20.15. Using PAM for Pass Through Authentication
Many systems already have authentication mechanisms in place for Unix and Linux users. One of the most common authentication frameworks is Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM). Since many networks already have existing authentication services available, administrators may want to continue using those services. A PAM module can be configured to tell Directory Server to use an existing authentication store for LDAP clients.
The PAM pass through authentication in Red Hat Directory Server uses the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in, which enables the Directory Server to enable the PAM service to authenticate LDAP clients.
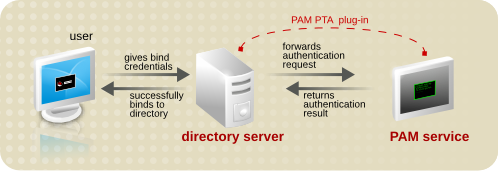
Figure 20.3. PAM Pass Through Authentication Process
Note
The PAM pass through authentication works together with account inactivation when authenticating users, assuming that the appropriate mapping method (ENTRY) is used. However, the PAM pass through authentication does not validate passwords against password policies set either globally or locally, because the passwords are set and stored in the PAM module, not in the Directory Server.
20.15.1. PAM Pass Through Authentication Configuration Options
The PAM pass through authentication is configured in child entries beneath the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in container entry. There can be multiple PAM pass through authentication policies, applied to different suffixes or to different entries within suffixes.
There are several different areas that can be configured for the PAM pass through:
- The suffixes that are controlled by the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in. This covers suffixes to exclude, suffixes to include, and how to handle a missing suffix.
- Individual entries within the configured suffixes which are the target of the authentication configuration. By default, all entries within a suffix are included in the authentication scope, but it is possible to configure multiple, different PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in instances and then apply different plug-in configuration to different users.
- The PAM attribute mapping. The credentials that are offered to the Directory Server have to be mapped in some way to an LDAP entry and then, back to the credentials in the PAM service. This is done by defining a mapping method and then, optionally, which LDAP attribute to use to match the credentials.
- General configuration such as using TLS connections, the PAM service to use, and whether to fallback to LDAP authentication if PAM authentication fails.
Note
There can be multiple configuration instances of the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in. An instance of the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in can be applied to a subset of user entries by using the
pamFilter attribute to set an LDAP filter to search for the specific entries to use with the plug-in.
For a list of attributes you can set, see the PAM Pass Through Auth Plug-in Attributes section in Red Hat Directory Server Configuration, Command, and File Reference.
20.15.1.1. Specifying the Suffixes to Target for PAM PTA
The PAM PTA plug-in is applied globally, to all suffixes, by default unless they are explicitly excluded. Excluding and including suffixes can help target what areas in the directory use PAM authentication instead of LDAP authentication.
Note
The target of a PAM Pass Through authentication entry must be a suffix, not an arbitrary subtree. As described in Section 2.1, “Creating and Maintaining Suffixes”, a suffix is a subtree which is associated with a specific back end database, such as
cn=config which is associated with the root suffix dc=example,dc=com which is associated with userRoot.
The
pamExcludeSuffix attribute excludes a suffix. By default, only the configuration subtree (cn=config) is excluded. Alternatively, the PAM PTA plug-in can be applied to a suffix with the pamIncludeSuffix attribute. Both of these attributes are multi-valued.
If the include attribute is set, for example, all other suffixes are automatically excluded. Likewise, if an exclude attribute is set, all other suffixes are automatically included.
pamExcludeSuffix: cn=config
With
pamIncludeSuffix, only the given suffix is included and all others are automatically excluded. Since this attribute is multi-valued, more than one suffix can be included in the PAM evaluation by explicitly listing the suffixes.
pamIncludeSuffix: ou=Engineering,dc=example,dc=com pamIncludeSuffix: ou=QE,dc=example,dc=com
The
pamMissingSuffix attribute tells the server how to handle a failure if the specified suffix (include or exclude) does not exist. If it is set to IGNORE, then if the suffix does not exist, the plug-in simply skips that suffix and tries the next.
pamMissingSuffix: IGNORE pamIncludeSuffix: ou=Engineering,dc=example,dc=com pamIncludeSuffix: ou=Not Real,dc=example,dc=com
20.15.1.2. Applying Different PAM Pass Through Authentication Configurations to Different Entries
By default, a PAM pass through authentication policy applies to all entries within the designated suffixes. However, it is possible to specify an LDAP filter in the
pamFilter attribute which identifies specific entries within the suffix to which to apply the PAM pass through authentication policy.
This is useful for applying different PAM configurations or mapping methods to different user types, using multiple PAM pass through authentication policies.
20.15.1.3. Setting PAM PTA Mappings
There has to be a way to connect the LDAP identity to the PAM identity. The first thing to define is the method to use to map the entries. There are three options: DN, RDN, and ENTRY. ENTRY uses a user-defined attribute in the entry.
Multiple mapping methods can be supplied in an ordered, space-separated list. The plug-in attempts to use each mapping method in the order listed until authentication succeeds or until it reaches the end of the list.
For example, this mapping method first maps the RDN method, then ENTRY, then DN, in the order the methods are listed:
pamIDMapMethod: RDN ENTRY DN
The different mapping methods are listed in Table 20.4, “Mapping Methods for PAM Authentication”.
Note
Directory Server user account inactivation is only validated using the ENTRY mapping method. With RDN or DN, a Directory Server user whose account is inactivated can still bind to the server successfully.
| Mapping | Description |
|---|---|
| RDN | This method uses the value from the leftmost RDN in the bind DN. The mapping for this method is defined by Directory Server. This is the default mapping method, if none is given. |
| ENTRY | This method pulls the value of the PAM identity from a user-defined attribute in the bind DN entry. The identity attribute is defined in the pamIDAttr attribute. For example: pamIDAttr: customPamUid |
| DN | This method uses the full distinguished name from the bind DN. The mapping for this method is defined by Directory Server. |
20.15.1.4. Configuring General PAM PTA Settings
Three general configuration settings can be set for PAM authentication:
- The service name to send to PAM (
pamService); this is the name of the configuration file to use in/etc/pam.d - Whether to require a secure connection (
pamSecure) - Whether to fall back to LDAP authentication if PAM authentication fails (
pamFallback)
pamFallback: false pamSecure: false pamService: ldapserver
20.15.2. Configuring PAM Pass Through Authentication
Note
Multiple instances of configuration may exist for a pluggable authentication module (PAM) Pass Through Authentication. An instance of the PAM Pass Through Authentication can be applied to a subset of user entries by using the
pamFilter attribute to set an LDAP filter to search for the specific entries to use with the plug-in.
PAM Pass Through Authentication is configured through the command line.
- Make sure the PAM service is fully configured.
- Remove the
pam_fprintd.somodule from the PAM configuration file.Important
Thepam_fprintd.somodule cannot be in the configuration file referenced by thepamServiceattribute of the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in configuration. Using the PAMfprintdmodule causes the Directory Server to hit the max file descriptor limit and can cause the Directory Server process to abort. - Enable the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in:
# dsconf -D "cn=Directory Manager" ldap://server.example.com plugin set "PAM Pass Through Auth" --enabled on
- Create the PAM Pass Through Auth configuration entry:
# dsconf -D "cn=Directory Manager" ldap://server.example.com plugin pass-through-auth pam-config "Admin PAM PTA Config" add --exclude-suffix="cn=config" --id_map_method="RDN ENTRY" --id-attr="customPamUid" --filter="(manager=uid=example_user,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com pamFallback: FALSE" --secure="TRUE" --service="ldapserver"
- Restart the instance:
# dsctl instance_name restart
20.15.3. Using PAM Pass Through Authentication with Active Directory as the Back End
PAM Pass Through Authentication forwards the credentials from the Directory Server to the PAM service. One option is to set up and configure PAM modules specifically for Directory Server. Another option — and one which may be more repeatable and more convenient in some infrastructures — is to use the System Security Services Daemon (SSSD) to configure PAM. Because SSSD can use a variety of different identity stores, a lot of different servers or services can be used to provide credentials, including Active Directory.
Using the pass through authentication through SSSD is a daisy chain of services. The PAM PTA plug-in is configured as normal. It points to the given PAM service file to use. This service file is managed by SSSD, and SSSD is configured to connect with whatever identity provider is required, even multiple providers.
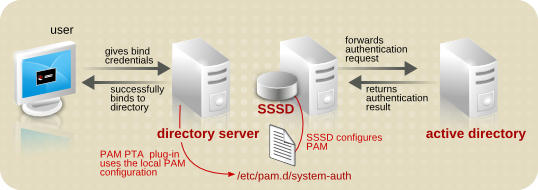
Figure 20.4. PAM Pass Through Authentication with SSSD
To configure PAM Pass Through Authentication with Active Directory:
- Configure SSSD to use the Active Directory server as one of its identity providers.This configuration is covered in the Connecting RHEL systems directly to AD using SSSD section in Integrating RHEL systems directly with Windows Active Directory.
- Enable the PAM Pass Through Auth plug-in as follows:
# dsconf -D "cn=Directory Manager" ldap://server.example.com plugin set "PAM Pass Through Auth" --enabled on
- Create the PAM Pass Through Auth configuration entry as follows:
# dsconf -D "cn=Directory Manager" ldap://server.example.com plugin pass-through-auth pam-config "AD PAM PTA Config" add --id_map_method="ENTRY" --id-attr="uid" --service="login" --include-suffix="ou=people,dc=example,dc=com" --missing-suffix="ERROR"
The example uses theuid LDAPattribute as the username to pass to Active Directory and enables this configuration only for the people OU. - Restart the directory server instance to load the configuration.
# dsctl instance_name restart