Debugger
The Camel Debugger is intended for 3rd party tooling to make it possible to debug routes, trace messages and to use breakpoints with the EIP patterns in the Camel routes.
The Debugger allows tooling or the likes to attach breakpoints which is being invoked when Exchanges are routed.
Debugging Camel routes
If you are developing unit tests using the camel-test-junit5 component, then
the Debugger is available if you turn it on via overriding the isUseDebugger()
method and return true.
In this unit test
public class DebugTest extends CamelTestSupportWe want to debug the following route
@Override
protected RouteBuilder createRouteBuilder() throws Exception {
return new RouteBuilder() {
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
// this is the route we want to debug
from("direct:start")
.to("mock:a")
.transform(body().prepend("Hello "))
.to("mock:b");
}
};
}Which can easily done by overriding the debugBefore method as shown
@Override
public boolean isUseDebugger() {
// must enable debugger
return true;
}
@Override
protected void debugBefore(Exchange exchange, Processor processor,
ProcessorDefinition<?> definition, String id, String shortName) {
// this method is invoked before we are about to enter the given processor
// from your Java editor you can just add a breakpoint in the code line below
log.info("Before " + definition + " with body " + exchange.getIn().getBody());
}Then from your Java editor just add a breakpoint inside the
debugBefore method. Then fire up the unit test and wait for the Java
editor to hit the breakpoint. Then you can inspect the
Exchange during debugging while it advances during
routing. The ProcessorDefinition and the id and shortName
parameters is all information which tells you where in the route the
breakpoint was hit.
There is also a debugAfter method which is invoked after the processor
has been invoked. This allows you to see what happens to the
Exchange right after it has invoked a processor in the route.
|
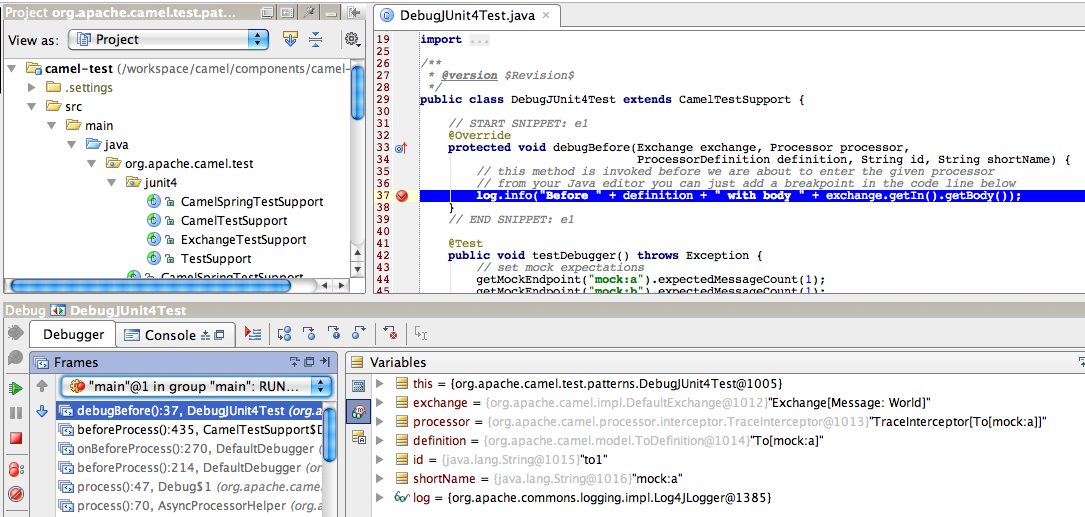
The screenshot below shows the Debugger in action. The IDE (IDEA) has hit the breakpoint, and we can inspect the parameters. Notice how we can see that the message is to be sent to the mock:a endpoint.
Implementing a custom debugger
The debugger API is defined in org.apache.camel.spi.Debugger.
This API has methods to attach and remove breakpoints.
And to suspend/resume all breakpoints etc. You can also attach a condition to the breakpoint, so it only reacts if the condition matches.
Camel provides a base implementation org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultDebugger,
which can be used to extend for custom implementations.
JMX debugger
There is also a Backlog Debugger which allows debugging from JMX, and some 3rd party tooling such as hawtio uses this for its web based debugging functionality.
Camel requires to have camel-management JAR on the classpath for having JMX enabled.