the server. This parameter is optional.
-
ca_file - Specifies the certificate file of the certificate authority for the server. This parameter is mandatory unless the
insecureparameter is set toTrue. -
port - Specifies the port to use when connecting, where it has not been provided as component of the
urlparameter. This parameter is optional. -
timeout - Specifies the amount of time in seconds that is allowed to pass before a request is considered to be timed out. This parameter is optional.
-
persistent_auth - Specifies whether persistent authentication is enabled for this connection. Valid values are
TrueandFalse. This parameter is optional and defaults toFalse. -
insecure - Allows a connection via SSL without a certificate authority. Valid values are
TrueandFalse, and the default isFalse. If theinsecureparameter is set toFalsethen the ca_file must be supplied to secure the connection.This option should be used with caution, as it may allow man-in-the-middle (MITM) attackers to spoof the identity of the server. -
filter - Specifies whether or not the user permission based filter is on or off. Valid values are
TrueandFalse, and the default isFalse. If thefilterparameter is set toFalse, the authentication credentials provided must be those of an administrative user. If thefilterparameter is set toTrue, any user can be used and the Console will filter the actions available to the user based on their permissions. -
debug - Specifies whether debug mode is enabled for this connection. Valid values are
TrueandFalse. This parameter is optional.
ovirtsdk.API Python class.
API class, refer to the PyDoc output for the ovirtsdk.api package.
16.2. Listing the Public Attributes of a Resource
dir() method returns a list of public variables, modules, and functions of a resource. The private attribute names start with an underscore character. To get a list of all the public attributes of a resource, use the following code snippet:
for name in (e for e in dir(api) if not e.startswith('_')):
print name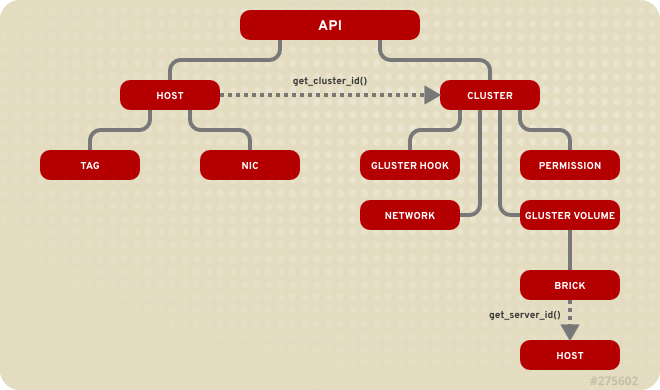
Figure 16.1. Object Hierarchy
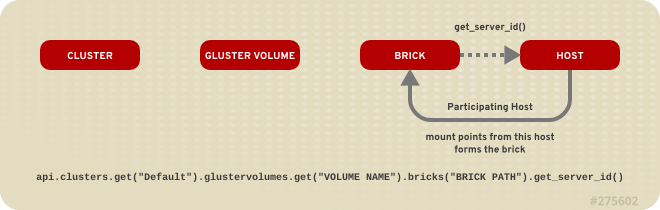
Figure 16.2. Relationship between a brick and a host

Figure 16.3. Relationship between a host and a cluster
16.3. Resources and Collections
- Collections
- A collection is a set of resources of the same type. The API provides both top-level collections and sub-collections. An example of a top-level collection is the volume collection which contains all bricks in the environment. An example of a sub-collection is the
volume.brickscollection which contains resources for CPUs attached to a cluster.The interface for interacting with collections provides methods for adding resources (add), getting resources (get), and listing resources (list). - Resources
- A resource in a RESTful API is an object with a fixed interface that also contains a set of attributes that are relevant to the specific type of resource being represented. The interface for interacting with resources provides methods for updating (
update) and deleting (delete) resources. Additionally, some resources support actions specific to the resource type. One example of this is theapprovemethod ofHostresources.
16.4. Retrieving Resources from a Collection
get and list methods.
-
get - Retrieves a single resource from the collection. The item to retrieve is determined based on the name provided as an argument. The
getmethod takes these arguments:name- The name of the resource to retrieve from the collection.id- The globally unique identifier (GUID) of the resource to retrieve from the collection.
-
list - Retrieves any number of resources from the collection. The items to retrieve are determined based on the criteria provided. The
listmethod takes these arguments:**kwargs- A dictionary of additional arguments allowing keyword-based filtering.query- A query written in the same format as that used for searches executed using the Red Hat Storage Console.max- The maximum number of resources to retrieve.case_sensitive- Whether or not search terms are to be treated as case sensitive (TrueorFalse, the default isTrue).
Example 16.1. Retrieving a List of Resources in a Collection Matching a Keyword Based Filter
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@internal",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
clusterName="CLUSTERNAME"
volume_list= api.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.list(**{"volume_type": "distribute"})
for volume in volume_list:
print "VolumeName:", volume.get_name()
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
16.4.1. Retrieving a Specific Resource from a Collection
get method.
name parameter of the get method:
cl = api.clusters.get("Default")cl = api.clusters.get(name="Default")
16.4.2. Retrieving a List of Resources from a Collection
list method.
Example 16.2. Listing All Clusters
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST,
username="USER@DOMAIN",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
c_list = api.clusters.list()
for c in c_list:
print "%s (%s)" % (c.get_name(), c.get_id())
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
c1 (42c68146-0036-4374-a6e0-bf8d5874d890) cl1 (d62cb3a2-1bea-4267-af3a-72aadac8ee21) cl2 (49bc2dc6-b5fb-4da2-83ba-fad736757c14) cl3 (0c4b3cb9-1557-4448-9fda-a9209830cec9) Default (99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95) tcl (cbc131f6-09f1-4f0e-8d8e-89a7c3288984)
get_name() method provides the name of the cluster and the get_gluster_service() returns true or false based on glusterFS support in the cluster:
Example 16.3. Listing All Hosts
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@DOMAIN",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
h_list = api.hosts.list()
for h in h_list:
print "%s (%s)" % (h.get_name(), h.get_id())
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
api.hosts.list() provides a dictionary list that contains the host name and the host ID.
h1 (51b29199-3a7f-49e4-b0d5-92afdeea1f15) h2 (4e8c3642-e654-456c-9dff-a240c8a43b1f) host1 (14e3823d-d557-4635-bd9f-0c6157ab7f07)
Important
list method of a collection is restricted to returning only as many elements as allowed by the SearchResultsLimit configuration key in the Red Hat Storage Console. To ensure that all records in a the list are returned, it is recommended to paginate through the results as illustrated in this example. Alternatively, set the max parameter of the list method to the maximum number of records that you wish to retrieve.
Example 16.4. Listing All Red Hat Storage Volumes
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
clusterName="CLUSTERNAME"
for volume in api.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.list():
print "VolumeName:", volume.get_name()
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
VolumeName: vol1
Example 16.5. Listing All Users
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
for user in api.users.list():
print "User name: %s (User ID: %s)" % (user.get_name(), user.get_id())
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
User name: admin (User ID: fdfc627c-d875-11e0-90f0-83df133b58cc)
Example 16.6. Listing All Roles
getUsers() function lists all the roles in the Red Hat Storage Console.
def listRoles():
""" Return list of user roles """
roles = []
for role in api.roles.list():
roles.append(role)
return rolesfor i in api.roles.list(): print i.name
SuperUser ClusterAdmin HostAdmin NetworkAdmin GlusterAdmin ExternalEventsCreator ExternalTasksCreator
Example 16.7. Listing All Network Details
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
try:
API = API(url="https://HOST",
username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt") hostName = "HOSTNAME"
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
for nic in host.nics.list():
print "NIC Name:", nic.get_name()
print "IPAddress:", nic.get_ip().get_address()
print "MAC Address:", nic.get_mac().get_address()
print "netStatus:", nic.get_status().get_state()
API.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
nic.get_status().get_state() returns the network status as either up or down.
NIC Name: eth0 IPAddress: 10.70.37.194 MAC Address: 00:1a:4a:46:24:9e netStatus: up
nic.get_ip().set_address()nic.get_ip()set_netmask()nic.get_ip().set_gateway()nic.set_bridged()
16.5. Adding a Resource to a Collection
add method adds a resource to a collection. The resource to be added is created based on the parameters provided. Parameters are provided to the add method using an instance of an object from the ovirtsdk.xml.params module. Selecting the specific class from the module to use varies based on the type of resource being created.
Example 16.8. Adding a Resource to a Collection
GlusterBricks collection.
br_param = params.GlusterBrick(
brick_dir='/exports/music_2',
server_id='0f5a7016-bb36-4f2b-a226-3b16c3eeca0c')
bricksParam = params.GlusterBricks()
bricksParam.add_brick(br_param)
Procedure 16.1. Creating a Red Hat Storage Resource
- Create an instance of the parameter object for the type of resource being created.
- Identify the collection to which the resource will be added.
- Call the
addmethod of the collection passing the parameter object as a parameter.
16.6. Updating a Resource in a Collection
update method for the resource to save the changes. Parameter modification is performed by using the set_* methods on the retrieved resource:
Example 16.9. Updating a Network Address
def setHostIp(hostName, hostIP):
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
host.set_address(hostIP)
host.update()16.7. Removing a Resource from a Collection
delete method on the resource.
Example 16.10. Removing a Resource from a Collection
cl = api.clusters.get("DemoCluster")
cl.delete()16.8. Handling Errors
ovirtsdk.infrastructure.errors module:
- ConnectionError
- Raised when a transport layer error has occurred.
- DisconnectedError
- Raised when attempting to use SDK after it was explicitly disconnected.
- ImmutableError
- Raised when initiating SDK while an SDK instance already exists under the same domain. Applicable to SDK versions before 3.2.
- NoCertificatesError
- Raised when no CA certificate is provided and
insecureisFalse. - UnsecuredConnectionAttemptError
- Raised when HTTP protocol is used while the server is running HTTPS.
- MissingParametersError
- Raised when using the
get()method without providingidorname.
Example 16.11. ConnectionError Exception
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
from ovirtsdk.infrastructure import errors
try:
api=API(url="https://INVALID_HOSTNAME", username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
except errors.ConnectionError, err:
print "Connection failed: %s" % errChapter 17. Python Reference Documentation
17.1. Python Reference Documentation
ovirtsdk.apiovirtsdk.infrastructure.brokers
pydoc generated documentation on your local machine provide the name of the module you are interested in as an argument to the pydoc command:
$ pydoc MODULEAppendix A. SDK Examples
A.1. Common Functions and Wrappers
__test__ = False import config import states from time import sleep import logging import ovirtsdk.api from ovirtsdk.xml import params from ovirtsdk.infrastructure import errors from ovirtsdk.infrastructure import contextmanager from functools import wraps MB = 1024*1024 GB = 1024*MB logging.basicConfig(filename='messages.log',level=logging.DEBUG) LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__) _major = int(config.OVIRT_VERSION[0]) _minor = int(config.OVIRT_VERSION[2:]) VERSION = params.Version(major=_major, minor=_minor)
def disconnect():
proxy = contextmanager.get('proxy')
persistent_auth = contextmanager.get('persistent_auth')
filter_header = contextmanager.get('filter')
if proxy and persistent_auth:
try:
proxy.request(method='GET',
url='/api',
headers={'Filter': filter_header},
last=True)
except Exception:
pass
contextmanager._clear(force=True)
def _getApi():
""" Return ovirtsdk api.
Will not create another API instance when reloading this module in
ipython (when common.API is already defined).
Works around problem when reloading, which would
otherwise cause the error `ImmutableError: [ERROR]::'proxy' is immutable.`.
"""
try:
return API
except NameError:
disconnect()
return ovirtsdk.api.API(
url=config.OVIRT_URL, insecure=True,
username=config.OVIRT_USERNAME+'@'+config.OVIRT_DOMAIN,
password=config.OVIRT_PASSWORD)
API = _getApi()
def waitForState(obj, desiredStates, failStates=None, timeout=config.TIMEOUT,
sampling=1, restoreState=None):
""" Waits for oVirt object to change state using :py:func:`time.sleep`.
:param obj: the oVirt object (host, VM, ...) for which to wait
:param desiredStates: the desired oVirt object states, accepts both a
list of states or a single state
:param failStates: fail if the object reaches one of these states
:param timeout: (int) time in seconds to wait for desired state
:param sampling: (int) how often to check state, in seconds
:param restoreState state, tryies to maintentce->up host, when it is non_operational
:raises AssertionError: when timeout is exceeded and the object still isn't
in the desired state or if failState was reached
.. seealso:: :mod:`tests.states`
"""
# 120 seconds is not enougn to wait for start
if type(obj).__name__ == 'VM' and desiredStates == states.vm.up:
timeout = 240
global res
if obj is None:
return
if type(desiredStates) is not list:
desiredStates = [desiredStates]
if type(failStates) is not list and failStates is not None:
failStates = [failStates]
elif failStates is None:
failStates = []
assert type(obj) is not str, "Bad use of 'waitForState()'"
t = 0
state = newState(obj)
while state not in desiredStates and t <= timeout:
sleep(sampling)
t += sampling
state = newState(obj)
assert state not in failStates, \
"Failed to get %s into state '%s' because it reached the fail \
state '%s'" % (objectDescr(obj), desiredStates, state)
if t > timeout:
LOGGER.error("%s didn't reach one of states %s in timout \
of %i sec, current state is '%s'"
% (objectDescr(obj), str(desiredStates), timeout, state))
assert state in desiredStates, \
"Failed to get %s into desired state" % objectDescr(obj)
if type(obj).__name__ == 'VM':
disks = obj.get_disks().list()
if disks is not None:
for disk in disks:
waitForState(disk, states.disk.ok)
def (obj):
""" Obtain new state of an oVirt object.
:param obj: oVirt object (host, VM, storage, ...)
:return: (string) the new state of the object
.. seealso:: :func:`updateObject`, :mod:`tests.states`
"""
assert type(obj) is not str, "Bad use of 'newState()'"
updatedObject = updateObject(obj)
if updatedObject is None:
LOGGER.warning("Object %s has no status" % (objectDescr(obj)))
return None
if type(updatedObject).__name__ == 'VMSnapshot':
return updatedObject.snapshot_status
status = updatedObject.status
if status is None:
LOGGER.warning("Object %s has no status" % (objectDescr(obj)))
return None
return status.state
""" Return ovirt object description param obj: ovirt object (glustervolumes, glusterbrick) :return: (string) ... typeName = type(obj).__name__ if 'GlusterVolume' in typeName: typeName = "Gluster Volume" return "%s '%s'" % (typeName, obj.name)
A.2. Python SDK Example: Hosts
def createHost(clusterName, hostName, hostAddress, hostPassword):
""" create host """
msg = "Installing host '%s' on '%s'"
LOGGER.info(msg % (hostAddress, clusterName))
cluster = API.clusters.get(clusterName)
assert api.clusters.get(
name="c1").get_gluster_service() is True
API.hosts.add(params.Host(
name=hostName,
address=hostAddress,
cluster=cluster,
root_password=hostPassword))
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
assert host is not None
waitForState(host, states.host.up,
failStates = states.host.install_failed,
timeout = config.HOST_INSTALL_TIMEOUT,
restoreState=states.host.non_operational)
def waitForTasks(host, max_times=3, sleep_time=10):
"""
Max 3(default) times try to deactive host, if there are running tasks
So try to wait about 30seconds, 3x10s(default)
Parameters:
* host - host to be deactivated
* max_times - max times time try to deactive host
* sleep_time - time to sleep between tryies
"""
while max_times > 0:
try:
host.deactivate()
break
except errors.RequestError as er:
max_times -= 1
if max_times == 0:
raise er
sleep(sleep_time)
def removeHost(hostName):
""" remove Host"""
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
if host is not None:
LOGGER.info("Deactivating host '%s'" % hostName)
# Max 3 times try to deactive host, if there are running tasks
# So try to wait about 30seconds, 3x10s
waitForTasks(host)
waitForState(host, states.host.maintenance)
LOGGER.info("Deleting host")
host.delete()
assert updateObject(host) is None, "Failed to remove host"
else:
raise errors.RequestError("Unable to see any host")
#dc = API.datacenters.get(config.MAIN_DC_NAME) ???
#waitForState(dc, 'up')
def activeDeactiveHost(hostName):
""" Active, deactive host """
LOGGER.info("Activating/deactivating host '%s'" %hostName)
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
waitForTasks(host)
LOGGER.info("Waiting for maintence")
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
waitForState(host, states.host.maintenance)
host.activate()
LOGGER.info("Waiting for 'up' state")
waitForHostUpState(host)
# Check DC state
dc = API.datacenters.get(config.MAIN_DC_NAME)
waitForState(dc, 'up')
def checkHostStatus(hostName):
""" Check if is status up -> do UP """
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
if host is None:
LOGGER.info("Host '%s' dont exists." % hostName)
return
if host.status.state != states.host.up:
LOGGER.info("Host '%s' state is '%s'" % (hostName, host.status.state))
if host.status.state != states.host.maintenance:
host.deactivate()
waitForState(host, states.host.maintenance, timeout=180)
LOGGER.info("Activating")
host.activate()
#waitForState(host, states.host.up)
waitForHostUpState(host)
def configureHostNetwork(hostName):
"""
Try to change network properties.
Parameters:
* hostName - name of host to be changed
"""
h = getFilterHeader()
# Deactive host - need to be before configuring network
loginAsAdmin()
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
waitForTasks(host)
waitForState(host, states.host.maintenance)
try:
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
loginAsUser(filter_=h)
for nic in host.nics.list():
if nic.status.state == 'up':
nic.set_boot_protocol("dhcp")
nic.update()
break
except Exception as e:
raise e
else:
pass
finally:
# Activate host after test
loginAsAdmin()
host = API.hosts.get(hostName)
host.activate()
waitForHostUpState(host)
dc = API.datacenters.get(config.MAIN_DC_NAME)
waitForState(dc, states.host.up)
loginAsUser(filter_=h)
maxTry = 3
def waitForHostUpState(host):
"""
Wait for host, when its state is up.
Wait for 3x 240s. Could happend that host don't come up, so try again.
Parameters:
* host - host that should be wait for
"""
try:
waitForState(host, states.host.up, timeout=240)
except Exception as e:
global maxTry
maxTry -= 1
if maxTry == 0:
maxTry = 3
raise e
if host.status.state == states.host.non_operational or\
host.status.state == states.host.unassigned:
host.deactivate()
waitForState(host, states.host.maintenance)
host.activate()
waitForHostUpState(host)
A.3. Python SDK Example: Cluster
def createCluster(name, datacenterName,
cpu_type=config.HOST_CPU_TYPE, version=VERSION, enable_virt=False, enable_gluster=True):
""" Creates cluster """
LOGGER.info("create_cluster")
dc = API.datacenters.get(datacenterName)
API.clusters.add(params.Cluster(
name=name,
cpu=params.CPU(id=cpu_type),
data_center=dc,
version=VERSION,
virt_service=enable_virt,
gluster_service=enable_gluster))
cluster = API.clusters.get(name)
LOGGER.info("Creating cluster '%s'" % name)
assert cluster is not None
Example A.1. Building a cluster object
api.clusters.add() function.
api.clusters.add(params.Cluster(name="mytest.cluster.3", cpu=params.CPU(id="Intel Nehalem Family"), data_center=dc, virt_service=False, gluster_service=True))
def removeCluster(name):
""" Removes cluster """
cluster = API.clusters.get(name)
if cluster is not None:
cluster.delete()
LOGGER.info("Removing cluster '%s'" % name)
assert updateObject(cluster) is None, "Can't remove cluster"
A.4. Python SDK Example: Volumes
try:
api = API(url=URL,
username=USERNAME,
password=PASSWORD,
insecure=True)
brick1 = params.GlusterBrick(
brick_dir='/exports/music_1',
server_id='0f5a7016-bb36-4f2b-a226-3b16c3eeca0c')
brick2 = params.GlusterBrick(
brick_dir='/exports/music_2',
server_id='0f5a7016-bb36-4f2b-a226-3b16c3eeca0c')
bricksParam = params.GlusterBricks()
bricksParam.add_brick(brick1)
bricksParam.add_brick(brick2)
volume1 = params.GlusterVolume(
name="music",
cluster=api.clusters.get(name="Gluster"),
volume_type="distribute",
bricks=bricksParam)
api.clusters.get("Gluster").glustervolumes.add(volume1)
api.disconnect()
except Exception as e:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % eapi.host collection.
def glusterVolumeDelete(clusterName, volumeName):
try:
API.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.get(volumeName).delete()
return True
except:
return False
glusterVolumeStart() function.
def glusterVolumeStart(clusterName, volumeName):
try:
API.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.get(volumeName).start()
return True
except:
return FalseglusterVolumeStart() function.
def glusterVolumeStop(clusterName, volumeName):
try:
API.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.get(volumeName).stop()
return True
except:
return FalsestartRebalance and stopRebalance functions and the jobID to the rebalanceStatus function.
import ovirtsdk
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
# This function returns a stop rebalance task instance. Using this
# we can reterive the status of the stop rebalance.
# ex. volume = stopRebalance(clusterName, volumeName)
# print volume.status.state
def stopRebalance(clusterName, volumeName):
volume = api.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.get(volumeName)
try:
return volume.stoprebalance()
except ovirtsdk.infrastructure.errors.RequestError, e:
print "Error"
def startRebalance(clusterName, volumeName):
volume = api.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.get(volumeName)
return volume.rebalance()
def rebalanceStatus(jobId):
# jobs.get accepts job name and job id as an optional
# parameters to provide the job details.
return api.jobs.get(None, jobId)
clusterName="Default" # name of the cluser
volumeName="music" # name of the volume which belongs
# to the purticular cluster
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
status = startRebalance(clusterName, volumeName)
jobId = status.job.get_id()
# jobId return by startRebalance can be stored somewhere
# for later use. With out the jobId it would be very
# difficult to find out the actual status of this task.
print jobId
privStatus = None
while True:
status = rebalanceStatus(jobId)
jobStatus = status.get_status().get_state()
if jobStatus != privStatus:
print "Description: ", status.get_description()
print "Status: ", jobStatus
if "FINISHED" == jobStatus:
break
privStatus = jobStatus
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
A.5. Python SDK Example: Bricks
brick3 = params.GlusterBrick(
brick_dir='/exports/music_3',
server_id='0f5a7016-bb36-4f2b-a226-3b16c3eeca0c')
brick4 = params.GlusterBrick(
brick_dir='/exports/music_4',
server_id='0f5a7016-bb36-4f2b-a226-3b16c3eeca0c')
bricksParam = params.GlusterBricks()
bricksParam.add_brick(brick3)
bricksParam.add_brick(brick4)
try:
for volume in api.clusters.get(
CLUSTERNAME).glustervolumes.list():
for brick in volume.bricks.list():
if brick.name == BRICKNAME:
brick.delete()
api.disconnect()
except Exception as e:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % e
startRemoveBrick and removeBrickStatus
import ovirtsdk
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
api = None
clusterName = "Default" # name of the cluster
volumeName = "music" # name of the volume which belongs #to the particular cluster
brickName = "10.70.42.164:/home/music_b1"
# brick name. We can get the brick details which are associated to the #volume using getGlusterVolumeBrickDetails(..)
def startRemoveBrick(clusterName, volumeName, brickName):
volume = api.clusters.get(clusterName).glustervolumes.get(volumeName)
bricks = volume.get_bricks()
if not bricks:
return None
brick = bricks.get(brickName)
if not brick:
return None
try:
return brick.delete()
except ovirtsdk.infrastructure.errors.RequestError as e:
print e
def removeBrickStatus(jobId):
# jobs.get accepts job name and job id as an optional
# parameters to provide the job details.
return api.jobs.get(None, jobId)
try:
api = API (url="https://HOST",
username="USER@domain",
password="PASS",
ca_file="ca.crt")
status = startRemoveBrick(clusterName, volumeName, brickName)
if status:
jobId = status.job.get_id()
privStatus = None
while True:
status = removeBrickStatus(jobId)
jobStatus = status.get_status().get_state()
if jobStatus != privStatus:
print "Description: ", status.get_description()
print "Status: ", jobStatus
if "FINISHED" == jobStatus:
break
privStatus = jobStatus
else:
print "Unable to retrieve the brick details"
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % ex
Note
Important
A.6. Python SDK Example: Permissions
def getRoles():
""" Return list of all roles """
return [role.get_name() for role in API.roles.list()]
def getRolePermissions(roleName):
""" Return permissions of role """
role = API.roles.get(roleName)
return [perm.get_name() for perm in role.get_permits().list()]
def getSuperUserPermissions():
""" Return SuperUser permissions(all possible permissions) """
return getRolePermissions('SuperUser')
def addRoleToUser(roleName, userName=config.USER_NAME, domainName=config.USER_DOMAIN):
"""
Add system permissions to user.
Parameters:
* roleName - role permissions to add
* userName - name of user who will be added permissions
* domainName - domain of user
"""
LOGGER.info("Adding role '%s' to user '%s'" % (roleName, userName))
user = getUser(userName, domainName)
if user is None:
return
user.roles.add(API.roles.get(roleName))
assert user.roles.get(roleName) is not None
def removeAllRolesFromUser(userName=config.USER_NAME, domainName=config.USER_DOMAIN):
"""
Removes all permissions from user.
Parameters:
* userName - name of user
* domainName - domain of user
"""
LOGGER.info("Removing all roles from user %s" % userName)
user = getUser(userName, domainName)
if user is None:
return
for role in user.roles.list():
LOGGER.info("Removing " + role.get_name())
role.delete()
assert len(user.roles.list()) == 0, "Unable to remove roles from user '%s'" % user.get_name()
def removeRoleFromUser(roleName, userName=config.USER_NAME, domainName=config.USER_DOMAIN):
"""
Remove role(System permissions) from user.
Parameters:
* roleName - name of role
* userName - name of user
* domainName - domain of user
"""
LOGGER.info("Removing role %s to user %s" % (roleName, userName))
user = getUser(userName, domainName)
if user is None:
return
role = user.roles.get(roleName)
role.delete()
role = user.roles.get(roleName)
assert role is None, "Unable to remove role '%s'" % roleName
def givePermissionsToGroup(templateName, roleName='UserTemplateBasedVm', group="Everyone"):
"""
Give permission to group.
Parameters:
* templateName - name of template to add group perms
* roleName - name of role which perms to be added
* group - On which group should be perms added
"""
template = getObjectByName(API.templates, templateName)
r = API.roles.get(roleName)
g = API.groups.get(group)
g.permissions.add(params.Permission(role=r, template=template))
LOGGER.info("Adding permissions on template '%s' role '%s' for group '%s'.",
template.get_name(), roleName, group)
def givePermissionToObject(rhsc_object, roleName, userName=config.USER_NAME,
domainName=config.USER_DOMAIN, user_object=None,
role_object=None):
"""
Add role permission to user on object.
Parameters:
* rhsc_object - object to add role permissions on
* roleName - Role permissions to be added
* userName - user who should be added permissions
* domainName - domain of user
* user_object - temporaly, because uf bug 869334
* role_object - temporaly, because uf bug 869334
"""
# FIXME: rhsc_object can be one of:
# [API.clusters, API.datacenters, API.disks, API.groups, API.hosts,
# API.storagedomains, API.templates, API.vms, API.vmpools]
try:
user = getUser(userName, domainName)
if user is None:
return
except errors.RequestError as e:
# User cant access /users url. Bug 869334. Workaround
user = user_object
try:
role = API.roles.get(roleName)
except errors.RequestError as e:
# User cant access /roles url. Bug 869334. Workaround
role = role_object
if rhsc_object is None or user is None or role is None:
LOGGER.warning("Unable to add permissions on 'None' object")
returnremoving the first digit from a line
permissionParam = params.Permission(user=user, role=role)
try:
rhsc_object.permissions.add(permissionParam)
except AttributeError as e:
# Bz 869334 - after BZ ok, could be removed
pass
msg = "Added permission on '%s' with role '%s' for user '%s'"
LOGGER.info(msg % (type(rhsc_object).__name__, roleName, user.get_name()))
def removeAllPermissionFromCluster(clusterName):
cluster = getObjectByName(API.clusters, clusterName)
removeAllPermissionFromObject(cluster)
def removeAllPermissionFromObject(rhsc_object):
"""
Removes all permissions from object
Parameters:
* rhsc_object - object from which permissions should be removed
"""
LOGGER.info("Removing all permissions from object '%s'" % type(rhsc_object).__name__)
if rhsc_object is None:
LOGGER.info("Tying to remove perms from object that dont exists")
return
permissions = rhsc_object.permissions.list()
for perm in permissions:
perm.delete()
def removeAllPermissionFromCluster(clusterName):
cluster = getObjectByName(API.clusters, clusterName)
removeAllPermissionFromObject(cluster)
A.7. Python SDK Example: Users
def getFilterHeader():
""" Has user admin role or user role? """
return contextmanager.get('filter')
def loginAsUser(userName=config.USER_NAME,
domain=config.USER_DOMAIN,
password=config.USER_PASSWORD,
filter_=True):
LOGGER.info("Login as %s" % userName)
global API
API.disconnect()
API = ovirtsdk.api.API(url=config.OVIRT_URL, insecure=True,
username=userName+'@'+domain,
password=password, filter=filter_)
def loginAsAdmin():
loginAsUser(config.OVIRT_USERNAME,
config.OVIRT_DOMAIN,
config.OVIRT_PASSWORD,
filter_=False)
def editObject(rhsc_object, name, newName=None, description=None, append=False):
"""
Edit object property.
Parameters:
* rhsc_object - object to be edited
* name - name of object
* newName - new name of object
* description - description to be updated
* append - True if append to old description else create new
"""
obj = rhsc_object.get(name)
old_name = obj.get_name()
old_desc = obj.get_description()
if newName is not None:removing the first digit from a line
LOGGER.info("Updating name from '%s' to '%s'" %(name, newName))
obj.set_name(newName)
obj.update()
obj = rhsc_object.get(name)
assert old_name != obj.get_name(), "Failed to update object name"
if description is not None:
LOGGER.info("Updating desc from '%s' to '%s'" %(name, description))
if old_desc is None:
old_desc = ""
obj.set_description(old_desc + description if append else description)
obj.update()
obj = rhsc_object.get(name)
assert old_desc != obj.get_description(), "Failed to update object description"
def hasUserPermissions(obj, role, user=config.USER_NAME, domain=config.USER_DOMAIN):
"""
Tests if user have role permssions on rhsc_object
Parameters:
* obj - object which we wanna tests
* role - role we wanna test
* user - user we wanna test
* domain - domain where user belongs
"""
perms = obj.permissions.list()
for perm in perms:
role_name = API.roles.get(id=perm.get_role().get_id()).get_name()
user_name = API.users.get(id=perm.get_user().get_id()).get_user_name()
if user_name + '@' + domain == user and role_name == role:
return True
return False
def hasPermissions(role):
""" Get a list of permissions the user role has.
:param role: (string) oVirt user role
:return: (list of strings) permissions the role should have
"""
return getRolePermissions(role)
# If bz plugin is not enabled, use this
def bz(*ids):
def decorator(func):
return func
return decorator
# If tcms plugin is not enabled, use this
def tcms(*ids):
def decorator(func):
return func
return decorator
A.8. Python SDK Example: Hooks
import pprint
import ovirtsdk
from ovirtsdk.api import API
from ovirtsdk.xml import params
api = None
clusterName = "Default" # name of the cluser
def getGlusterHook(clusterName, hookName):
for hook in api.clusters.get(clusterName).glusterhooks.list():
if hookName == hook.name:
return hook
def enableHook(clusterName, hookName):
""" Returns enable hook status """
hook = getGlusterHook(clusterName, hookName)
if hook:
return hook.enable()
return None
def disableHook(clusterName, hookName):
""" Returns disable hook status """
hook = getGlusterHook(clusterName, hookName)
if hook:
return hook.disable()
return None
def resolveHook(clusterName, hookName):
""" Returns resolve hook status """
hook = getGlusterHook(clusterName, hookName)
if hook:
return hook.resolve()
return None
def glusterHookDetails(clusterName):
# Returns hook content """
hooks=[]
for hook in api.clusters.get(clusterName).glusterhooks.list():
hooks.append({"hookName": hook.name,
"glusterCommand": hook.get_gluster_command(),
"level": hook.get_stage(),#indicates whether this is a post gluster command hook or pre gluster command hook.
"state": hook.get_status().state,
"md5sum": hook.get_checksum(),
"content": hook.get_content()})
return hooks
def glusterHookList(clusterName):
# Returns list of hook names """
hookList=[]
for hook in api.clusters.get(clusterName).glusterhooks.list():
hookList.append(hook.name)
return hookList
try:
api = API (url="https://10.70.43.95",
username="admin@internal",
password="redhat",
insecure=True)
#ca_file="ca.crt")
hookList = glusterHookList(clusterName)
print hookList
print disableHook(clusterName, hookList[-1])
pprint.pprint(glusterHookDetails(clusterName))
print enableHook(clusterName, hookList[-1])
api.disconnect()
except Exception as ex:
print "Unexpected error: %s" % exNote
get_status().state. And it will raise an ovirtsdk.infrastructure.errors.RequestError when there is a failure.
Appendix B. API Usage with cURL
A Red Hat Enterprise Linux user installs cURL with the following terminal command:
yum install curl
cURL uses a command line interface to send requests to a HTTP server. Integrating a request requires the following command syntax:
Usage: curl [options]uriuri refers to target HTTP address to send the request. This is a location on your Red Hat Storage Console host within the API entry point path (/api).
cURL options
- -X COMMAND, --request COMMAND
- The request command to use. In the context of the REST API, use
GET,POST,PUTorDELETE.Example:-X GET - -H LINE, --header LINE
- HTTP header to include with the request. Use multiple header options if more than one header is required.Example:
-H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" - -u USERNAME:PASSWORD, --user USERNAME:PASSWORD
- The username and password of the Red Hat Storage Console user. This attribute acts as a convenient replacement for the
Authorization:header.Example:-u admin@internal:p@55w0rd! - --cacert CERTIFICATE
- The location of the certificate file for SSL communication to the REST API. The certificate file is saved locally on the client machine. Use the
-kattribute to bypass SSL. See Chapter 2, Authentication and Security for more information on obtaining a certificate.Example:--cacert ~/Certificates/rhsc.cer - -d BODY, --data BODY
- The body to send for requests. Use with
POST,PUTandDELETErequests. Ensure to specify theContent-Type: application/xmlheader if a body exists in the request.Example:-d "<bricks><brick><server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick3</brick_dir></brick></bricks>"
The following examples show how to adapt REST requests to cURL command syntax:
Example B.1. GET request
GET request lists the clusters in the cluster collection. Note that a GET request does not contain a body.
GET /api/clusters HTTP/1.1 Accept: application/xml
GET), header (Accept: application/xml) and URI (https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters) into the following cURL command:
$ curl -X GET -H "Accept: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters
clusters collection displays.
Example B.2. POST request
POST request creates a volume in the server collection. Note that a POST request requires a body.
POST api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<gluster_volume>
<name>data</name>
<volume_type>DISTRIBUTE</volume_type>
<bricks>
<brick>
<server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick1</brick_dir>
</brick>
<brick>
<server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id>
<brick_dir>/export/data/brick2</brick_dir>
</brick>
</bricks>
</gluster_volume>
POST), headers (Accept: application/xml and Content-type: application/xml), URI (https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes) and request body into the following cURL command:
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-Type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC HOST]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95/glustervolumes -d "<gluster_volume><name>data</name><volume_type>DISTRIBUTE</volume_type><bricks><brick><server_id>fcb46b88-f32e-11e1-918a-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick1</brick_dir></brick><brick><server_id>de173e6a-fb05-11e1-a2fc-0050568c4349</server_id><brick_dir>/export/data/brick2</brick_dir></brick></bricks></gluster_volume>"
Example B.3. PUT request
PUT request updates the cluster. Note that a PUT request requires a body.
PUT /api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95 HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<cluster>
<description>Cluster 1</description>
</cluster>
PUT), headers (Accept: application/xml and Content-type: application/xml), URI (https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95) and request body into the following cURL command:
$ curl -X PUT -H "Accept: application/xml" -H "Content-type: application/xml" -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] -d "<cluster><description>Cluster 1</description></cluster>" https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/99408929-82cf-4dc7-a532-9d998063fa95
Example B.4. DELETE request
DELETE request removes a cluster resource.
DELETE /api/clusters/082c794b-771f-452f-83c9-b2b5a19c0399 HTTP/1.1
DELETE) and URI (https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/082c794b-771f-452f-83c9-b2b5a19c0399) into the following cURL command:
$ curl -X DELETE -u [USER:PASS] --cacert [CERT] https://[RHSC Host]/api/clusters/082c794b-771f-452f-83c9-b2b5a19c0399
Accept: application/xml request header is optional due to the empty result of DELETE requests.
In addition the the standard command line tools, cURL also features libcurl, a library for programming language integration. For more information on supported programming languages and integration methods, see the libcurl website (http://curl.haxx.se/libcurl/).
Appendix C. Event Codes
C.1. Event Codes
Table C.1. Event Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | UNASSIGNED |
| 1 | VDC_START |
| 2 | VDC_STOP |
| 12 | VDS_FAILURE |
| 13 | VDS_DETECTED |
| 14 | VDS_RECOVER |
| 15 | VDS_MAINTENANCE |
| 16 | VDS_ACTIVATE |
| 17 | VDS_MAINTENANCE_FAILED |
| 18 | VDS_ACTIVATE |
| 19 | VDS_RECOVER_FAILED |
| 123 | VDS_SLOW_STORAGE_RESPONSE_TIME |
| 493 | VDS_ALREADY_IN_REQUESTED_STATUS |
| 494 | VDS_MANUAL_FENCE_STATUS |
| 495 | VDS_MANUAL_FENCE_STATUS_FAILED |
| 530 | VDS_MANUAL_FENCE_FAILED_CALL_FENCE_SPM |
| 531 | VDS_LOW_MEM |
| 532 | VDS_HIGH_MEM_USE |
| 533 | VDS_HIGH_NETWORK_USE |
| 534 | VDS_HIGH_CPU_USE |
| 535 | VDS_HIGH_SWAP_USE |
| 536 | VDS_LOW_SWAP |
| 496 | VDS_FENCE_STATUS |
| 497 | VDS_FENCE_STATUS_FAILED |
| 498 | VDS_APPROVE |
| 499 | VDS_APPROVE_FAILED |
| 500 | VDS_FAILED_TO_RUN_VMS |
| 504 | VDS_INSTALL |
| 505 | VDS_INSTALL_FAILED |
| 506 | VDS_INITIATED_RUN_VM |
| 537 | VDS_INITIATED_RUN_VM_AS_STATELESS |
| 507 | VDS_INITIATED_RUN_VM_FAILED |
| 509 | VDS_INSTALL_IN_PROGRESS |
| 510 | VDS_INSTALL_IN_PROGRESS_WARNING |
| 511 | VDS_INSTALL_IN_PROGRESS_ERROR |
| 513 | VDS_RECOVER_FAILED_VMS_UNKNOWN |
| 514 | VDS_INITIALIZING |
| 515 | VDS_CPU_LOWER_THAN_CLUSTER |
| 516 | VDS_CPU_RETRIEVE_FAILED |
| 517 | VDS_FAILED_TO_GET_HOST_HARDWARE_INFO |
| 533 | VDS_STORAGE_CONNECTION_FAILED_BUT_LAST_VDS |
| 535 | VDS_STORAGES_CONNECTION_FAILED |
| 534 | VDS_STORAGE_VDS_STATS_FAILED |
| 517 | VDS_SET_NONOPERATIONAL |
| 518 | VDS_SET_NONOPERATIONAL_FAILED |
| 519 | VDS_SET_NONOPERATIONAL_NETWORK |
| 603 | VDS_SET_NONOPERATIONAL_IFACE_DOWN |
| 522 | VDS_SET_NONOPERATIONAL_DOMAIN |
| 523 | VDS_SET_NONOPERATIONAL_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 524 | VDS_DOMAIN_DELAY_INTERVAL |
| 23 | VDS_LOW_DISK_SPACE |
| 24 | VDS_LOW_DISK_SPACE_ERROR |
| 600 | USER_VDS_MAINTENANCE |
| 601 | CPU_FLAGS_NX_IS_MISSING |
| 602 | USER_VDS_MAINTENANCE_MIGRATION_FAILED |
| 121 | SYSTEM_VDS_RESTART |
| 122 | SYSTEM_FAILED_VDS_RESTART |
| 604 | VDS_TIME_DRIFT_ALERT |
| 605 | PROXY_HOST_SELECTION |
| 606 | HOST_REFRESHED_CAPABILITIES |
| 607 | HOST_REFRESH_CAPABILITIES_FAILED |
| 22 | IRS_FAILURE |
| 26 | IRS_DISK_SPACE_LOW |
| 201 | IRS_DISK_SPACE_LOW_ERROR |
| 204 | IRS_HOSTED_ON_VDS |
| 30 | USER_VDC_LOGIN |
| 114 | USER_VDC_LOGIN_FAILED |
| 31 | USER_VDC_LOGOUT |
| 815 | USER_VDC_LOGOUT_FAILED |
| 150 | USER_INITIATED_RUN_VM |
| 156 | USER_INITIATED_RUN_VM_AND_PAUSE |
| 153 | USER_STARTED_VM |
| 151 | USER_INITIATED_RUN_VM_FAILED |
| 32 | USER_RUN_VM |
| 538 | USER_RUN_VM_AS_STATELESS |
| 54 | USER_FAILED_RUN_VM |
| 70 | USER_RUN_VM_AS_STATELESS_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 171 | USER_RUN_VM_AS_STATELESS_WITH_DISKS_NOT_ALLOWING_SNAPSHOT |
| 1001 | USER_RUN_VM_FAILURE_STATELESS_SNAPSHOT_LEFT |
| 152 | USER_RUN_VM_ON_NON_DEFAULT_VDS |
| 33 | USER_STOP_VM |
| 111 | USER_STOP_SUSPENDED_VM |
| 112 | USER_STOP_SUSPENDED_VM_FAILED |
| 56 | USER_FAILED_STOP_VM |
| 34 | USER_ADD_VM |
| 37 | USER_ADD_VM_STARTED |
| 53 | USER_ADD_VM_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 60 | USER_ADD_VM_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 57 | USER_FAILED_ADD_VM |
| 35 | USER_UPDATE_VM |
| 58 | USER_FAILED_UPDATE_VM |
| 250 | USER_UPDATE_VM_CLUSTER_DEFAULT_HOST_CLEARED |
| 113 | USER_REMOVE_VM_FINISHED |
| 172 | USER_REMOVE_VM_FINISHED_WITH_ILLEGAL_DISKS |
| 149 | USER_ADD |
| 59 | USER_FAILED_REMOVE_VM |
| 38 | USER_CHANGE_DISK_VM |
| 102 | USER_FAILED_CHANGE_DISK_VM |
| 72 | USER_CHANGE_FLOPPY_VM |
| 75 | USER_FAILED_CHANGE_FLOPPY_VM |
| 39 | USER_PAUSE_VM |
| 55 | USER_FAILED_PAUSE_VM |
| 501 | USER_SUSPEND_VM |
| 512 | USER_SUSPEND_VM_FINISH_SUCCESS |
| 521 | USER_SUSPEND_VM_FINISH_FAILURE |
| 532 | USER_SUSPEND_VM_FINISH_FAILURE_WILL_TRY_AGAIN |
| 502 | USER_FAILED_SUSPEND_VM |
| 503 | USER_SUSPEND_VM_OK |
| 40 | USER_RESUME_VM |
| 103 | USER_FAILED_RESUME_VM |
| 73 | USER_INITIATED_SHUTDOWN_VM |
| 74 | USER_FAILED_SHUTDOWN_VM |
| 76 | USER_STOPPED_VM_INSTEAD_OF_SHUTDOWN |
| 77 | USER_FAILED_STOPPING_VM_INSTEAD_OF_SHUTDOWN |
| 78 | USER_ADD_DISK_TO_VM |
| 97 | USER_ADD_DISK_TO_VM_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 98 | USER_ADD_DISK_TO_VM_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 79 | USER_FAILED_ADD_DISK_TO_VM |
| 80 | USER_REMOVE_DISK_FROM_VM |
| 81 | USER_FAILED_REMOVE_DISK_FROM_VM |
| 91 | USER_MOVED_VM |
| 92 | USER_MOVED_VM_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 83 | USER_MOVED_VM_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 84 | USER_FAILED_MOVE_VM |
| 93 | USER_MOVED_TEMPLATE |
| 94 | USER_MOVED_TEMPLATE_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 85 | USER_MOVED_TEMPLATE_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 86 | USER_FAILED_MOVE_TEMPLATE |
| 95 | USER_COPIED_TEMPLATE |
| 96 | USER_COPIED_TEMPLATE_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 87 | USER_COPIED_TEMPLATE_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 88 | USER_FAILED_COPY_TEMPLATE |
| 89 | USER_UPDATE_VM_DISK |
| 2000 | USER_FAILED_UPDATE_VM_DISK |
| 2001 | USER_HOTPLUG_DISK |
| 2002 | USER_FAILED_HOTPLUG_DISK |
| 2003 | USER_HOTUNPLUG_DISK |
| 2004 | USER_FAILED_HOTUNPLUG_DISK |
| 2005 | USER_COPIED_TEMPLATE_DISK |
| 2006 | USER_COPIED_TEMPLATE_DISK_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 2007 | USER_COPIED_TEMPLATE_DISK_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 2008 | USER_MOVED_VM_DISK |
| 2009 | USER_FAILED_MOVED_VM_DISK |
| 2010 | USER_MOVED_VM_DISK_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 2011 | USER_MOVED_VM_DISK_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 2014 | USER_FINISHED_REMOVE_DISK |
| 2015 | USER_FINISHED_FAILED_REMOVE_DISK |
| 2016 | USER_ATTACH_DISK_TO_VM |
| 2017 | USER_FAILED_ATTACH_DISK_TO_VM |
| 2018 | USER_DETACH_DISK_FROM_VM |
| 2019 | USER_FAILED_DETACH_DISK_FROM_VM |
| 2020 | USER_ADD_DISK |
| 2021 | USER_ADD_DISK_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 2022 | USER_ADD_DISK_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 2023 | USER_FAILED_ADD_DISK |
| 2024 | USER_RUN_UNLOCK_ENTITY_SCRIPT |
| 2025 | USER_MOVE_IMAGE_GROUP_FAILED_TO_DELETE_SRC_IMAGE |
| 2026 | USER_MOVE_IMAGE_GROUP_FAILED_TO_DELETE_DST_IMAGE |
| 3000 | USER_ADD_QUOTA |
| 3001, 3002 | USER_FAILED_ADD_QUOTA |
| 3003 | USER_FAILED_UPDATE_QUOTA |
| 3004 | USER_DELETE_QUOTA |
| 3005 | USER_FAILED_DELETE_QUOTA |
| 3006 | USER_EXCEEDED_QUOTA_VDS_GROUP_GRACE_LIMIT |
| 3007 | USER_EXCEEDED_QUOTA_VDS_GROUP_LIMIT |
| 3008 | USER_EXCEEDED_QUOTA_VDS_GROUP_THRESHOLD |
| 3009 | USER_EXCEEDED_QUOTA_STORAGE_GRACE_LIMIT |
| 3010 | USER_EXCEEDED_QUOTA_STORAGE_LIMIT |
| 3011 | USER_EXCEEDED_QUOTA_STORAGE_THRESHOLD |
| 3012 | QUOTA_STORAGE_RESIZE_LOWER_THEN_CONSUMPTION |
| 3013 | MISSING_QUOTA_STORAGE_PARAMETERS_PERMISSIVE_MODE |
| 3014 | MISSING_QUOTA_CLUSTER_PARAMETERS_PERMISSIVE_MODE |
| 4000 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_CREATE |
| 4001 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_CREATE_FAILED |
| 4002 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTION_ADDED |
| 4003 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTION_SET_FAILED |
| 4004 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_START |
| 4005 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_START_FAILED |
| 4006 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_STOP |
| 4007 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_STOP_FAILED |
| 4008 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTIONS_RESET |
| 4009 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTIONS_RESET_FAILED |
| 4010 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_DELETE |
| 4011 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_DELETE_FAILED |
| 4012 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REBALANCE_START |
| 4013 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REBALANCE_START_FAILED |
| 4014 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REMOVE_BRICKS |
| 4015 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REMOVE_BRICKS_FAILED |
| 4016 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REPLACE_BRICK_FAILED |
| 4017 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REPLACE_BRICK_START |
| 4018 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_REPLACE_BRICK_START_FAILED |
| 4019 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_ADD_BRICK |
| 4020 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_ADD_BRICK_FAILED |
| 4021 | GLUSTER_SERVER_REMOVE_FAILED |
| 4022 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_PROFILE_START |
| 4023 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_PROFILE_START_FAILED |
| 4024 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_PROFILE_STOP |
| 4025 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_PROFILE_STOP_FAILED |
| 4026 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_CREATED_FROM_CLI |
| 4027 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_DELETED_FROM_CLI |
| 4028 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTION_SET_FROM_CLI |
| 4029 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTION_RESET_FROM_CLI |
| 4030 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_PROPERTIES_CHANGED_FROM_CLI |
| 4031 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_BRICK_ADDED_FROM_CLI |
| 4032 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_BRICK_REMOVED_FROM_CLI |
| 4033 | GLUSTER_SERVER_REMOVED_FROM_CLI |
| 4034 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_INFO_FAILED |
| 4035 | GLUSTER_COMMAND_FAILED |
| 4036 | GLUSTER_SERVER_ADD_FAILED |
| 4037 | GLUSTER_SERVERS_LIST_FAILED |
| 4038 | GLUSTER_SERVER_REMOVE |
| 4039 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_STARTED_FROM_CLI |
| 4040 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_STOPPED_FROM_CLI |
| 4041 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTION_CHANGED_FROM_CLI |
| 4042 | GLUSTER_HOOK_ENABLE |
| 4043 | GLUSTER_HOOK_ENABLE_FAILED |
| 4044 | GLUSTER_HOOK_ENABLE_PARTIAL |
| 4045 | GLUSTER_HOOK_DISABLE |
| 4046 | GLUSTER_HOOK_DISABLE_FAILED |
| 4047 | GLUSTER_HOOK_DISABLE_PARTIAL |
| 4048 | GLUSTER_HOOK_LIST_FAILED |
| 4049 | GLUSTER_HOOK_CONFLICT_DETECTED |
| 4050 | GLUSTER_HOOK_DETECTED_NEW |
| 4051 | GLUSTER_HOOK_DETECTED_DELETE |
| 4052 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTION_MODIFIED |
| 4053 | GLUSTER_HOOK_GETCONTENT_FAILED |
| 4054 | GLUSTER_SERVICES_LIST_FAILED |
| 4055 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_TYPE_ADDED_TO_CLUSTER |
| 4056 | GLUSTER_CLUSTER_SERVICE_STATUS_CHANGED |
| 4057 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_ADDED_TO_SERVER |
| 4058 | GLUSTER_SERVER_SERVICE_STATUS_CHANGED |
| 4059 | GLUSTER_HOOK_UPDATED |
| 4060 | GLUSTER_HOOK_UPDATE_FAILED |
| 4061 | GLUSTER_HOOK_ADDED |
| 4062 | GLUSTER_HOOK_ADD_FAILED |
| 4063 | GLUSTER_HOOK_REMOVED |
| 4064 | GLUSTER_HOOK_REMOVE_FAILED |
| 4065 | GLUSTER_HOOK_REFRESH |
| 4066 | GLUSTER_HOOK_REFRESH_FAILED |
| 4067 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_STARTED |
| 4068 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_START_FAILED |
| 4069 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_STOPPED |
| 4070 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_STOP_FAILED |
| 4071 | GLUSTER_SERVICES_LIST_NOT_FETCHED |
| 4072 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_RESTARTED |
| 4073 | GLUSTER_SERVICE_RESTART_FAILED |
| 4074 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_OPTIONS_RESET_ALL |
| 4075 | GLUSTER_HOST_UUID_NOT_FOUND |
| 4076 | GLUSTER_VOLUME_BRICK_ADDED |
| 4077 | GLUSTER_CLUSTER_SERVICE_STATUS_ADDED |
| 41 | USER_VDS_RESTART |
| 107 | USER_FAILED_VDS_RESTART |
| 20 | USER_VDS_START |
| 118 | USER_FAILED_VDS_START |
| 21 | USER_VDS_STOP |
| 137 | USER_FAILED_VDS_STOP |
| 42 | USER_ADD_VDS |
| 104 | USER_FAILED_ADD_VDS |
| 43 | USER_UPDATE_VDS |
| 105 | USER_FAILED_UPDATE_VDS |
| 44 | USER_REMOVE_VDS |
| 106 | USER_FAILED_REMOVE_VDS |
| 45 | USER_CREATE_SNAPSHOT |
| 68 | USER_CREATE_SNAPSHOT_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 69 | USER_CREATE_SNAPSHOT_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 170 | USER_CREATE_LIVE_SNAPSHOT_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 117 | USER_FAILED_CREATE_SNAPSHOT |
| 342 | USER_REMOVE_SNAPSHOT |
| 343 | USER_FAILED_REMOVE_SNAPSHOT |
| 356 | USER_REMOVE_SNAPSHOT_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 357 | USER_REMOVE_SNAPSHOT_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 46 | USER_TRY_BACK_TO_SNAPSHOT |
| 71 | USER_TRY_BACK_TO_SNAPSHOT_FINISH_SUCCESS |
| 99 | USER_TRY_BACK_TO_SNAPSHOT_FINISH_FAILURE |
| 115 | USER_FAILED_TRY_BACK_TO_SNAPSHOT |
| 47 | USER_RESTORE_FROM_SNAPSHOT |
| 1190 | USER_RESTORE_FROM_SNAPSHOT_START |
| 100 | USER_RESTORE_FROM_SNAPSHOT_FINISH_SUCCESS |
| 101 | USER_RESTORE_FROM_SNAPSHOT_FINISH_FAILURE |
| 116 | USER_FAILED_RESTORE_FROM_SNAPSHOT |
| 48 | USER_ADD_VM_TEMPLATE |
| 51 | USER_ADD_VM_TEMPLATE_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 52 | USER_ADD_VM_TEMPLATE_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 108 | USER_FAILED_ADD_VM_TEMPLATE |
| 49 | USER_UPDATE_VM_TEMPLATE |
| 109 | USER_FAILED_UPDATE_VM_TEMPLATE |
| 50 | USER_REMOVE_VM_TEMPLATE |
| 251 | USER_REMOVE_VM_TEMPLATE_FINISHED |
| 110 | USER_FAILED_REMOVE_VM_TEMPLATE |
| 135 | TEMPLATE_IMPORT |
| 136 | TEMPLATE_IMPORT_FAILED |
| 520 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_VM |
| 360 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_VM |
| 361 | USER_FAILED_DETACH_USER_FROM_VM |
| 182 | USER_FAILED_ATTACH_USER_TO_VM |
| 325 | USER_REMOVE_ADUSER |
| 326 | USER_FAILED_REMOVE_ADUSER |
| 327 | USER_FAILED_ADD_ADUSER |
| 346 | USER_PASSWORD_CHANGED |
| 347 | USER_PASSWORD_CHANGE_FAILED |
| 348 | USER_CLEAR_UNKNOWN_VMS |
| 349 | USER_FAILED_CLEAR_UNKNOWN_VMS |
| 528 | USER_EJECT_VM_DISK |
| 529 | USER_EJECT_VM_FLOPPY |
| 61 | VM_DOWN |
| 119 | VM_DOWN_ERROR |
| 62 | VM_MIGRATION_START |
| 63 | VM_MIGRATION_DONE |
| 64 | VM_MIGRATION_ABORT |
| 65 | VM_MIGRATION_FAILED |
| 66 | VM_FAILURE |
| 67 | VM_MIGRATION_START_SYSTEM_INITIATED |
| 120 | VM_MIGRATION_FAILED_FROM_TO |
| 128 | VM_MIGRATION_TRYING_RERUN |
| 161 | VM_CANCEL_MIGRATION |
| 162 | VM_CANCEL_MIGRATION_FAILED |
| 163 | VM_STATUS_RESTORED |
| 140 | VM_MIGRATION_FAILED_DURING_MOVE_TO_MAINTENANCE |
| 142 | VM_SET_TO_UNKNOWN_STATUS |
| 143 | VM_WAS_SET_DOWN_DUE_TO_HOST_REBOOT_OR_MANUAL_FENCE |
| 131 | USER_EXPORT_VM |
| 132 | USER_EXPORT_VM_FAILED |
| 133 | USER_EXPORT_TEMPLATE |
| 134 | USER_EXPORT_TEMPLATE_FAILED |
| 124 | VM_IMPORT |
| 125 | VM_IMPORT_FAILED |
| 126 | VM_NOT_RESPONDING |
| 127 | VDS_RUN_IN_NO_KVM_MODE |
| 141 | VDS_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED_FOR_CLUSTER |
| 129 | VM_CLEARED |
| 138 | VM_PAUSED_ENOSPC |
| 139 | VM_PAUSED_ERROR |
| 144 | VM_IMPORT_INFO |
| 145 | VM_PAUSED_EIO |
| 146 | VM_PAUSED_EPERM |
| 147 | VM_POWER_DOWN_FAILED |
| 300 | USER_ADD_VM_POOL |
| 301 | USER_ADD_VM_POOL_FAILED |
| 302 | USER_ADD_VM_POOL_WITH_VMS |
| 303 | USER_ADD_VM_POOL_WITH_VMS_FAILED |
| 320 | USER_ADD_VM_POOL_WITH_VMS_ADD_VDS_FAILED |
| 304 | USER_REMOVE_VM_POOL |
| 305 | USER_REMOVE_VM_POOL_FAILED |
| 306 | USER_ADD_VM_TO_POOL |
| 307 | USER_ADD_VM_TO_POOL_FAILED |
| 308 | USER_REMOVE_VM_FROM_POOL |
| 309 | USER_REMOVE_VM_FROM_POOL_FAILED |
| 310 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_POOL |
| 472 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_POOL_INTERNAL |
| 311 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_POOL_FAILED |
| 473 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_POOL_FAILED_INTERNAL |
| 312 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_POOL |
| 313 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_POOL_FAILED |
| 314 | USER_UPDATE_VM_POOL |
| 315 | USER_UPDATE_VM_POOL_FAILED |
| 316 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_VM_FROM_POOL |
| 318 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_VM_FROM_POOL_FINISHED_SUCCESS |
| 319 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_VM_FROM_POOL_FINISHED_FAILURE |
| 317 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_VM_FROM_POOL_FAILED |
| 344 | USER_UPDATE_VM_POOL_WITH_VMS |
| 345 | USER_UPDATE_VM_POOL_WITH_VMS_FAILED |
| 358 | USER_VM_POOL_MAX_SUBSEQUENT_FAILURES_REACHED |
| 328 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 329 | USER_ATTACH_USER_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 330 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 331 | USER_ATTACH_USER_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 332 | USER_ATTACH_AD_GROUP_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 333 | USER_ATTACH_AD_GROUP_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 334 | USER_DETACH_AD_GROUP_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 335 | USER_DETACH_AD_GROUP_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 336 | USER_UPDATE_USER_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 337 | USER_UPDATE_USER_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 338 | USER_UPDATE_AD_GROUP_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 337 | USER_UPDATE_AD_GROUP_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 338 | USER_UPDATE_AD_GROUP_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL |
| 339 | USER_UPDATE_AD_GROUP_TO_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED |
| 350 | USER_ADD_BOOKMARK |
| 351 | USER_ADD_BOOKMARK_FAILED |
| 352 | USER_UPDATE_BOOKMARK |
| 353 | USER_UPDATE_BOOKMARK_FAILED |
| 354 | USER_REMOVE_BOOKMARK |
| 355 | USER_REMOVE_BOOKMARK_FAILED |
| 400 | USER_ATTACH_VM_TO_AD_GROUP |
| 401 | USER_ATTACH_VM_TO_AD_GROUP_FAILED |
| 402 | USER_DETACH_VM_TO_AD_GROUP |
| 403 | USER_DETACH_VM_TO_AD_GROUP_FAILED |
| 404 | USER_ATTACH_VM_POOL_TO_AD_GROUP |
| 470 | USER_ATTACH_VM_POOL_TO_AD_GROUP_INTERNAL |
| 405 | USER_ATTACH_VM_POOL_TO_AD_GROUP_FAILED |
| 471 | USER_ATTACH_VM_POOL_TO_AD_GROUP_FAILED_INTERNAL |
| 406 | USER_DETACH_VM_POOL_TO_AD_GROUP |
| 407 | USER_DETACH_VM_POOL_TO_AD_GROUP_FAILED |
| 408 | USER_REMOVE_AD_GROUP |
| 409 | USER_REMOVE_AD_GROUP_FAILED |
| 430 | USER_UPDATE_TAG |
| 431 | USER_UPDATE_TAG_FAILED |
| 432 | USER_ADD_TAG |
| 433 | USER_UPDATE_TAG_FAILED |
| 434 | USER_REMOVE_TAG |
| 435 | USER_REMOVE_TAG_FAILED |
| 436 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_USER |
| 437 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_USER_FAILED |
| 438 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_USER_GROUP |
| 439 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_USER_GROUP_FAILED |
| 440 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_VM |
| 441 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_VM_FAILED |
| 442 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_VDS |
| 443 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_VDS_FAILED |
| 444 | USER_DETACH_VDS_FROM_TAG |
| 445 | USER_DETACH_VDS_FROM_TAG_FAILED |
| 446 | USER_DETACH_VM_FROM_TAG |
| 447 | USER_DETACH_VM_FROM_TAG_FAILED |
| 448 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_TAG |
| 449 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_TAG_FAILED |
| 450 | USER_DETACH_USER_GROUP_FROM_TAG |
| 451 | USER_DETACH_USER_GROUP_FROM_TAG_FAILED |
| 452 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_USER_EXISTS |
| 453 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_USER_GROUP_EXISTS |
| 454 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_VM_EXISTS |
| 455 | USER_ATTACH_TAG_TO_VDS_EXISTS |
| 555 | USER_MOVE_TAG |
| 556 | USER_MOVE_TAG_FAILED |
| 456 | USER_LOGGED_IN_VM |
| 457 | USER_LOGGED_OUT_VM |
| 458 | USER_LOCKED_VM |
| 459 | USER_UNLOCKED_VM |
| 460 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL_INTERNAL |
| 461 | USER_DETACH_USER_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED_INTERNAL |
| 462 | USER_DETACH_AD_GROUP_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL_INTERNAL |
| 463 | USER_DETACH_AD_GROUP_FROM_TIME_LEASED_POOL_FAILED_INTERNAL |
| 467 | UPDATE_TAGS_VM_DEFAULT_DISPLAY_TYPE |
| 468 | UPDATE_TAGS_VM_DEFAULT_DISPLAY_TYPE_FAILED |
| 809 | USER_ADD_VDS_GROUP |
| 810 | USER_ADD_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 811 | USER_UPDATE_VDS_GROUP |
| 812 | USER_UPDATE_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 835 | SYSTEM_UPDATE_VDS_GROUP |
| 836 | SYSTEM_UPDATE_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 813 | USER_REMOVE_VDS_GROUP |
| 814 | USER_REMOVE_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 816 | MAC_POOL_EMPTY |
| 833 | MAC_ADDRESS_IS_IN_USE |
| 838 | MAC_ADDRESS_IS_IN_USE_UNPLUG |
| 817 | CERTIFICATE_FILE_NOT_FOUND |
| 818 | RUN_VM_FAILED |
| 837 | MAC_ADDRESSES_POOL_NOT_INITIALIZED |
| 819 | VDS_REGISTER_ERROR_UPDATING_HOST |
| 820 | VDS_REGISTER_ERROR_UPDATING_HOST_ALL_TAKEN |
| 821 | VDS_REGISTER_HOST_IS_ACTIVE |
| 822 | VDS_REGISTER_ERROR_UPDATING_NAME |
| 823 | VDS_REGISTER_ERROR_UPDATING_NAMES_ALL_TAKEN |
| 824 | VDS_REGISTER_NAME_IS_ACTIVE |
| 825 | VDS_REGISTER_AUTO_APPROVE_PATTERN |
| 826 | VDS_REGISTER_FAILED |
| 827 | VDS_REGISTER_EXISTING_VDS_UPDATE_FAILED |
| 828 | VDS_REGISTER_SUCCEEDED |
| 834 | VDS_REGISTER_EMPTY_ID |
| 829 | VM_MIGRATION_ON_CONNECT_CHECK_FAILED |
| 830 | VM_MIGRATION_ON_CONNECT_CHECK_SUCCEEDED |
| 920 | NETWORK_ATTACH_NETWORK_TO_VDS |
| 921 | NETWORK_ATTACH_NETWORK_TO_VDS_FAILED |
| 922 | NETWORK_DETACH_NETWORK_FROM_VDS |
| 923 | NETWORK_DETACH_NETWORK_FROM_VDS_FAILED |
| 924 | NETWORK_ADD_BOND |
| 925 | NETWORK_ADD_BOND_FAILED |
| 926 | NETWORK_REMOVE_BOND |
| 927 | NETWORK_REMOVE_BOND_FAILED |
| 928 | NETWORK_VDS_NETWORK_MATCH_CLUSTER |
| 929 | NETWORK_VDS_NETWORK_NOT_MATCH_CLUSTER |
| 930 | NETWORK_REMOVE_VM_INTERFACE |
| 931 | NETWORK_REMOVE_VM_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 932 | NETWORK_ADD_VM_INTERFACE |
| 933 | NETWORK_ADD_VM_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 934 | NETWORK_UPDATE_VM_INTERFACE |
| 935 | NETWORK_UPDATE_VM_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 936 | NETWORK_ADD_TEMPLATE_INTERFACE |
| 937 | NETWORK_ADD_TEMPLATE_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 938 | NETWORK_REMOVE_TEMPLATE_INTERFACE |
| 939 | NETWORK_REMOVE_TEMPLATE_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 940 | NETWORK_UPDATE_TEMPLATE_INTERFACE |
| 941 | NETWORK_UPDATE_TEMPLATE_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 942 | NETWORK_ADD_NETWORK |
| 943 | NETWORK_ADD_NETWORK_FAILED |
| 944 | NETWORK_REMOVE_NETWORK |
| 945 | NETWORK_REMOVE_NETWORK_FAILED |
| 946 | NETWORK_ATTACH_NETWORK_TO_VDS_GROUP |
| 947 | NETWORK_ATTACH_NETWORK_TO_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 948 | NETWORK_DETACH_NETWORK_TO_VDS_GROUP |
| 949 | NETWORK_DETACH_NETWORK_TO_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 1102 | NETWORK_ACTIVATE_VM_INTERFACE_SUCCESS |
| 1103 | NETWORK_ACTIVATE_VM_INTERFACE_FAILURE |
| 1104 | NETWORK_DEACTIVATE_VM_INTERFACE_SUCCESS |
| 1105 | NETWORK_DEACTIVATE_VM_INTERFACE_FAILURE |
| 1100 | NETWORK_UPDATE_DISPLAY_TO_VDS_GROUP |
| 1101 | NETWORK_UPDATE_DISPLAY_TO_VDS_GROUP_FAILED |
| 1102 | NETWORK_UPDATE_NETWORK_TO_VDS_INTERFACE |
| 1103 | NETWORK_UPDATE_NETWORK_TO_VDS_INTERFACE_FAILED |
| 1104 | NETWORK_COMMINT_NETWORK_CHANGES |
| 1105 | NETWORK_COMMINT_NETWORK_CHANGES_FAILED |
| 1106 | NETWORK_HOST_USING_WRONG_CLUSER_VLAN |
| 1107 | NETWORK_HOST_MISSING_CLUSER_VLAN |
| 1108 | VDS_NETWORK_MTU_DIFFER_FROM_LOGICAL_NETWORK |
| 1109 | BRIDGED_NETWORK_OVER_MULTIPLE_INTERFACES |
| 1110 | VDS_NETWORKS_OUT_OF_SYNC |
| 1112 | NETWORK_UPDTAE_NETWORK_ON_CLUSTER |
| 1113 | NETWORK_UPDTAE_NETWORK_ON_CLUSTER_FAILED |
| 1114 | NETWORK_UPDATE_NETWORK |
| 1115 | NETWORK_UPDATE_NETWORK_FAILED |
| 1116 | NETWORK_UPDATE_VM_INTERFACE_LINK_UP |
| 1117 | NETWORK_UPDATE_VM_INTERFACE_LINK_DOWN |
| 1118 | INVALID_INTERFACE_FOR_MANAGEMENT_NETWORK_CONFIGURATION |
| 1119 | VLAN_ID_MISMATCH_FOR_MANAGEMENT_NETWORK_CONFIGURATION |
| 1120 | SETUP_NETWORK_FAILED_FOR_MANAGEMENT_NETWORK_CONFIGURATION |
| 1121 | PERSIST_NETWORK_FAILED_FOR_MANAGEMENT_NETWORK |
| 1162 | IMPORTEXPORT_STARTING_EXPORT_VM |
| 1150 | IMPORTEXPORT_EXPORT_VM |
| 1151 | IMPORTEXPORT_EXPORT_VM_FAILED |
| 1165 | IMPORTEXPORT_STARTING_IMPORT_VM |
| 1152 | IMPORTEXPORT_IMPORT_VM |
| 1153 | IMPORTEXPORT_IMPORT_VM_FAILED |
| 1166 | IMPORTEXPORT_STARTING_REMOVE_TEMPLATE |
| 1154 | IMPORTEXPORT_REMOVE_TEMPLATE |
| 1155 | IMPORTEXPORT_REMOVE_TEMPLATE_FAILED |
| 1156 | IMPORTEXPORT_EXPORT_TEMPLATE |
| 1164 | IMPORTEXPORT_STARTING_EXPORT_TEMPLATE |
| 1157 | IMPORTEXPORT_EXPORT_TEMPLATE_FAILED |
| 1163 | IMPORTEXPORT_STARTING_IMPORT_TEMPLATE |
| 1158 | IMPORTEXPORT_IMPORT_TEMPLATE |
| 1159 | IMPORTEXPORT_IMPORT_TEMPLATE_FAILED |
| 1167 | IMPORTEXPORT_STARTING_REMOVE_VM |
| 1160 | IMPORTEXPORT_REMOVE_VM |
| 1161 | IMPORTEXPORT_REMOVE_VM_FAILED |
| 1162 | IMPORTEXPORT_GET_VMS_INFO_FAILED |
| 1168 | IMPORTEXPORT_FAILED_TO_IMPORT_VM |
| 1169 | IMPORTEXPORT_FAILED_TO_IMPORT_TEMPLATE |
| 1170 | IMPORTEXPORT_IMPORT_TEMPLATE_INVALID_INTERFACES |
| 850 | USER_ADD_PERMISSION |
| 851 | USER_ADD_PERMISSION_FAILED |
| 852 | USER_REMOVE_PERMISSION |
| 853 | USER_REMOVE_PERMISSION_FAILED |
| 854 | USER_ADD_ROLE |
| 855 | USER_ADD_ROLE_FAILED |
| 856 | USER_UPDATE_ROLE |
| 857 | USER_UPDATE_ROLE_FAILED |
| 858 | USER_REMOVE_ROLE859 |
| 859 | USER_REMOVE_ROLE_FAILED |
| 860 | USER_ATTACHED_ACTION_GROUP_TO_ROLE |
| 861 | USER_ATTACHED_ACTION_GROUP_TO_ROLE_FAILED |
| 962 | USER_DETACHED_ACTION_GROUP_FROM_ROLE |
| 863 | USER_DETACHED_ACTION_GROUP_FROM_ROLE_FAILED |
| 864 | USER_ADD_ROLE_WITH_ACTION_GROUP |
| 865 | USER_ADD_ROLE_WITH_ACTION_GROUP_FAILED |
| 900 | AD_COMPUTER_ACCOUNT_SUCCEEDED |
| 901 | AD_COMPUTER_ACCOUNT_FAILED |
| 950 | USER_ADD_STORAGE_POOL |
| 951 | USER_ADD_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 952 | USER_UPDATE_STORAGE_POOL |
| 953 | USER_UPDATE_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 954 | USER_REMOVE_STORAGE_POOL |
| 955 | USER_REMOVE_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 918 | USER_FORCE_REMOVE_STORAGE_POOL |
| 919 | USER_FORCE_REMOVE_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 956 | USER_ADD_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 957 | USER_ADD_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 958 | USER_UPDATE_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 959 | USER_UPDATE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 960 | USER_REMOVE_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 961 | USER_REMOVE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 962 | USER_ATTACH_STORAGE_DOMAIN_TO_POOL |
| 963 | USER_ATTACH_STORAGE_DOMAIN_TO_POOL_FAILED |
| 964 | USER_DETACH_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FROM_POOL |
| 965 | USER_DETACH_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FROM_POOL_FAILED |
| 966 | USER_ACTIVATED_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 967 | USER_ACTIVATE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 968 | USER_DEACTIVATED_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 969 | USER_DEACTIVATE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 970 | SYSTEM_DEACTIVATED_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 971 | SYSTEM_DEACTIVATE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 972 | USER_EXTENDED_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 973 | USER_EXTENDED_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 974 | USER_REMOVE_VG |
| 975 | USER_REMOVE_VG_FAILED |
| 976 | USER_ACTIVATE_STORAGE_POOL |
| 977 | USER_ACTIVATE_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 978 | SYSTEM_FAILED_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS |
| 979 | SYSTEM_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS_NO_HOST_FOR_SPM |
| 980 | SYSTEM_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS_PROBLEMATIC |
| 981 | USER_FORCE_REMOVE_STORAGE_DOMAIN |
| 982 | USER_FORCE_REMOVE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED |
| 983 | RECONSTRUCT_MASTER_FAILED_NO_MASTER |
| 984 | RECONSTRUCT_MASTER_DONE |
| 985 | RECONSTRUCT_MASTER_FAILED |
| 986 | SYSTEM_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS_PROBLEMATIC_SEARCHING_NEW_SPM |
| 987 | SYSTEM_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS_PROBLEMATIC_WITH_ERROR |
| 988 | USER_CONNECT_HOSTS_TO_LUN_FAILED |
| 989 | SYSTEM_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS_PROBLEMATIC_FROM_NON_OPERATIONAL |
| 990 | SYSTEM_MASTER_DOMAIN_NOT_IN_SYNC |
| 991 | RECOVERY_STORAGE_POOL |
| 992 | RECOVERY_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 993 | SYSTEM_CHANGE_STORAGE_POOL_STATUS_RESET_IRS |
| 994 | CONNECT_STORAGE_SERVERS_FAILED |
| 995 | CONNECT_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 996 | STORAGE_DOMAIN_ERROR |
| 997 | REFRESH_REPOSITORY_FILE_LIST_FAILED |
| 998 | REFRESH_REPOSITORY_FILE_LIST_SUCCEEDED |
| 999 | STORAGE_ALERT_VG_METADATA_CRITICALLY_FULL |
| 1000 | STORAGE_ALERT_SMALL_VG_METADATA |
| 1002 | USER_ATTACH_STORAGE_DOMAINS_TO_POOL |
| 1003 | USER_ATTACH_STORAGE_DOMAINS_TO_POOL_FAILED |
| 1004 | STORAGE_DOMAIN_TASKS_ERROR |
| 1005 | UPDATE_OVF_FOR_STORAGE_POOL_FAILED |
| 1006 | UPGRADE_STORAGE_POOL_ENCOUNTERED_PROBLEMS |
| 1010 | RELOAD_CONFIGURATIONS_SUCCESS |
| 1101 | RELOAD_CONFIGURATIONS_FAILURE |
| 1100 | USER_ACCOUNT_DISABLED_OR_LOCKED |
| 1101 | USER_ACCOUNT_PASSWORD_EXPIRED |
| 1150 | PROVIDER_ADDED |
| 1151 | PROVIDER_ADDITION_FAILED |
| 1152 | PROVIDER_UPDATED |
| 1153 | PROVIDER_UPDATE_FAILED |
| 1154 | PROVIDER_REMOVED |
| 1155 | PROVIDER_REMOVAL_FAILED |
| 1156 | PROVIDER_CERTIFICATE_CHAIN_IMPORTED |
| 1157 | PROVIDER_CERTIFICATE_CHAIN_IMPORT_FAILED |
| 1200 | ENTITY_RENAMED |
| 9000 | VDS_ALERT_FENCE_IS_NOT_CONFIGURED |
| 9001 | VDS_ALERT_FENCE_TEST_FAILED |
| 9002 | VDS_ALERT_FENCE_OPERATION_FAILED |
| 9003 | VDS_ALERT_FENCE_OPERATION_SKIPPED |
| 9004 | VDS_ALERT_FENCE_NO_PROXY_HOST |
| 9005 | VDS_ALERT_FENCE_STATUS_VERIFICATION_FAILED |
| 9006 | CANNOT_HIBERNATE_RUNNING_VMS_AFTER_CLUSTER_CPU_UPGRADE |
| 9007 | VDS_ALERT_SECONDARY_AGENT_USED_FOR_FENCE_OPERATION |
| 9500 | TASK_STOPPING_ASYNC_TASK |
| 9501 | TASK_CLEARING_ASYNC_TASK |
| 9502 | VDS_ACTIVATE_ASYNC |
| 9503 | VDS_ACTIVATE_FAILED_ASYNC |
| 9504 | STORAGE_ACTIVATE_ASYNC |
| 9505 | USER_ACTIVATED_STORAGE_DOMAIN_ASYNC |
| 9506 | USER_ACTIVATE_STORAGE_DOMAIN_FAILED_ASYNC |
| 9600 | IMPORTEXPORT_IMPORT_VM_INVALID_INTERFACES |
| 9601 | VDS_SET_NON_OPERATIONAL_VM_NETWORK_IS_BRIDGELESS |
| 9604 | EMULATED_MACHINES_INCOMPATIBLE_WITH_CLUSTER |
| 9602 | HA_VM_FAILED |
| 9603 | HA_VM_RESTART_FAILED |
| 9701 | DWH_STOPPED |
| 9700 | DWH_STARTED |
| 9704 | DWH_ERROR |
| 9801 | EXTERNAL_EVENT_NORMAL |
| 9802 | EXTERNAL_EVENT_WARNING |
| 9803 | EXTERNAL_EVENT_ERROR |
| 9804 | EXTERNAL_ALERT |
| 9901 | WATCHDOG_EVENT |
| 10000 | VDS_UNTRUSTED |
Appendix D. Java Keystores
Procedure D.1. Import a certificate into a new Java keystore
rhsc.cer certificate from Section 2.1, “TLS/SSL Certification” into a Java keystore. This procedure requires the keytool management utility from the Java Development Kit (JDK) available for Linux and Windows systems.
- Access your client machine and locate the
rhsc.cercertificate. - Import the
rhsc.cercertificate using the Java keytool management utility.keytool -importcert -v -trustcacerts -keystore restapi.jks -noprompt -alias rhsc -file rhsc.cer
The keytool utility creates a new keystore file namedrestapi.jks. - keytool asks for the keystore password. Enter a password and keytool asks to verify it.
- keytool adds the
rhsc.cercertificate to therestapi.jkskeystore. Use keytool -list command to view the certificate's entry in the keystore:keytool -list -keystore restapi.jks -storepass [password]
Important
openssl x509 -in rhsc.cer -out rhsc.new -outform [pem|der]This creates a file called
rhsc.new to use in place of rhsc.cer.
Appendix E. Certificates
E.1. Creating SSL/TLS Certificates
SSL/TLS certificates provide a layer of security for accessing your installation over HTTPS. This procedure provides instructions for creating certificates and configuring your server with them.
openssl. To install this tool, run the following command on your server:
#yum install opensslProcedure E.1. Creating a Certificate Authority
- Run the following command:
#openssl req -new -x509 -keyout ca.key -out ca.crt -days 3650This command requests a new CA pair valid for 3650 days. - Enter a password to protect your CA:
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ......................................................................................................................................+++ ..................................................................................................+++ writing new private key to 'ca.key' Enter PEM pass phrase: Verifying - Enter PEM pass phrase:
- Enter the following details about your organization:
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:AU State or Province Name (full name) []:Queensland Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Brisbane Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Red Hat Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Engineering Content Services Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.example.com Email Address []:dmacpher@redhat.com
This information forms the Distinguished Name (DN) in your certificate.
You have created a Certificate Authority. openssl creates two files: ca.key, which is a key that administrators use to sign certificates, and ca.crt, which is the public CA certificate that users obtain to verify the validity of signed certificates they receive. Make sure users accessing your server have a copy of ca.crt so that they can import it into their client's trusted CA store.
E.2. Creating an SSL Certificate
The following procedure creates an SSL certificate and signs it with the CA key. SSL/TLS certificates provide a layer of security for accessing your installation over HTTPS. This procedure provides instructions for creating certificates and configuring the server with them.
openssl. To install this tool, run the following command on your server:
#yum install opensslProcedure E.2. Creating an SSL Certificate
- Create a key for your server:
#openssl genrsa -out ssl.keyThis creates anssl.keyfile. - Use the key to create a signing request for your certificate:
#openssl req -new -key ssl.key -out ssl.csrThe signing request asks for some organization details to form the Distinguished Name (DN) in your certificate.Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:IN State or Province Name (full name) []:Karnataka Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Bangalore Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Red Hat Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Engineering Content Services Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.example.com Email Address []:psriniva@redhat.com
This creates anssl.csrsigning request file. - Create the signed SSL certificate:
Create the signed SSL certificate:
opensslasks for your CA key's password.This creates a certificate file namedssl.crt.
Important
Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Enter pass phrase for ca.key:
/etc/pki/CA/index.txt: No such file or directory
unable to open '/etc/pki/CA/index.txt'
139883256969032:error:02001002:system library:fopen:No such file or directory:bss_file.c:355:fopen('/etc/pki/CA/index.txt','r')
139883256969032:error:20074002:BIO routines:FILE_CTRL:system lib:bss_file.c:357:Procedure E.3. Resolving this error
- Create the index.txt file.
#touch /etc/pki/CA/index.txt - Create a serial file to label the CA and all subsequent certificates.
#echo '1000' > /etc/pki/CA/serial
#openssl ca -cert ca.crt -keyfile ca.key -out ssl.crt -infiles ssl.csrssl.crt and ssl.key form the certificate pair that your server uses to encrypt data via HTTPS.
You have created an SSL certificate and signed it with the CA key. openssl creates two files: ca.key, which is a key that administrators use to sign certificates, and ca.crt, which is the public CA certificate that users obtain to verify the validity of signed certificates they receive. Make sure users accessing your server have a copy of the ca.crt so that they can import it into their client's trusted CA store.
E.3. Configuring HTTPS Communication
Configure HTTPS to use the SSL certificate key on your system.
Procedure E.4. Configuring HTTPS Communication
- Edit the
/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conffile and modify the following settings:SSLCertificateFile [location of your ssl.crt] SSLCertificateKeyFile [location of your ssl.key]
- After editing these settings, restart your web server:
#service httpd restart
You have configured HTTPS to use the SSL certificate key on your system.
E.4. Network Security Services (NSS) Database
cURL, use NSS to verify trusted SSL communication. This process helps a user import the rhsc.cer certificate into the local NSS database.
rhsc.cer certificate using the following command:
$certutil -d sql:$HOME/.pki/nssdb -A -t TC -n "Red Hat Storage Console" -i rhsc.cerrhsc.cer certificate as root using the following command:
#certutil -d sql:/etc/pki/nssdb -A -t TC -n "Red Hat Storage Console" -i rhsc.cerE.5. Java Keystores
keytool management utility from the Java Development Kit (JDK) available for Linux and Windows systems.
Procedure E.5. Import a Certificate into a New Java Keystore
- Access your client machine and locate the
rhsc.cercertificate. - Import the
rhsc.cercertificate using the Javakeytoolmanagement utility.keytool -importcert -v -trustcacerts -keystore restapi.jks -noprompt -alias rhsc -file rhsc.cer
Thekeytoolutility creates a new keystore file namedrestapi.jks. keytoolasks for thekeystorepassword. Enter a password andkeytoolasks to verify it.keytooladds therhsc.cercertificate to the restapi.jks keystore. Usekeytool -listcommand to view the certificate's entry in the keystore:keytool -list -keystore restapi.jks -storepass [password]
Important
keytool parse the certificate incorrectly. If keytool does not recognize the certificate, convert it to a different X.509 format with the openssl tool:
openssl x509 -in rhsc.cer -out rhsc.new -outform [pem|der]
Appendix F. Revision History
| Revision History | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Revision 3-10 | Mon Sep 22 2014 | Divya Muntimadugu | |
| |||

