Chapter 10. Deploying the same SELinux configuration on multiple systems
You can deploy your verified SELinux configuration on multiple systems by using one of the following methods:
- Using RHEL system roles and Ansible
- Using the RHEL web console
-
Using
semanageexport and import commands in your scripts
10.1. Introduction to the selinux RHEL system role
RHEL system roles is a collection of Ansible roles and modules that provide a consistent configuration interface to remotely manage multiple RHEL systems. You can perform the following actions by using the selinux RHEL system role:
- Cleaning local policy modifications related to SELinux booleans, file contexts, ports, and logins.
- Setting SELinux policy booleans, file contexts, ports, and logins.
- Restoring file contexts on specified files or directories.
- Managing SELinux modules.
The /usr/share/doc/rhel-system-roles/selinux/example-selinux-playbook.yml example playbook installed by the rhel-system-roles package demonstrates how to set the targeted policy in enforcing mode. The playbook also applies several local policy modifications and restores file contexts in the /tmp/test_dir/ directory.
Additional resources
-
/usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/README.mdfile -
/usr/share/doc/rhel-system-roles/selinux/directory
10.2. Using the selinux RHEL system role to apply SELinux settings on multiple systems
With the selinux RHEL system role, you can prepare and apply an Ansible playbook with your verified SELinux settings.
Prerequisites
- You have prepared the control node and the managed nodes
- You are logged in to the control node as a user who can run playbooks on the managed nodes.
-
The account you use to connect to the managed nodes has
sudopermissions on them.
Procedure
Prepare your playbook. You can either start from scratch or modify the example playbook installed as a part of the
rhel-system-rolespackage:# cp /usr/share/doc/rhel-system-roles/selinux/example-selinux-playbook.yml <my-selinux-playbook.yml> # vi <my-selinux-playbook.yml>
Change the content of the playbook to fit your scenario. For example, the following part ensures that the system installs and enables the
selinux-local-1.ppSELinux module:selinux_modules: - { path: "selinux-local-1.pp", priority: "400" }- Save the changes, and exit the text editor.
Validate the playbook syntax:
$ ansible-playbook <my-selinux-playbook.yml> --syntax-checkNote that this command only validates the syntax and does not protect against a wrong but valid configuration.
Run your playbook:
$ ansible-playbook <my-selinux-playbook.yml>
Additional resources
-
/usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/README.mdfile -
/usr/share/doc/rhel-system-roles/selinux/directory - SELinux hardening with Ansible Knowledgebase article
10.3. Managing ports by using the selinux RHEL system role
You can automate managing port access in SELinux consistently across multiple systems by using the selinux RHEL system role. This might be useful, for example, when configuring an Apache HTTP server to listen on a different port. You can do this by creating a playbook with the selinux RHEL system role that assigns the http_port_t SELinux type to a specific port number. After you run the playbook on the managed nodes, specific services defined in the SELinux policy can access this port.
You can automate managing port access in SELinux either by using the seport module, which is quicker than using the entire role, or by using the selinux RHEL system role, which is more useful when you also make other changes in SELinux configuration. The methods are equivalent, in fact the selinux RHEL system role uses the seport module when configuring ports. Each of the methods has the same effect as entering the command semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp <port_number> on the managed node.
Prerequisites
- You have prepared the control node and the managed nodes
- You are logged in to the control node as a user who can run playbooks on the managed nodes.
-
The account you use to connect to the managed nodes has
sudopermissions on them. -
Optional: To verify port status by using the
semanagecommand, thepolicycoreutils-python-utilspackage must be installed.
Procedure
To configure just the port number without making other changes, use the
seportmodule:- name: Allow Apache to listen on tcp port <port_number> community.general.seport: ports: <port_number> proto: tcp setype: http_port_t state: present
Replace
<port_number>with the port number to which you want to assign thehttp_port_ttype.For more complex configuration of the managed nodes that involves other customizations of SELinux, use the
selinuxRHEL system role. Create a playbook file, for example,~/playbook.yml, and add the following content:--- - name: Modify SELinux port mapping example hosts: all vars: # Map tcp port <port_number> to the 'http_port_t' SELinux port type selinux_ports: - ports: <port_number> proto: tcp setype: http_port_t state: present tasks: - name: Include selinux role ansible.builtin.include_role: name: rhel-system-roles.selinuxReplace
<port_number>with the port number to which you want to assign thehttp_port_ttype.
Verification
Verify that the port is assigned to the
http_port_ttype:# semanage port --list | grep http_port_t http_port_t tcp <port_number>, 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000
Additional resources
-
/usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/README.mdfile -
/usr/share/doc/rhel-system-roles/selinux/directory
10.4. Creating an SELinux configuration Ansible playbook in the web console
In the web console, you can generate a shell script or an Ansible playbook of your SELinux configuration. In case of the Ansible playbook, you can conveniently apply the configuration on multiple systems.
Prerequisites
You have installed the RHEL 8 web console.
For instructions, see Installing and enabling the web console.
Procedure
Log in to the RHEL 8 web console.
For details, see Logging in to the web console.
- Click SELinux.
Click .
A window with the generated script opens. You can navigate between a shell script and an Ansible playbook generation options tab.
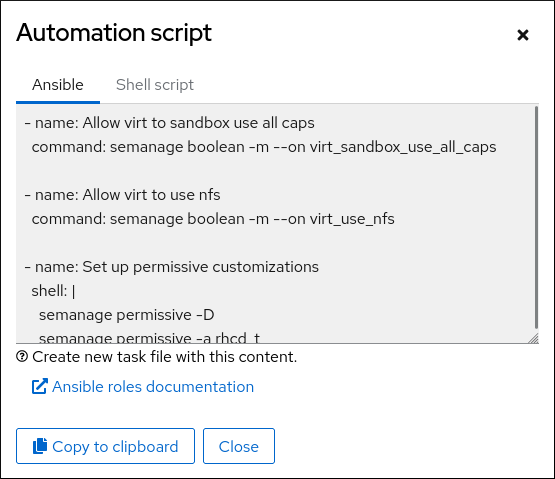
- Click the button to select the script or playbook and apply it.
As a result, you have an automation script that you can apply to more machines.
Additional resources
- Troubleshooting problems related to SELinux
- Deploying the same SELinux configuration on multiple systems
-
ansible-playbook(1)man page on your system
10.5. Transferring SELinux settings to another system with semanage
Use the following steps for transferring your custom and verified SELinux settings between RHEL 8-based systems.
Prerequisites
-
The
policycoreutils-python-utilspackage is installed on your system.
Procedure
Export your verified SELinux settings:
# semanage export -f ./my-selinux-settings.modCopy the file with the settings to the new system:
# scp ./my-selinux-settings.mod new-system-hostname:Log in on the new system:
$ ssh root@new-system-hostnameImport the settings on the new system:
new-system-hostname# semanage import -f ./my-selinux-settings.mod
Additional resources
-
semanage-export(8)andsemanage-import(8)man pages on your system