Building applications
Configuring OpenShift Dedicated for your applications
Abstract
Chapter 1. Building applications overview
Using OpenShift Dedicated, you can create, edit, delete, and manage applications using the web console or command line interface (CLI).
1.1. Working on a project
Using projects, you can organize and manage applications in isolation. You can manage the entire project lifecycle, including creating, viewing, and deleting a project in OpenShift Dedicated.
After you create the project, you can grant or revoke access to a project and manage cluster roles for the users using the Developer perspective. You can also edit the project configuration resource while creating a project template that is used for automatic provisioning of new projects.
As a user with dedicated administrator permissions, you can choose to prevent an authenticated user group from self-provisioning new projects.
1.2. Working on an application
1.2.1. Creating an application
To create applications, you must have created a project or have access to a project with the appropriate roles and permissions. You can create an application by using either the Developer perspective in the web console, installed Operators, or the OpenShift Dedicated CLI. You can source the applications to be added to the project from Git, JAR files, devfiles, or the developer catalog.
You can also use components that include source or binary code, images, and templates to create an application by using the OpenShift Dedicated CLI. With the OpenShift Dedicated web console, you can create an application from an Operator installed by a cluster administrator.
1.2.2. Maintaining an application
After you create the application you can use the web console to monitor your project or application metrics. You can also edit or delete the application using the web console. When the application is running, not all applications resources are used. As a cluster administrator, you can choose to idle these scalable resources to reduce resource consumption.
1.2.3. Connecting an application to services
An application uses backing services to build and connect workloads, which vary according to the service provider. Using the Service Binding Operator, as a developer, you can bind workloads together with Operator-managed backing services, without any manual procedures to configure the binding connection.
1.2.4. Deploying an application
You can deploy your application using Deployment or DeploymentConfig objects and manage them from the web console. You can create deployment strategies that help reduce downtime during a change or an upgrade to the application.
You can also use Helm, a software package manager that simplifies deployment of applications and services to OpenShift Dedicated clusters.
1.3. Using the Red Hat Marketplace
The Red Hat Marketplace is an open cloud marketplace where you can discover and access certified software for container-based environments that run on public clouds and on-premises.
Chapter 2. Projects
2.1. Working with projects
A project allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities.
Projects starting with openshift- and kube- are default projects. These projects host cluster components that run as pods and other infrastructure components. As such, OpenShift Dedicated does not allow you to create projects starting with openshift- or kube- using the oc new-project command. For OpenShift Dedicated clusters that use the Customer Cloud Subscription (CCS) model, users with cluster-admin privileges can create these projects using the oc adm new-project command.
In OpenShift Dedicated clusters that use the Customer Cloud Subscription (CCS) model, you cannot assign an SCC to pods created in one of the default namespaces: default, kube-system, kube-public, openshift-node, openshift-infra, and openshift. You cannot use these namespaces for running pods or services. You cannot create any SCCs for OpenShift Dedicated clusters that use a Red Hat cloud account, because SCC resource creation requires cluster-admin privileges.
2.1.1. Creating a project using the web console
If allowed by your cluster administrator, you can create a new project.
Projects starting with openshift- and kube- are considered critical by OpenShift Dedicated. As such, OpenShift Dedicated does not allow you to create Projects starting with openshift- using the web console.
Procedure
- Navigate to Home → Projects.
- Click Create Project.
- Enter your project details.
- Click Create.
2.1.2. Creating a project using the Developer perspective in the web console
You can use the Developer perspective in the OpenShift Dedicated web console to create a project in your cluster.
Projects starting with openshift- and kube- are considered critical by OpenShift Dedicated. As such, OpenShift Dedicated does not allow you to create projects starting with openshift- or kube- using the Developer perspective. For OpenShift Dedicated clusters that use the Customer Cloud Subscription (CCS) model, users with cluster-admin privileges can create these projects using the oc adm new-project command.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have the appropriate roles and permissions to create projects, applications, and other workloads in OpenShift Dedicated.
Procedure
You can create a project using the Developer perspective, as follows:
Click the Project drop-down menu to see a list of all available projects. Select Create Project.
Figure 2.1. Create project
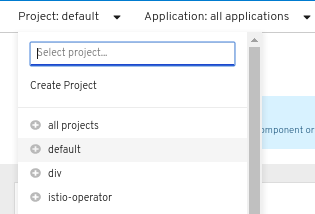
-
In the Create Project dialog box, enter a unique name, such as
myproject, in the Name field. - Optional: Add the Display Name and Description details for the project.
- Click Create.
- Use the left navigation panel to navigate to the Project view and see the dashboard for your project.
Optional:
- Use the Project drop-down menu at the top of the screen and select all projects to list all of the projects in your cluster.
- Use the Details tab to see the project details.
- If you have adequate permissions for a project, you can use the Project Access tab to provide or revoke administrator, edit, and view privileges for the project.
2.1.3. Creating a project using the CLI
If allowed by your cluster administrator, you can create a new project.
Projects starting with openshift- and kube- are considered critical by OpenShift Dedicated. As such, OpenShift Dedicated does not allow you to create Projects starting with openshift- or kube- using the oc new-project command. For OpenShift Dedicated clusters that use the Customer Cloud Subscription (CCS) model, users with cluster-admin privileges can create these projects using the oc adm new-project command.
Procedure
Run:
$ oc new-project <project_name> \ --description="<description>" --display-name="<display_name>"For example:
$ oc new-project hello-openshift \ --description="This is an example project" \ --display-name="Hello OpenShift"
The number of projects you are allowed to create might be limited by the system administrator. After your limit is reached, you might have to delete an existing project in order to create a new one.
2.1.4. Viewing a project using the web console
Procedure
- Navigate to Home → Projects.
Select a project to view.
On this page, click Workloads to see workloads in the project.
2.1.5. Viewing a project using the CLI
When viewing projects, you are restricted to seeing only the projects you have access to view based on the authorization policy.
Procedure
To view a list of projects, run:
$ oc get projects
You can change from the current project to a different project for CLI operations. The specified project is then used in all subsequent operations that manipulate project-scoped content:
$ oc project <project_name>
2.1.6. Providing access permissions to your project using the Developer perspective
You can use the Project view in the Developer perspective to grant or revoke access permissions to your project.
Procedure
To add users to your project and provide Admin, Edit, or View access to them:
- In the Developer perspective, navigate to the Project view.
- In the Project page, select the Project Access tab.
Click Add Access to add a new row of permissions to the default ones.
Figure 2.2. Project permissions
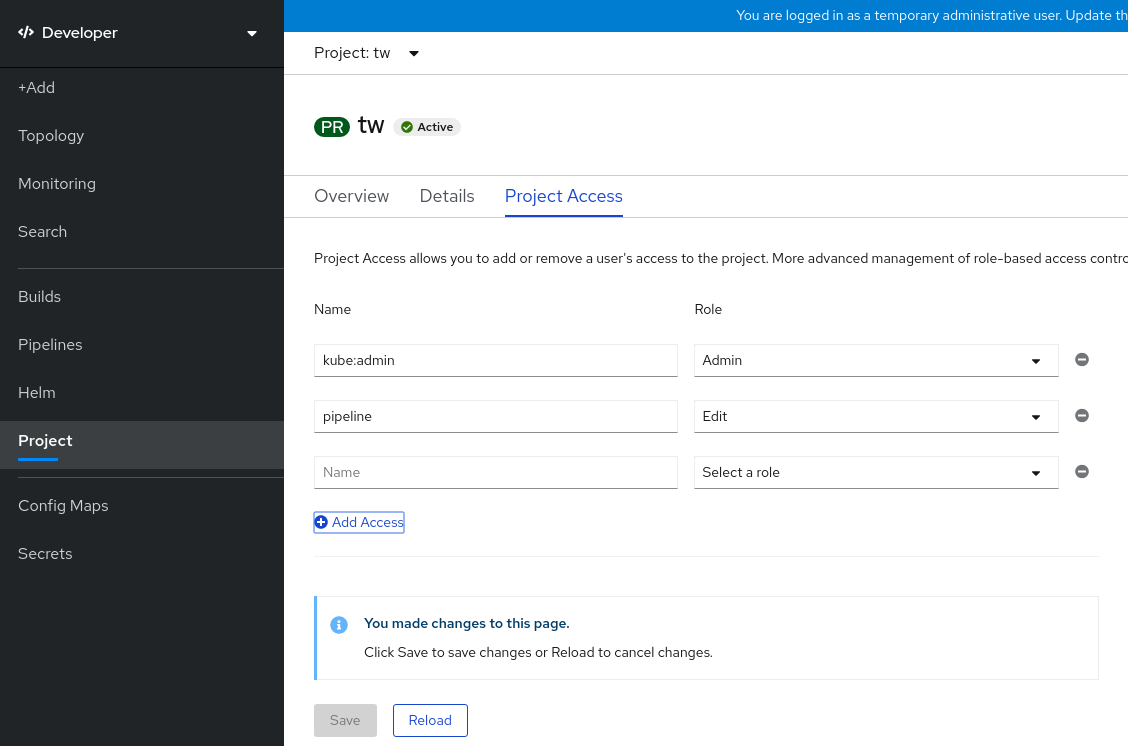
- Enter the user name, click the Select a role drop-down list, and select an appropriate role.
- Click Save to add the new permissions.
You can also use:
- The Select a role drop-down list, to modify the access permissions of an existing user.
- The Remove Access icon, to completely remove the access permissions of an existing user to the project.
Advanced role-based access control is managed in the Roles and Roles Binding views in the Administrator perspective.
2.1.7. Customizing the available cluster roles using the Developer perspective
The users of a project are assigned to a cluster role based on their access control. You can access these cluster roles by navigating to the Project → Project access → Role. By default, these roles are Admin, Edit, and View.
To add or edit the cluster roles for a project, you can customize the YAML code of the cluster.
Procedure
To customize the different cluster roles of a project:
-
In the Search view, use the Resources drop-down list to search for
Console. From the available options, select the Console
operator.openshift.io/v1.Figure 2.3. Searching Console resource

- Select cluster under the Name list.
- Navigate to the YAML tab to view and edit the YAML code.
In the YAML code under
spec, add or edit the list ofavailableClusterRolesand save your changes:spec: customization: projectAccess: availableClusterRoles: - admin - edit - view
2.1.8. Adding to a project
Procedure
- Select Developer from the context selector at the top of the web console navigation menu.
- Click +Add
- At the top of the page, select the name of the project that you want to add to.
- Click a method for adding to your project, and then follow the workflow.
You can also add components to the topology using quick search.
2.1.9. Checking project status using the web console
Procedure
- Navigate to Home → Projects.
- Select a project to see its status.
2.1.10. Checking project status using the CLI
Procedure
Run:
$ oc status
This command provides a high-level overview of the current project, with its components and their relationships.
2.1.11. Deleting a project using the web console
You can delete a project by using the OpenShift Dedicated web console.
If you do not have permissions to delete the project, the Delete Project option is not available.
Procedure
- Navigate to Home → Projects.
- Locate the project that you want to delete from the list of projects.
-
On the far right side of the project listing, select Delete Project from the Options menu
 .
.
- When the Delete Project pane opens, enter the name of the project that you want to delete in the field.
- Click Delete.
2.1.12. Deleting a project using the CLI
When you delete a project, the server updates the project status to Terminating from Active. Then, the server clears all content from a project that is in the Terminating state before finally removing the project. While a project is in Terminating status, you cannot add new content to the project. Projects can be deleted from the CLI or the web console.
Procedure
Run:
$ oc delete project <project_name>
2.2. Configuring project creation
In OpenShift Dedicated, projects are used to group and isolate related objects. When a request is made to create a new project using the web console or oc new-project command, an endpoint in OpenShift Dedicated is used to provision the project according to a template, which can be customized.
As a cluster administrator, you can allow and configure how developers and service accounts can create, or self-provision, their own projects.
2.2.1. About project creation
The OpenShift Dedicated API server automatically provisions new projects based on the project template that is identified by the projectRequestTemplate parameter in the cluster’s project configuration resource. If the parameter is not defined, the API server creates a default template that creates a project with the requested name, and assigns the requesting user to the admin role for that project.
When a project request is submitted, the API substitutes the following parameters into the template:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The name of the project. Required. |
|
| The display name of the project. May be empty. |
|
| The description of the project. May be empty. |
|
| The user name of the administrating user. |
|
| The user name of the requesting user. |
Access to the API is granted to developers with the self-provisioner role and the self-provisioners cluster role binding. This role is available to all authenticated developers by default.
2.2.2. Modifying the template for new projects
As a cluster administrator, you can modify the default project template so that new projects are created using your custom requirements.
To create your own custom project template:
Prerequisites
-
You have access to an OpenShift Dedicated cluster using an account with
dedicated-adminpermissions.
Procedure
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. Generate the default project template:
$ oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yaml
-
Use a text editor to modify the generated
template.yamlfile by adding objects or modifying existing objects. The project template must be created in the
openshift-confignamespace. Load your modified template:$ oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-config
Edit the project configuration resource using the web console or CLI.
Using the web console:
- Navigate to the Administration → Cluster Settings page.
- Click Configuration to view all configuration resources.
- Find the entry for Project and click Edit YAML.
Using the CLI:
Edit the
project.config.openshift.io/clusterresource:$ oc edit project.config.openshift.io/cluster
Update the
specsection to include theprojectRequestTemplateandnameparameters, and set the name of your uploaded project template. The default name isproject-request.Project configuration resource with custom project template
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Project metadata: ... spec: projectRequestTemplate: name: <template_name>- After you save your changes, create a new project to verify that your changes were successfully applied.
2.2.3. Disabling project self-provisioning
You can prevent an authenticated user group from self-provisioning new projects.
Procedure
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. View the
self-provisionerscluster role binding usage by running the following command:$ oc describe clusterrolebinding.rbac self-provisioners
Example output
Name: self-provisioners Labels: <none> Annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate=true Role: Kind: ClusterRole Name: self-provisioner Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- Group system:authenticated:oauth
Review the subjects in the
self-provisionerssection.Remove the
self-provisionercluster role from the groupsystem:authenticated:oauth.If the
self-provisionerscluster role binding binds only theself-provisionerrole to thesystem:authenticated:oauthgroup, run the following command:$ oc patch clusterrolebinding.rbac self-provisioners -p '{"subjects": null}'If the
self-provisionerscluster role binding binds theself-provisionerrole to more users, groups, or service accounts than thesystem:authenticated:oauthgroup, run the following command:$ oc adm policy \ remove-cluster-role-from-group self-provisioner \ system:authenticated:oauth
Edit the
self-provisionerscluster role binding to prevent automatic updates to the role. Automatic updates reset the cluster roles to the default state.To update the role binding using the CLI:
Run the following command:
$ oc edit clusterrolebinding.rbac self-provisioners
In the displayed role binding, set the
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdateparameter value tofalse, as shown in the following example:apiVersion: authorization.openshift.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "false" ...
To update the role binding by using a single command:
$ oc patch clusterrolebinding.rbac self-provisioners -p '{ "metadata": { "annotations": { "rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate": "false" } } }'
Log in as an authenticated user and verify that it can no longer self-provision a project:
$ oc new-project test
Example output
Error from server (Forbidden): You may not request a new project via this API.
Consider customizing this project request message to provide more helpful instructions specific to your organization.
2.2.4. Customizing the project request message
When a developer or a service account that is unable to self-provision projects makes a project creation request using the web console or CLI, the following error message is returned by default:
You may not request a new project via this API.
Cluster administrators can customize this message. Consider updating it to provide further instructions on how to request a new project specific to your organization. For example:
-
To request a project, contact your system administrator at
projectname@example.com. -
To request a new project, fill out the project request form located at
https://internal.example.com/openshift-project-request.
To customize the project request message:
Procedure
Edit the project configuration resource using the web console or CLI.
Using the web console:
- Navigate to the Administration → Cluster Settings page.
- Click Configuration to view all configuration resources.
- Find the entry for Project and click Edit YAML.
Using the CLI:
-
Log in as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. Edit the
project.config.openshift.io/clusterresource:$ oc edit project.config.openshift.io/cluster
-
Log in as a user with
Update the
specsection to include theprojectRequestMessageparameter and set the value to your custom message:Project configuration resource with custom project request message
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Project metadata: ... spec: projectRequestMessage: <message_string>
For example:
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Project metadata: ... spec: projectRequestMessage: To request a project, contact your system administrator at projectname@example.com.
- After you save your changes, attempt to create a new project as a developer or service account that is unable to self-provision projects to verify that your changes were successfully applied.
Chapter 3. Creating applications
3.1. Creating applications using the Developer perspective
The Developer perspective in the web console provides you the following options from the +Add view to create applications and associated services and deploy them on OpenShift Dedicated:
Getting started resources: Use these resources to help you get started with Developer Console. You can choose to hide the header using the Options menu
 .
.
- Creating applications using samples: Use existing code samples to get started with creating applications on the OpenShift Dedicated.
- Build with guided documentation: Follow the guided documentation to build applications and familiarize yourself with key concepts and terminologies.
- Explore new developer features: Explore the new features and resources within the Developer perspective.
Developer catalog: Explore the Developer Catalog to select the required applications, services, or source to image builders, and then add it to your project.
- All Services: Browse the catalog to discover services across OpenShift Dedicated.
- Database: Select the required database service and add it to your application.
- Operator Backed: Select and deploy the required Operator-managed service.
- Helm chart: Select the required Helm chart to simplify deployment of applications and services.
- Devfile: Select a devfile from the Devfile registry to declaratively define a development environment.
Event Source: Select an event source to register interest in a class of events from a particular system.
NoteThe Managed services option is also available if the RHOAS Operator is installed.
- Git repository: Import an existing codebase, Devfile, or Dockerfile from your Git repository using the From Git, From Devfile, or From Dockerfile options respectively, to build and deploy an application on OpenShift Dedicated.
- Container images: Use existing images from an image stream or registry to deploy it on to the OpenShift Dedicated.
- Pipelines: Use Tekton pipeline to create CI/CD pipelines for your software delivery process on the OpenShift Dedicated.
Serverless: Explore the Serverless options to create, build, and deploy stateless and serverless applications on the OpenShift Dedicated.
- Channel: Create a Knative channel to create an event forwarding and persistence layer with in-memory and reliable implementations.
- Samples: Explore the available sample applications to create, build, and deploy an application quickly.
- Quick Starts: Explore the quick start options to create, import, and run applications with step-by-step instructions and tasks.
From Local Machine: Explore the From Local Machine tile to import or upload files on your local machine for building and deploying applications easily.
- Import YAML: Upload a YAML file to create and define resources for building and deploying applications.
- Upload JAR file: Upload a JAR file to build and deploy Java applications.
- Share my Project: Use this option to add or remove users to a project and provide accessibility options to them.
- Helm Chart repositories: Use this option to add Helm Chart repositories in a namespace.
- Re-ordering of resources: Use these resources to re-order pinned resources added to your navigation pane. The drag-and-drop icon is displayed on the left side of the pinned resource when you hover over it in the navigation pane. The dragged resource can be dropped only in the section where it resides.
Note that the Pipelines option is displayed only when the OpenShift Pipelines Operator is installed.
3.1.1. Prerequisites
To create applications using the Developer perspective ensure that:
- You have logged in to the web console.
3.1.2. Creating Sample applications
You can use the sample applications in the +Add flow of the Developer perspective to create, build, and deploy applications quickly.
Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the OpenShift Dedicated web console and are in the Developer perspective.
Procedure
- In the +Add view, click on the Samples tile to see the Samples page.
- On the Samples page, select one of the available sample applications to see the Create Sample Application form.
In the Create Sample Application Form:
- In the Name field, the deployment name is displayed by default. You can modify this name as required.
- In the Builder Image Version, a builder image is selected by default. You can modify this image version by using the Builder Image Version drop-down list.
- A sample Git repository URL is added by default.
- Click Create to create the sample application. The build status of the sample application is displayed on the Topology view. After the sample application is created, you can see the deployment added to the application.
3.1.3. Creating applications using Quick Starts
The Quick Starts page shows you how to create, import, and run applications on OpenShift Dedicated, with step-by-step instructions and tasks.
Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the OpenShift Dedicated web console and are in the Developer perspective.
Procedure
- In the +Add view, click the View all quick starts link to view the Quick Starts page.
- In the Quick Starts page, click the tile for the quick start that you want to use.
- Click Start to begin the quick start.
3.1.4. Importing a codebase from Git to create an application
You can use the Developer perspective to create, build, and deploy an application on OpenShift Dedicated using an existing codebase in GitHub.
The following procedure walks you through the From Git option in the Developer perspective to create an application.
Procedure
- In the +Add view, click From Git in the Git Repository tile to see the Import from git form.
-
In the Git section, enter the Git repository URL for the codebase you want to use to create an application. For example, enter the URL of this sample Node.js application
https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-ex. The URL is then validated. Optional: You can click Show Advanced Git Options to add details such as:
- Git Reference to point to code in a specific branch, tag, or commit to be used to build the application.
- Context Dir to specify the subdirectory for the application source code you want to use to build the application.
- Source Secret to create a Secret Name with credentials for pulling your source code from a private repository.
Optional: You can import a
Devfile, aDockerfile,Builder Image, or aServerless Functionthrough your Git repository to further customize your deployment.-
If your Git repository contains a
Devfile, aDockerfile, aBuilder Image, or afunc.yaml, it is automatically detected and populated on the respective path fields. -
If a
Devfile, aDockerfile, or aBuilder Imageare detected in the same repository, theDevfileis selected by default. -
If
func.yamlis detected in the Git repository, the Import Strategy changes toServerless Function. - Alternatively, you can create a serverless function by clicking Create Serverless function in the +Add view using the Git repository URL.
- To edit the file import type and select a different strategy, click Edit import strategy option.
-
If multiple
Devfiles, aDockerfiles, or aBuilder Imagesare detected, to import a specific instance, specify the respective paths relative to the context directory.
-
If your Git repository contains a
After the Git URL is validated, the recommended builder image is selected and marked with a star. If the builder image is not auto-detected, select a builder image. For the
https://github.com/sclorg/nodejs-exGit URL, by default the Node.js builder image is selected.- Optional: Use the Builder Image Version drop-down to specify a version.
- Optional: Use the Edit import strategy to select a different strategy.
- Optional: For the Node.js builder image, use the Run command field to override the command to run the application.
In the General section:
-
In the Application field, enter a unique name for the application grouping, for example,
myapp. Ensure that the application name is unique in a namespace. The Name field to identify the resources created for this application is automatically populated based on the Git repository URL if there are no existing applications. If there are existing applications, you can choose to deploy the component within an existing application, create a new application, or keep the component unassigned.
NoteThe resource name must be unique in a namespace. Modify the resource name if you get an error.
-
In the Application field, enter a unique name for the application grouping, for example,
In the Resources section, select:
- Deployment, to create an application in plain Kubernetes style.
- Deployment Config, to create an OpenShift Dedicated style application.
In the Pipelines section, select Add Pipeline, and then click Show Pipeline Visualization to see the pipeline for the application. A default pipeline is selected, but you can choose the pipeline you want from the list of available pipelines for the application.
NoteThe Add pipeline checkbox is checked and Configure PAC is selected by default if the following criterias are fulfilled:
- Pipeline operator is installed
-
pipelines-as-codeis enabled -
.tektondirectory is detected in the Git repository
Add a webhook to your repository. If Configure PAC is checked and the GitHub App is set up, you can see the Use GitHub App and Setup a webhook options. If GitHub App is not set up, you can only see the Setup a webhook option:
- Go to Settings → Webhooks and click Add webhook.
- Set the Payload URL to the Pipelines as Code controller public URL.
- Select the content type as application/json.
-
Add a webhook secret and note it in an alternate location. With
opensslinstalled on your local machine, generate a random secret. - Click Let me select individual events and select these events: Commit comments, Issue comments, Pull request, and Pushes.
- Click Add webhook.
Optional: In the Advanced Options section, the Target port and the Create a route to the application is selected by default so that you can access your application using a publicly available URL.
If your application does not expose its data on the default public port, 80, clear the check box, and set the target port number you want to expose.
- Optional: You can use the following advanced options to further customize your application:
- Routing
By clicking the Routing link, you can perform the following actions:
- Customize the hostname for the route.
- Specify the path the router watches.
- Select the target port for the traffic from the drop-down list.
Secure your route by selecting the Secure Route check box. Select the required TLS termination type and set a policy for insecure traffic from the respective drop-down lists.
NoteFor serverless applications, the Knative service manages all the routing options above. However, you can customize the target port for traffic, if required. If the target port is not specified, the default port of
8080is used.
- Health Checks
Click the Health Checks link to add Readiness, Liveness, and Startup probes to your application. All the probes have prepopulated default data; you can add the probes with the default data or customize it as required.
To customize the health probes:
- Click Add Readiness Probe, if required, modify the parameters to check if the container is ready to handle requests, and select the check mark to add the probe.
- Click Add Liveness Probe, if required, modify the parameters to check if a container is still running, and select the check mark to add the probe.
Click Add Startup Probe, if required, modify the parameters to check if the application within the container has started, and select the check mark to add the probe.
For each of the probes, you can specify the request type - HTTP GET, Container Command, or TCP Socket, from the drop-down list. The form changes as per the selected request type. You can then modify the default values for the other parameters, such as the success and failure thresholds for the probe, number of seconds before performing the first probe after the container starts, frequency of the probe, and the timeout value.
- Build Configuration and Deployment
Click the Build Configuration and Deployment links to see the respective configuration options. Some options are selected by default; you can customize them further by adding the necessary triggers and environment variables.
For serverless applications, the Deployment option is not displayed as the Knative configuration resource maintains the desired state for your deployment instead of a
DeploymentConfigresource.
- Scaling
Click the Scaling link to define the number of pods or instances of the application you want to deploy initially.
If you are creating a serverless deployment, you can also configure the following settings:
-
Min Pods determines the lower limit for the number of pods that must be running at any given time for a Knative service. This is also known as the
minScalesetting. -
Max Pods determines the upper limit for the number of pods that can be running at any given time for a Knative service. This is also known as the
maxScalesetting. - Concurrency target determines the number of concurrent requests desired for each instance of the application at a given time.
- Concurrency limit determines the limit for the number of concurrent requests allowed for each instance of the application at a given time.
- Concurrency utilization determines the percentage of the concurrent requests limit that must be met before Knative scales up additional pods to handle additional traffic.
-
Autoscale window defines the time window over which metrics are averaged to provide input for scaling decisions when the autoscaler is not in panic mode. A service is scaled-to-zero if no requests are received during this window. The default duration for the autoscale window is
60s. This is also known as the stable window.
-
Min Pods determines the lower limit for the number of pods that must be running at any given time for a Knative service. This is also known as the
- Resource Limit
- Click the Resource Limit link to set the amount of CPU and Memory resources a container is guaranteed or allowed to use when running.
- Labels
Click the Labels link to add custom labels to your application.
- Click Create to create the application and a success notification is displayed. You can see the build status of the application in the Topology view.
3.1.5. Creating applications by deploying container image
You can use an external image registry or an image stream tag from an internal registry to deploy an application on your cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the OpenShift Dedicated web console and are in the Developer perspective.
Procedure
- In the +Add view, click Container images to view the Deploy Images page.
In the Image section:
- Select Image name from external registry to deploy an image from a public or a private registry, or select Image stream tag from internal registry to deploy an image from an internal registry.
- Select an icon for your image in the Runtime icon tab.
In the General section:
- In the Application name field, enter a unique name for the application grouping.
- In the Name field, enter a unique name to identify the resources created for this component.
In the Resource type section, select the resource type to generate:
-
Select Deployment to enable declarative updates for
PodandReplicaSetobjects. -
Select DeploymentConfig to define the template for a
Podobject, and manage deploying new images and configuration sources.
-
Select Deployment to enable declarative updates for
- Click Create. You can view the build status of the application in the Topology view.
3.1.6. Deploying a Java application by uploading a JAR file
You can use the web console Developer perspective to upload a JAR file by using the following options:
- Navigate to the +Add view of the Developer perspective, and click Upload JAR file in the From Local Machine tile. Browse and select your JAR file, or drag a JAR file to deploy your application.
- Navigate to the Topology view and use the Upload JAR file option, or drag a JAR file to deploy your application.
- Use the in-context menu in the Topology view, and then use the Upload JAR file option to upload your JAR file to deploy your application.
Prerequisites
-
The Cluster Samples Operator must be installed by a user with the
dedicated-adminrole. - You have access to the OpenShift Dedicated web console and are in the Developer perspective.
Procedure
- In the Topology view, right-click anywhere to view the Add to Project menu.
- Hover over the Add to Project menu to see the menu options, and then select the Upload JAR file option to see the Upload JAR file form. Alternatively, you can drag the JAR file into the Topology view.
- In the JAR file field, browse for the required JAR file on your local machine and upload it. Alternatively, you can drag the JAR file on to the field. A toast alert is displayed at the top right if an incompatible file type is dragged into the Topology view. A field error is displayed if an incompatible file type is dropped on the field in the upload form.
- The runtime icon and builder image are selected by default. If a builder image is not auto-detected, select a builder image. If required, you can change the version using the Builder Image Version drop-down list.
- Optional: In the Application Name field, enter a unique name for your application to use for resource labelling.
- In the Name field, enter a unique component name for the associated resources.
- Optional: Use the Resource type drop-down list to change the resource type.
- In the Advanced options menu, click Create a Route to the Application to configure a public URL for your deployed application.
- Click Create to deploy the application. A toast notification is shown to notify you that the JAR file is being uploaded. The toast notification also includes a link to view the build logs.
If you attempt to close the browser tab while the build is running, a web alert is displayed.
After the JAR file is uploaded and the application is deployed, you can view the application in the Topology view.
3.1.7. Using the Devfile registry to access devfiles
You can use the devfiles in the +Add flow of the Developer perspective to create an application. The +Add flow provides a complete integration with the devfile community registry. A devfile is a portable YAML file that describes your development environment without needing to configure it from scratch. Using the Devfile registry, you can use a preconfigured devfile to create an application.
Procedure
- Navigate to Developer Perspective → +Add → Developer Catalog → All Services. A list of all the available services in the Developer Catalog is displayed.
- Under All Services, select Devfiles to browse for devfiles that support a particular language or framework. Alternatively, you can use the keyword filter to search for a particular devfile using their name, tag, or description.
- Click the devfile you want to use to create an application. The devfile tile displays the details of the devfile, including the name, description, provider, and the documentation of the devfile.
- Click Create to create an application and view the application in the Topology view.
3.1.8. Using the Developer Catalog to add services or components to your application
You use the Developer Catalog to deploy applications and services based on Operator backed services such as Databases, Builder Images, and Helm Charts. The Developer Catalog contains a collection of application components, services, event sources, or source-to-image builders that you can add to your project. Cluster administrators can customize the content made available in the catalog.
Procedure
- In the Developer perspective, navigate to the +Add view and from the Developer Catalog tile, click All Services to view all the available services in the Developer Catalog.
- Under All Services, select the kind of service or the component you need to add to your project. For this example, select Databases to list all the database services and then click MariaDB to see the details for the service.
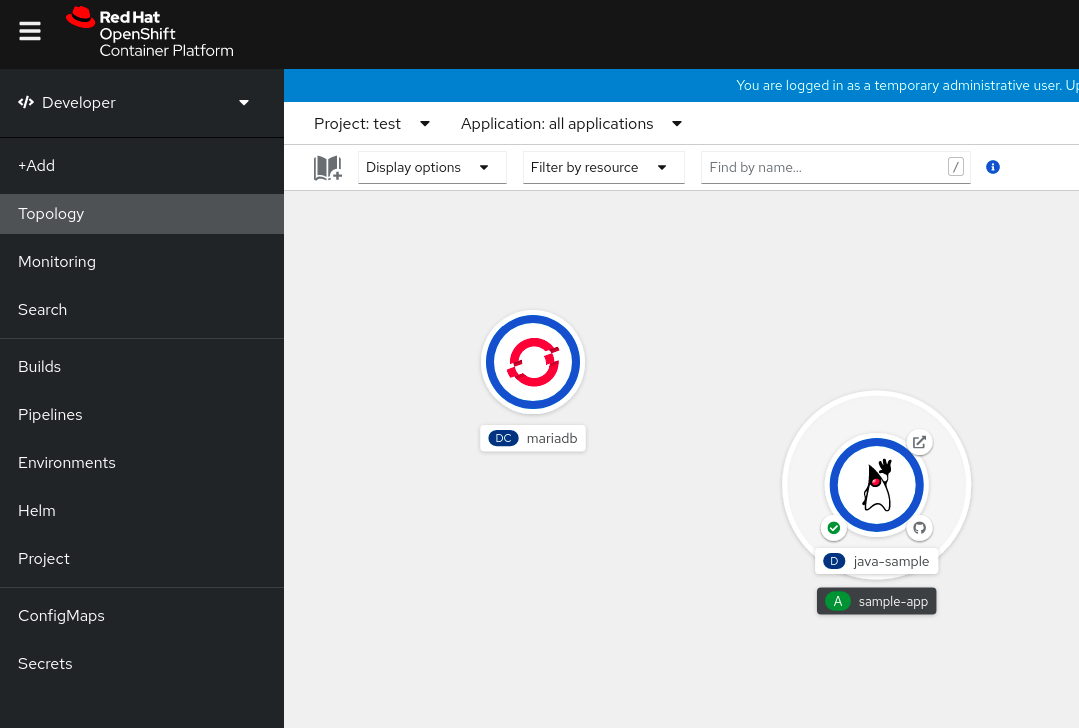
Click Instantiate Template to see an automatically populated template with details for the MariaDB service, and then click Create to create and view the MariaDB service in the Topology view.
Figure 3.1. MariaDB in Topology
3.1.9. Additional resources
- For more information about Knative routing settings for OpenShift Serverless, see Routing.
- For more information about domain mapping settings for OpenShift Serverless, see Configuring a custom domain for a Knative service.
- For more information about Knative autoscaling settings for OpenShift Serverless, see Autoscaling.
- For more information about adding a new user to a project, see Working with projects.
- For more information about creating a Helm Chart repository, see Creating Helm Chart repositories.
3.2. Creating applications from installed Operators
Operators are a method of packaging, deploying, and managing a Kubernetes application. You can create applications on OpenShift Dedicated using Operators that have been installed by a cluster administrator.
This guide walks developers through an example of creating applications from an installed Operator using the OpenShift Dedicated web console.
3.2.1. Creating an etcd cluster using an Operator
This procedure walks through creating a new etcd cluster using the etcd Operator, managed by Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM).
Prerequisites
- Access to an OpenShift Dedicated cluster.
- The etcd Operator already installed cluster-wide by an administrator.
Procedure
-
Create a new project in the OpenShift Dedicated web console for this procedure. This example uses a project called
my-etcd. Navigate to the Operators → Installed Operators page. The Operators that have been installed to the cluster by the dedicated-admin and are available for use are shown here as a list of cluster service versions (CSVs). CSVs are used to launch and manage the software provided by the Operator.
TipYou can get this list from the CLI using:
$ oc get csv
On the Installed Operators page, click the etcd Operator to view more details and available actions.
As shown under Provided APIs, this Operator makes available three new resource types, including one for an etcd Cluster (the
EtcdClusterresource). These objects work similar to the built-in native Kubernetes ones, such asDeploymentorReplicaSet, but contain logic specific to managing etcd.Create a new etcd cluster:
- In the etcd Cluster API box, click Create instance.
-
The next page allows you to make any modifications to the minimal starting template of an
EtcdClusterobject, such as the size of the cluster. For now, click Create to finalize. This triggers the Operator to start up the pods, services, and other components of the new etcd cluster.
Click the example etcd cluster, then click the Resources tab to see that your project now contains a number of resources created and configured automatically by the Operator.
Verify that a Kubernetes service has been created that allows you to access the database from other pods in your project.
All users with the
editrole in a given project can create, manage, and delete application instances (an etcd cluster, in this example) managed by Operators that have already been created in the project, in a self-service manner, just like a cloud service. If you want to enable additional users with this ability, project administrators can add the role using the following command:$ oc policy add-role-to-user edit <user> -n <target_project>
You now have an etcd cluster that will react to failures and rebalance data as pods become unhealthy or are migrated between nodes in the cluster. Most importantly, dedicated-admins or developers with proper access can now easily use the database with their applications.
3.3. Creating applications using the CLI
You can create an OpenShift Dedicated application from components that include source or binary code, images, and templates by using the OpenShift Dedicated CLI.
The set of objects created by new-app depends on the artifacts passed as input: source repositories, images, or templates.
3.3.1. Creating an application from source code
With the new-app command you can create applications from source code in a local or remote Git repository.
The new-app command creates a build configuration, which itself creates a new application image from your source code. The new-app command typically also creates a Deployment object to deploy the new image, and a service to provide load-balanced access to the deployment running your image.
OpenShift Dedicated automatically detects whether the pipeline, source, or docker build strategy should be used, and in the case of source build, detects an appropriate language builder image.
3.3.1.1. Local
To create an application from a Git repository in a local directory:
$ oc new-app /<path to source code>
If you use a local Git repository, the repository must have a remote named origin that points to a URL that is accessible by the OpenShift Dedicated cluster. If there is no recognized remote, running the new-app command will create a binary build.
3.3.1.2. Remote
To create an application from a remote Git repository:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/sclorg/cakephp-ex
To create an application from a private remote Git repository:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/youruser/yourprivaterepo --source-secret=yoursecret
If you use a private remote Git repository, you can use the --source-secret flag to specify an existing source clone secret that will get injected into your build config to access the repository.
You can use a subdirectory of your source code repository by specifying a --context-dir flag. To create an application from a remote Git repository and a context subdirectory:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/sclorg/s2i-ruby-container.git \
--context-dir=2.0/test/puma-test-app
Also, when specifying a remote URL, you can specify a Git branch to use by appending #<branch_name> to the end of the URL:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world.git#beta4
3.3.1.3. Build strategy detection
OpenShift Dedicated automatically determines which build strategy to use by detecting certain files:
If a Jenkins file exists in the root or specified context directory of the source repository when creating a new application, OpenShift Dedicated generates a pipeline build strategy.
NoteThe
pipelinebuild strategy is deprecated; consider using Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines instead.- If a Dockerfile exists in the root or specified context directory of the source repository when creating a new application, OpenShift Dedicated generates a docker build strategy.
- If neither a Jenkins file nor a Dockerfile is detected, OpenShift Dedicated generates a source build strategy.
Override the automatically detected build strategy by setting the --strategy flag to docker, pipeline, or source.
$ oc new-app /home/user/code/myapp --strategy=docker
The oc command requires that files containing build sources are available in a remote Git repository. For all source builds, you must use git remote -v.
3.3.1.4. Language detection
If you use the source build strategy, new-app attempts to determine the language builder to use by the presence of certain files in the root or specified context directory of the repository:
| Language | Files |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
After a language is detected, new-app searches the OpenShift Dedicated server for image stream tags that have a supports annotation matching the detected language, or an image stream that matches the name of the detected language. If a match is not found, new-app searches the Docker Hub registry for an image that matches the detected language based on name.
You can override the image the builder uses for a particular source repository by specifying the image, either an image stream or container specification, and the repository with a ~ as a separator. Note that if this is done, build strategy detection and language detection are not carried out.
For example, to use the myproject/my-ruby imagestream with the source in a remote repository:
$ oc new-app myproject/my-ruby~https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world.git
To use the openshift/ruby-20-centos7:latest container image stream with the source in a local repository:
$ oc new-app openshift/ruby-20-centos7:latest~/home/user/code/my-ruby-app
Language detection requires the Git client to be locally installed so that your repository can be cloned and inspected. If Git is not available, you can avoid the language detection step by specifying the builder image to use with your repository with the <image>~<repository> syntax.
The -i <image> <repository> invocation requires that new-app attempt to clone repository to determine what type of artifact it is, so this will fail if Git is not available.
The -i <image> --code <repository> invocation requires new-app clone repository to determine whether image should be used as a builder for the source code, or deployed separately, as in the case of a database image.
3.3.2. Creating an application from an image
You can deploy an application from an existing image. Images can come from image streams in the OpenShift Dedicated server, images in a specific registry, or images in the local Docker server.
The new-app command attempts to determine the type of image specified in the arguments passed to it. However, you can explicitly tell new-app whether the image is a container image using the --docker-image argument or an image stream using the -i|--image-stream argument.
If you specify an image from your local Docker repository, you must ensure that the same image is available to the OpenShift Dedicated cluster nodes.
3.3.2.1. Docker Hub MySQL image
Create an application from the Docker Hub MySQL image, for example:
$ oc new-app mysql
3.3.2.2. Image in a private registry
Create an application using an image in a private registry, specify the full container image specification:
$ oc new-app myregistry:5000/example/myimage
3.3.2.3. Existing image stream and optional image stream tag
Create an application from an existing image stream and optional image stream tag:
$ oc new-app my-stream:v1
3.3.3. Creating an application from a template
You can create an application from a previously stored template or from a template file, by specifying the name of the template as an argument. For example, you can store a sample application template and use it to create an application.
Upload an application template to your current project’s template library. The following example uploads an application template from a file called examples/sample-app/application-template-stibuild.json:
$ oc create -f examples/sample-app/application-template-stibuild.json
Then create a new application by referencing the application template. In this example, the template name is ruby-helloworld-sample:
$ oc new-app ruby-helloworld-sample
To create a new application by referencing a template file in your local file system, without first storing it in OpenShift Dedicated, use the -f|--file argument. For example:
$ oc new-app -f examples/sample-app/application-template-stibuild.json
3.3.3.1. Template parameters
When creating an application based on a template, use the -p|--param argument to set parameter values that are defined by the template:
$ oc new-app ruby-helloworld-sample \
-p ADMIN_USERNAME=admin -p ADMIN_PASSWORD=mypassword
You can store your parameters in a file, then use that file with --param-file when instantiating a template. If you want to read the parameters from standard input, use --param-file=-. The following is an example file called helloworld.params:
ADMIN_USERNAME=admin ADMIN_PASSWORD=mypassword
Reference the parameters in the file when instantiating a template:
$ oc new-app ruby-helloworld-sample --param-file=helloworld.params
3.3.4. Modifying application creation
The new-app command generates OpenShift Dedicated objects that build, deploy, and run the application that is created. Normally, these objects are created in the current project and assigned names that are derived from the input source repositories or the input images. However, with new-app you can modify this behavior.
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A |
|
|
For the |
|
|
A |
|
|
The |
| Other | Other objects can be generated when instantiating templates, according to the template. |
3.3.4.1. Specifying environment variables
When generating applications from a template, source, or an image, you can use the -e|--env argument to pass environment variables to the application container at run time:
$ oc new-app openshift/postgresql-92-centos7 \
-e POSTGRESQL_USER=user \
-e POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=db \
-e POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=password
The variables can also be read from file using the --env-file argument. The following is an example file called postgresql.env:
POSTGRESQL_USER=user POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=db POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=password
Read the variables from the file:
$ oc new-app openshift/postgresql-92-centos7 --env-file=postgresql.env
Additionally, environment variables can be given on standard input by using --env-file=-:
$ cat postgresql.env | oc new-app openshift/postgresql-92-centos7 --env-file=-
Any BuildConfig objects created as part of new-app processing are not updated with environment variables passed with the -e|--env or --env-file argument.
3.3.4.2. Specifying build environment variables
When generating applications from a template, source, or an image, you can use the --build-env argument to pass environment variables to the build container at run time:
$ oc new-app openshift/ruby-23-centos7 \
--build-env HTTP_PROXY=http://myproxy.net:1337/ \
--build-env GEM_HOME=~/.gem
The variables can also be read from a file using the --build-env-file argument. The following is an example file called ruby.env:
HTTP_PROXY=http://myproxy.net:1337/ GEM_HOME=~/.gem
Read the variables from the file:
$ oc new-app openshift/ruby-23-centos7 --build-env-file=ruby.env
Additionally, environment variables can be given on standard input by using --build-env-file=-:
$ cat ruby.env | oc new-app openshift/ruby-23-centos7 --build-env-file=-
3.3.4.3. Specifying labels
When generating applications from source, images, or templates, you can use the -l|--label argument to add labels to the created objects. Labels make it easy to collectively select, configure, and delete objects associated with the application.
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world -l name=hello-world
3.3.4.4. Viewing the output without creation
To see a dry-run of running the new-app command, you can use the -o|--output argument with a yaml or json value. You can then use the output to preview the objects that are created or redirect it to a file that you can edit. After you are satisfied, you can use oc create to create the OpenShift Dedicated objects.
To output new-app artifacts to a file, run the following:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world \
-o yaml > myapp.yamlEdit the file:
$ vi myapp.yaml
Create a new application by referencing the file:
$ oc create -f myapp.yaml
3.3.4.5. Creating objects with different names
Objects created by new-app are normally named after the source repository, or the image used to generate them. You can set the name of the objects produced by adding a --name flag to the command:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world --name=myapp
3.3.4.6. Creating objects in a different project
Normally, new-app creates objects in the current project. However, you can create objects in a different project by using the -n|--namespace argument:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world -n myproject
3.3.4.7. Creating multiple objects
The new-app command allows creating multiple applications specifying multiple parameters to new-app. Labels specified in the command line apply to all objects created by the single command. Environment variables apply to all components created from source or images.
To create an application from a source repository and a Docker Hub image:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world mysql
If a source code repository and a builder image are specified as separate arguments, new-app uses the builder image as the builder for the source code repository. If this is not the intent, specify the required builder image for the source using the ~ separator.
3.3.4.8. Grouping images and source in a single pod
The new-app command allows deploying multiple images together in a single pod. To specify which images to group together, use the + separator. The --group command line argument can also be used to specify the images that should be grouped together. To group the image built from a source repository with other images, specify its builder image in the group:
$ oc new-app ruby+mysql
To deploy an image built from source and an external image together:
$ oc new-app \
ruby~https://github.com/openshift/ruby-hello-world \
mysql \
--group=ruby+mysql3.3.4.9. Searching for images, templates, and other inputs
To search for images, templates, and other inputs for the oc new-app command, add the --search and --list flags. For example, to find all of the images or templates that include PHP:
$ oc new-app --search php
3.3.4.10. Setting the import mode
To set the import mode when using oc new-app, add the --import-mode flag. This flag can be appended with Legacy or PreserveOriginal, which provides users the option to create image streams using a single sub-manifest, or all manifests, respectively.
$ oc new-app --image=registry.redhat.io/ubi8/httpd-24:latest --import-mode=Legacy --name=test
$ oc new-app --image=registry.redhat.io/ubi8/httpd-24:latest --import-mode=PreserveOriginal --name=test
Chapter 4. Viewing application composition using the Topology view
The Topology view in the Developer perspective of the web console provides a visual representation of all the applications within a project, their build status, and the components and services associated with them.
4.1. Prerequisites
To view your applications in the Topology view and interact with them, ensure that:
- You have logged in to the web console.
- You are in the Developer perspective.
4.2. Viewing the topology of your application
You can navigate to the Topology view using the left navigation panel in the Developer perspective. After you deploy an application, you are directed automatically to the Graph view where you can see the status of the application pods, quickly access the application on a public URL, access the source code to modify it, and see the status of your last build. You can zoom in and out to see more details for a particular application.
The Topology view provides you the option to monitor your applications using the List view. Use the List view icon (
![]() ) to see a list of all your applications and use the Graph view icon (
) to see a list of all your applications and use the Graph view icon (
![]() ) to switch back to the graph view.
) to switch back to the graph view.
You can customize the views as required using the following:
- Use the Find by name field to find the required components. Search results may appear outside of the visible area; click Fit to Screen from the lower-left toolbar to resize the Topology view to show all components.
Use the Display Options drop-down list to configure the Topology view of the various application groupings. The options are available depending on the types of components deployed in the project:
Mode (Connectivity or Consumption)
- Connectivity: Select to show all the connections between the different nodes in the topology.
- Consumption: Select to show the resource consumption for all nodes in the topology.
Expand group
- Virtual Machines: Toggle to show or hide the virtual machines.
- Application Groupings: Clear to condense the application groups into cards with an overview of an application group and alerts associated with it.
- Helm Releases: Clear to condense the components deployed as Helm Release into cards with an overview of a given release.
- Operator Groupings: Clear to condense the components deployed with an Operator into cards with an overview of the given group.
Show elements based on Pod Count or Labels
- Pod Count: Select to show the number of pods of a component in the component icon.
- Labels: Toggle to show or hide the component labels.
4.3. Interacting with applications and components
The Topology view in the Developer perspective of the web console provides the following options to interact with applications and components:
-
Click Open URL (
 ) to see your application exposed by the route on a public URL.
) to see your application exposed by the route on a public URL.
Click Edit Source code to access your source code and modify it.
NoteThis feature is available only when you create applications using the From Git, From Catalog, and the From Dockerfile options.
-
Hover your cursor over the lower left icon on the pod to see the name of the latest build and its status. The status of the application build is indicated as New (
 ), Pending (
), Pending (
 ), Running (
), Running (
 ), Completed (
), Completed (
 ), Failed (
), Failed (
 ), and Canceled (
), and Canceled (
 ).
).
The status or phase of the pod is indicated by different colors and tooltips as:
-
Running (
 ): The pod is bound to a node and all of the containers are created. At least one container is still running or is in the process of starting or restarting.
): The pod is bound to a node and all of the containers are created. At least one container is still running or is in the process of starting or restarting.
-
Not Ready (
 ): The pods which are running multiple containers, not all containers are ready.
): The pods which are running multiple containers, not all containers are ready.
-
Warning(
 ): Containers in pods are being terminated, however termination did not succeed. Some containers may be other states.
): Containers in pods are being terminated, however termination did not succeed. Some containers may be other states.
-
Failed(
 ): All containers in the pod terminated but least one container has terminated in failure. That is, the container either exited with non-zero status or was terminated by the system.
): All containers in the pod terminated but least one container has terminated in failure. That is, the container either exited with non-zero status or was terminated by the system.
-
Pending(
 ): The pod is accepted by the Kubernetes cluster, but one or more of the containers has not been set up and made ready to run. This includes time a pod spends waiting to be scheduled as well as the time spent downloading container images over the network.
): The pod is accepted by the Kubernetes cluster, but one or more of the containers has not been set up and made ready to run. This includes time a pod spends waiting to be scheduled as well as the time spent downloading container images over the network.
-
Succeeded(
 ): All containers in the pod terminated successfully and will not be restarted.
): All containers in the pod terminated successfully and will not be restarted.
-
Terminating(
 ): When a pod is being deleted, it is shown as Terminating by some kubectl commands. Terminating status is not one of the pod phases. A pod is granted a graceful termination period, which defaults to 30 seconds.
): When a pod is being deleted, it is shown as Terminating by some kubectl commands. Terminating status is not one of the pod phases. A pod is granted a graceful termination period, which defaults to 30 seconds.
-
Unknown(
 ): The state of the pod could not be obtained. This phase typically occurs due to an error in communicating with the node where the pod should be running.
): The state of the pod could not be obtained. This phase typically occurs due to an error in communicating with the node where the pod should be running.
-
Running (
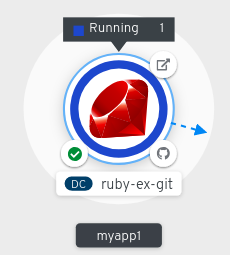
After you create an application and an image is deployed, the status is shown as Pending. After the application is built, it is displayed as Running.
Figure 4.1. Application topology
The application resource name is appended with indicators for the different types of resource objects as follows:
-
CJ:
CronJob -
D:
Deployment -
DC:
DeploymentConfig -
DS:
DaemonSet -
J:
Job -
P:
Pod -
SS:
StatefulSet  (Knative): A serverless application
Note
(Knative): A serverless application
NoteServerless applications take some time to load and display on the Graph view. When you deploy a serverless application, it first creates a service resource and then a revision. After that, it is deployed and displayed on the Graph view. If it is the only workload, you might be redirected to the Add page. After the revision is deployed, the serverless application is displayed on the Graph view.
-
CJ:
4.4. Scaling application pods and checking builds and routes
The Topology view provides the details of the deployed components in the Overview panel. You can use the Overview and Resources tabs to scale the application pods, check build status, services, and routes as follows:
Click on the component node to see the Overview panel to the right. Use the Overview tab to:
- Scale your pods using the up and down arrows to increase or decrease the number of instances of the application manually. For serverless applications, the pods are automatically scaled down to zero when idle and scaled up depending on the channel traffic.
- Check the Labels, Annotations, and Status of the application.
Click the Resources tab to:
- See the list of all the pods, view their status, access logs, and click on the pod to see the pod details.
- See the builds, their status, access logs, and start a new build if needed.
- See the services and routes used by the component.
For serverless applications, the Resources tab provides information on the revision, routes, and the configurations used for that component.
4.5. Adding components to an existing project
Procedure
-
Click Add to Project (
 ) next to left navigation pane or press Ctrl+Space
) next to left navigation pane or press Ctrl+Space
- Search for the component and select Create or press Enter to add the component to the project and see it in the topology Graph view.
Figure 4.2. Adding component via quick search
Alternatively, you can also use the Import from Git, Container Image, Database, From Catalog, Operator Backed, Helm Charts, Samples, or Upload JAR file options in the context menu by right-clicking in the topology Graph view to add a component to your project.
Figure 4.3. Context menu to add services
4.6. Grouping multiple components within an application
You can use the +Add view to add multiple components or services to your project and use the topology Graph view to group applications and resources within an application group.
Prerequisites
- You have created and deployed minimum two or more components on OpenShift Dedicated using the Developer perspective.
Procedure
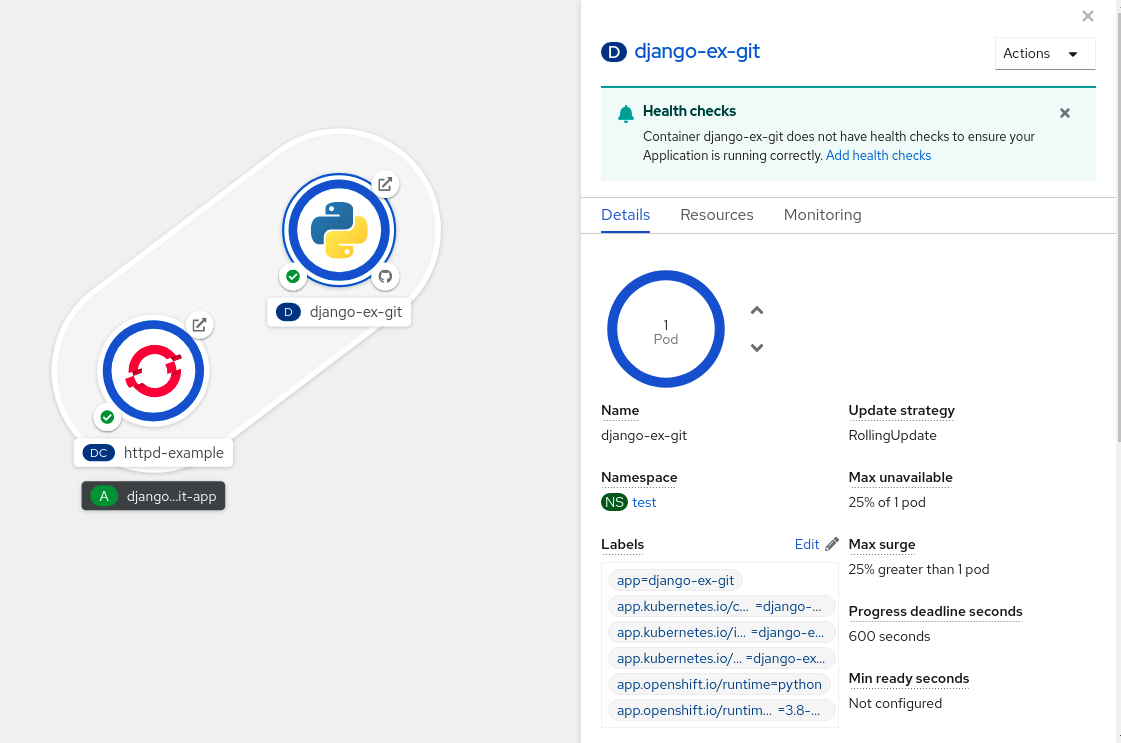
To add a service to the existing application group, press Shift+ drag it to the existing application group. Dragging a component and adding it to an application group adds the required labels to the component.
Figure 4.4. Application grouping
Alternatively, you can also add the component to an application as follows:
- Click the service pod to see the Overview panel to the right.
- Click the Actions drop-down menu and select Edit Application Grouping.
- In the Edit Application Grouping dialog box, click the Application drop-down list, and select an appropriate application group.
- Click Save to add the service to the application group.
You can remove a component from an application group by selecting the component and using Shift+ drag to drag it out of the application group.
4.7. Adding services to your application
To add a service to your application use the +Add actions using the context menu in the topology Graph view.
In addition to the context menu, you can add services by using the sidebar or hovering and dragging the dangling arrow from the application group.
Procedure
Right-click an application group in the topology Graph view to display the context menu.
Figure 4.5. Add resource context menu
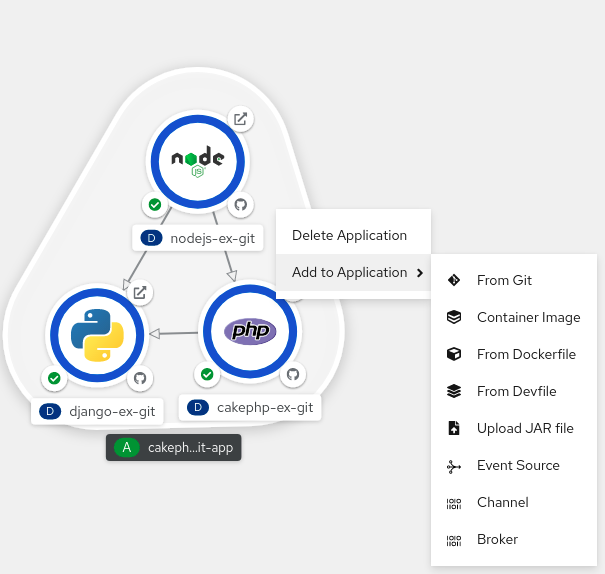
- Use Add to Application to select a method for adding a service to the application group, such as From Git, Container Image, From Dockerfile, From Devfile, Upload JAR file, Event Source, Channel, or Broker.
- Complete the form for the method you choose and click Create. For example, to add a service based on the source code in your Git repository, choose the From Git method, fill in the Import from Git form, and click Create.
4.8. Removing services from your application
In the topology Graph view remove a service from your application using the context menu.
Procedure
- Right-click on a service in an application group in the topology Graph view to display the context menu.
Select Delete Deployment to delete the service.
Figure 4.6. Deleting deployment option
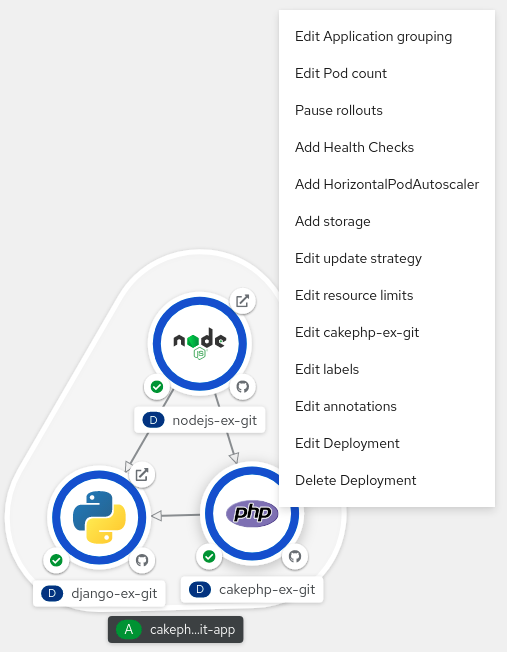
4.9. Labels and annotations used for the Topology view
The Topology view uses the following labels and annotations:
- Icon displayed in the node
-
Icons in the node are defined by looking for matching icons using the
app.openshift.io/runtimelabel, followed by theapp.kubernetes.io/namelabel. This matching is done using a predefined set of icons. - Link to the source code editor or the source
-
The
app.openshift.io/vcs-uriannotation is used to create links to the source code editor. - Node Connector
-
The
app.openshift.io/connects-toannotation is used to connect the nodes. - App grouping
-
The
app.kubernetes.io/part-of=<appname>label is used to group the applications, services, and components.
For detailed information on the labels and annotations OpenShift Dedicated applications must use, see Guidelines for labels and annotations for OpenShift applications.
4.10. Additional resources
- See Importing a codebase from Git to create an application for more information on creating an application from Git.
- See Connecting an application to a service using the Developer perspective.
Chapter 5. Connecting applications to services
5.1. Release notes for Service Binding Operator
The Service Binding Operator consists of a controller and an accompanying custom resource definition (CRD) for service binding. It manages the data plane for workloads and backing services. The Service Binding Controller reads the data made available by the control plane of backing services. Then, it projects this data to workloads according to the rules specified through the ServiceBinding resource.
With Service Binding Operator, you can:
- Bind your workloads together with Operator-managed backing services.
- Automate configuration of binding data.
- Provide service operators a low-touch administrative experience to provision and manage access to services.
- Enrich development lifecycle with a consistent and declarative service binding method that eliminates discrepancies in cluster environments.
The custom resource definition (CRD) of the Service Binding Operator supports the following APIs:
-
Service Binding with the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. -
Service Binding (Spec API) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group.
5.1.1. Support matrix
Some features in the following table are in Technology Preview. These experimental features are not intended for production use.
In the table, features are marked with the following statuses:
- TP: Technology Preview
- GA: General Availability
Note the following scope of support on the Red Hat Customer Portal for these features:
| Service Binding Operator | API Group and Support Status | OpenShift Versions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Version |
|
| |
| 1.3.3 | GA | GA | 4.9-4.12 |
| 1.3.1 | GA | GA | 4.9-4.11 |
| 1.3 | GA | GA | 4.9-4.11 |
| 1.2 | GA | GA | 4.7-4.11 |
| 1.1.1 | GA | TP | 4.7-4.10 |
| 1.1 | GA | TP | 4.7-4.10 |
| 1.0.1 | GA | TP | 4.7-4.9 |
| 1.0 | GA | TP | 4.7-4.9 |
5.1.2. Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code, documentation, and web properties. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Because of the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be implemented gradually over several upcoming releases. For more details, see Red Hat CTO Chris Wright’s message.
5.1.3. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.3.3
Service Binding Operator 1.3.3 is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.9, 4.10, 4.11 and 4.12.
5.1.3.1. Fixed issues
-
Before this update, a security vulnerability
CVE-2022-41717was noted for Service Binding Operator. This update fixes theCVE-2022-41717error and updates thegolang.org/x/netpackage from v0.0.0-20220906165146-f3363e06e74c to v0.4.0. APPSVC-1256 - Before this update, Provisioned Services were only detected if the respective resource had the "servicebinding.io/provisioned-service: true" annotation set while other Provisioned Services were missed. With this update, the detection mechanism identifies all Provisioned Services correctly based on the "status.binding.name" attribute. APPSVC-1204
5.1.4. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.3.1
Service Binding Operator 1.3.1 is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.9, 4.10, and 4.11.
5.1.4.1. Fixed issues
-
Before this update, a security vulnerability
CVE-2022-32149was noted for Service Binding Operator. This update fixes theCVE-2022-32149error and updates thegolang.org/x/textpackage from v0.3.7 to v0.3.8. APPSVC-1220
5.1.5. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.3
Service Binding Operator 1.3 is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.9, 4.10, and 4.11.
5.1.5.1. Removed functionality
- In Service Binding Operator 1.3, the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) descriptor feature has been removed to improve resource utilization. As an alternative to OLM descriptors, you can use CRD annotations to declare binding data.
5.1.6. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.2
Service Binding Operator 1.2 is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.7, 4.8, 4.9, 4.10, and 4.11.
5.1.6.1. New features
This section highlights what is new in Service Binding Operator 1.2:
-
Enable Service Binding Operator to consider optional fields in the annotations by setting the
optionalflag value totrue. -
Support for
servicebinding.io/v1beta1resources. - Improvements to the discoverability of bindable services by exposing the relevant binding secret without requiring a workload to be present.
5.1.6.2. Known issues
- Currently, when you install Service Binding Operator on OpenShift Dedicated 4.11, the memory footprint of Service Binding Operator increases beyond expected limits. With low usage, however, the memory footprint stays within the expected ranges of your environment or scenarios. In comparison with OpenShift Dedicated 4.10, under stress, both the average and maximum memory footprint increase considerably. This issue is evident in the previous versions of Service Binding Operator as well. There is currently no workaround for this issue. APPSVC-1200
-
By default, the projected files get their permissions set to 0644. Service Binding Operator cannot set specific permissions due to a bug in Kubernetes that causes issues if the service expects specific permissions such as,
0600. As a workaround, you can modify the code of the program or the application that is running inside a workload resource to copy the file to the/tmpdirectory and set the appropriate permissions. APPSVC-1127 There is currently a known issue with installing Service Binding Operator in a single namespace installation mode. The absence of an appropriate namespace-scoped role-based access control (RBAC) rule prevents the successful binding of an application to a few known Operator-backed services that the Service Binding Operator can automatically detect and bind to. When this happens, it generates an error message similar to the following example:
Example error message
`postgresclusters.postgres-operator.crunchydata.com "hippo" is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:my-petclinic:service-binding-operator" cannot get resource "postgresclusters" in API group "postgres-operator.crunchydata.com" in the namespace "my-petclinic"`Workaround 1: Install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode. As a result, the appropriate cluster-scoped RBAC rule now exists and the binding succeeds.Workaround 2: If you cannot install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode, install the following role binding into the namespace where the Service Binding Operator is installed:Example: Role binding for Crunchy Postgres Operator
kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: service-binding-operator roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer-roleAccording to the specification, when you change the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources, Service Binding Operator must use the previous version of theClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource to remove the binding data that was being projected until now. Currently, when you change theClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources, the Service Binding Operator uses the latest version of theClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource to remove the binding data. As a result, {the servicebinding-title} might remove the binding data incorrectly. As a workaround, perform the following steps:-
Delete any
ServiceBindingresources that use the correspondingClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. -
Modify the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. -
Re-apply the
ServiceBindingresources that you previously removed in step 1.
-
Delete any
5.1.7. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.1.1
Service Binding Operator 1.1.1 is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.7, 4.8, 4.9, and 4.10.
5.1.7.1. Fixed issues
-
Before this update, a security vulnerability
CVE-2021-38561was noted for Service Binding Operator Helm chart. This update fixes theCVE-2021-38561error and updates thegolang.org/x/textpackage from v0.3.6 to v0.3.7. APPSVC-1124 -
Before this update, users of the Developer Sandbox did not have sufficient permissions to read
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources. As a result, Service Binding Operator prevented all service bindings from being successful. With this update, the Service Binding Operator now includes the appropriate role-based access control (RBAC) rules for any authenticated subject including the Developer Sandbox users. These RBAC rules allow the Service Binding Operator toget,list, andwatchtheClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources for the Developer Sandbox users and to process service bindings successfully. APPSVC-1135
5.1.7.2. Known issues
There is currently a known issue with installing Service Binding Operator in a single namespace installation mode. The absence of an appropriate namespace-scoped role-based access control (RBAC) rule prevents the successful binding of an application to a few known Operator-backed services that the Service Binding Operator can automatically detect and bind to. When this happens, it generates an error message similar to the following example:
Example error message
`postgresclusters.postgres-operator.crunchydata.com "hippo" is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:my-petclinic:service-binding-operator" cannot get resource "postgresclusters" in API group "postgres-operator.crunchydata.com" in the namespace "my-petclinic"`Workaround 1: Install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode. As a result, the appropriate cluster-scoped RBAC rule now exists and the binding succeeds.Workaround 2: If you cannot install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode, install the following role binding into the namespace where the Service Binding Operator is installed:Example: Role binding for Crunchy Postgres Operator
kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: service-binding-operator roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer-roleCurrently, when you modify the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources, the Service Binding Operator does not implement correct behavior. As a workaround, perform the following steps:-
Delete any
ServiceBindingresources that use the correspondingClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. -
Modify the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. -
Re-apply the
ServiceBindingresources that you previously removed in step 1.
-
Delete any
5.1.8. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.1
Service Binding Operator is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.7, 4.8, 4.9, and 4.10.
5.1.8.1. New features
This section highlights what is new in Service Binding Operator 1.1:
Service Binding Options
- Workload resource mapping: Define exactly where binding data needs to be projected for the secondary workloads.
- Bind new workloads using a label selector.
5.1.8.2. Fixed issues
- Before this update, service bindings that used label selectors to pick up workloads did not project service binding data into the new workloads that matched the given label selectors. As a result, the Service Binding Operator could not periodically bind such new workloads. With this update, service bindings now project service binding data into the new workloads that match the given label selector. The Service Binding Operator now periodically attempts to find and bind such new workloads. APPSVC-1083
5.1.8.3. Known issues
There is currently a known issue with installing Service Binding Operator in a single namespace installation mode. The absence of an appropriate namespace-scoped role-based access control (RBAC) rule prevents the successful binding of an application to a few known Operator-backed services that the Service Binding Operator can automatically detect and bind to. When this happens, it generates an error message similar to the following example:
Example error message
`postgresclusters.postgres-operator.crunchydata.com "hippo" is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:my-petclinic:service-binding-operator" cannot get resource "postgresclusters" in API group "postgres-operator.crunchydata.com" in the namespace "my-petclinic"`Workaround 1: Install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode. As a result, the appropriate cluster-scoped RBAC rule now exists and the binding succeeds.Workaround 2: If you cannot install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode, install the following role binding into the namespace where the Service Binding Operator is installed:Example: Role binding for Crunchy Postgres Operator
kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: service-binding-operator roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer-roleCurrently, when you modify the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources, the Service Binding Operator does not implement correct behavior. As a workaround, perform the following steps:-
Delete any
ServiceBindingresources that use the correspondingClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. -
Modify the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. -
Re-apply the
ServiceBindingresources that you previously removed in step 1.
-
Delete any
5.1.9. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.0.1
Service Binding Operator is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.7, 4.8 and 4.9.
Service Binding Operator 1.0.1 supports OpenShift Container Platform 4.9 and later running on:
- IBM Power Systems
- IBM Z and LinuxONE
The custom resource definition (CRD) of the Service Binding Operator 1.0.1 supports the following APIs:
-
Service Binding with the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. Service Binding (Spec API Tech Preview) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group.ImportantService Binding (Spec API Tech Preview) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
5.1.9.1. Support matrix
Some features in this release are currently in Technology Preview. These experimental features are not intended for production use.
Technology Preview Features Support Scope
In the table below, features are marked with the following statuses:
- TP: Technology Preview
- GA: General Availability
Note the following scope of support on the Red Hat Customer Portal for these features:
| Feature | Service Binding Operator 1.0.1 |
|---|---|
|
| GA |
|
| TP |
5.1.9.2. Fixed issues
-
Before this update, binding the data values from a
Clustercustom resource (CR) of thepostgresql.k8s.enterpriesedb.io/v1API collected thehostbinding value from the.metadata.namefield of the CR. The collected binding value is an incorrect hostname and the correct hostname is available at the.status.writeServicefield. With this update, the annotations that the Service Binding Operator uses to expose the binding data values from the backing service CR are now modified to collect thehostbinding value from the.status.writeServicefield. The Service Binding Operator uses these modified annotations to project the correct hostname in thehostandproviderbindings. APPSVC-1040 -
Before this update, when you would bind a
PostgresClusterCR of thepostgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1API, the binding data values did not include the values for the database certificates. As a result, the application failed to connect to the database. With this update, modifications to the annotations that the Service Binding Operator uses to expose the binding data from the backing service CR now include the database certificates. The Service Binding Operator uses these modified annotations to project the correctca.crt,tls.crt, andtls.keycertificate files. APPSVC-1045 -
Before this update, when you would bind a
PerconaXtraDBClustercustom resource (CR) of thepxc.percona.comAPI, the binding data values did not include theportanddatabasevalues. These binding values along with the others already projected are necessary for an application to successfully connect to the database service. With this update, the annotations that the Service Binding Operator uses to expose the binding data values from the backing service CR are now modified to project the additionalportanddatabasebinding values. The Service Binding Operator uses these modified annotations to project the complete set of binding values that the application can use to successfully connect to the database service. APPSVC-1073
5.1.9.3. Known issues
Currently, when you install the Service Binding Operator in the single namespace installation mode, the absence of an appropriate namespace-scoped role-based access control (RBAC) rule prevents the successful binding of an application to a few known Operator-backed services that the Service Binding Operator can automatically detect and bind to. In addition, the following error message is generated:
Example error message
`postgresclusters.postgres-operator.crunchydata.com "hippo" is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:my-petclinic:service-binding-operator" cannot get resource "postgresclusters" in API group "postgres-operator.crunchydata.com" in the namespace "my-petclinic"`Workaround 1: Install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode. As a result, the appropriate cluster-scoped RBAC rule now exists and the binding succeeds.Workaround 2: If you cannot install the Service Binding Operator in the
all namespacesinstallation mode, install the following role binding into the namespace where the Service Binding Operator is installed:Example: Role binding for Crunchy Postgres Operator
kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: service-binding-operator roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: service-binding-crunchy-postgres-viewer-role
5.1.10. Release notes for Service Binding Operator 1.0
Service Binding Operator is now available on OpenShift Dedicated 4.7, 4.8 and 4.9.
The custom resource definition (CRD) of the Service Binding Operator 1.0 supports the following APIs:
-
Service Binding with the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. Service Binding (Spec API Tech Preview) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group.ImportantService Binding (Spec API Tech Preview) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see Technology Preview Features Support Scope.
5.1.10.1. Support matrix
Some features in this release are currently in Technology Preview. These experimental features are not intended for production use.
Technology Preview Features Support Scope
In the table below, features are marked with the following statuses:
- TP: Technology Preview
- GA: General Availability
Note the following scope of support on the Red Hat Customer Portal for these features:
| Feature | Service Binding Operator 1.0 |
|---|---|
|
| GA |
|
| TP |
5.1.10.2. New features
Service Binding Operator 1.0 supports OpenShift Container Platform 4.9 and later running on:
- IBM Power Systems
- IBM Z and LinuxONE
This section highlights what is new in Service Binding Operator 1.0:
Exposal of binding data from services
- Based on annotations present in CRD, custom resources (CRs), or resources.
- Based on descriptors present in Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) descriptors.
- Support for provisioned services
Workload projection
- Projection of binding data as files, with volume mounts.
- Projection of binding data as environment variables.
Service Binding Options
- Bind backing services in a namespace that is different from the workload namespace.
- Project binding data into the specific container workloads.
- Auto-detection of the binding data from resources owned by the backing service CR.
- Compose custom binding data from the exposed binding data.
-
Support for non-
PodSpeccompliant workload resources.
Security
- Support for role-based access control (RBAC).
5.1.11. Additional resources
5.2. Understanding Service Binding Operator
Application developers need access to backing services to build and connect workloads. Connecting workloads to backing services is always a challenge because each service provider suggests a different way to access their secrets and consume them in a workload. In addition, manual configuration and maintenance of this binding together of workloads and backing services make the process tedious, inefficient, and error-prone.
The Service Binding Operator enables application developers to easily bind workloads together with Operator-managed backing services, without any manual procedures to configure the binding connection.
5.2.1. Service Binding terminology
This section summarizes the basic terms used in Service Binding.
| Service binding | The representation of the action of providing information about a service to a workload. Examples include establishing the exchange of credentials between a Java application and a database that it requires. |
| Backing service | Any service or software that the application consumes over the network as part of its normal operation. Examples include a database, a message broker, an application with REST endpoints, an event stream, an Application Performance Monitor (APM), or a Hardware Security Module (HSM). |
| Workload (application) | Any process running within a container. Examples include a Spring Boot application, a NodeJS Express application, or a Ruby on Rails application. |
| Binding data | Information about a service that you use to configure the behavior of other resources within the cluster. Examples include credentials, connection details, volume mounts, or secrets. |
| Binding connection | Any connection that establishes an interaction between the connected components, such as a bindable backing service and an application requiring that backing service. |
5.2.2. About Service Binding Operator
The Service Binding Operator consists of a controller and an accompanying custom resource definition (CRD) for service binding. It manages the data plane for workloads and backing services. The Service Binding Controller reads the data made available by the control plane of backing services. Then, it projects this data to workloads according to the rules specified through the ServiceBinding resource.
As a result, the Service Binding Operator enables workloads to use backing services or external services by automatically collecting and sharing binding data with the workloads. The process involves making the backing service bindable and binding the workload and the service together.
5.2.2.1. Making an Operator-managed backing service bindable
To make a service bindable, as an Operator provider, you need to expose the binding data required by workloads to bind with the services provided by the Operator. You can provide the binding data either as annotations or as descriptors in the CRD of the Operator that manages the backing service.
5.2.2.2. Binding a workload together with a backing service
By using the Service Binding Operator, as an application developer, you need to declare the intent of establishing a binding connection. You must create a ServiceBinding CR that references the backing service. This action triggers the Service Binding Operator to project the exposed binding data into the workload. The Service Binding Operator receives the declared intent and binds the workload together with the backing service.
The CRD of the Service Binding Operator supports the following APIs:
-
Service Binding with the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. -
Service Binding (Spec API) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group.
With Service Binding Operator, you can:
- Bind your workloads to Operator-managed backing services.
- Automate configuration of binding data.
- Provide service operators with a low-touch administrative experience to provision and manage access to services.
- Enrich the development lifecycle with a consistent and declarative service binding method that eliminates discrepancies in cluster environments.
5.2.3. Key features
Exposal of binding data from services
- Based on annotations present in CRD, custom resources (CRs), or resources.
Workload projection
- Projection of binding data as files, with volume mounts.
- Projection of binding data as environment variables.
Service Binding Options
- Bind backing services in a namespace that is different from the workload namespace.
- Project binding data into the specific container workloads.
- Auto-detection of the binding data from resources owned by the backing service CR.
- Compose custom binding data from the exposed binding data.
-
Support for non-
PodSpeccompliant workload resources.
Security
- Support for role-based access control (RBAC).
5.2.4. API differences
The CRD of the Service Binding Operator supports the following APIs:
-
Service Binding with the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. -
Service Binding (Spec API) with the
servicebinding.ioAPI group.
Both of these API groups have similar features, but they are not completely identical. Here is the complete list of differences between these API groups:
| Feature | Supported by the binding.operators.coreos.com API group | Supported by the servicebinding.io API group | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binding to provisioned services | Yes | Yes | Not applicable (N/A) |
| Direct secret projection | Yes | Yes | Not applicable (N/A) |
| Bind as files | Yes | Yes |
|
| Bind as environment variables | Yes | Yes |
|
| Selecting workload with a label selector | Yes | Yes | Not applicable (N/A) |
|
Detecting binding resources ( | Yes | No |
The |
| Naming strategies | Yes | No |
There is no current mechanism within the |
| Container path | Yes | Partial |
Because a service binding of the |
| Container name filtering | No | Yes |
The |
| Secret path | Yes | No |
The |
| Alternative binding sources (for example, binding data from annotations) | Yes | Allowed by Service Binding Operator | The specification requires support for getting binding data from provisioned services and secrets. However, a strict reading of the specification suggests that support for other binding data sources is allowed. Using this fact, Service Binding Operator can pull the binding data from various sources (for example, pulling binding data from annotations). Service Binding Operator supports these sources on both the API groups. |
5.2.5. Additional resources
5.3. Installing Service Binding Operator
This guide walks cluster administrators through the process of installing the Service Binding Operator to an OpenShift Dedicated cluster.
You can install Service Binding Operator on OpenShift Dedicated 4.7 and later.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to an OpenShift Dedicated cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions.
5.3.1. Installing the Service Binding Operator using the web console
You can install Service Binding Operator using the OpenShift Dedicated OperatorHub. When you install the Service Binding Operator, the custom resources (CRs) required for the service binding configuration are automatically installed along with the Operator.
Procedure
- In the Administrator perspective of the web console, navigate to Operators → OperatorHub.
-
Use the Filter by keyword box to search for
Service Binding Operatorin the catalog. Click the Service Binding Operator tile. - Read the brief description about the Operator on the Service Binding Operator page. Click Install.
On the Install Operator page:
-
Select All namespaces on the cluster (default) for the Installation Mode. This mode installs the Operator in the default
openshift-operatorsnamespace, which enables the Operator to watch and be made available to all namespaces in the cluster. - Select Automatic for the Approval Strategy. This ensures that the future upgrades to the Operator are handled automatically by the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM). If you select the Manual approval strategy, OLM creates an update request. As a cluster administrator, you must then manually approve the OLM update request to update the Operator to the new version.
Select an Update Channel.
- By default, the stable channel enables installation of the latest stable and supported release of the Service Binding Operator.
-
Select All namespaces on the cluster (default) for the Installation Mode. This mode installs the Operator in the default
Click Install.
NoteThe Operator is installed automatically into the
openshift-operatorsnamespace.- On the Installed Operator — ready for use pane, click View Operator. You will see the Operator listed on the Installed Operators page.
- Verify that the Status is set to Succeeded to confirm successful installation of Service Binding Operator.
5.3.2. Additional Resources
5.4. Getting started with service binding
The Service Binding Operator manages the data plane for workloads and backing services. This guide provides instructions with examples to help you create a database instance, deploy an application, and use the Service Binding Operator to create a binding connection between the application and the database service.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to an OpenShift Dedicated cluster using an account with
dedicated-adminpermissions. -
You have installed the
ocCLI. - You have installed Service Binding Operator from OperatorHub.
5.4.1. Creating a PostgreSQL database instance
To create a PostgreSQL database instance, you must create a PostgresCluster custom resource (CR) and configure the database.
Procedure
Create the
PostgresClusterCR in themy-petclinicnamespace by running the following command in shell:$ oc apply -n my-petclinic -f - << EOD --- apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1 kind: PostgresCluster metadata: name: hippo spec: image: registry.developers.crunchydata.com/crunchydata/crunchy-postgres:ubi8-14.4-0 postgresVersion: 14 instances: - name: instance1 dataVolumeClaimSpec: accessModes: - "ReadWriteOnce" resources: requests: storage: 1Gi backups: pgbackrest: image: registry.developers.crunchydata.com/crunchydata/crunchy-pgbackrest:ubi8-2.38-0 repos: - name: repo1 volume: volumeClaimSpec: accessModes: - "ReadWriteOnce" resources: requests: storage: 1Gi EODThe annotations added in this
PostgresClusterCR enable the service binding connection and trigger the Operator reconciliation.The output verifies that the database instance is created:
Example output
postgrescluster.postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/hippo created
After you have created the database instance, ensure that all the pods in the
my-petclinicnamespace are running:$ oc get pods -n my-petclinic
The output, which takes a few minutes to display, verifies that the database is created and configured:
Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE hippo-backup-9rxm-88rzq 0/1 Completed 0 2m2s hippo-instance1-6psd-0 4/4 Running 0 3m28s hippo-repo-host-0 2/2 Running 0 3m28s
After the database is configured, you can deploy the sample application and connect it to the database service.
5.4.2. Deploying the Spring PetClinic sample application
To deploy the Spring PetClinic sample application on an OpenShift Dedicated cluster, you must use a deployment configuration and configure your local environment to be able to test the application.
Procedure
Deploy the
spring-petclinicapplication with thePostgresClustercustom resource (CR) by running the following command in shell:$ oc apply -n my-petclinic -f - << EOD --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: spring-petclinic labels: app: spring-petclinic spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: spring-petclinic template: metadata: labels: app: spring-petclinic spec: containers: - name: app image: quay.io/service-binding/spring-petclinic:latest imagePullPolicy: Always env: - name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE value: postgres ports: - name: http containerPort: 8080 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: spring-petclinic name: spring-petclinic spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 selector: app: spring-petclinic EODThe output verifies that the Spring PetClinic sample application is created and deployed:
Example output
deployment.apps/spring-petclinic created service/spring-petclinic created
NoteIf you are deploying the application using Container images in the Developer perspective of the web console, you must enter the following environment variables under the Deployment section of the Advanced options:
- Name: SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE
- Value: postgres
Verify that the application is not yet connected to the database service by running the following command:
$ oc get pods -n my-petclinic
The output takes a few minutes to display the
CrashLoopBackOffstatus:Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE spring-petclinic-5b4c7999d4-wzdtz 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 4 (13s ago) 2m25s
At this stage, the pod fails to start. If you try to interact with the application, it returns errors.
Expose the service to create a route for your application:
$ oc expose service spring-petclinic -n my-petclinic
The output verifies that the
spring-petclinicservice is exposed and a route for the Spring PetClinic sample application is created:Example output
route.route.openshift.io/spring-petclinic exposed
You can now use the Service Binding Operator to connect the application to the database service.
5.4.3. Connecting the Spring PetClinic sample application to the PostgreSQL database service
To connect the sample application to the database service, you must create a ServiceBinding custom resource (CR) that triggers the Service Binding Operator to project the binding data into the application.
Procedure
Create a
ServiceBindingCR to project the binding data:$ oc apply -n my-petclinic -f - << EOD --- apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: ServiceBinding metadata: name: spring-petclinic-pgcluster spec: services: 1 - group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com version: v1beta1 kind: PostgresCluster 2 name: hippo application: 3 name: spring-petclinic group: apps version: v1 resource: deployments EOD
The output verifies that the
ServiceBindingCR is created to project the binding data into the sample application.Example output
servicebinding.binding.operators.coreos.com/spring-petclinic created
Verify that the request for service binding is successful:
$ oc get servicebindings -n my-petclinic
Example output
NAME READY REASON AGE spring-petclinic-pgcluster True ApplicationsBound 7s
By default, the values from the binding data of the database service are projected as files into the workload container that runs the sample application. For example, all the values from the Secret resource are projected into the
bindings/spring-petclinic-pgclusterdirectory.NoteOptionally, you can also verify that the files in the application contain the projected binding data, by printing out the directory contents:
$ for i in username password host port type; do oc exec -it deploy/spring-petclinic -n my-petclinic -- /bin/bash -c 'cd /tmp; find /bindings/*/'$i' -exec echo -n {}:" " \; -exec cat {} \;'; echo; doneExample output: With all the values from the secret resource
/bindings/spring-petclinic-pgcluster/username: <username> /bindings/spring-petclinic-pgcluster/password: <password> /bindings/spring-petclinic-pgcluster/host: hippo-primary.my-petclinic.svc /bindings/spring-petclinic-pgcluster/port: 5432 /bindings/spring-petclinic-pgcluster/type: postgresql
Set up the port forwarding from the application port to access the sample application from your local environment:
$ oc port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 svc/spring-petclinic 8080:80 -n my-petclinic
Example output
Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:8080 -> 8080 Handling connection for 8080
Access http://localhost:8080/petclinic.
You can now remotely access the Spring PetClinic sample application at localhost:8080 and see that the application is now connected to the database service.
5.4.4. Additional Resources
5.5. Exposing binding data from a service
Application developers need access to backing services to build and connect workloads. Connecting workloads to backing services is always a challenge because each service provider requires a different way to access their secrets and consume them in a workload.
The Service Binding Operator enables application developers to easily bind workloads together with operator-managed backing services, without any manual procedures to configure the binding connection. For the Service Binding Operator to provide the binding data, as an Operator provider or user who creates backing services, you must expose the binding data to be automatically detected by the Service Binding Operator. Then, the Service Binding Operator automatically collects the binding data from the backing service and shares it with a workload to provide a consistent and predictable experience.
5.5.1. Methods of exposing binding data
This section describes the methods you can use to expose the binding data.
Ensure that you know and understand your workload requirements and environment, and how it works with the provided services.
Binding data is exposed under the following circumstances:
Backing service is available as a provisioned service resource.
The service you intend to connect to is compliant with the Service Binding specification. You must create a
Secretresource with all the required binding data values and reference it in the backing service custom resource (CR). The detection of all the binding data values is automatic.Backing service is not available as a provisioned service resource.
You must expose the binding data from the backing service. Depending on your workload requirements and environment, you can choose any of the following methods to expose the binding data:
- Direct secret reference
- Declaring binding data through custom resource definition (CRD) or CR annotations
- Detection of binding data through owned resources
5.5.1.1. Provisioned service
Provisioned service represents a backing service CR with a reference to a Secret resource placed in the .status.binding.name field of the backing service CR.
As an Operator provider or the user who creates backing services, you can use this method to be compliant with the Service Binding specification, by creating a Secret resource and referencing it in the .status.binding.name section of the backing service CR. This Secret resource must provide all the binding data values required for a workload to connect to the backing service.
The following examples show an AccountService CR that represents a backing service and a Secret resource referenced from the CR.
Example: AccountService CR
apiVersion: example.com/v1alpha1
kind: AccountService
name: prod-account-service
spec:
...
status:
binding:
name: hippo-pguser-hippo
Example: Referenced Secret resource
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: hippo-pguser-hippo data: password: "<password>" user: "<username>" ...
When creating a service binding resource, you can directly give the details of the AccountService resource in the ServiceBinding specification as follows:
Example: ServiceBinding resource
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: account-service
spec:
...
services:
- group: "example.com"
version: v1alpha1
kind: AccountService
name: prod-account-service
application:
name: spring-petclinic
group: apps
version: v1
resource: deployments
Example: ServiceBinding resource in Specification API
apiVersion: servicebinding.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: account-service
spec:
...
service:
apiVersion: example.com/v1alpha1
kind: AccountService
name: prod-account-service
workload:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: spring-petclinic
This method exposes all the keys in the hippo-pguser-hippo referenced Secret resource as binding data that is to be projected into the workload.
5.5.1.2. Direct secret reference
You can use this method, if all the required binding data values are available in a Secret resource that you can reference in your Service Binding definition. In this method, a ServiceBinding resource directly references a Secret resource to connect to a service. All the keys in the Secret resource are exposed as binding data.
Example: Specification with the binding.operators.coreos.com API
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: account-service
spec:
...
services:
- group: ""
version: v1
kind: Secret
name: hippo-pguser-hippo
Example: Specification that is compliant with the servicebinding.io API
apiVersion: servicebinding.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: account-service
spec:
...
service:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
name: hippo-pguser-hippo
5.5.1.3. Declaring binding data through CRD or CR annotations
You can use this method to annotate the resources of the backing service to expose the binding data with specific annotations. Adding annotations under the metadata section alters the CRs and CRDs of the backing services. Service Binding Operator detects the annotations added to the CRs and CRDs and then creates a Secret resource with the values extracted based on the annotations.
The following examples show the annotations that are added under the metadata section and a referenced ConfigMap object from a resource:
Example: Exposing binding data from a Secret object defined in the CR annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
service.binding: 'path={.metadata.name}-pguser-{.metadata.name},objectType=Secret'
...
The previous example places the name of the secret name in the {.metadata.name}-pguser-{.metadata.name} template that resolves to hippo-pguser-hippo. The template can contain multiple JSONPath expressions.
Example: Referenced Secret object from a resource
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: hippo-pguser-hippo data: password: "<password>" user: "<username>"
Example: Exposing binding data from a ConfigMap object defined in the CR annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
service.binding: 'path={.metadata.name}-config,objectType=ConfigMap'
...
The previous example places the name of the config map in the {.metadata.name}-config template that resolves to hippo-config. The template can contain multiple JSONPath expressions.
Example: Referenced ConfigMap object from a resource
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: hippo-config data: db_timeout: "10s" user: "hippo"
5.5.1.4. Detection of binding data through owned resources
You can use this method if your backing service owns one or more Kubernetes resources such as route, service, config map, or secret that you can use to detect the binding data. In this method, the Service Binding Operator detects the binding data from resources owned by the backing service CR.
The following examples show the detectBindingResources API option set to true in the ServiceBinding CR:
Example
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: spring-petclinic-detect-all
namespace: my-petclinic
spec:
detectBindingResources: true
services:
- group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com
version: v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
name: hippo
application:
name: spring-petclinic
group: apps
version: v1
resource: deployments
In the previous example, PostgresCluster custom service resource owns one or more Kubernetes resources such as route, service, config map, or secret.
The Service Binding Operator automatically detects the binding data exposed on each of the owned resources.
5.5.2. Data model
The data model used in the annotations follows specific conventions.
Service binding annotations must use the following convention:
service.binding(/<NAME>)?:
"<VALUE>|(path=<JSONPATH_TEMPLATE>(,objectType=<OBJECT_TYPE>)?(,elementType=<ELEMENT_TYPE>)?(,sourceKey=<SOURCE_KEY>)?(,sourceValue=<SOURCE_VALUE>)?)"where:
|
|
Specifies the name under which the binding value is to be exposed. You can exclude it only when the |
|
|
Specifies the constant value exposed when no |
The data model provides the details on the allowed values and semantic for the path, elementType, objectType, sourceKey, and sourceValue parameters.
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
|
| JSONPath template that consists JSONPath expressions enclosed by curly braces {}. | N/A |
|
|
Specifies whether the value of the element referenced in the
|
|
|
|
Specifies whether the value of the element indicated in the |
|
|
|
Specifies the key in the Note:
| N/A |
|
|
Specifies the key in the slice of maps. Note:
| N/A |
The sourceKey and sourceValue parameters are applicable only if the element indicated in the path parameter refers to a ConfigMap or Secret resource.
5.5.3. Setting annotations mapping to be optional
You can have optional fields in the annotations. For example, a path to the credentials might not be present if the service endpoint does not require authentication. In such cases, a field might not exist in the target path of the annotations. As a result, Service Binding Operator generates an error, by default.
As a service provider, to indicate whether you require annotations mapping, you can set a value for the optional flag in your annotations when enabling services. Service Binding Operator provides annotations mapping only if the target path is available. When the target path is not available, the Service Binding Operator skips the optional mapping and continues with the projection of the existing mappings without throwing any errors.
Procedure
To make a field in the annotations optional, set the
optionalflag value totrue:Example
apiVersion: apps.example.org/v1beta1 kind: Database metadata: name: my-db namespace: my-petclinic annotations: service.binding/username: path={.spec.name},optional=true ...
-
If you set the
optionalflag value tofalseand the Service Binding Operator is unable to find the target path, the Operator fails the annotations mapping. -
If the
optionalflag has no value set, the Service Binding Operator considers the value asfalseby default and fails the annotations mapping.
5.5.4. RBAC requirements
To expose the backing service binding data using the Service Binding Operator, you require certain Role-based access control (RBAC) permissions. Specify certain verbs under the rules field of the ClusterRole resource to grant the RBAC permissions for the backing service resources. When you define these rules, you allow the Service Binding Operator to read the binding data of the backing service resources throughout the cluster. If the users do not have permissions to read binding data or modify application resource, the Service Binding Operator prevents such users to bind services to application. Adhering to the RBAC requirements avoids unnecessary permission elevation for the user and prevents access to unauthorized services or applications.
The Service Binding Operator performs requests against the Kubernetes API using a dedicated service account. By default, this account has permissions to bind services to workloads, both represented by the following standard Kubernetes or OpenShift objects:
-
Deployments -
DaemonSets -
ReplicaSets -
StatefulSets -
DeploymentConfigs
The Operator service account is bound to an aggregated cluster role, allowing Operator providers or cluster administrators to enable binding custom service resources to workloads. To grant the required permissions within a ClusterRole, label it with the servicebinding.io/controller flag and set the flag value to true. The following example shows how to allow the Service Binding Operator to get, watch, and list the custom resources (CRs) of Crunchy PostgreSQL Operator:
Example: Enable binding to PostgreSQL database instances provisioned by Crunchy PostgreSQL Operator
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: postgrescluster-reader
labels:
servicebinding.io/controller: "true"
rules:
- apiGroups:
- postgres-operator.crunchydata.com
resources:
- postgresclusters
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
...
This cluster role can be deployed during the installation of the backing service Operator.
5.5.5. Categories of exposable binding data
The Service Binding Operator enables you to expose the binding data values from the backing service resources and custom resource definitions (CRDs).
This section provides examples to show how you can use the various categories of exposable binding data. You must modify these examples to suit your work environment and requirements.
5.5.5.1. Exposing a string from a resource
The following example shows how to expose the string from the metadata.name field of the PostgresCluster custom resource (CR) as a username:
Example
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
service.binding/username: path={.metadata.name}
...
5.5.5.2. Exposing a constant value as the binding item
The following examples show how to expose a constant value from the PostgresCluster custom resource (CR):
Example: Exposing a constant value
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
"service.binding/type": "postgresql" 1
- 1
- Binding
typeto be exposed with thepostgresqlvalue.
5.5.5.3. Exposing an entire config map or secret that is referenced from a resource
The following examples show how to expose an entire secret through annotations:
Example: Exposing an entire secret through annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
service.binding: 'path={.metadata.name}-pguser-{.metadata.name},objectType=Secret'
Example: The referenced secret from the backing service resource
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: hippo-pguser-hippo data: password: "<password>" user: "<username>"
5.5.5.4. Exposing a specific entry from a config map or secret that is referenced from a resource
The following examples show how to expose a specific entry from a config map through annotations:
Example: Exposing an entry from a config map through annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
service.binding: 'path={.metadata.name}-config,objectType=ConfigMap,sourceKey=user'
Example: The referenced config map from the backing service resource
The binding data should have a key with name as db_timeout and value as 10s:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: hippo-config data: db_timeout: "10s" user: "hippo"
5.5.5.5. Exposing a resource definition value
The following example shows how to expose a resource definition value through annotations:
Example: Exposing a resource definition value through annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
service.binding/username: path={.metadata.name}
...
5.5.5.6. Exposing entries of a collection with the key and value from each entry
The following example shows how to expose the entries of a collection with the key and value from each entry through annotations:
Example: Exposing the entries of a collection through annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
"service.binding/uri": "path={.status.connections},elementType=sliceOfMaps,sourceKey=type,sourceValue=url"
spec:
...
status:
connections:
- type: primary
url: primary.example.com
- type: secondary
url: secondary.example.com
- type: '404'
url: black-hole.example.com
The following example shows how the previous entries of a collection in annotations are projected into the bound application.
Example: Binding data files
/bindings/<binding-name>/uri_primary => primary.example.com /bindings/<binding-name>/uri_secondary => secondary.example.com /bindings/<binding-name>/uri_404 => black-hole.example.com
Example: Configuration from a backing service resource
status:
connections:
- type: primary
url: primary.example.com
- type: secondary
url: secondary.example.com
- type: '404'
url: black-hole.example.com
The previous example helps you to project all those values with keys such as primary, secondary, and so on.
5.5.5.7. Exposing items of a collection with one key per item
The following example shows how to expose the items of a collection with one key per item through annotations:
Example: Exposing the items of a collection through annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
"service.binding/tags": "path={.spec.tags},elementType=sliceOfStrings"
spec:
tags:
- knowledge
- is
- power
The following example shows how the previous items of a collection in annotations are projected into the bound application.
Example: Binding data files
/bindings/<binding-name>/tags_0 => knowledge /bindings/<binding-name>/tags_1 => is /bindings/<binding-name>/tags_2 => power
Example: Configuration from a backing service resource
spec: tags: - knowledge - is - power
5.5.5.8. Exposing values of collection entries with one key per entry value
The following example shows how to expose the values of collection entries with one key per entry value through annotations:
Example: Exposing the values of collection entries through annotations
apiVersion: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
metadata:
name: hippo
namespace: my-petclinic
annotations:
"service.binding/url": "path={.spec.connections},elementType=sliceOfStrings,sourceValue=url"
spec:
connections:
- type: primary
url: primary.example.com
- type: secondary
url: secondary.example.com
- type: '404'
url: black-hole.example.com
The following example shows how the previous values of a collection in annotations are projected into the bound application.
Example: Binding data files
/bindings/<binding-name>/url_0 => primary.example.com /bindings/<binding-name>/url_1 => secondary.example.com /bindings/<binding-name>/url_2 => black-hole.example.com
5.5.6. Additional resources
5.6. Projecting binding data
This section provides information on how you can consume the binding data.
5.6.1. Consumption of binding data
After the backing service exposes the binding data, for a workload to access and consume this data, you must project it into the workload from a backing service. Service Binding Operator automatically projects this set of data into the workload in the following methods:
- By default, as files.
-
As environment variables, after you configure the
.spec.bindAsFilesparameter from theServiceBindingresource.
5.6.2. Configuration of the directory path to project the binding data inside workload container
By default, Service Binding Operator mounts the binding data as files at a specific directory in your workload resource. You can configure the directory path using the SERVICE_BINDING_ROOT environment variable setup in the container where your workload runs.
Example: Binding data mounted as files
$SERVICE_BINDING_ROOT 1 ├── account-database 2 │ ├── type 3 │ ├── provider 4 │ ├── uri │ ├── username │ └── password └── transaction-event-stream 5 ├── type ├── connection-count ├── uri ├── certificates └── private-key
- 1
- Root directory.
- 2 5
- Directory that stores the binding data.
- 3
- Mandatory identifier that identifies the type of the binding data projected into the corresponding directory.
- 4
- Optional: Identifier to identify the provider so that the application can identify the type of backing service it can connect to.
To consume the binding data as environment variables, use the built-in language feature of your programming language of choice that can read environment variables.
Example: Python client usage
import os
username = os.getenv("USERNAME")
password = os.getenv("PASSWORD")
For using the binding data directory name to look up the binding data
Service Binding Operator uses the ServiceBinding resource name (.metadata.name) as the binding data directory name. The spec also provides a way to override that name through the .spec.name field. As a result, there is a chance for binding data name collision if there are multiple ServiceBinding resources in the namespace. However, due to the nature of the volume mount in Kubernetes, the binding data directory will contain values from only one of the Secret resources.
5.6.2.1. Computation of the final path for projecting the binding data as files
The following table summarizes the configuration of how the final path for the binding data projection is computed when files are mounted at a specific directory:
SERVICE_BINDING_ROOT | Final path |
|---|---|
| Not available |
|
|
|
|
In the previous table, the <ServiceBinding_ResourceName> entry specifies the name of the ServiceBinding resource that you configure in the .metadata.name section of the custom resource (CR).
By default, the projected files get their permissions set to 0644. Service Binding Operator cannot set specific permissions due to a bug in Kubernetes that causes issues if the service expects specific permissions such as 0600. As a workaround, you can modify the code of the program or the application that is running inside a workload resource to copy the file to the /tmp directory and set the appropriate permissions.
To access and consume the binding data within the existing SERVICE_BINDING_ROOT environment variable, use the built-in language feature of your programming language of choice that can read environment variables.
Example: Python client usage
from pyservicebinding import binding
try:
sb = binding.ServiceBinding()
except binding.ServiceBindingRootMissingError as msg:
# log the error message and retry/exit
print("SERVICE_BINDING_ROOT env var not set")
sb = binding.ServiceBinding()
bindings_list = sb.bindings("postgresql")
In the previous example, the bindings_list variable contains the binding data for the postgresql database service type.
5.6.3. Projecting the binding data
Depending on your workload requirements and environment, you can choose to project the binding data either as files or environment variables.
Prerequisites
You understand the following concepts:
- Environment and requirements of your workload, and how it works with the provided services.
- Consumption of the binding data in your workload resource.
- Configuration of how the final path for data projection is computed for the default method.
- The binding data is exposed from the backing service.
Procedure
-
To project the binding data as files, determine the destination folder by ensuring that the existing
SERVICE_BINDING_ROOTenvironment variable is present in the container where your workload runs. -
To project the binding data as environment variables, set the value for the
.spec.bindAsFilesparameter tofalsefrom theServiceBindingresource in the custom resource (CR).
5.6.4. Additional resources
5.7. Binding workloads using Service Binding Operator
Application developers must bind a workload to one or more backing services by using a binding secret. This secret is generated for the purpose of storing information to be consumed by the workload.
As an example, consider that the service you want to connect to is already exposing the binding data. In this case, you would also need a workload to be used along with the ServiceBinding custom resource (CR). By using this ServiceBinding CR, the workload sends a binding request with the details of the services to bind with.
Example of ServiceBinding CR
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: spring-petclinic-pgcluster
namespace: my-petclinic
spec:
services: 1
- group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com
version: v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
name: hippo
application: 2
name: spring-petclinic
group: apps
version: v1
resource: deployments
As shown in the previous example, you can also directly use a ConfigMap or a Secret itself as a service resource to be used as a source of binding data.
5.7.1. Naming strategies
Naming strategies are available only for the binding.operators.coreos.com API group.
Naming strategies use Go templates to help you define custom binding names through the service binding request. Naming strategies apply for all attributes including the mappings in the ServiceBinding custom resource (CR).
A backing service projects the binding names as files or environment variables into the workload. If a workload expects the projected binding names in a particular format, but the binding names to be projected from the backing service are not available in that format, then you can change the binding names using naming strategies.
Predefined post-processing functions
While using naming strategies, depending on the expectations or requirements of your workload, you can use the following predefined post-processing functions in any combination to convert the character strings:
-
upper: Converts the character strings into capital or uppercase letters. -
lower: Converts the character strings into lowercase letters. -
title: Converts the character strings where the first letter of each word is capitalized except for certain minor words.
Predefined naming strategies
Binding names declared through annotations are processed for their name change before their projection into the workload according to the following predefined naming strategies:
none: When applied, there are no changes in the binding names.Example
After the template compilation, the binding names take the
{{ .name }}form.host: hippo-pgbouncer port: 5432
upper: Applied when nonamingStrategyis defined. When applied, converts all the character strings of the binding name key into capital or uppercase letters.Example
After the template compilation, the binding names take the
{{ .service.kind | upper}}_{{ .name | upper }}form.DATABASE_HOST: hippo-pgbouncer DATABASE_PORT: 5432
If your workload requires a different format, you can define a custom naming strategy and change the binding name using a prefix and a separator, for example,
PORT_DATABASE.
-
When the binding names are projected as files, by default the predefined
nonenaming strategy is applied, and the binding names do not change. -
When the binding names are projected as environment variables and no
namingStrategyis defined, by default the predefineduppercasenaming strategy is applied. - You can override the predefined naming strategies by defining custom naming strategies using different combinations of custom binding names and predefined post-processing functions.
5.7.2. Advanced binding options
You can define the ServiceBinding custom resource (CR) to use the following advanced binding options:
-
Changing binding names: This option is available only for the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. -
Composing custom binding data: This option is available only for the
binding.operators.coreos.comAPI group. -
Binding workloads using label selectors: This option is available for both the
binding.operators.coreos.comandservicebinding.ioAPI groups.
5.7.2.1. Changing the binding names before projecting them into the workload
You can specify the rules to change the binding names in the .spec.namingStrategy attribute of the ServiceBinding CR. For example, consider a Spring PetClinic sample application that connects to the PostgreSQL database. In this case, the PostgreSQL database service exposes the host and port fields of the database to use for binding. The Spring PetClinic sample application can access this exposed binding data through the binding names.
Example: Spring PetClinic sample application in the ServiceBinding CR
...
application:
name: spring-petclinic
group: apps
version: v1
resource: deployments
...
Example: PostgreSQL database service in the ServiceBinding CR
...
services:
- group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com
version: v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
name: hippo
...
If namingStrategy is not defined and the binding names are projected as environment variables, then the host: hippo-pgbouncer value in the backing service and the projected environment variable would appear as shown in the following example:
Example
DATABASE_HOST: hippo-pgbouncer
where:
|
|
Specifies the |
|
| Specifies the binding name. |
After applying the POSTGRESQL_{{ .service.kind | upper }}_{{ .name | upper }}_ENV naming strategy, the list of custom binding names prepared by the service binding request appears as shown in the following example:
Example
POSTGRESQL_DATABASE_HOST_ENV: hippo-pgbouncer POSTGRESQL_DATABASE_PORT_ENV: 5432
The following items describe the expressions defined in the POSTGRESQL_{{ .service.kind | upper }}_{{ .name | upper }}_ENV naming strategy:
-
.name: Refers to the binding name exposed by the backing service. In the previous example, the binding names areHOSTandPORT. -
.service.kind: Refers to the kind of service resource whose binding names are changed with the naming strategy. -
upper: String function used to post-process the character string while compiling the Go template string. -
POSTGRESQL: Prefix of the custom binding name. -
ENV: Suffix of the custom binding name.
Similar to the previous example, you can define the string templates in namingStrategy to define how each key of the binding names should be prepared by the service binding request.
5.7.2.2. Composing custom binding data
As an application developer, you can compose custom binding data under the following circumstances:
- The backing service does not expose binding data.
- The values exposed are not available in the required format as expected by the workload.
For example, consider a case where the backing service CR exposes the host, port, and database user as binding data, but the workload requires that the binding data be consumed as a connection string. You can compose custom binding data using attributes in the Kubernetes resource representing the backing service.
Example
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: spring-petclinic-pgcluster
namespace: my-petclinic
spec:
services:
- group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com
version: v1beta1
kind: PostgresCluster
name: hippo 1
id: postgresDB 2
- group: ""
version: v1
kind: Secret
name: hippo-pguser-hippo
id: postgresSecret
application:
name: spring-petclinic
group: apps
version: v1
resource: deployments
mappings:
## From the database service
- name: JDBC_URL
value: 'jdbc:postgresql://{{ .postgresDB.metadata.annotations.proxy }}:{{ .postgresDB.spec.port }}/{{ .postgresDB.metadata.name }}'
## From both the services!
- name: CREDENTIALS
value: '{{ .postgresDB.metadata.name }}{{ translationService.postgresSecret.data.password }}'
## Generate JSON
- name: DB_JSON 3
value: {{ json .postgresDB.status }} 4
- 1
- Name of the backing service resource.
- 2
- Optional identifier.
- 3
- The JSON name that the Service Binding Operator generates. The Service Binding Operator projects this JSON name as the name of a file or environment variable.
- 4
- The JSON value that the Service Binding Operator generates. The Service Binding Operator projects this JSON value as a file or environment variable. The JSON value contains the attributes from your specified field of the backing service custom resource.
5.7.2.3. Binding workloads using a label selector
You can use a label selector to specify the workload to bind. If you declare a service binding using the label selectors to pick up workloads, the Service Binding Operator periodically attempts to find and bind new workloads that match the given label selector.
For example, as a cluster administrator, you can bind a service to every Deployment in a namespace with the environment: production label by setting an appropriate labelSelector field in the ServiceBinding CR. This enables the Service Binding Operator to bind each of these workloads with one ServiceBinding CR.
Example ServiceBinding CR in the binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 API
apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: multi-application-binding
namespace: service-binding-demo
spec:
application:
labelSelector: 1
matchLabels:
environment: production
group: apps
version: v1
resource: deployments
services:
group: ""
version: v1
kind: Secret
name: super-secret-data
- 1
- Specifies the workload that is being bound.
Example ServiceBinding CR in the servicebinding.io API
apiVersion: servicebindings.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceBinding
metadata:
name: multi-application-binding
namespace: service-binding-demo
spec:
workload:
selector: 1
matchLabels:
environment: production
apiVersion: app/v1
kind: Deployment
service:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
name: super-secret-data
- 1
- Specifies the workload that is being bound.
If you define the following pairs of fields, Service Binding Operator refuses the binding operation and generates an error:
-
The
nameandlabelSelectorfields in thebinding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1API. -
The
nameandselectorfields in theservicebinding.ioAPI (Spec API).
Understanding the rebinding behavior
Consider a case where, after a successful binding, you use the name field to identify a workload. If you delete and recreate that workload, the ServiceBinding reconciler does not rebind the workload, and the Operator cannot project the binding data to the workload. However, if you use the labelSelector field to identify a workload, the ServiceBinding reconciler rebinds the workload, and the Operator projects the binding data.
5.7.3. Binding secondary workloads that are not compliant with PodSpec
A typical scenario in service binding involves configuring the backing service, the workload (Deployment), and Service Binding Operator. Consider a scenario that involves a secondary workload (which can also be an application Operator) that is not compliant with PodSpec and is between the primary workload (Deployment) and Service Binding Operator.
For such secondary workload resources, the location of the container path is arbitrary. For service binding, if the secondary workload in a CR is not compliant with the PodSpec, you must specify the location of the container path. Doing so projects the binding data into the container path specified in the secondary workload of the ServiceBinding custom resource (CR), for example, when you do not want the binding data inside a pod.
In Service Binding Operator, you can configure the path of where containers or secrets reside within a workload and bind these paths at a custom location.
5.7.3.1. Configuring the custom location of the container path
This custom location is available for the binding.operators.coreos.com API group when Service Binding Operator projects the binding data as environment variables.
Consider a secondary workload CR, which is not compliant with the PodSpec and has containers located at the spec.containers path:
Example: Secondary workload CR
apiVersion: "operator.sbo.com/v1"
kind: SecondaryWorkload
metadata:
name: secondary-workload
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-world
image: quay.io/baijum/secondary-workload:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
Procedure
Configure the
spec.containerspath by specifying a value in theServiceBindingCR and bind this path to aspec.application.bindingPath.containersPathcustom location:Example:
ServiceBindingCR with thespec.containerspath in a custom locationapiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: ServiceBinding metadata: name: spring-petclinic-pgcluster spec: services: - group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com version: v1beta1 kind: PostgresCluster name: hippo id: postgresDB - group: "" version: v1 kind: Secret name: hippo-pguser-hippo id: postgresSecret application: 1 name: spring-petclinic group: apps version: v1 resource: deployments application: 2 name: secondary-workload group: operator.sbo.com version: v1 resource: secondaryworkloads bindingPath: containersPath: spec.containers 3
After you specify the location of the container path, Service Binding Operator generates the binding data, which becomes available in the container path specified in the secondary workload of the ServiceBinding CR.
The following example shows the spec.containers path with the envFrom and secretRef fields:
Example: Secondary workload CR with the envFrom and secretRef fields
apiVersion: "operator.sbo.com/v1"
kind: SecondaryWorkload
metadata:
name: secondary-workload
spec:
containers:
- env: 1
- name: ServiceBindingOperatorChangeTriggerEnvVar
value: "31793"
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: secret-resource-name 2
image: quay.io/baijum/secondary-workload:latest
name: hello-world
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
resources: {}
5.7.3.2. Configuring the custom location of the secret path
This custom location is available for the binding.operators.coreos.com API group when Service Binding Operator projects the binding data as environment variables.
Consider a secondary workload CR, which is not compliant with the PodSpec, with only the secret at the spec.secret path:
Example: Secondary workload CR
apiVersion: "operator.sbo.com/v1"
kind: SecondaryWorkload
metadata:
name: secondary-workload
spec:
secret: ""
Procedure
Configure the
spec.secretpath by specifying a value in theServiceBindingCR and bind this path at aspec.application.bindingPath.secretPathcustom location:Example:
ServiceBindingCR with thespec.secretpath in a custom locationapiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: ServiceBinding metadata: name: spring-petclinic-pgcluster spec: ... application: 1 name: secondary-workload group: operator.sbo.com version: v1 resource: secondaryworkloads bindingPath: secretPath: spec.secret 2 ...
After you specify the location of the secret path, Service Binding Operator generates the binding data, which becomes available in the secret path specified in the secondary workload of the ServiceBinding CR.
The following example shows the spec.secret path with the binding-request value:
Example: Secondary workload CR with the binding-request value
...
apiVersion: "operator.sbo.com/v1"
kind: SecondaryWorkload
metadata:
name: secondary-workload
spec:
secret: binding-request-72ddc0c540ab3a290e138726940591debf14c581 1
...
- 1
- The unique name of the
Secretresource that Service Binding Operator generates.
5.7.3.3. Workload resource mapping
-
Workload resource mapping is available for the secondary workloads of the
ServiceBindingcustom resource (CR) for both the API groups:binding.operators.coreos.comandservicebinding.io. -
You must define
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources only under theservicebinding.ioAPI group. However, theClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresources interact withServiceBindingresources under both thebinding.operators.coreos.comandservicebinding.ioAPI groups.
If you cannot configure custom path locations by using the configuration method for container path, you can define exactly where binding data needs to be projected. Specify where to project the binding data for a given workload kind by defining the ClusterWorkloadResourceMapping resources in the servicebinding.io API group.
The following example shows how to define a mapping for the CronJob.batch/v1 resources.
Example: Mapping for CronJob.batch/v1 resources
apiVersion: servicebinding.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterWorkloadResourceMapping metadata: name: cronjobs.batch 1 spec: versions: - version: "v1" 2 annotations: .spec.jobTemplate.spec.template.metadata.annotations 3 containers: - path: .spec.jobTemplate.spec.template.spec.containers[*] 4 - path: .spec.jobTemplate.spec.template.spec.initContainers[*] name: .name 5 env: .env 6 volumeMounts: .volumeMounts 7 volumes: .spec.jobTemplate.spec.template.spec.volumes 8
- 1
- Name of the
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource, which must be qualified as theplural.groupof the mapped workload resource. - 2
- Version of the resource that is being mapped. Any version that is not specified can be matched with the "*" wildcard.
- 3
- Optional: Identifier of the
.annotationsfield in a pod, specified with a fixed JSONPath. The default value is.spec.template.spec.annotations. - 4
- Identifier of the
.containersand.initContainersfields in a pod, specified with a JSONPath. If no entries under thecontainersfield are defined, the Service Binding Operator defaults to two paths:.spec.template.spec.containers[*]and.spec.template.spec.initContainers[\*], with all other fields set as their default. However, if you specify an entry, then you must define the.pathfield. - 5
- Optional: Identifier of the
.namefield in a container, specified with a fixed JSONPath. The default value is.name. - 6
- Optional: Identifier of the
.envfield in a container, specified with a fixed JSONPath. The default value is.env. - 7
- Optional: Identifier of the
.volumeMountsfield in a container, specified with a fixed JSONPath. The default value is.volumeMounts. - 8
- Optional: Identifier of the
.volumesfield in a pod, specified with a fixed JSONPath. The default value is.spec.template.spec.volumes.
In this context, a fixed JSONPath is a subset of the JSONPath grammar that accepts only the following operations:
-
Field lookup:
.spec.template -
Array indexing:
.spec['template']
All other operations are not accepted.
-
Field lookup:
-
Most of these fields are optional. When they are not specified, the Service Binding Operator assumes defaults compatible with
PodSpecresources. -
The Service Binding Operator requires that each of these fields is structurally equivalent to the corresponding field in a pod deployment. For example, the contents of the
.envfield in a workload resource must be able to accept the same structure of data that the.envfield in a Pod resource would. Otherwise, projecting binding data into such a workload might result in unexpected behavior from the Service Binding Operator.
Behavior specific to the binding.operators.coreos.com API group
You can expect the following behaviors when ClusterWorkloadResourceMapping resources interact with ServiceBinding resources under the binding.operators.coreos.com API group:
-
If a
ServiceBindingresource with thebindAsFiles: falseflag value is created together with one of these mappings, then environment variables are projected into the.envFromfield underneath eachpathfield specified in the correspondingClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource. As a cluster administrator, you can specify both a
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource and the.spec.application.bindingPath.containersPathfield in aServiceBinding.bindings.coreos.comresource for binding purposes.The Service Binding Operator attempts to project binding data into the locations specified in both a
ClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource and the.spec.application.bindingPath.containersPathfield. This behavior is equivalent to adding a container entry to the correspondingClusterWorkloadResourceMappingresource with thepath: $containersPathattribute, with all other values taking their default value.
5.7.4. Unbinding workloads from a backing service
You can unbind a workload from a backing service by using the oc tool.
To unbind a workload from a backing service, delete the
ServiceBindingcustom resource (CR) linked to it:$ oc delete ServiceBinding <.metadata.name>
Example
$ oc delete ServiceBinding spring-petclinic-pgcluster
where:
spring-petclinic-pgclusterSpecifies the name of the
ServiceBindingCR.
5.7.5. Additional resources
5.8. Connecting an application to a service using the Developer perspective
Use the Topology view for the following purposes:
- Group multiple components within an application.
- Connect components with each other.
- Connect multiple resources to services with labels.
You can either use a binding or a visual connector to connect components.
A binding connection between the components can be established only if the target node is an Operator-backed service. This is indicated by the Create a binding connector tool-tip which appears when you drag an arrow to such a target node. When an application is connected to a service by using a binding connector a ServiceBinding resource is created. Then, the Service Binding Operator controller projects the necessary binding data into the application deployment. After the request is successful, the application is redeployed establishing an interaction between the connected components.
A visual connector establishes only a visual connection between the components, depicting an intent to connect. No interaction between the components is established. If the target node is not an Operator-backed service the Create a visual connector tool-tip is displayed when you drag an arrow to a target node.
5.8.1. Discovering and identifying Operator-backed bindable services
As a user, if you want to create a bindable service, you must know which services are bindable. Bindable services are services that the applications can consume easily because they expose their binding data such as credentials, connection details, volume mounts, secrets, and other binding data in a standard way. The Developer perspective helps you discover and identify such bindable services.
Procedure
To discover and identify Operator-backed bindable services, consider the following alternative approaches:
- Click +Add → Developer Catalog → Operator Backed to see the Operator-backed tiles. Operator-backed services that support service binding features have a Bindable badge on the tiles.
On the left pane of the Operator Backed page, select the Bindable checkbox.
TipClick the help icon next to Service binding to see more information about bindable services.
- Click +Add → Add and search for Operator-backed services. When you click the bindable service, you can view the Bindable badge in the side panel to the right.
5.8.2. Creating a visual connection between components
You can depict an intent to connect application components by using the visual connector.
This procedure walks you through an example of creating a visual connection between a PostgreSQL Database service and a Spring PetClinic sample application.
Prerequisites
- You have created and deployed a Spring PetClinic sample application by using the Developer perspective.
-
You have created and deployed a Crunchy PostgreSQL database instance by using the Developer perspective. This instance has the following components:
hippo-backup,hippo-instance,hippo-repo-host, andhippo-pgbouncer.
Procedure
Hover over the Spring PetClinic sample application to see a dangling arrow on the node.
Figure 5.1. Visual connector
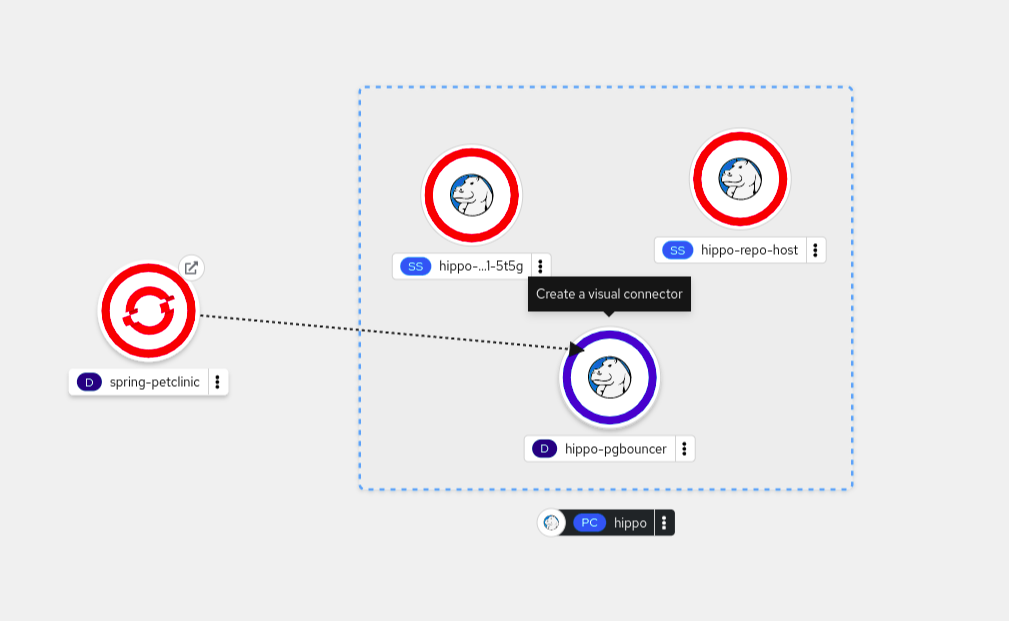
-
Click and drag the arrow towards the
hippo-pgbouncerdeployment to connect the Spring PetClinic sample application with it. -
Click the
spring-petclinicdeployment to see the Overview panel. Under the Details tab, click the edit icon in the Annotations section to see the Key =app.openshift.io/connects-toand Value =[{"apiVersion":"apps/v1","kind":"Deployment","name":"hippo-pgbouncer"}]annotation added to the deployment. Optional: You can repeat these steps to establish visual connections between other applications and components you create.
Figure 5.2. Connecting multiple applications
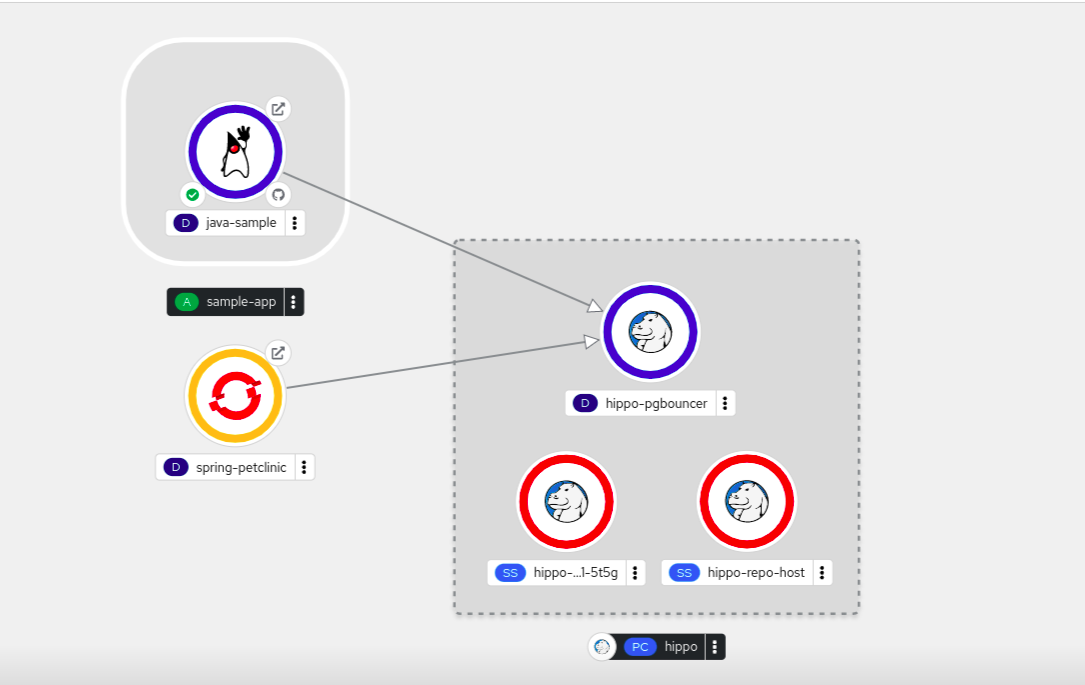
5.8.3. Creating a binding connection between components
You can create a binding connection with Operator-backed components, as demonstrated in the following example, which uses a PostgreSQL Database service and a Spring PetClinic sample application. To create a binding connection with a service that the PostgreSQL Database Operator backs, you must first add the Red Hat-provided PostgreSQL Database Operator to the OperatorHub, and then install the Operator. The PostreSQL Database Operator then creates and manages the Database resource, which exposes the binding data in secrets, config maps, status, and spec attributes.
Prerequisites
- You created and deployed a Spring PetClinic sample application in the Developer perspective.
- You installed Service Binding Operator from the OperatorHub.
-
You installed the Crunchy Postgres for Kubernetes Operator from the OperatorHub in the
v5Update channel. -
You created a PostgresCluster resource in the Developer perspective, which resulted in a Crunchy PostgreSQL database instance with the following components:
hippo-backup,hippo-instance,hippo-repo-host, andhippo-pgbouncer.
Procedure
-
In the Developer perspective, switch to the relevant project, for example,
my-petclinic. - In the Topology view, hover over the Spring PetClinic sample application to see a dangling arrow on the node.
- Drag and drop the arrow onto the hippo database icon in the Postgres Cluster to make a binding connection with the Spring PetClinic sample application.
In the Create Service Binding dialog, keep the default name or add a different name for the service binding, and then click Create.
Figure 5.3. Service Binding dialog
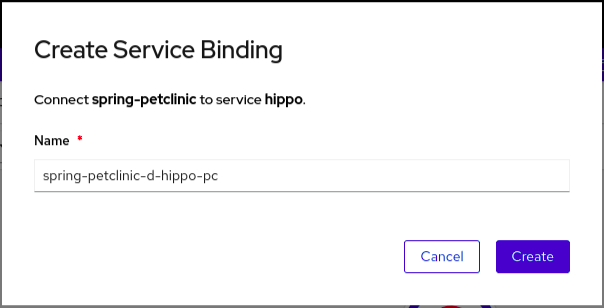
- Optional: If there is difficulty in making a binding connection using the Topology view, go to +Add → YAML → Import YAML.
Optional: In the YAML editor, add the
ServiceBindingresource:apiVersion: binding.operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: ServiceBinding metadata: name: spring-petclinic-pgcluster namespace: my-petclinic spec: services: - group: postgres-operator.crunchydata.com version: v1beta1 kind: PostgresCluster name: hippo application: name: spring-petclinic group: apps version: v1 resource: deploymentsA service binding request is created and a binding connection is created through a
ServiceBindingresource. When the database service connection request succeeds, the application is redeployed and the connection is established.Figure 5.4. Binding connector
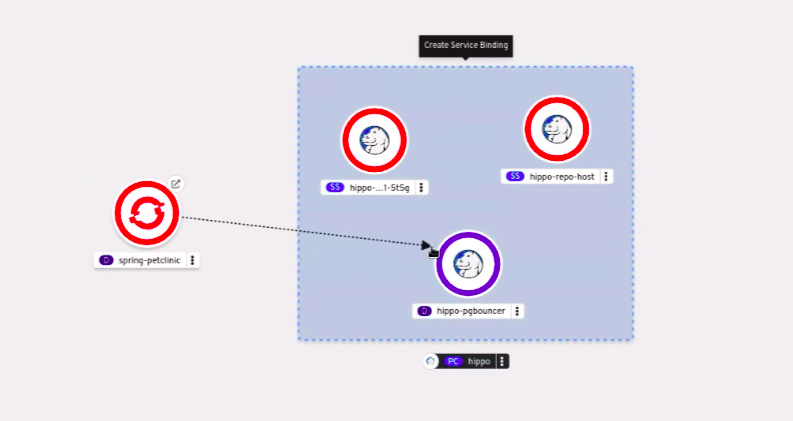 Tip
TipYou can also use the context menu by dragging the dangling arrow to add and create a binding connection to an operator-backed service.
Figure 5.5. Context menu to create binding connection

- In the navigation menu, click Topology. The spring-petclinic deployment in the Topology view includes an Open URL link to view its web page.
- Click the Open URL link.
You can now view the Spring PetClinic sample application remotely to confirm that the application is now connected to the database service and that the data has been successfully projected to the application from the Crunchy PostgreSQL database service.
The Service Binding Operator has successfully created a working connection between the application and the database service.
5.8.4. Verifying the status of your service binding from the Topology view
The Developer perspective helps you verify the status of your service binding through the Topology view.
Procedure
If a service binding was successful, click the binding connector. A side panel appears displaying the Connected status under the Details tab.
Optionally, you can view the Connected status on the following pages from the Developer perspective:
- The ServiceBindings page.
- The ServiceBinding details page. In addition, the page title displays a Connected badge.
If a service binding was unsuccessful, the binding connector shows a red arrowhead and a red cross in the middle of the connection. Click this connector to view the Error status in the side panel under the Details tab. Optionally, click the Error status to view specific information about the underlying problem.
You can also view the Error status and a tooltip on the following pages from the Developer perspective:
- The ServiceBindings page.
- The ServiceBinding details page. In addition, the page title displays an Error badge.
In the ServiceBindings page, use the Filter dropdown to list the service bindings based on their status.
5.8.5. Visualizing the binding connections to resources
As a user, use Label Selector in the Topology view to visualize a service binding and simplify the process of binding applications to backing services. When creating ServiceBinding resources, specify labels by using Label Selector to find and connect applications instead of using the name of the application. The Service Binding Operator then consumes these ServiceBinding resources and specified labels to find the applications to create a service binding with.
To navigate to a list of all connected resources, click the label selector associated with the ServiceBinding resource.
To view the Label Selector, consider the following approaches:
After you import a
ServiceBindingresource, view the Label Selector associated with the service binding on the ServiceBinding details page.Figure 5.6. ServiceBinding details page
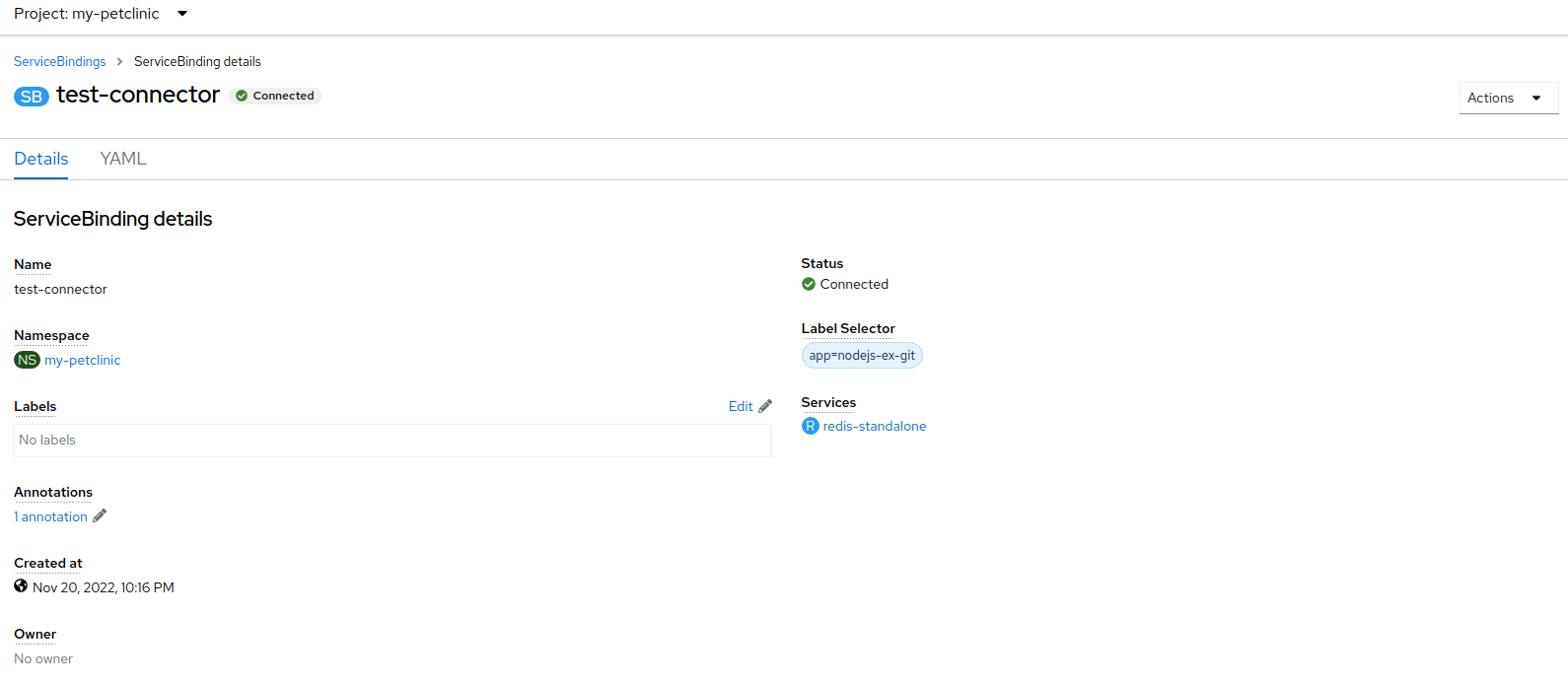
To use Label Selector and to create one or more connections at once, you must import the YAML file of the ServiceBinding resource.
After the connection is established and when you click the binding connector, the service binding connector Details side panel appears. You can view the Label Selector associated with the service binding on this panel.
Figure 5.7. Topology label selector side panel
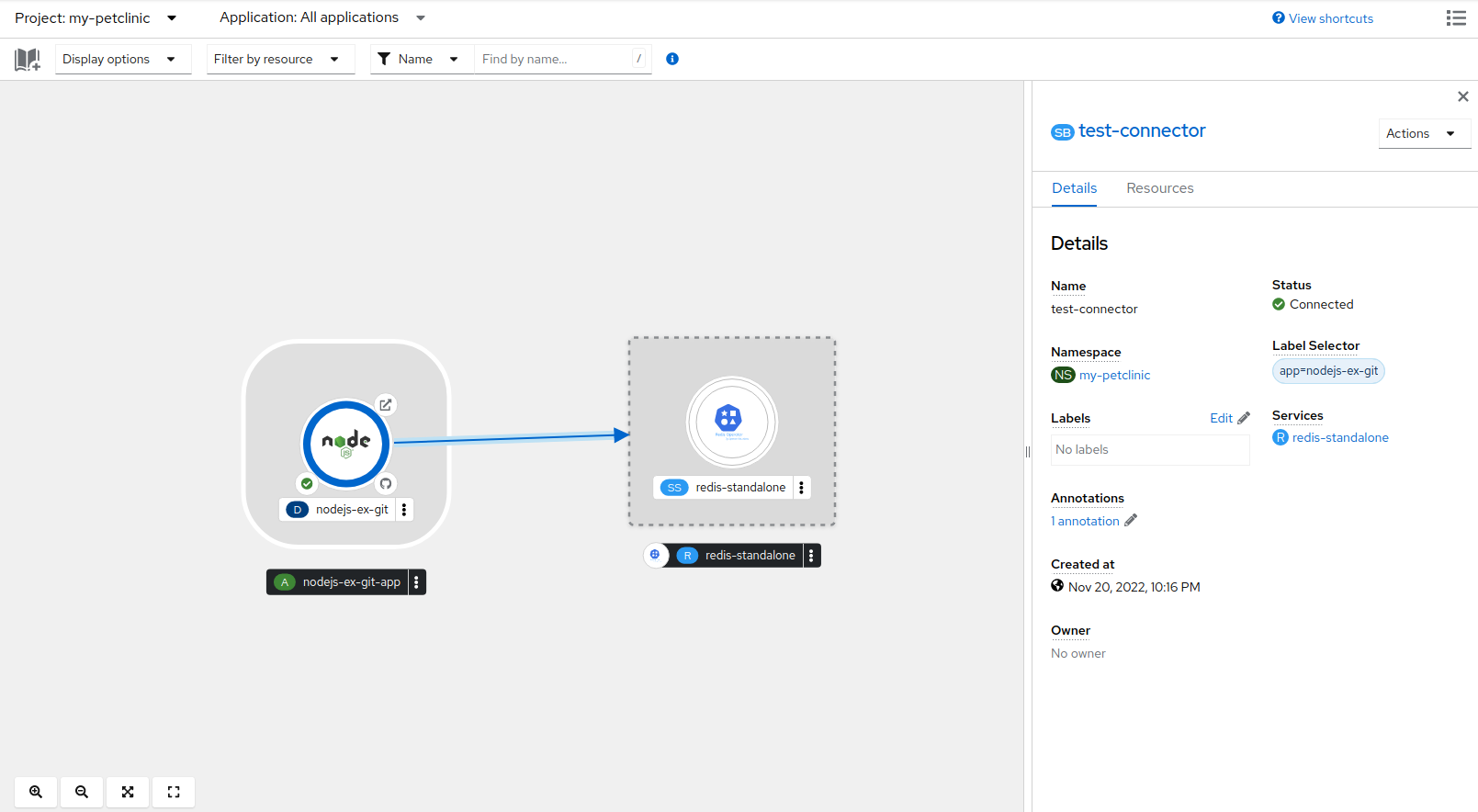 Note
NoteWhen you delete a binding connector (a single connection within Topology along with a service binding), the action removes all connections that are tied to the deleted service binding. While deleting a binding connector, a confirmation dialog appears, which informs that all connectors will be deleted.
Figure 5.8. Delete ServiceBinding confirmation dialog
5.8.6. Additional resources
Chapter 6. Working with Helm charts
6.1. Understanding Helm
Helm is a software package manager that simplifies deployment of applications and services to OpenShift Dedicated clusters.
Helm uses a packaging format called charts. A Helm chart is a collection of files that describes the OpenShift Dedicated resources.
Creating a chart in a cluster creates a running instance of the chart known as a release.
Each time a chart is created, or a release is upgraded or rolled back, an incremental revision is created.
6.1.1. Key features
Helm provides the ability to:
- Search through a large collection of charts stored in the chart repository.
- Modify existing charts.
- Create your own charts with OpenShift Dedicated or Kubernetes resources.
- Package and share your applications as charts.
6.1.2. Red Hat Certification of Helm charts for OpenShift
You can choose to verify and certify your Helm charts by Red Hat for all the components you will be deploying on the Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated. Charts go through an automated Red Hat OpenShift certification workflow that guarantees security compliance as well as best integration and experience with the platform. Certification assures the integrity of the chart and ensures that the Helm chart works seamlessly on Red Hat OpenShift clusters.
6.1.3. Additional resources
- For more information on how to certify your Helm charts as a Red Hat partner, see Red Hat Certification of Helm charts for OpenShift.
- For more information on OpenShift and Container certification guides for Red Hat partners, see Partner Guide for OpenShift and Container Certification.
-
For a list of the charts, see the Red Hat
Helm indexfile. - You can view the available charts at the Red Hat Marketplace. For more information, see Using the Red Hat Marketplace.
6.2. Installing Helm
The following section describes how to install Helm on different platforms using the CLI.
You can also find the URL to the latest binaries from the OpenShift Dedicated web console by clicking the ? icon in the upper-right corner and selecting Command Line Tools.
Prerequisites
- You have installed Go, version 1.13 or higher.
6.2.1. On Linux
Download the Linux x86_64 or Linux amd64 Helm binary and add it to your path:
# curl -L https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/clients/helm/latest/helm-linux-amd64 -o /usr/local/bin/helm
Make the binary file executable:
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/helm
Check the installed version:
$ helm version
Example output
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.0", GitCommit:"b31719aab7963acf4887a1c1e6d5e53378e34d93", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.13.4"}
6.2.2. On Windows 7/8
-
Download the latest
.exefile and put in a directory of your preference. - Right click Start and click Control Panel.
- Select System and Security and then click System.
- From the menu on the left, select Advanced systems settings and click Environment Variables at the bottom.
- Select Path from the Variable section and click Edit.
-
Click New and type the path to the folder with the
.exefile into the field or click Browse and select the directory, and click OK.
6.2.3. On Windows 10
-
Download the latest
.exefile and put in a directory of your preference. -
Click Search and type
envorenvironment. - Select Edit environment variables for your account.
- Select Path from the Variable section and click Edit.
- Click New and type the path to the directory with the exe file into the field or click Browse and select the directory, and click OK.
6.2.4. On MacOS
Download the Helm binary and add it to your path:
# curl -L https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/clients/helm/latest/helm-darwin-amd64 -o /usr/local/bin/helm
Make the binary file executable:
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/helm
Check the installed version:
$ helm version
Example output
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.0", GitCommit:"b31719aab7963acf4887a1c1e6d5e53378e34d93", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.13.4"}
6.3. Configuring custom Helm chart repositories
The Developer Catalog, in the Developer perspective of the web console, displays the Helm charts available in the cluster. By default, it lists the Helm charts from the Red Hat OpenShift Helm chart repository. For a list of the charts, see the Red Hat Helm index file.
As a cluster administrator, you can add multiple cluster-scoped and namespace-scoped Helm chart repositories, separate from the default cluster-scoped Helm repository, and display the Helm charts from these repositories in the Developer Catalog.
As a regular user or project member with the appropriate role-based access control (RBAC) permissions, you can add multiple namespace-scoped Helm chart repositories, apart from the default cluster-scoped Helm repository, and display the Helm charts from these repositories in the Developer Catalog.
In the Developer perspective of the web console, you can use the Helm page to:
- Create Helm Releases and Repositories using the Create button.
- Create, update, or delete a cluster-scoped or namespace-scoped Helm chart repository.
- View the list of the existing Helm chart repositories in the Repositories tab, which can also be easily distinguished as either cluster scoped or namespace scoped.
6.3.1. Creating Helm releases using the Developer perspective
You can use either the Developer perspective in the web console or the CLI to select and create a release from the Helm charts listed in the Developer Catalog. You can create Helm releases by installing Helm charts and see them in the Developer perspective of the web console.
Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the web console and have switched to the Developer perspective.
Procedure
To create Helm releases from the Helm charts provided in the Developer Catalog:
- In the Developer perspective, navigate to the +Add view and select a project. Then click Helm Chart option to see all the Helm Charts in the Developer Catalog.
- Select a chart and read the description, README, and other details about the chart.
Click Create.
Figure 6.1. Helm charts in developer catalog
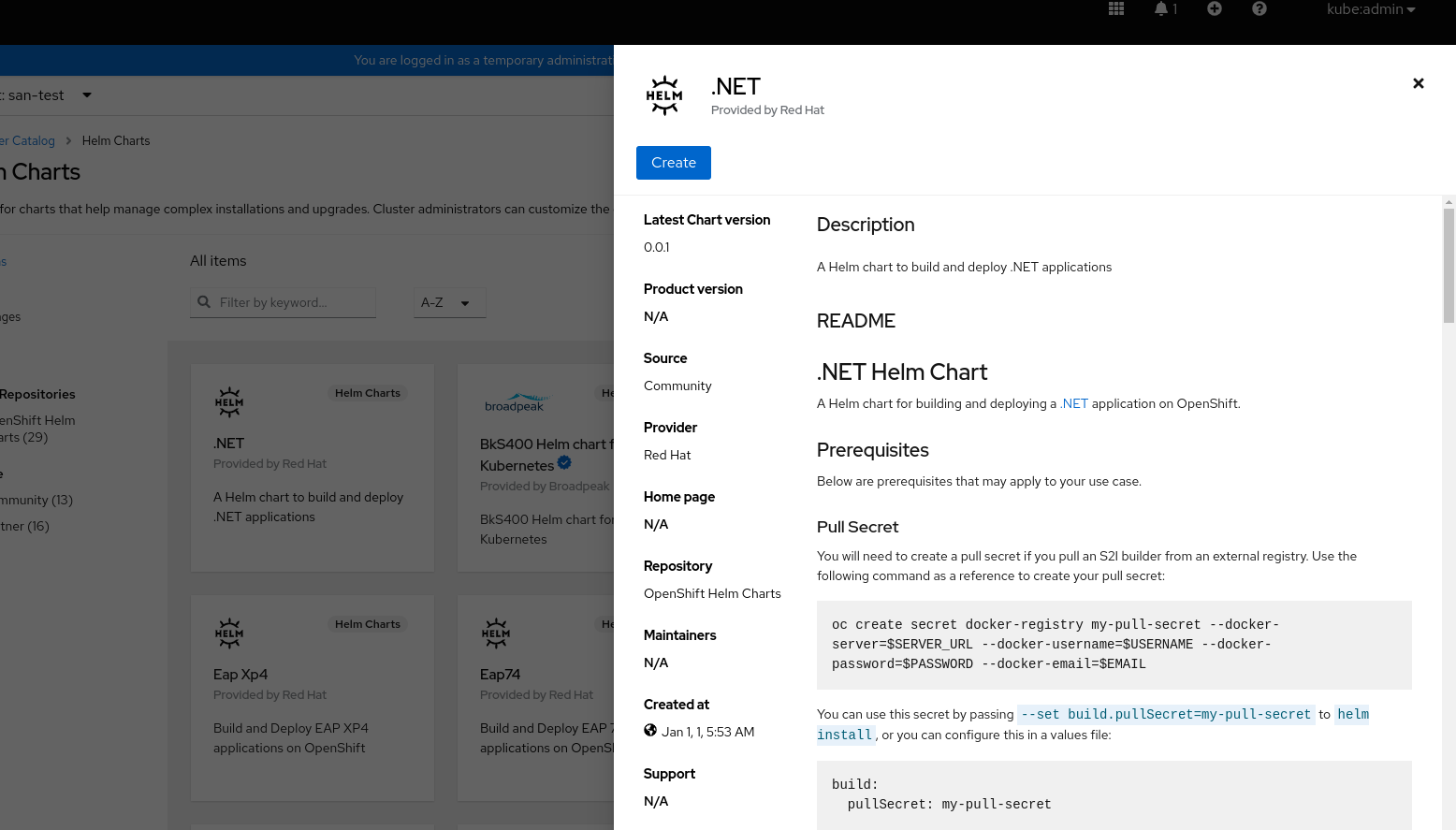
In the Create Helm Release page:
- Enter a unique name for the release in the Release Name field.
- Select the required chart version from the Chart Version drop-down list.
Configure your Helm chart by using the Form View or the YAML View.
NoteWhere available, you can switch between the YAML View and Form View. The data is persisted when switching between the views.
Click Create to create a Helm release. The web console displays the new release in the Topology view.
If a Helm chart has release notes, the web console displays them.
If a Helm chart creates workloads, the web console displays them on the Topology or Helm release details page. The workloads are
DaemonSet,CronJob,Pod,Deployment, andDeploymentConfig.- View the newly created Helm release in the Helm Releases page.
You can upgrade, rollback, or delete a Helm release by using the Actions button on the side panel or by right-clicking a Helm release.
6.3.2. Using Helm in the web terminal
You can use Helm by Accessing the web terminal in the Developer perspective of the web console.
6.3.3. Creating a custom Helm chart on OpenShift Dedicated
Procedure
Create a new project:
$ oc new-project nodejs-ex-k
Download an example Node.js chart that contains OpenShift Dedicated objects:
$ git clone https://github.com/redhat-developer/redhat-helm-charts
Go to the directory with the sample chart:
$ cd redhat-helm-charts/alpha/nodejs-ex-k/
Edit the
Chart.yamlfile and add a description of your chart:apiVersion: v2 1 name: nodejs-ex-k 2 description: A Helm chart for OpenShift 3 icon: https://static.redhat.com/libs/redhat/brand-assets/latest/corp/logo.svg 4 version: 0.2.1 5
Verify that the chart is formatted properly:
$ helm lint
Example output
[INFO] Chart.yaml: icon is recommended 1 chart(s) linted, 0 chart(s) failed
Navigate to the previous directory level:
$ cd ..
Install the chart:
$ helm install nodejs-chart nodejs-ex-k
Verify that the chart has installed successfully:
$ helm list
Example output
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION nodejs-chart nodejs-ex-k 1 2019-12-05 15:06:51.379134163 -0500 EST deployed nodejs-0.1.0 1.16.0
6.3.4. Filtering Helm Charts by their certification level
You can filter Helm charts based on their certification level in the Developer Catalog.
Procedure
- In the Developer perspective, navigate to the +Add view and select a project.
- From the Developer Catalog tile, select the Helm Chart option to see all the Helm charts in the Developer Catalog.
Use the filters to the left of the list of Helm charts to filter the required charts:
- Use the Chart Repositories filter to filter charts provided by Red Hat Certification Charts or OpenShift Helm Charts.
-
Use the Source filter to filter charts sourced from Partners, Community, or Red Hat. Certified charts are indicated with the (
 ) icon.
) icon.
The Source filter will not be visible when there is only one provider type.
You can now select the required chart and install it.
6.4. Working with Helm releases
You can use the Developer perspective in the web console to update, rollback, or delete a Helm release.
6.4.1. Prerequisites
- You have logged in to the web console and have switched to the Developer perspective.
6.4.2. Upgrading a Helm release
You can upgrade a Helm release to upgrade to a new chart version or update your release configuration.
Procedure
- In the Topology view, select the Helm release to see the side panel.
- Click Actions → Upgrade Helm Release.
- In the Upgrade Helm Release page, select the Chart Version you want to upgrade to, and then click Upgrade to create another Helm release. The Helm Releases page displays the two revisions.
6.4.3. Rolling back a Helm release
If a release fails, you can rollback the Helm release to a previous version.
Procedure
To rollback a release using the Helm view:
- In the Developer perspective, navigate to the Helm view to see the Helm Releases in the namespace.
-
Click the Options menu
 adjoining the listed release, and select Rollback.
adjoining the listed release, and select Rollback.
- In the Rollback Helm Release page, select the Revision you want to rollback to and click Rollback.
- In the Helm Releases page, click on the chart to see the details and resources for that release.
Go to the Revision History tab to see all the revisions for the chart.
Figure 6.2. Helm revision history
-
If required, you can further use the Options menu
 adjoining a particular revision and select the revision to rollback to.
adjoining a particular revision and select the revision to rollback to.
6.4.4. Deleting a Helm release
Procedure
- In the Topology view, right-click the Helm release and select Delete Helm Release.
- In the confirmation prompt, enter the name of the chart and click Delete.
Chapter 7. Deployments
7.1. Custom domains for applications
Starting with OpenShift Dedicated 4.14, the Custom Domain Operator is deprecated. To manage Ingress in OpenShift Dedicated 4.14, use the Ingress Operator. The functionality is unchanged for OpenShift Dedicated 4.13 and earlier versions.
You can configure a custom domain for your applications. Custom domains are specific wildcard domains that can be used with OpenShift Dedicated applications.
7.1.1. Configuring custom domains for applications
The top-level domains (TLDs) are owned by the customer that is operating the OpenShift Dedicated cluster. The Custom Domains Operator sets up a new ingress controller with a custom certificate as a second day operation. The public DNS record for this ingress controller can then be used by an external DNS to create a wildcard CNAME record for use with a custom domain.
Custom API domains are not supported because Red Hat controls the API domain. However, customers can change their application domains. For private custom domains with a private IngressController, set .spec.scope to Internal in the CustomDomain CR.
Prerequisites
-
A user account with
dedicated-adminprivileges -
A unique domain or wildcard domain, such as
*.apps.<company_name>.io -
A custom certificate or wildcard custom certificate, such as
CN=*.apps.<company_name>.io -
Access to a cluster with the latest version of the
ocCLI installed
Do not use the reserved names default or apps*, such as apps or apps2, in the metadata/name: section of the CustomDomain CR.
Procedure
Create a new TLS secret from a private key and a public certificate, where
fullchain.pemandprivkey.pemare your public or private wildcard certificates.Example
$ oc create secret tls <name>-tls --cert=fullchain.pem --key=privkey.pem -n <my_project>
Create a new
CustomDomaincustom resource (CR):Example
<company_name>-custom-domain.yamlapiVersion: managed.openshift.io/v1alpha1 kind: CustomDomain metadata: name: <company_name> spec: domain: apps.<company_name>.io 1 scope: External loadBalancerType: Classic 2 certificate: name: <name>-tls 3 namespace: <my_project> routeSelector: 4 matchLabels: route: acme namespaceSelector: 5 matchLabels: type: sharded
- 1
- The custom domain.
- 2
- The type of load balancer for your custom domain. This type can be the default
classicorNLBif you use a network load balancer. - 3
- The secret created in the previous step.
- 4
- Optional: Filters the set of routes serviced by the CustomDomain ingress. If no value is provided, the default is no filtering.
- 5
- Optional: Filters the set of namespaces serviced by the CustomDomain ingress. If no value is provided, the default is no filtering.
Apply the CR:
Example
$ oc apply -f <company_name>-custom-domain.yaml
Get the status of your newly created CR:
$ oc get customdomains
Example output
NAME ENDPOINT DOMAIN STATUS <company_name> xxrywp.<company_name>.cluster-01.opln.s1.openshiftapps.com *.apps.<company_name>.io Ready
Using the endpoint value, add a new wildcard CNAME recordset to your managed DNS provider, such as Route53, Azure DNS, or Google DNS.
Example
*.apps.<company_name>.io -> xxrywp.<company_name>.cluster-01.opln.s1.openshiftapps.com
Create a new application and expose it:
Example
$ oc new-app --docker-image=docker.io/openshift/hello-openshift -n my-project
$ oc create route <route_name> --service=hello-openshift hello-openshift-tls --hostname hello-openshift-tls-my-project.apps.<company_name>.io -n my-project
$ oc get route -n my-project
$ curl https://hello-openshift-tls-my-project.apps.<company_name>.io Hello OpenShift!
7.1.2. Renewing a certificate for custom domains
You can renew certificates with the Custom Domains Operator (CDO) by using the oc CLI tool.
Prerequisites
-
You have the latest version
ocCLI tool installed.
Procedure
Create new secret
$ oc create secret tls <secret-new> --cert=fullchain.pem --key=privkey.pem -n <my_project>
Patch CustomDomain CR
$ oc patch customdomain <company_name> --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"certificate":{"name":"<secret-new>"}}}'Delete old secret
$ oc delete secret <secret-old> -n <my_project>
Troubleshooting
7.2. Understanding deployments
The Deployment and DeploymentConfig API objects in OpenShift Dedicated provide two similar but different methods for fine-grained management over common user applications. They are composed of the following separate API objects:
-
A
DeploymentorDeploymentConfigobject, either of which describes the desired state of a particular component of the application as a pod template. -
Deploymentobjects involve one or more replica sets, which contain a point-in-time record of the state of a deployment as a pod template. Similarly,DeploymentConfigobjects involve one or more replication controllers, which preceded replica sets. - One or more pods, which represent an instance of a particular version of an application.
Use Deployment objects unless you need a specific feature or behavior provided by DeploymentConfig objects.
As of OpenShift Dedicated 4.14, DeploymentConfig objects are deprecated. DeploymentConfig objects are still supported, but are not recommended for new installations. Only security-related and critical issues will be fixed.
Instead, use Deployment objects or another alternative to provide declarative updates for pods.
7.2.1. Building blocks of a deployment
Deployments and deployment configs are enabled by the use of native Kubernetes API objects ReplicaSet and ReplicationController, respectively, as their building blocks.
Users do not have to manipulate replica sets, replication controllers, or pods owned by Deployment or DeploymentConfig objects. The deployment systems ensure changes are propagated appropriately.
If the existing deployment strategies are not suited for your use case and you must run manual steps during the lifecycle of your deployment, then you should consider creating a custom deployment strategy.
The following sections provide further details on these objects.
7.2.1.1. Replica sets
A ReplicaSet is a native Kubernetes API object that ensures a specified number of pod replicas are running at any given time.
Only use replica sets if you require custom update orchestration or do not require updates at all. Otherwise, use deployments. Replica sets can be used independently, but are used by deployments to orchestrate pod creation, deletion, and updates. Deployments manage their replica sets automatically, provide declarative updates to pods, and do not have to manually manage the replica sets that they create.
The following is an example ReplicaSet definition:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: frontend-1
labels:
tier: frontend
spec:
replicas: 3
selector: 1
matchLabels: 2
tier: frontend
matchExpressions: 3
- {key: tier, operator: In, values: [frontend]}
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: frontend
spec:
containers:
- image: openshift/hello-openshift
name: helloworld
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
restartPolicy: Always- 1
- A label query over a set of resources. The result of
matchLabelsandmatchExpressionsare logically conjoined. - 2
- Equality-based selector to specify resources with labels that match the selector.
- 3
- Set-based selector to filter keys. This selects all resources with key equal to
tierand value equal tofrontend.
7.2.1.2. Replication controllers
Similar to a replica set, a replication controller ensures that a specified number of replicas of a pod are running at all times. If pods exit or are deleted, the replication controller instantiates more up to the defined number. Likewise, if there are more running than desired, it deletes as many as necessary to match the defined amount. The difference between a replica set and a replication controller is that a replica set supports set-based selector requirements whereas a replication controller only supports equality-based selector requirements.
A replication controller configuration consists of:
- The number of replicas desired, which can be adjusted at run time.
-
A
Poddefinition to use when creating a replicated pod. - A selector for identifying managed pods.
A selector is a set of labels assigned to the pods that are managed by the replication controller. These labels are included in the Pod definition that the replication controller instantiates. The replication controller uses the selector to determine how many instances of the pod are already running in order to adjust as needed.
The replication controller does not perform auto-scaling based on load or traffic, as it does not track either. Rather, this requires its replica count to be adjusted by an external auto-scaler.
Use a DeploymentConfig to create a replication controller instead of creating replication controllers directly.
If you require custom orchestration or do not require updates, use replica sets instead of replication controllers.
The following is an example definition of a replication controller:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ReplicationController metadata: name: frontend-1 spec: replicas: 1 1 selector: 2 name: frontend template: 3 metadata: labels: 4 name: frontend 5 spec: containers: - image: openshift/hello-openshift name: helloworld ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP restartPolicy: Always
7.2.2. Deployments
Kubernetes provides a first-class, native API object type in OpenShift Dedicated called Deployment. Deployment objects describe the desired state of a particular component of an application as a pod template. Deployments create replica sets, which orchestrate pod lifecycles.
For example, the following deployment definition creates a replica set to bring up one hello-openshift pod:
Deployment definition
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-openshift
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-openshift
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-openshift
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-openshift
image: openshift/hello-openshift:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
7.2.3. DeploymentConfig objects
As of OpenShift Dedicated 4.14, DeploymentConfig objects are deprecated. DeploymentConfig objects are still supported, but are not recommended for new installations. Only security-related and critical issues will be fixed.
Instead, use Deployment objects or another alternative to provide declarative updates for pods.
Building on replication controllers, OpenShift Dedicated adds expanded support for the software development and deployment lifecycle with the concept of DeploymentConfig objects. In the simplest case, a DeploymentConfig object creates a new replication controller and lets it start up pods.
However, OpenShift Dedicated deployments from DeploymentConfig objects also provide the ability to transition from an existing deployment of an image to a new one and also define hooks to be run before or after creating the replication controller.
The DeploymentConfig deployment system provides the following capabilities:
-
A
DeploymentConfigobject, which is a template for running applications. - Triggers that drive automated deployments in response to events.
- User-customizable deployment strategies to transition from the previous version to the new version. A strategy runs inside a pod commonly referred as the deployment process.
- A set of hooks (lifecycle hooks) for executing custom behavior in different points during the lifecycle of a deployment.
- Versioning of your application to support rollbacks either manually or automatically in case of deployment failure.
- Manual replication scaling and autoscaling.
When you create a DeploymentConfig object, a replication controller is created representing the DeploymentConfig object’s pod template. If the deployment changes, a new replication controller is created with the latest pod template, and a deployment process runs to scale down the old replication controller and scale up the new one.
Instances of your application are automatically added and removed from both service load balancers and routers as they are created. As long as your application supports graceful shutdown when it receives the TERM signal, you can ensure that running user connections are given a chance to complete normally.
The OpenShift Dedicated DeploymentConfig object defines the following details:
-
The elements of a
ReplicationControllerdefinition. - Triggers for creating a new deployment automatically.
- The strategy for transitioning between deployments.
- Lifecycle hooks.
Each time a deployment is triggered, whether manually or automatically, a deployer pod manages the deployment (including scaling down the old replication controller, scaling up the new one, and running hooks). The deployment pod remains for an indefinite amount of time after it completes the deployment to retain its logs of the deployment. When a deployment is superseded by another, the previous replication controller is retained to enable easy rollback if needed.
Example DeploymentConfig definition
apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1
kind: DeploymentConfig
metadata:
name: frontend
spec:
replicas: 5
selector:
name: frontend
template: { ... }
triggers:
- type: ConfigChange 1
- imageChangeParams:
automatic: true
containerNames:
- helloworld
from:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: hello-openshift:latest
type: ImageChange 2
strategy:
type: Rolling 3
- 1
- A configuration change trigger results in a new replication controller whenever changes are detected in the pod template of the deployment configuration.
- 2
- An image change trigger causes a new deployment to be created each time a new version of the backing image is available in the named image stream.
- 3
- The default
Rollingstrategy makes a downtime-free transition between deployments.
7.2.4. Comparing Deployment and DeploymentConfig objects
Both Kubernetes Deployment objects and OpenShift Dedicated-provided DeploymentConfig objects are supported in OpenShift Dedicated; however, it is recommended to use Deployment objects unless you need a specific feature or behavior provided by DeploymentConfig objects.
The following sections go into more detail on the differences between the two object types to further help you decide which type to use.
As of OpenShift Dedicated 4.14, DeploymentConfig objects are deprecated. DeploymentConfig objects are still supported, but are not recommended for new installations. Only security-related and critical issues will be fixed.
Instead, use Deployment objects or another alternative to provide declarative updates for pods.
7.2.4.1. Design
One important difference between Deployment and DeploymentConfig objects is the properties of the CAP theorem that each design has chosen for the rollout process. DeploymentConfig objects prefer consistency, whereas Deployments objects take availability over consistency.
For DeploymentConfig objects, if a node running a deployer pod goes down, it will not get replaced. The process waits until the node comes back online or is manually deleted. Manually deleting the node also deletes the corresponding pod. This means that you can not delete the pod to unstick the rollout, as the kubelet is responsible for deleting the associated pod.
However, deployment rollouts are driven from a controller manager. The controller manager runs in high availability mode on masters and uses leader election algorithms to value availability over consistency. During a failure it is possible for other masters to act on the same deployment at the same time, but this issue will be reconciled shortly after the failure occurs.
7.2.4.2. Deployment-specific features
Rollover
The deployment process for Deployment objects is driven by a controller loop, in contrast to DeploymentConfig objects that use deployer pods for every new rollout. This means that the Deployment object can have as many active replica sets as possible, and eventually the deployment controller will scale down all old replica sets and scale up the newest one.
DeploymentConfig objects can have at most one deployer pod running, otherwise multiple deployers might conflict when trying to scale up what they think should be the newest replication controller. Because of this, only two replication controllers can be active at any point in time. Ultimately, this results in faster rapid rollouts for Deployment objects.
Proportional scaling
Because the deployment controller is the sole source of truth for the sizes of new and old replica sets owned by a Deployment object, it can scale ongoing rollouts. Additional replicas are distributed proportionally based on the size of each replica set.
DeploymentConfig objects cannot be scaled when a rollout is ongoing because the controller will have issues with the deployer process about the size of the new replication controller.
Pausing mid-rollout
Deployments can be paused at any point in time, meaning you can also pause ongoing rollouts. However, you currently cannot pause deployer pods; if you try to pause a deployment in the middle of a rollout, the deployer process is not affected and continues until it finishes.
7.2.4.3. DeploymentConfig object-specific features
Automatic rollbacks
Currently, deployments do not support automatically rolling back to the last successfully deployed replica set in case of a failure.
Triggers
Deployments have an implicit config change trigger in that every change in the pod template of a deployment automatically triggers a new rollout. If you do not want new rollouts on pod template changes, pause the deployment:
$ oc rollout pause deployments/<name>
Lifecycle hooks
Deployments do not yet support any lifecycle hooks.
Custom strategies
Deployments do not support user-specified custom deployment strategies.
7.3. Managing deployment processes
7.3.1. Managing DeploymentConfig objects
As of OpenShift Dedicated 4.14, DeploymentConfig objects are deprecated. DeploymentConfig objects are still supported, but are not recommended for new installations. Only security-related and critical issues will be fixed.
Instead, use Deployment objects or another alternative to provide declarative updates for pods.
DeploymentConfig objects can be managed from the OpenShift Dedicated web console’s Workloads page or using the oc CLI. The following procedures show CLI usage unless otherwise stated.
7.3.1.1. Starting a deployment
You can start a rollout to begin the deployment process of your application.
Procedure
To start a new deployment process from an existing
DeploymentConfigobject, run the following command:$ oc rollout latest dc/<name>
NoteIf a deployment process is already in progress, the command displays a message and a new replication controller will not be deployed.
7.3.1.2. Viewing a deployment
You can view a deployment to get basic information about all the available revisions of your application.
Procedure
To show details about all recently created replication controllers for the provided
DeploymentConfigobject, including any currently running deployment process, run the following command:$ oc rollout history dc/<name>
To view details specific to a revision, add the
--revisionflag:$ oc rollout history dc/<name> --revision=1
For more detailed information about a
DeploymentConfigobject and its latest revision, use theoc describecommand:$ oc describe dc <name>
7.3.1.3. Retrying a deployment
If the current revision of your DeploymentConfig object failed to deploy, you can restart the deployment process.
Procedure
To restart a failed deployment process:
$ oc rollout retry dc/<name>
If the latest revision of it was deployed successfully, the command displays a message and the deployment process is not retried.
NoteRetrying a deployment restarts the deployment process and does not create a new deployment revision. The restarted replication controller has the same configuration it had when it failed.
7.3.1.4. Rolling back a deployment
Rollbacks revert an application back to a previous revision and can be performed using the REST API, the CLI, or the web console.
Procedure
To rollback to the last successful deployed revision of your configuration:
$ oc rollout undo dc/<name>
The
DeploymentConfigobject’s template is reverted to match the deployment revision specified in the undo command, and a new replication controller is started. If no revision is specified with--to-revision, then the last successfully deployed revision is used.Image change triggers on the
DeploymentConfigobject are disabled as part of the rollback to prevent accidentally starting a new deployment process soon after the rollback is complete.To re-enable the image change triggers:
$ oc set triggers dc/<name> --auto
Deployment configs also support automatically rolling back to the last successful revision of the configuration in case the latest deployment process fails. In that case, the latest template that failed to deploy stays intact by the system and it is up to users to fix their configurations.
7.3.1.5. Executing commands inside a container
You can add a command to a container, which modifies the container’s startup behavior by overruling the image’s ENTRYPOINT. This is different from a lifecycle hook, which instead can be run once per deployment at a specified time.
Procedure
Add the
commandparameters to thespecfield of theDeploymentConfigobject. You can also add anargsfield, which modifies thecommand(or theENTRYPOINTifcommanddoes not exist).spec: containers: - name: <container_name> image: 'image' command: - '<command>' args: - '<argument_1>' - '<argument_2>' - '<argument_3>'For example, to execute the
javacommand with the-jarand/opt/app-root/springboots2idemo.jararguments:spec: containers: - name: example-spring-boot image: 'image' command: - java args: - '-jar' - /opt/app-root/springboots2idemo.jar
7.3.1.6. Viewing deployment logs
Procedure
To stream the logs of the latest revision for a given
DeploymentConfigobject:$ oc logs -f dc/<name>
If the latest revision is running or failed, the command returns the logs of the process that is responsible for deploying your pods. If it is successful, it returns the logs from a pod of your application.
You can also view logs from older failed deployment processes, if and only if these processes (old replication controllers and their deployer pods) exist and have not been pruned or deleted manually:
$ oc logs --version=1 dc/<name>
7.3.1.7. Deployment triggers
A DeploymentConfig object can contain triggers, which drive the creation of new deployment processes in response to events inside the cluster.
If no triggers are defined on a DeploymentConfig object, a config change trigger is added by default. If triggers are defined as an empty field, deployments must be started manually.
Config change deployment triggers
The config change trigger results in a new replication controller whenever configuration changes are detected in the pod template of the DeploymentConfig object.
If a config change trigger is defined on a DeploymentConfig object, the first replication controller is automatically created soon after the DeploymentConfig object itself is created and it is not paused.
Config change deployment trigger
triggers: - type: "ConfigChange"
Image change deployment triggers
The image change trigger results in a new replication controller whenever the content of an image stream tag changes (when a new version of the image is pushed).
Image change deployment trigger
triggers:
- type: "ImageChange"
imageChangeParams:
automatic: true 1
from:
kind: "ImageStreamTag"
name: "origin-ruby-sample:latest"
namespace: "myproject"
containerNames:
- "helloworld"
- 1
- If the
imageChangeParams.automaticfield is set tofalse, the trigger is disabled.
With the above example, when the latest tag value of the origin-ruby-sample image stream changes and the new image value differs from the current image specified in the DeploymentConfig object’s helloworld container, a new replication controller is created using the new image for the helloworld container.
If an image change trigger is defined on a DeploymentConfig object (with a config change trigger and automatic=false, or with automatic=true) and the image stream tag pointed by the image change trigger does not exist yet, the initial deployment process will automatically start as soon as an image is imported or pushed by a build to the image stream tag.
7.3.1.7.1. Setting deployment triggers
Procedure
You can set deployment triggers for a
DeploymentConfigobject using theoc set triggerscommand. For example, to set a image change trigger, use the following command:$ oc set triggers dc/<dc_name> \ --from-image=<project>/<image>:<tag> -c <container_name>
7.3.1.8. Setting deployment resources
A deployment is completed by a pod that consumes resources (memory, CPU, and ephemeral storage) on a node. By default, pods consume unbounded node resources. However, if a project specifies default container limits, then pods consume resources up to those limits.
The minimum memory limit for a deployment is 12 MB. If a container fails to start due to a Cannot allocate memory pod event, the memory limit is too low. Either increase or remove the memory limit. Removing the limit allows pods to consume unbounded node resources.
You can also limit resource use by specifying resource limits as part of the deployment strategy. Deployment resources can be used with the recreate, rolling, or custom deployment strategies.
Procedure
In the following example, each of
resources,cpu,memory, andephemeral-storageis optional:type: "Recreate" resources: limits: cpu: "100m" 1 memory: "256Mi" 2 ephemeral-storage: "1Gi" 3However, if a quota has been defined for your project, one of the following two items is required:
A
resourcessection set with an explicitrequests:type: "Recreate" resources: requests: 1 cpu: "100m" memory: "256Mi" ephemeral-storage: "1Gi"- 1
- The
requestsobject contains the list of resources that correspond to the list of resources in the quota.
-
A limit range defined in your project, where the defaults from the
LimitRangeobject apply to pods created during the deployment process.
To set deployment resources, choose one of the above options. Otherwise, deploy pod creation fails, citing a failure to satisfy quota.
7.3.1.9. Scaling manually
In addition to rollbacks, you can exercise fine-grained control over the number of replicas by manually scaling them.
Pods can also be auto-scaled using the oc autoscale command.
Procedure
To manually scale a
DeploymentConfigobject, use theoc scalecommand. For example, the following command sets the replicas in thefrontendDeploymentConfigobject to3.$ oc scale dc frontend --replicas=3
The number of replicas eventually propagates to the desired and current state of the deployment configured by the
DeploymentConfigobjectfrontend.
7.3.1.10. Accessing private repositories from DeploymentConfig objects
You can add a secret to your DeploymentConfig object so that it can access images from a private repository. This procedure shows the OpenShift Dedicated web console method.
Procedure
- Create a new project.
- From the Workloads page, create a secret that contains credentials for accessing a private image repository.
-
Create a
DeploymentConfigobject. -
On the
DeploymentConfigobject editor page, set the Pull Secret and save your changes.
7.3.1.11. Running a pod with a different service account
You can run a pod with a service account other than the default.
Procedure
Edit the
DeploymentConfigobject:$ oc edit dc/<deployment_config>
Add the
serviceAccountandserviceAccountNameparameters to thespecfield, and specify the service account you want to use:spec: securityContext: {} serviceAccount: <service_account> serviceAccountName: <service_account>
7.4. Using deployment strategies
Deployment strategies are used to change or upgrade applications without downtime so that users barely notice a change.
Because users generally access applications through a route handled by a router, deployment strategies can focus on DeploymentConfig object features or routing features. Strategies that focus on DeploymentConfig object features impact all routes that use the application. Strategies that use router features target individual routes.
Most deployment strategies are supported through the DeploymentConfig object, and some additional strategies are supported through router features.
7.4.1. Choosing a deployment strategy
Consider the following when choosing a deployment strategy:
- Long-running connections must be handled gracefully.
- Database conversions can be complex and must be done and rolled back along with the application.
- If the application is a hybrid of microservices and traditional components, downtime might be required to complete the transition.
- You must have the infrastructure to do this.
- If you have a non-isolated test environment, you can break both new and old versions.
A deployment strategy uses readiness checks to determine if a new pod is ready for use. If a readiness check fails, the DeploymentConfig object retries to run the pod until it times out. The default timeout is 10m, a value set in TimeoutSeconds in dc.spec.strategy.*params.
7.4.2. Rolling strategy
A rolling deployment slowly replaces instances of the previous version of an application with instances of the new version of the application. The rolling strategy is the default deployment strategy used if no strategy is specified on a DeploymentConfig object.
A rolling deployment typically waits for new pods to become ready via a readiness check before scaling down the old components. If a significant issue occurs, the rolling deployment can be aborted.
When to use a rolling deployment:
- When you want to take no downtime during an application update.
- When your application supports having old code and new code running at the same time.
A rolling deployment means you have both old and new versions of your code running at the same time. This typically requires that your application handle N-1 compatibility.
Example rolling strategy definition
strategy:
type: Rolling
rollingParams:
updatePeriodSeconds: 1 1
intervalSeconds: 1 2
timeoutSeconds: 120 3
maxSurge: "20%" 4
maxUnavailable: "10%" 5
pre: {} 6
post: {}
- 1
- The time to wait between individual pod updates. If unspecified, this value defaults to
1. - 2
- The time to wait between polling the deployment status after update. If unspecified, this value defaults to
1. - 3
- The time to wait for a scaling event before giving up. Optional; the default is
600. Here, giving up means automatically rolling back to the previous complete deployment. - 4
maxSurgeis optional and defaults to25%if not specified. See the information below the following procedure.- 5
maxUnavailableis optional and defaults to25%if not specified. See the information below the following procedure.- 6
preandpostare both lifecycle hooks.
The rolling strategy:
-
Executes any
prelifecycle hook. - Scales up the new replication controller based on the surge count.
- Scales down the old replication controller based on the max unavailable count.
- Repeats this scaling until the new replication controller has reached the desired replica count and the old replication controller has been scaled to zero.
-
Executes any
postlifecycle hook.
When scaling down, the rolling strategy waits for pods to become ready so it can decide whether further scaling would affect availability. If scaled up pods never become ready, the deployment process will eventually time out and result in a deployment failure.
The maxUnavailable parameter is the maximum number of pods that can be unavailable during the update. The maxSurge parameter is the maximum number of pods that can be scheduled above the original number of pods. Both parameters can be set to either a percentage (e.g., 10%) or an absolute value (e.g., 2). The default value for both is 25%.
These parameters allow the deployment to be tuned for availability and speed. For example:
-
maxUnavailable*=0andmaxSurge*=20%ensures full capacity is maintained during the update and rapid scale up. -
maxUnavailable*=10%andmaxSurge*=0performs an update using no extra capacity (an in-place update). -
maxUnavailable*=10%andmaxSurge*=10%scales up and down quickly with some potential for capacity loss.
Generally, if you want fast rollouts, use maxSurge. If you have to take into account resource quota and can accept partial unavailability, use maxUnavailable.
7.4.2.1. Canary deployments
All rolling deployments in OpenShift Dedicated are canary deployments; a new version (the canary) is tested before all of the old instances are replaced. If the readiness check never succeeds, the canary instance is removed and the DeploymentConfig object will be automatically rolled back.
The readiness check is part of the application code and can be as sophisticated as necessary to ensure the new instance is ready to be used. If you must implement more complex checks of the application (such as sending real user workloads to the new instance), consider implementing a custom deployment or using a blue-green deployment strategy.
7.4.2.2. Creating a rolling deployment
Rolling deployments are the default type in OpenShift Dedicated. You can create a rolling deployment using the CLI.
Procedure
Create an application based on the example deployment images found in Quay.io:
$ oc new-app quay.io/openshifttest/deployment-example:latest
If you have the router installed, make the application available via a route or use the service IP directly.
$ oc expose svc/deployment-example
-
Browse to the application at
deployment-example.<project>.<router_domain>to verify you see thev1image. Scale the
DeploymentConfigobject up to three replicas:$ oc scale dc/deployment-example --replicas=3
Trigger a new deployment automatically by tagging a new version of the example as the
latesttag:$ oc tag deployment-example:v2 deployment-example:latest
-
In your browser, refresh the page until you see the
v2image. When using the CLI, the following command shows how many pods are on version 1 and how many are on version 2. In the web console, the pods are progressively added to v2 and removed from v1:
$ oc describe dc deployment-example
During the deployment process, the new replication controller is incrementally scaled up. After the new pods are marked as ready (by passing their readiness check), the deployment process continues.
If the pods do not become ready, the process aborts, and the deployment rolls back to its previous version.
7.4.2.3. Editing a deployment by using the Developer perspective
You can edit the deployment strategy, image settings, environment variables, and advanced options for your deployment by using the Developer perspective.
Prerequisites
- You are in the Developer perspective of the web console.
- You have created an application.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Topology view. Click on your application to see the Details panel.
- In the Actions drop-down menu, select Edit Deployment to view the Edit Deployment page.
You can edit the following Advanced options for your deployment:
Optional: You can pause rollouts by clicking Pause rollouts, and then selecting the Pause rollouts for this deployment checkbox.
By pausing rollouts, you can make changes to your application without triggering a rollout. You can resume rollouts at any time.
- Optional: Click Scaling to change the number of instances of your image by modifying the number of Replicas.
- Click Save.
7.4.2.4. Starting a rolling deployment using the Developer perspective
You can upgrade an application by starting a rolling deployment.
Prerequisites
- You are in the Developer perspective of the web console.
- You have created an application.
Procedure
- In the Topology view of the Developer perspective, click on the application node to see the Overview tab in the side panel. Note that the Update Strategy is set to the default Rolling strategy.
In the Actions drop-down menu, select Start Rollout to start a rolling update. The rolling deployment spins up the new version of the application and then terminates the old one.
Figure 7.1. Rolling update

7.4.3. Recreate strategy
The recreate strategy has basic rollout behavior and supports lifecycle hooks for injecting code into the deployment process.
Example recreate strategy definition
strategy: type: Recreate recreateParams: 1 pre: {} 2 mid: {} post: {}
The recreate strategy:
-
Executes any
prelifecycle hook. - Scales down the previous deployment to zero.
-
Executes any
midlifecycle hook. - Scales up the new deployment.
-
Executes any
postlifecycle hook.
During scale up, if the replica count of the deployment is greater than one, the first replica of the deployment will be validated for readiness before fully scaling up the deployment. If the validation of the first replica fails, the deployment will be considered a failure.
When to use a recreate deployment:
- When you must run migrations or other data transformations before your new code starts.
- When you do not support having new and old versions of your application code running at the same time.
- When you want to use a RWO volume, which is not supported being shared between multiple replicas.
A recreate deployment incurs downtime because, for a brief period, no instances of your application are running. However, your old code and new code do not run at the same time.
7.4.3.1. Editing a deployment by using the Developer perspective
You can edit the deployment strategy, image settings, environment variables, and advanced options for your deployment by using the Developer perspective.
Prerequisites
- You are in the Developer perspective of the web console.
- You have created an application.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Topology view. Click on your application to see the Details panel.
- In the Actions drop-down menu, select Edit Deployment to view the Edit Deployment page.
You can edit the following Advanced options for your deployment:
Optional: You can pause rollouts by clicking Pause rollouts, and then selecting the Pause rollouts for this deployment checkbox.
By pausing rollouts, you can make changes to your application without triggering a rollout. You can resume rollouts at any time.
- Optional: Click Scaling to change the number of instances of your image by modifying the number of Replicas.
- Click Save.
7.4.3.2. Starting a recreate deployment using the Developer perspective
You can switch the deployment strategy from the default rolling update to a recreate update using the Developer perspective in the web console.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you are in the Developer perspective of the web console.
- Ensure that you have created an application using the Add view and see it deployed in the Topology view.
Procedure
To switch to a recreate update strategy and to upgrade an application:
- In the Actions drop-down menu, select Edit Deployment Config to see the deployment configuration details of the application.
-
In the YAML editor, change the
spec.strategy.typetoRecreateand click Save. - In the Topology view, select the node to see the Overview tab in the side panel. The Update Strategy is now set to Recreate.
Use the Actions drop-down menu to select Start Rollout to start an update using the recreate strategy. The recreate strategy first terminates pods for the older version of the application and then spins up pods for the new version.
Figure 7.2. Recreate update
7.4.4. Custom strategy
The custom strategy allows you to provide your own deployment behavior.
Example custom strategy definition
strategy:
type: Custom
customParams:
image: organization/strategy
command: [ "command", "arg1" ]
environment:
- name: ENV_1
value: VALUE_1
In the above example, the organization/strategy container image provides the deployment behavior. The optional command array overrides any CMD directive specified in the image’s Dockerfile. The optional environment variables provided are added to the execution environment of the strategy process.
Additionally, OpenShift Dedicated provides the following environment variables to the deployment process:
| Environment variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The name of the new deployment, a replication controller. |
|
| The name space of the new deployment. |
The replica count of the new deployment will initially be zero. The responsibility of the strategy is to make the new deployment active using the logic that best serves the needs of the user.
Alternatively, use the customParams object to inject the custom deployment logic into the existing deployment strategies. Provide a custom shell script logic and call the openshift-deploy binary. Users do not have to supply their custom deployer container image; in this case, the default OpenShift Dedicated deployer image is used instead:
strategy:
type: Rolling
customParams:
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- |
set -e
openshift-deploy --until=50%
echo Halfway there
openshift-deploy
echo CompleteThis results in following deployment:
Started deployment #2
--> Scaling up custom-deployment-2 from 0 to 2, scaling down custom-deployment-1 from 2 to 0 (keep 2 pods available, don't exceed 3 pods)
Scaling custom-deployment-2 up to 1
--> Reached 50% (currently 50%)
Halfway there
--> Scaling up custom-deployment-2 from 1 to 2, scaling down custom-deployment-1 from 2 to 0 (keep 2 pods available, don't exceed 3 pods)
Scaling custom-deployment-1 down to 1
Scaling custom-deployment-2 up to 2
Scaling custom-deployment-1 down to 0
--> Success
CompleteIf the custom deployment strategy process requires access to the OpenShift Dedicated API or the Kubernetes API the container that executes the strategy can use the service account token available inside the container for authentication.
7.4.4.1. Editing a deployment by using the Developer perspective
You can edit the deployment strategy, image settings, environment variables, and advanced options for your deployment by using the Developer perspective.
Prerequisites
- You are in the Developer perspective of the web console.
- You have created an application.
Procedure
- Navigate to the Topology view. Click on your application to see the Details panel.
- In the Actions drop-down menu, select Edit Deployment to view the Edit Deployment page.
You can edit the following Advanced options for your deployment:
Optional: You can pause rollouts by clicking Pause rollouts, and then selecting the Pause rollouts for this deployment checkbox.
By pausing rollouts, you can make changes to your application without triggering a rollout. You can resume rollouts at any time.
- Optional: Click Scaling to change the number of instances of your image by modifying the number of Replicas.
- Click Save.
7.4.5. Lifecycle hooks
The rolling and recreate strategies support lifecycle hooks, or deployment hooks, which allow behavior to be injected into the deployment process at predefined points within the strategy:
Example pre lifecycle hook
pre:
failurePolicy: Abort
execNewPod: {} 1
- 1
execNewPodis a pod-based lifecycle hook.
Every hook has a failure policy, which defines the action the strategy should take when a hook failure is encountered:
|
| The deployment process will be considered a failure if the hook fails. |
|
| The hook execution should be retried until it succeeds. |
|
| Any hook failure should be ignored and the deployment should proceed. |
Hooks have a type-specific field that describes how to execute the hook. Currently, pod-based hooks are the only supported hook type, specified by the execNewPod field.
Pod-based lifecycle hook
Pod-based lifecycle hooks execute hook code in a new pod derived from the template in a DeploymentConfig object.
The following simplified example deployment uses the rolling strategy. Triggers and some other minor details are omitted for brevity:
kind: DeploymentConfig
apiVersion: apps.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: frontend
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: helloworld
image: openshift/origin-ruby-sample
replicas: 5
selector:
name: frontend
strategy:
type: Rolling
rollingParams:
pre:
failurePolicy: Abort
execNewPod:
containerName: helloworld 1
command: [ "/usr/bin/command", "arg1", "arg2" ] 2
env: 3
- name: CUSTOM_VAR1
value: custom_value1
volumes:
- data 4- 1
- The
helloworldname refers tospec.template.spec.containers[0].name. - 2
- This
commandoverrides anyENTRYPOINTdefined by theopenshift/origin-ruby-sampleimage. - 3
envis an optional set of environment variables for the hook container.- 4
volumesis an optional set of volume references for the hook container.
In this example, the pre hook will be executed in a new pod using the openshift/origin-ruby-sample image from the helloworld container. The hook pod has the following properties:
-
The hook command is
/usr/bin/command arg1 arg2. -
The hook container has the
CUSTOM_VAR1=custom_value1environment variable. -
The hook failure policy is
Abort, meaning the deployment process fails if the hook fails. -
The hook pod inherits the
datavolume from theDeploymentConfigobject pod.
7.4.5.1. Setting lifecycle hooks
You can set lifecycle hooks, or deployment hooks, for a deployment using the CLI.
Procedure
Use the
oc set deployment-hookcommand to set the type of hook you want:--pre,--mid, or--post. For example, to set a pre-deployment hook:$ oc set deployment-hook dc/frontend \ --pre -c helloworld -e CUSTOM_VAR1=custom_value1 \ --volumes data --failure-policy=abort -- /usr/bin/command arg1 arg2
7.5. Using route-based deployment strategies
Deployment strategies provide a way for the application to evolve. Some strategies use Deployment objects to make changes that are seen by users of all routes that resolve to the application. Other advanced strategies, such as the ones described in this section, use router features in conjunction with Deployment objects to impact specific routes.
The most common route-based strategy is to use a blue-green deployment. The new version (the green version) is brought up for testing and evaluation, while the users still use the stable version (the blue version). When ready, the users are switched to the green version. If a problem arises, you can switch back to the blue version.
A common alternative strategy is to use A/B versions that are both active at the same time and some users use one version, and some users use the other version. This can be used for experimenting with user interface changes and other features to get user feedback. It can also be used to verify proper operation in a production context where problems impact a limited number of users.
A canary deployment tests the new version but when a problem is detected it quickly falls back to the previous version. This can be done with both of the above strategies.
The route-based deployment strategies do not scale the number of pods in the services. To maintain desired performance characteristics the deployment configurations might have to be scaled.
7.5.1. Proxy shards and traffic splitting
In production environments, you can precisely control the distribution of traffic that lands on a particular shard. When dealing with large numbers of instances, you can use the relative scale of individual shards to implement percentage based traffic. That combines well with a proxy shard, which forwards or splits the traffic it receives to a separate service or application running elsewhere.
In the simplest configuration, the proxy forwards requests unchanged. In more complex setups, you can duplicate the incoming requests and send to both a separate cluster as well as to a local instance of the application, and compare the result. Other patterns include keeping the caches of a DR installation warm, or sampling incoming traffic for analysis purposes.
Any TCP (or UDP) proxy could be run under the desired shard. Use the oc scale command to alter the relative number of instances serving requests under the proxy shard. For more complex traffic management, consider customizing the OpenShift Dedicated router with proportional balancing capabilities.
7.5.2. N-1 compatibility
Applications that have new code and old code running at the same time must be careful to ensure that data written by the new code can be read and handled (or gracefully ignored) by the old version of the code. This is sometimes called schema evolution and is a complex problem.
This can take many forms: data stored on disk, in a database, in a temporary cache, or that is part of a user’s browser session. While most web applications can support rolling deployments, it is important to test and design your application to handle it.
For some applications, the period of time that old code and new code is running side by side is short, so bugs or some failed user transactions are acceptable. For others, the failure pattern may result in the entire application becoming non-functional.
One way to validate N-1 compatibility is to use an A/B deployment: run the old code and new code at the same time in a controlled way in a test environment, and verify that traffic that flows to the new deployment does not cause failures in the old deployment.
7.5.3. Graceful termination
OpenShift Dedicated and Kubernetes give application instances time to shut down before removing them from load balancing rotations. However, applications must ensure they cleanly terminate user connections as well before they exit.
On shutdown, OpenShift Dedicated sends a TERM signal to the processes in the container. Application code, on receiving SIGTERM, stop accepting new connections. This ensures that load balancers route traffic to other active instances. The application code then waits until all open connections are closed, or gracefully terminate individual connections at the next opportunity, before exiting.
After the graceful termination period expires, a process that has not exited is sent the KILL signal, which immediately ends the process. The terminationGracePeriodSeconds attribute of a pod or pod template controls the graceful termination period (default 30 seconds) and can be customized per application as necessary.
7.5.4. Blue-green deployments
Blue-green deployments involve running two versions of an application at the same time and moving traffic from the in-production version (the blue version) to the newer version (the green version). You can use a rolling strategy or switch services in a route.
Because many applications depend on persistent data, you must have an application that supports N-1 compatibility, which means it shares data and implements live migration between the database, store, or disk by creating two copies of the data layer.
Consider the data used in testing the new version. If it is the production data, a bug in the new version can break the production version.
7.5.4.1. Setting up a blue-green deployment
Blue-green deployments use two Deployment objects. Both are running, and the one in production depends on the service the route specifies, with each Deployment object exposed to a different service.
Routes are intended for web (HTTP and HTTPS) traffic, so this technique is best suited for web applications.
You can create a new route to the new version and test it. When ready, change the service in the production route to point to the new service and the new (green) version is live.
If necessary, you can roll back to the older (blue) version by switching the service back to the previous version.
Procedure
Create two independent application components.
Create a copy of the example application running the
v1image under theexample-blueservice:$ oc new-app openshift/deployment-example:v1 --name=example-blue
Create a second copy that uses the
v2image under theexample-greenservice:$ oc new-app openshift/deployment-example:v2 --name=example-green
Create a route that points to the old service:
$ oc expose svc/example-blue --name=bluegreen-example
-
Browse to the application at
bluegreen-example-<project>.<router_domain>to verify you see thev1image. Edit the route and change the service name to
example-green:$ oc patch route/bluegreen-example -p '{"spec":{"to":{"name":"example-green"}}}'-
To verify that the route has changed, refresh the browser until you see the
v2image.
7.5.5. A/B deployments
The A/B deployment strategy lets you try a new version of the application in a limited way in the production environment. You can specify that the production version gets most of the user requests while a limited fraction of requests go to the new version.
Because you control the portion of requests to each version, as testing progresses you can increase the fraction of requests to the new version and ultimately stop using the previous version. As you adjust the request load on each version, the number of pods in each service might have to be scaled as well to provide the expected performance.
In addition to upgrading software, you can use this feature to experiment with versions of the user interface. Since some users get the old version and some the new, you can evaluate the user’s reaction to the different versions to inform design decisions.
For this to be effective, both the old and new versions must be similar enough that both can run at the same time. This is common with bug fix releases and when new features do not interfere with the old. The versions require N-1 compatibility to properly work together.
OpenShift Dedicated supports N-1 compatibility through the web console as well as the CLI.
7.5.5.1. Load balancing for A/B testing
The user sets up a route with multiple services. Each service handles a version of the application.
Each service is assigned a weight and the portion of requests to each service is the service_weight divided by the sum_of_weights. The weight for each service is distributed to the service’s endpoints so that the sum of the endpoint weights is the service weight.
The route can have up to four services. The weight for the service can be between 0 and 256. When the weight is 0, the service does not participate in load-balancing but continues to serve existing persistent connections. When the service weight is not 0, each endpoint has a minimum weight of 1. Because of this, a service with a lot of endpoints can end up with higher weight than intended. In this case, reduce the number of pods to get the expected load balance weight.
Procedure
To set up the A/B environment:
Create the two applications and give them different names. Each creates a
Deploymentobject. The applications are versions of the same program; one is usually the current production version and the other the proposed new version.Create the first application. The following example creates an application called
ab-example-a:$ oc new-app openshift/deployment-example --name=ab-example-a
Create the second application:
$ oc new-app openshift/deployment-example:v2 --name=ab-example-b
Both applications are deployed and services are created.
Make the application available externally via a route. At this point, you can expose either. It can be convenient to expose the current production version first and later modify the route to add the new version.
$ oc expose svc/ab-example-a
Browse to the application at
ab-example-a.<project>.<router_domain>to verify that you see the expected version.When you deploy the route, the router balances the traffic according to the
weightsspecified for the services. At this point, there is a single service with defaultweight=1so all requests go to it. Adding the other service as analternateBackendsand adjusting theweightsbrings the A/B setup to life. This can be done by theoc set route-backendscommand or by editing the route.NoteWhen using
alternateBackends, also use theroundrobinload-balancing strategy to ensure requests are distributed as expected to the services based on weight.roundrobincan be set for a route by using a route annotation.Setting the
oc set route-backendto0means the service does not participate in load-balancing, but continues to serve existing persistent connections.NoteChanges to the route just change the portion of traffic to the various services. You might have to scale the deployment to adjust the number of pods to handle the anticipated loads.
To edit the route, run:
$ oc edit route <route_name>
Example output
... metadata: name: route-alternate-service annotations: haproxy.router.openshift.io/balance: roundrobin spec: host: ab-example.my-project.my-domain to: kind: Service name: ab-example-a weight: 10 alternateBackends: - kind: Service name: ab-example-b weight: 15 ...
7.5.5.1.1. Managing weights of an existing route using the web console
Procedure
- Navigate to the Networking → Routes page.
-
Click the Actions menu
 next to the route you want to edit and select Edit Route.
next to the route you want to edit and select Edit Route.
-
Edit the YAML file. Update the
weightto be an integer between0and256that specifies the relative weight of the target against other target reference objects. The value0suppresses requests to this back end. The default is100. Runoc explain routes.spec.alternateBackendsfor more information about the options. - Click Save.
7.5.5.1.2. Managing weights of an new route using the web console
- Navigate to the Networking → Routes page.
- Click Create Route.
- Enter the route Name.
- Select the Service.
- Click Add Alternate Service.
-
Enter a value for Weight and Alternate Service Weight. Enter a number between
0and255that depicts relative weight compared with other targets. The default is100. - Select the Target Port.
- Click Create.
7.5.5.1.3. Managing weights using the CLI
Procedure
To manage the services and corresponding weights load balanced by the route, use the
oc set route-backendscommand:$ oc set route-backends ROUTENAME \ [--zero|--equal] [--adjust] SERVICE=WEIGHT[%] [...] [options]For example, the following sets
ab-example-aas the primary service withweight=198andab-example-bas the first alternate service with aweight=2:$ oc set route-backends ab-example ab-example-a=198 ab-example-b=2
This means 99% of traffic is sent to service
ab-example-aand 1% to serviceab-example-b.This command does not scale the deployment. You might be required to do so to have enough pods to handle the request load.
Run the command with no flags to verify the current configuration:
$ oc set route-backends ab-example
Example output
NAME KIND TO WEIGHT routes/ab-example Service ab-example-a 198 (99%) routes/ab-example Service ab-example-b 2 (1%)
To alter the weight of an individual service relative to itself or to the primary service, use the
--adjustflag. Specifying a percentage adjusts the service relative to either the primary or the first alternate (if you specify the primary). If there are other backends, their weights are kept proportional to the changed.The following example alters the weight of
ab-example-aandab-example-bservices:$ oc set route-backends ab-example --adjust ab-example-a=200 ab-example-b=10
Alternatively, alter the weight of a service by specifying a percentage:
$ oc set route-backends ab-example --adjust ab-example-b=5%
By specifying
+before the percentage declaration, you can adjust a weighting relative to the current setting. For example:$ oc set route-backends ab-example --adjust ab-example-b=+15%
The
--equalflag sets theweightof all services to100:$ oc set route-backends ab-example --equal
The
--zeroflag sets theweightof all services to0. All requests then return with a 503 error.NoteNot all routers may support multiple or weighted backends.
7.5.5.1.4. One service, multiple Deployment objects
Procedure
Create a new application, adding a label
ab-example=truethat will be common to all shards:$ oc new-app openshift/deployment-example --name=ab-example-a --as-deployment-config=true --labels=ab-example=true --env=SUBTITLE\=shardA $ oc delete svc/ab-example-a
The application is deployed and a service is created. This is the first shard.
Make the application available via a route, or use the service IP directly:
$ oc expose deployment ab-example-a --name=ab-example --selector=ab-example\=true $ oc expose service ab-example
-
Browse to the application at
ab-example-<project_name>.<router_domain>to verify you see thev1image. Create a second shard based on the same source image and label as the first shard, but with a different tagged version and unique environment variables:
$ oc new-app openshift/deployment-example:v2 \ --name=ab-example-b --labels=ab-example=true \ SUBTITLE="shard B" COLOR="red" --as-deployment-config=true $ oc delete svc/ab-example-bAt this point, both sets of pods are being served under the route. However, because both browsers (by leaving a connection open) and the router (by default, through a cookie) attempt to preserve your connection to a back-end server, you might not see both shards being returned to you.
To force your browser to one or the other shard:
Use the
oc scalecommand to reduce replicas ofab-example-ato0.$ oc scale dc/ab-example-a --replicas=0
Refresh your browser to show
v2andshard B(in red).Scale
ab-example-ato1replica andab-example-bto0:$ oc scale dc/ab-example-a --replicas=1; oc scale dc/ab-example-b --replicas=0
Refresh your browser to show
v1andshard A(in blue).
If you trigger a deployment on either shard, only the pods in that shard are affected. You can trigger a deployment by changing the
SUBTITLEenvironment variable in eitherDeploymentobject:$ oc edit dc/ab-example-a
or
$ oc edit dc/ab-example-b
Chapter 8. Quotas
8.1. Resource quotas per project
A resource quota, defined by a ResourceQuota object, provides constraints that limit aggregate resource consumption per project. It can limit the quantity of objects that can be created in a project by type, as well as the total amount of compute resources and storage that might be consumed by resources in that project.
This guide describes how resource quotas work, how cluster administrators can set and manage resource quotas on a per project basis, and how developers and cluster administrators can view them.
8.1.1. Resources managed by quotas
The following describes the set of compute resources and object types that can be managed by a quota.
A pod is in a terminal state if status.phase in (Failed, Succeeded) is true.
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The sum of CPU requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of memory requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of CPU requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of memory requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The sum of CPU limits across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The sum of memory limits across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The sum of storage requests across all persistent volume claims in any state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The total number of persistent volume claims that can exist in the project. |
|
| The sum of storage requests across all persistent volume claims in any state that have a matching storage class, cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The total number of persistent volume claims with a matching storage class that can exist in the project. |
|
|
The sum of local ephemeral storage requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of ephemeral storage requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The sum of ephemeral storage limits across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The total number of pods in a non-terminal state that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of ReplicationControllers that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of resource quotas that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of services that can exist in the project. |
|
|
The total number of services of type |
|
|
The total number of services of type |
|
| The total number of secrets that can exist in the project. |
|
|
The total number of |
|
| The total number of persistent volume claims that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of imagestreams that can exist in the project. |
8.1.2. Quota scopes
Each quota can have an associated set of scopes. A quota only measures usage for a resource if it matches the intersection of enumerated scopes.
Adding a scope to a quota restricts the set of resources to which that quota can apply. Specifying a resource outside of the allowed set results in a validation error.
| Scope | Description |
|
|
Match pods that have best effort quality of service for either |
|
|
Match pods that do not have best effort quality of service for |
A BestEffort scope restricts a quota to limiting the following resources:
-
pods
A NotBestEffort scope restricts a quota to tracking the following resources:
-
pods -
memory -
requests.memory -
limits.memory -
cpu -
requests.cpu -
limits.cpu
8.1.3. Quota enforcement
After a resource quota for a project is first created, the project restricts the ability to create any new resources that may violate a quota constraint until it has calculated updated usage statistics.
After a quota is created and usage statistics are updated, the project accepts the creation of new content. When you create or modify resources, your quota usage is incremented immediately upon the request to create or modify the resource.
When you delete a resource, your quota use is decremented during the next full recalculation of quota statistics for the project. A configurable amount of time determines how long it takes to reduce quota usage statistics to their current observed system value.
If project modifications exceed a quota usage limit, the server denies the action, and an appropriate error message is returned to the user explaining the quota constraint violated, and what their currently observed usage statistics are in the system.
8.1.4. Requests versus limits
When allocating compute resources, each container might specify a request and a limit value each for CPU, memory, and ephemeral storage. Quotas can restrict any of these values.
If the quota has a value specified for requests.cpu or requests.memory, then it requires that every incoming container make an explicit request for those resources. If the quota has a value specified for limits.cpu or limits.memory, then it requires that every incoming container specify an explicit limit for those resources.
8.1.5. Sample resource quota definitions
core-object-counts.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: core-object-counts
spec:
hard:
configmaps: "10" 1
persistentvolumeclaims: "4" 2
replicationcontrollers: "20" 3
secrets: "10" 4
services: "10" 5
services.loadbalancers: "2" 6
- 1
- The total number of
ConfigMapobjects that can exist in the project. - 2
- The total number of persistent volume claims (PVCs) that can exist in the project.
- 3
- The total number of replication controllers that can exist in the project.
- 4
- The total number of secrets that can exist in the project.
- 5
- The total number of services that can exist in the project.
- 6
- The total number of services of type
LoadBalancerthat can exist in the project.
openshift-object-counts.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: openshift-object-counts
spec:
hard:
openshift.io/imagestreams: "10" 1
- 1
- The total number of image streams that can exist in the project.
compute-resources.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: compute-resources
spec:
hard:
pods: "4" 1
requests.cpu: "1" 2
requests.memory: 1Gi 3
limits.cpu: "2" 4
limits.memory: 2Gi 5
- 1
- The total number of pods in a non-terminal state that can exist in the project.
- 2
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of CPU requests cannot exceed 1 core.
- 3
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory requests cannot exceed 1Gi.
- 4
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of CPU limits cannot exceed 2 cores.
- 5
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory limits cannot exceed 2Gi.
besteffort.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: besteffort
spec:
hard:
pods: "1" 1
scopes:
- BestEffort 2
compute-resources-long-running.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: compute-resources-long-running
spec:
hard:
pods: "4" 1
limits.cpu: "4" 2
limits.memory: "2Gi" 3
scopes:
- NotTerminating 4
- 1
- The total number of pods in a non-terminal state.
- 2
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of CPU limits cannot exceed this value.
- 3
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory limits cannot exceed this value.
- 4
- Restricts the quota to only matching pods where
spec.activeDeadlineSecondsis set tonil. Build pods fall underNotTerminatingunless theRestartNeverpolicy is applied.
compute-resources-time-bound.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: compute-resources-time-bound
spec:
hard:
pods: "2" 1
limits.cpu: "1" 2
limits.memory: "1Gi" 3
scopes:
- Terminating 4
- 1
- The total number of pods in a terminating state.
- 2
- Across all pods in a terminating state, the sum of CPU limits cannot exceed this value.
- 3
- Across all pods in a terminating state, the sum of memory limits cannot exceed this value.
- 4
- Restricts the quota to only matching pods where
spec.activeDeadlineSeconds >=0. For example, this quota charges for build or deployer pods, but not long running pods like a web server or database.
storage-consumption.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: storage-consumption
spec:
hard:
persistentvolumeclaims: "10" 1
requests.storage: "50Gi" 2
gold.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "10Gi" 3
silver.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "20Gi" 4
silver.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/persistentvolumeclaims: "5" 5
bronze.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "0" 6
bronze.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/persistentvolumeclaims: "0" 7
requests.ephemeral-storage: 2Gi 8
limits.ephemeral-storage: 4Gi 9
- 1
- The total number of persistent volume claims in a project
- 2
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested cannot exceed this value.
- 3
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the gold storage class cannot exceed this value.
- 4
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the silver storage class cannot exceed this value.
- 5
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the total number of claims in the silver storage class cannot exceed this value.
- 6
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the bronze storage class cannot exceed this value. When this is set to
0, it means bronze storage class cannot request storage. - 7
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the bronze storage class cannot exceed this value. When this is set to
0, it means bronze storage class cannot create claims. - 8
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of ephemeral storage requests cannot exceed 2Gi.
- 9
- Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of ephemeral storage limits cannot exceed 4Gi.
8.1.6. Creating a quota
You can create a quota to constrain resource usage in a given project.
Procedure
- Define the quota in a file.
Use the file to create the quota and apply it to a project:
$ oc create -f <file> [-n <project_name>]
For example:
$ oc create -f core-object-counts.yaml -n demoproject
8.1.6.1. Creating object count quotas
You can create an object count quota for all standard namespaced resource types on OpenShift Dedicated, such as BuildConfig and DeploymentConfig objects. An object quota count places a defined quota on all standard namespaced resource types.
When using a resource quota, an object is charged against the quota upon creation. These types of quotas are useful to protect against exhaustion of resources. The quota can only be created if there are enough spare resources within the project.
Procedure
To configure an object count quota for a resource:
Run the following command:
$ oc create quota <name> \ --hard=count/<resource>.<group>=<quota>,count/<resource>.<group>=<quota> 1- 1
- The
<resource>variable is the name of the resource, and<group>is the API group, if applicable. Use theoc api-resourcescommand for a list of resources and their associated API groups.
For example:
$ oc create quota test \ --hard=count/deployments.extensions=2,count/replicasets.extensions=4,count/pods=3,count/secrets=4Example output
resourcequota "test" created
This example limits the listed resources to the hard limit in each project in the cluster.
Verify that the quota was created:
$ oc describe quota test
Example output
Name: test Namespace: quota Resource Used Hard -------- ---- ---- count/deployments.extensions 0 2 count/pods 0 3 count/replicasets.extensions 0 4 count/secrets 0 4
8.1.6.2. Setting resource quota for extended resources
Overcommitment of resources is not allowed for extended resources, so you must specify requests and limits for the same extended resource in a quota. Currently, only quota items with the prefix requests. is allowed for extended resources. The following is an example scenario of how to set resource quota for the GPU resource nvidia.com/gpu.
Procedure
Determine how many GPUs are available on a node in your cluster. For example:
# oc describe node ip-172-31-27-209.us-west-2.compute.internal | egrep 'Capacity|Allocatable|gpu'
Example output
openshift.com/gpu-accelerator=true Capacity: nvidia.com/gpu: 2 Allocatable: nvidia.com/gpu: 2 nvidia.com/gpu 0 0
In this example, 2 GPUs are available.
Set a quota in the namespace
nvidia. In this example, the quota is1:# cat gpu-quota.yaml
Example output
apiVersion: v1 kind: ResourceQuota metadata: name: gpu-quota namespace: nvidia spec: hard: requests.nvidia.com/gpu: 1Create the quota:
# oc create -f gpu-quota.yaml
Example output
resourcequota/gpu-quota created
Verify that the namespace has the correct quota set:
# oc describe quota gpu-quota -n nvidia
Example output
Name: gpu-quota Namespace: nvidia Resource Used Hard -------- ---- ---- requests.nvidia.com/gpu 0 1
Define a pod that asks for a single GPU. The following example definition file is called
gpu-pod.yaml:apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: generateName: gpu-pod- namespace: nvidia spec: restartPolicy: OnFailure containers: - name: rhel7-gpu-pod image: rhel7 env: - name: NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES value: all - name: NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES value: "compute,utility" - name: NVIDIA_REQUIRE_CUDA value: "cuda>=5.0" command: ["sleep"] args: ["infinity"] resources: limits: nvidia.com/gpu: 1Create the pod:
# oc create -f gpu-pod.yaml
Verify that the pod is running:
# oc get pods
Example output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE gpu-pod-s46h7 1/1 Running 0 1m
Verify that the quota
Usedcounter is correct:# oc describe quota gpu-quota -n nvidia
Example output
Name: gpu-quota Namespace: nvidia Resource Used Hard -------- ---- ---- requests.nvidia.com/gpu 1 1
Attempt to create a second GPU pod in the
nvidianamespace. This is technically available on the node because it has 2 GPUs:# oc create -f gpu-pod.yaml
Example output
Error from server (Forbidden): error when creating "gpu-pod.yaml": pods "gpu-pod-f7z2w" is forbidden: exceeded quota: gpu-quota, requested: requests.nvidia.com/gpu=1, used: requests.nvidia.com/gpu=1, limited: requests.nvidia.com/gpu=1
This Forbidden error message is expected because you have a quota of 1 GPU and this pod tried to allocate a second GPU, which exceeds its quota.
8.1.7. Viewing a quota
You can view usage statistics related to any hard limits defined in a project’s quota by navigating in the web console to the project’s Quota page.
You can also use the CLI to view quota details.
Procedure
Get the list of quotas defined in the project. For example, for a project called
demoproject:$ oc get quota -n demoproject
Example output
NAME AGE besteffort 11m compute-resources 2m core-object-counts 29m
Describe the quota you are interested in, for example the
core-object-countsquota:$ oc describe quota core-object-counts -n demoproject
Example output
Name: core-object-counts Namespace: demoproject Resource Used Hard -------- ---- ---- configmaps 3 10 persistentvolumeclaims 0 4 replicationcontrollers 3 20 secrets 9 10 services 2 10
8.1.8. Configuring explicit resource quotas
Configure explicit resource quotas in a project request template to apply specific resource quotas in new projects.
Prerequisites
- Access to the cluster as a user with the cluster-admin role.
-
Install the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
Add a resource quota definition to a project request template:
If a project request template does not exist in a cluster:
Create a bootstrap project template and output it to a file called
template.yaml:$ oc adm create-bootstrap-project-template -o yaml > template.yaml
Add a resource quota definition to
template.yaml. The following example defines a resource quota named 'storage-consumption'. The definition must be added before theparameters:section in the template:- apiVersion: v1 kind: ResourceQuota metadata: name: storage-consumption namespace: ${PROJECT_NAME} spec: hard: persistentvolumeclaims: "10" 1 requests.storage: "50Gi" 2 gold.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "10Gi" 3 silver.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "20Gi" 4 silver.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/persistentvolumeclaims: "5" 5 bronze.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "0" 6 bronze.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/persistentvolumeclaims: "0" 7- 1
- The total number of persistent volume claims in a project.
- 2
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested cannot exceed this value.
- 3
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the gold storage class cannot exceed this value.
- 4
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the silver storage class cannot exceed this value.
- 5
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the total number of claims in the silver storage class cannot exceed this value.
- 6
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the bronze storage class cannot exceed this value. When this value is set to
0, the bronze storage class cannot request storage. - 7
- Across all persistent volume claims in a project, the sum of storage requested in the bronze storage class cannot exceed this value. When this value is set to
0, the bronze storage class cannot create claims.
Create a project request template from the modified
template.yamlfile in theopenshift-confignamespace:$ oc create -f template.yaml -n openshift-config
NoteTo include the configuration as a
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configurationannotation, add the--save-configoption to theoc createcommand.By default, the template is called
project-request.
If a project request template already exists within a cluster:
NoteIf you declaratively or imperatively manage objects within your cluster by using configuration files, edit the existing project request template through those files instead.
List templates in the
openshift-confignamespace:$ oc get templates -n openshift-config
Edit an existing project request template:
$ oc edit template <project_request_template> -n openshift-config
-
Add a resource quota definition, such as the preceding
storage-consumptionexample, into the existing template. The definition must be added before theparameters:section in the template.
If you created a project request template, reference it in the cluster’s project configuration resource:
Access the project configuration resource for editing:
By using the web console:
- Navigate to the Administration → Cluster Settings page.
- Click Configuration to view all configuration resources.
- Find the entry for Project and click Edit YAML.
By using the CLI:
Edit the
project.config.openshift.io/clusterresource:$ oc edit project.config.openshift.io/cluster
Update the
specsection of the project configuration resource to include theprojectRequestTemplateandnameparameters. The following example references the default project request template nameproject-request:apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1 kind: Project metadata: ... spec: projectRequestTemplate: name: project-request
Verify that the resource quota is applied when projects are created:
Create a project:
$ oc new-project <project_name>
List the project’s resource quotas:
$ oc get resourcequotas
Describe the resource quota in detail:
$ oc describe resourcequotas <resource_quota_name>
8.2. Resource quotas across multiple projects
A multi-project quota, defined by a ClusterResourceQuota object, allows quotas to be shared across multiple projects. Resources used in each selected project are aggregated and that aggregate is used to limit resources across all the selected projects.
This guide describes how cluster administrators can set and manage resource quotas across multiple projects.
Do not run workloads in or share access to default projects. Default projects are reserved for running core cluster components.
The following default projects are considered highly privileged: default, kube-public, kube-system, openshift, openshift-infra, openshift-node, and other system-created projects that have the openshift.io/run-level label set to 0 or 1. Functionality that relies on admission plugins, such as pod security admission, security context constraints, cluster resource quotas, and image reference resolution, does not work in highly privileged projects.
8.2.1. Selecting multiple projects during quota creation
When creating quotas, you can select multiple projects based on annotation selection, label selection, or both.
Procedure
To select projects based on annotations, run the following command:
$ oc create clusterquota for-user \ --project-annotation-selector openshift.io/requester=<user_name> \ --hard pods=10 \ --hard secrets=20This creates the following
ClusterResourceQuotaobject:apiVersion: quota.openshift.io/v1 kind: ClusterResourceQuota metadata: name: for-user spec: quota: 1 hard: pods: "10" secrets: "20" selector: annotations: 2 openshift.io/requester: <user_name> labels: null 3 status: namespaces: 4 - namespace: ns-one status: hard: pods: "10" secrets: "20" used: pods: "1" secrets: "9" total: 5 hard: pods: "10" secrets: "20" used: pods: "1" secrets: "9"
- 1
- The
ResourceQuotaSpecobject that will be enforced over the selected projects. - 2
- A simple key-value selector for annotations.
- 3
- A label selector that can be used to select projects.
- 4
- A per-namespace map that describes current quota usage in each selected project.
- 5
- The aggregate usage across all selected projects.
This multi-project quota document controls all projects requested by
<user_name>using the default project request endpoint. You are limited to 10 pods and 20 secrets.Similarly, to select projects based on labels, run this command:
$ oc create clusterresourcequota for-name \1 --project-label-selector=name=frontend \2 --hard=pods=10 --hard=secrets=20
This creates the following
ClusterResourceQuotaobject definition:apiVersion: quota.openshift.io/v1 kind: ClusterResourceQuota metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: for-name spec: quota: hard: pods: "10" secrets: "20" selector: annotations: null labels: matchLabels: name: frontend
8.2.2. Viewing applicable cluster resource quotas
A project administrator is not allowed to create or modify the multi-project quota that limits his or her project, but the administrator is allowed to view the multi-project quota documents that are applied to his or her project. The project administrator can do this via the AppliedClusterResourceQuota resource.
Procedure
To view quotas applied to a project, run:
$ oc describe AppliedClusterResourceQuota
Example output
Name: for-user Namespace: <none> Created: 19 hours ago Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Label Selector: <null> AnnotationSelector: map[openshift.io/requester:<user-name>] Resource Used Hard -------- ---- ---- pods 1 10 secrets 9 20
8.2.3. Selection granularity
Because of the locking consideration when claiming quota allocations, the number of active projects selected by a multi-project quota is an important consideration. Selecting more than 100 projects under a single multi-project quota can have detrimental effects on API server responsiveness in those projects.
Chapter 9. Using config maps with applications
Config maps allow you to decouple configuration artifacts from image content to keep containerized applications portable.
The following sections define config maps and how to create and use them.
For information on creating config maps, see Creating and using config maps.
9.1. Understanding config maps
Many applications require configuration by using some combination of configuration files, command line arguments, and environment variables. In OpenShift Dedicated, these configuration artifacts are decoupled from image content to keep containerized applications portable.
The ConfigMap object provides mechanisms to inject containers with configuration data while keeping containers agnostic of OpenShift Dedicated. A config map can be used to store fine-grained information like individual properties or coarse-grained information like entire configuration files or JSON blobs.
The ConfigMap object holds key-value pairs of configuration data that can be consumed in pods or used to store configuration data for system components such as controllers. For example:
ConfigMap Object Definition
kind: ConfigMap apiVersion: v1 metadata: creationTimestamp: 2016-02-18T19:14:38Z name: example-config namespace: my-namespace data: 1 example.property.1: hello example.property.2: world example.property.file: |- property.1=value-1 property.2=value-2 property.3=value-3 binaryData: bar: L3Jvb3QvMTAw 2
You can use the binaryData field when you create a config map from a binary file, such as an image.
Configuration data can be consumed in pods in a variety of ways. A config map can be used to:
- Populate environment variable values in containers
- Set command-line arguments in a container
- Populate configuration files in a volume
Users and system components can store configuration data in a config map.
A config map is similar to a secret, but designed to more conveniently support working with strings that do not contain sensitive information.
Config map restrictions
A config map must be created before its contents can be consumed in pods.
Controllers can be written to tolerate missing configuration data. Consult individual components configured by using config maps on a case-by-case basis.
ConfigMap objects reside in a project.
They can only be referenced by pods in the same project.
The Kubelet only supports the use of a config map for pods it gets from the API server.
This includes any pods created by using the CLI, or indirectly from a replication controller. It does not include pods created by using the OpenShift Dedicated node’s --manifest-url flag, its --config flag, or its REST API because these are not common ways to create pods.
9.2. Use cases: Consuming config maps in pods
The following sections describe some uses cases when consuming ConfigMap objects in pods.
9.2.1. Populating environment variables in containers by using config maps
You can use config maps to populate individual environment variables in containers or to populate environment variables in containers from all keys that form valid environment variable names.
As an example, consider the following config map:
ConfigMap with two environment variables
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: special-config 1 namespace: default 2 data: special.how: very 3 special.type: charm 4
ConfigMap with one environment variable
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: env-config 1 namespace: default data: log_level: INFO 2
Procedure
You can consume the keys of this
ConfigMapin a pod usingconfigMapKeyRefsections.Sample
Podspecification configured to inject specific environment variablesapiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: dapi-test-pod spec: containers: - name: test-container image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "env" ] env: 1 - name: SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY 2 valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: special-config 3 key: special.how 4 - name: SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: special-config 5 key: special.type 6 optional: true 7 envFrom: 8 - configMapRef: name: env-config 9 restartPolicy: Never- 1
- Stanza to pull the specified environment variables from a
ConfigMap. - 2
- Name of a pod environment variable that you are injecting a key’s value into.
- 3 5
- Name of the
ConfigMapto pull specific environment variables from. - 4 6
- Environment variable to pull from the
ConfigMap. - 7
- Makes the environment variable optional. As optional, the pod will be started even if the specified
ConfigMapand keys do not exist. - 8
- Stanza to pull all environment variables from a
ConfigMap. - 9
- Name of the
ConfigMapto pull all environment variables from.
When this pod is run, the pod logs will include the following output:
SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY=very log_level=INFO
SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY=charm is not listed in the example output because optional: true is set.
9.2.2. Setting command-line arguments for container commands with config maps
You can use a config map to set the value of the commands or arguments in a container by using the Kubernetes substitution syntax $(VAR_NAME).
As an example, consider the following config map:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: special-config namespace: default data: special.how: very special.type: charm
Procedure
To inject values into a command in a container, you must consume the keys you want to use as environment variables. Then you can refer to them in a container’s command using the
$(VAR_NAME)syntax.Sample pod specification configured to inject specific environment variables
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: dapi-test-pod spec: containers: - name: test-container image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "echo $(SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY) $(SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY)" ] 1 env: - name: SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: special-config key: special.how - name: SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: special-config key: special.type restartPolicy: Never- 1
- Inject the values into a command in a container using the keys you want to use as environment variables.
When this pod is run, the output from the echo command run in the test-container container is as follows:
very charm
9.2.3. Injecting content into a volume by using config maps
You can inject content into a volume by using config maps.
Example ConfigMap custom resource (CR)
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: special-config namespace: default data: special.how: very special.type: charm
Procedure
You have a couple different options for injecting content into a volume by using config maps.
The most basic way to inject content into a volume by using a config map is to populate the volume with files where the key is the file name and the content of the file is the value of the key:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: dapi-test-pod spec: containers: - name: test-container image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "cat", "/etc/config/special.how" ] volumeMounts: - name: config-volume mountPath: /etc/config volumes: - name: config-volume configMap: name: special-config 1 restartPolicy: Never- 1
- File containing key.
When this pod is run, the output of the cat command will be:
very
You can also control the paths within the volume where config map keys are projected:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: dapi-test-pod spec: containers: - name: test-container image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "cat", "/etc/config/path/to/special-key" ] volumeMounts: - name: config-volume mountPath: /etc/config volumes: - name: config-volume configMap: name: special-config items: - key: special.how path: path/to/special-key 1 restartPolicy: Never- 1
- Path to config map key.
When this pod is run, the output of the cat command will be:
very
Chapter 10. Monitoring project and application metrics using the Developer perspective
The Observe view in the Developer perspective provides options to monitor your project or application metrics, such as CPU, memory, and bandwidth usage, and network related information.
10.1. Prerequisites
- You have created and deployed applications on OpenShift Dedicated.
- You have logged in to the web console and have switched to the Developer perspective.
10.2. Monitoring your project metrics
After you create applications in your project and deploy them, you can use the Developer perspective in the web console to see the metrics for your project.
Procedure
- On the left navigation panel of the Developer perspective, click Observe to see the Dashboard, Metrics, Alerts, and Events for your project.
Optional: Use the Dashboard tab to see graphs depicting the following application metrics:
- CPU usage
- Memory usage
- Bandwidth consumption
- Network-related information such as the rate of transmitted and received packets and the rate of dropped packets.
In the Dashboard tab, you can access the Kubernetes compute resources dashboards.
Figure 10.1. Observe dashboard
 Note
NoteIn the Dashboard list, Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Pods) dashboard is selected by default.
Use the following options to see further details:
- Select a dashboard from the Dashboard list to see the filtered metrics. All dashboards produce additional sub-menus when selected, except Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Pods).
- Select an option from the Time Range list to determine the time frame for the data being captured.
- Set a custom time range by selecting Custom time range from the Time Range list. You can input or select the From and To dates and times. Click Save to save the custom time range.
- Select an option from the Refresh Interval list to determine the time period after which the data is refreshed.
- Hover your cursor over the graphs to see specific details for your pod.
- Click Inspect located in the upper-right corner of every graph to see any particular graph details. The graph details appear in the Metrics tab.
Optional: Use the Metrics tab to query for the required project metric.
Figure 10.2. Monitoring metrics
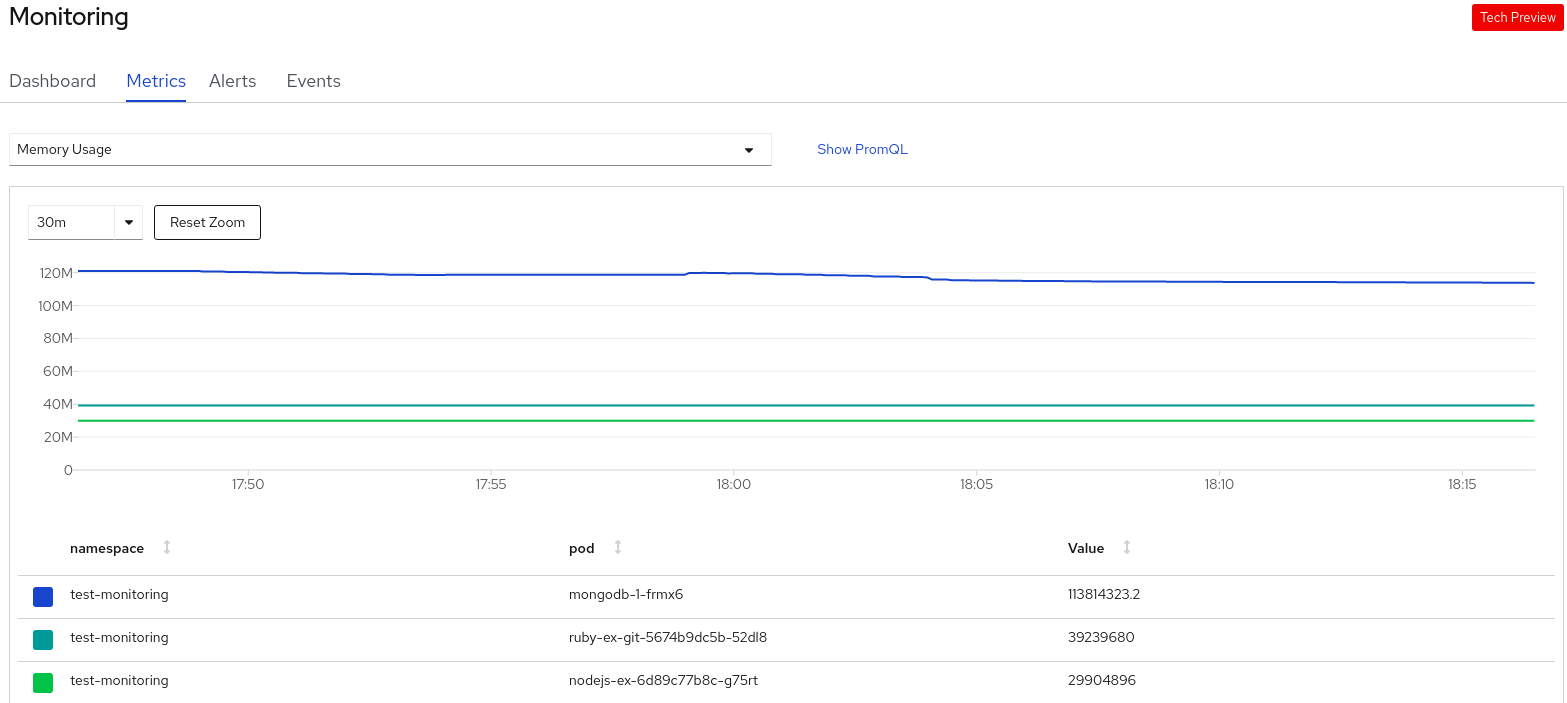
- In the Select Query list, select an option to filter the required details for your project. The filtered metrics for all the application pods in your project are displayed in the graph. The pods in your project are also listed below.
- From the list of pods, clear the colored square boxes to remove the metrics for specific pods to further filter your query result.
- Click Show PromQL to see the Prometheus query. You can further modify this query with the help of prompts to customize the query and filter the metrics you want to see for that namespace.
- Use the drop-down list to set a time range for the data being displayed. You can click Reset Zoom to reset it to the default time range.
- Optional: In the Select Query list, select Custom Query to create a custom Prometheus query and filter relevant metrics.
Optional: Use the Alerts tab to do the following tasks:
- See the rules that trigger alerts for the applications in your project.
- Identify the alerts firing in the project.
- Silence such alerts if required.
Figure 10.3. Monitoring alerts
Use the following options to see further details:
- Use the Filter list to filter the alerts by their Alert State and Severity.
- Click on an alert to go to the details page for that alert. In the Alerts Details page, you can click View Metrics to see the metrics for the alert.
- Use the Notifications toggle adjoining an alert rule to silence all the alerts for that rule, and then select the duration for which the alerts will be silenced from the Silence for list. You must have the permissions to edit alerts to see the Notifications toggle.
-
Use the Options menu
 adjoining an alert rule to see the details of the alerting rule.
adjoining an alert rule to see the details of the alerting rule.
Optional: Use the Events tab to see the events for your project.
Figure 10.4. Monitoring events
You can filter the displayed events using the following options:
- In the Resources list, select a resource to see events for that resource.
- In the All Types list, select a type of event to see events relevant to that type.
- Search for specific events using the Filter events by names or messages field.
10.3. Monitoring your application metrics
After you create applications in your project and deploy them, you can use the Topology view in the Developer perspective to see the alerts and metrics for your application. Critical and warning alerts for your application are indicated on the workload node in the Topology view.
Procedure
To see the alerts for your workload:
- In the Topology view, click the workload to see the workload details in the right panel.
Click the Observe tab to see the critical and warning alerts for the application; graphs for metrics, such as CPU, memory, and bandwidth usage; and all the events for the application.
NoteOnly critical and warning alerts in the Firing state are displayed in the Topology view. Alerts in the Silenced, Pending and Not Firing states are not displayed.
Figure 10.5. Monitoring application metrics

- Click the alert listed in the right panel to see the alert details in the Alert Details page.
- Click any of the charts to go to the Metrics tab to see the detailed metrics for the application.
- Click View monitoring dashboard to see the monitoring dashboard for that application.
10.4. Image vulnerabilities breakdown
In the developer perspective, the project dashboard shows the Image Vulnerabilities link in the Status section. Using this link, you can view the Image Vulnerabilities breakdown window, which includes details regarding vulnerable container images and fixable container images. The icon color indicates severity:
- Red: High priority. Fix immediately.
- Orange: Medium priority. Can be fixed after high-priority vulnerabilities.
- Yellow: Low priority. Can be fixed after high and medium-priority vulnerabilities.
Based on the severity level, you can prioritize vulnerabilities and fix them in an organized manner.
Figure 10.6. Viewing image vulnerabilities
10.5. Monitoring your application and image vulnerabilities metrics
After you create applications in your project and deploy them, use the Developer perspective in the web console to see the metrics for your application dependency vulnerabilities across your cluster. The metrics help you to analyze the following image vulnerabilities in detail:
- Total count of vulnerable images in a selected project
- Severity-based counts of all vulnerable images in a selected project
- Drilldown into severity to obtain the details, such as count of vulnerabilities, count of fixable vulnerabilities, and number of affected pods for each vulnerable image
Prerequisites
You have installed the Red Hat Quay Container Security operator from the Operator Hub.
NoteThe Red Hat Quay Container Security operator detects vulnerabilities by scanning the images that are in the quay registry.
Procedure
- For a general overview of the image vulnerabilities, on the navigation panel of the Developer perspective, click Project to see the project dashboard.
- Click Image Vulnerabilities in the Status section. The window that opens displays details such as Vulnerable Container Images and Fixable Container Images.
For a detailed vulnerabilities overview, click the Vulnerabilities tab on the project dashboard.
- To get more detail about an image, click its name.
- View the default graph with all types of vulnerabilities in the Details tab.
- Optional: Click the toggle button to view a specific type of vulnerability. For example, click App dependency to see vulnerabilities specific to application dependency.
- Optional: You can filter the list of vulnerabilities based on their Severity and Type or sort them by Severity, Package, Type, Source, Current Version, and Fixed in Version.
Click a Vulnerability to get its associated details:
- Base image vulnerabilities display information from a Red Hat Security Advisory (RHSA).
- App dependency vulnerabilities display information from the Snyk security application.
10.6. Additional resources
Chapter 11. Monitoring application health by using health checks
In software systems, components can become unhealthy due to transient issues such as temporary connectivity loss, configuration errors, or problems with external dependencies. OpenShift Dedicated applications have a number of options to detect and handle unhealthy containers.
11.1. Understanding health checks
A health check periodically performs diagnostics on a running container using any combination of the readiness, liveness, and startup health checks.
You can include one or more probes in the specification for the pod that contains the container which you want to perform the health checks.
If you want to add or edit health checks in an existing pod, you must edit the pod DeploymentConfig object or use the Developer perspective in the web console. You cannot use the CLI to add or edit health checks for an existing pod.
- Readiness probe
A readiness probe determines if a container is ready to accept service requests. If the readiness probe fails for a container, the kubelet removes the pod from the list of available service endpoints.
After a failure, the probe continues to examine the pod. If the pod becomes available, the kubelet adds the pod to the list of available service endpoints.
- Liveness health check
A liveness probe determines if a container is still running. If the liveness probe fails due to a condition such as a deadlock, the kubelet kills the container. The pod then responds based on its restart policy.
For example, a liveness probe on a pod with a
restartPolicyofAlwaysorOnFailurekills and restarts the container.- Startup probe
A startup probe indicates whether the application within a container is started. All other probes are disabled until the startup succeeds. If the startup probe does not succeed within a specified time period, the kubelet kills the container, and the container is subject to the pod
restartPolicy.Some applications can require additional startup time on their first initialization. You can use a startup probe with a liveness or readiness probe to delay that probe long enough to handle lengthy start-up time using the
failureThresholdandperiodSecondsparameters.For example, you can add a startup probe, with a
failureThresholdof 30 failures and aperiodSecondsof 10 seconds (30 * 10s = 300s) for a maximum of 5 minutes, to a liveness probe. After the startup probe succeeds the first time, the liveness probe takes over.
You can configure liveness, readiness, and startup probes with any of the following types of tests:
HTTP
GET: When using an HTTPGETtest, the test determines the healthiness of the container by using a web hook. The test is successful if the HTTP response code is between200and399.You can use an HTTP
GETtest with applications that return HTTP status codes when completely initialized.-
Container Command: When using a container command test, the probe executes a command inside the container. The probe is successful if the test exits with a
0status. - TCP socket: When using a TCP socket test, the probe attempts to open a socket to the container. The container is only considered healthy if the probe can establish a connection. You can use a TCP socket test with applications that do not start listening until initialization is complete.
You can configure several fields to control the behavior of a probe:
-
initialDelaySeconds: The time, in seconds, after the container starts before the probe can be scheduled. The default is 0. -
periodSeconds: The delay, in seconds, between performing probes. The default is10. This value must be greater thantimeoutSeconds. -
timeoutSeconds: The number of seconds of inactivity after which the probe times out and the container is assumed to have failed. The default is1. This value must be lower thanperiodSeconds. -
successThreshold: The number of times that the probe must report success after a failure to reset the container status to successful. The value must be1for a liveness probe. The default is1. failureThreshold: The number of times that the probe is allowed to fail. The default is 3. After the specified attempts:- for a liveness probe, the container is restarted
-
for a readiness probe, the pod is marked
Unready -
for a startup probe, the container is killed and is subject to the pod’s
restartPolicy
Example probes
The following are samples of different probes as they would appear in an object specification.
Sample readiness probe with a container command readiness probe in a pod spec
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: health-check
name: my-application
...
spec:
containers:
- name: goproxy-app 1
args:
image: registry.k8s.io/goproxy:0.1 2
readinessProbe: 3
exec: 4
command: 5
- cat
- /tmp/healthy
...
Sample container command startup probe and liveness probe with container command tests in a pod spec
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: health-check
name: my-application
...
spec:
containers:
- name: goproxy-app 1
args:
image: registry.k8s.io/goproxy:0.1 2
livenessProbe: 3
httpGet: 4
scheme: HTTPS 5
path: /healthz
port: 8080 6
httpHeaders:
- name: X-Custom-Header
value: Awesome
startupProbe: 7
httpGet: 8
path: /healthz
port: 8080 9
failureThreshold: 30 10
periodSeconds: 10 11
...
- 1
- The container name.
- 2
- Specify the container image to deploy.
- 3
- A liveness probe.
- 4
- An HTTP
GETtest. - 5
- The internet scheme:
HTTPorHTTPS. The default value isHTTP. - 6
- The port on which the container is listening.
- 7
- A startup probe.
- 8
- An HTTP
GETtest. - 9
- The port on which the container is listening.
- 10
- The number of times to try the probe after a failure.
- 11
- The number of seconds to perform the probe.
Sample liveness probe with a container command test that uses a timeout in a pod spec
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
test: health-check
name: my-application
...
spec:
containers:
- name: goproxy-app 1
args:
image: registry.k8s.io/goproxy:0.1 2
livenessProbe: 3
exec: 4
command: 5
- /bin/bash
- '-c'
- timeout 60 /opt/eap/bin/livenessProbe.sh
periodSeconds: 10 6
successThreshold: 1 7
failureThreshold: 3 8
...
- 1
- The container name.
- 2
- Specify the container image to deploy.
- 3
- The liveness probe.
- 4
- The type of probe, here a container command probe.
- 5
- The command line to execute inside the container.
- 6
- How often in seconds to perform the probe.
- 7
- The number of consecutive successes needed to show success after a failure.
- 8
- The number of times to try the probe after a failure.
Sample readiness probe and liveness probe with a TCP socket test in a deployment
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
...
spec:
...
template:
spec:
containers:
- resources: {}
readinessProbe: 1
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
timeoutSeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
name: ruby-ex
livenessProbe: 2
tcpSocket:
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 15
timeoutSeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
failureThreshold: 3
...
11.2. Configuring health checks using the CLI
To configure readiness, liveness, and startup probes, add one or more probes to the specification for the pod that contains the container which you want to perform the health checks
If you want to add or edit health checks in an existing pod, you must edit the pod DeploymentConfig object or use the Developer perspective in the web console. You cannot use the CLI to add or edit health checks for an existing pod.
Procedure
To add probes for a container:
Create a
Podobject to add one or more probes:apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: labels: test: health-check name: my-application spec: containers: - name: my-container 1 args: image: registry.k8s.io/goproxy:0.1 2 livenessProbe: 3 tcpSocket: 4 port: 8080 5 initialDelaySeconds: 15 6 periodSeconds: 20 7 timeoutSeconds: 10 8 readinessProbe: 9 httpGet: 10 host: my-host 11 scheme: HTTPS 12 path: /healthz port: 8080 13 startupProbe: 14 exec: 15 command: 16 - cat - /tmp/healthy failureThreshold: 30 17 periodSeconds: 20 18 timeoutSeconds: 10 19- 1
- Specify the container name.
- 2
- Specify the container image to deploy.
- 3
- Optional: Create a Liveness probe.
- 4
- Specify a test to perform, here a TCP Socket test.
- 5
- Specify the port on which the container is listening.
- 6
- Specify the time, in seconds, after the container starts before the probe can be scheduled.
- 7
- Specify the number of seconds to perform the probe. The default is
10. This value must be greater thantimeoutSeconds. - 8
- Specify the number of seconds of inactivity after which the probe is assumed to have failed. The default is
1. This value must be lower thanperiodSeconds. - 9
- Optional: Create a Readiness probe.
- 10
- Specify the type of test to perform, here an HTTP test.
- 11
- Specify a host IP address. When
hostis not defined, thePodIPis used. - 12
- Specify
HTTPorHTTPS. Whenschemeis not defined, theHTTPscheme is used. - 13
- Specify the port on which the container is listening.
- 14
- Optional: Create a Startup probe.
- 15
- Specify the type of test to perform, here an Container Execution probe.
- 16
- Specify the commands to execute on the container.
- 17
- Specify the number of times to try the probe after a failure.
- 18
- Specify the number of seconds to perform the probe. The default is
10. This value must be greater thantimeoutSeconds. - 19
- Specify the number of seconds of inactivity after which the probe is assumed to have failed. The default is
1. This value must be lower thanperiodSeconds.
NoteIf the
initialDelaySecondsvalue is lower than theperiodSecondsvalue, the first Readiness probe occurs at some point between the two periods due to an issue with timers.The
timeoutSecondsvalue must be lower than theperiodSecondsvalue.Create the
Podobject:$ oc create -f <file-name>.yaml
Verify the state of the health check pod:
$ oc describe pod health-check
Example output
Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal Scheduled 9s default-scheduler Successfully assigned openshift-logging/liveness-exec to ip-10-0-143-40.ec2.internal Normal Pulling 2s kubelet, ip-10-0-143-40.ec2.internal pulling image "registry.k8s.io/liveness" Normal Pulled 1s kubelet, ip-10-0-143-40.ec2.internal Successfully pulled image "registry.k8s.io/liveness" Normal Created 1s kubelet, ip-10-0-143-40.ec2.internal Created container Normal Started 1s kubelet, ip-10-0-143-40.ec2.internal Started container
The following is the output of a failed probe that restarted a container:
Sample Liveness check output with unhealthy container
$ oc describe pod pod1
Example output
.... Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal Scheduled <unknown> Successfully assigned aaa/liveness-http to ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Normal AddedInterface 47s multus Add eth0 [10.129.2.11/23] Normal Pulled 46s kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Successfully pulled image "registry.k8s.io/liveness" in 773.406244ms Normal Pulled 28s kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Successfully pulled image "registry.k8s.io/liveness" in 233.328564ms Normal Created 10s (x3 over 46s) kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Created container liveness Normal Started 10s (x3 over 46s) kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Started container liveness Warning Unhealthy 10s (x6 over 34s) kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Liveness probe failed: HTTP probe failed with statuscode: 500 Normal Killing 10s (x2 over 28s) kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Container liveness failed liveness probe, will be restarted Normal Pulling 10s (x3 over 47s) kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Pulling image "registry.k8s.io/liveness" Normal Pulled 10s kubelet, ci-ln-37hz77b-f76d1-wdpjv-worker-b-snzrj Successfully pulled image "registry.k8s.io/liveness" in 244.116568ms
11.3. Monitoring application health using the Developer perspective
You can use the Developer perspective to add three types of health probes to your container to ensure that your application is healthy:
- Use the Readiness probe to check if the container is ready to handle requests.
- Use the Liveness probe to check if the container is running.
- Use the Startup probe to check if the application within the container has started.
You can add health checks either while creating and deploying an application, or after you have deployed an application.
11.4. Adding health checks using the Developer perspective
You can use the Topology view to add health checks to your deployed application.
Prerequisites:
- You have switched to the Developer perspective in the web console.
- You have created and deployed an application on OpenShift Dedicated using the Developer perspective.
Procedure
- In the Topology view, click on the application node to see the side panel. If the container does not have health checks added to ensure the smooth running of your application, a Health Checks notification is displayed with a link to add health checks.
- In the displayed notification, click the Add Health Checks link.
- Alternatively, you can also click the Actions drop-down list and select Add Health Checks. Note that if the container already has health checks, you will see the Edit Health Checks option instead of the add option.
- In the Add Health Checks form, if you have deployed multiple containers, use the Container drop-down list to ensure that the appropriate container is selected.
Click the required health probe links to add them to the container. Default data for the health checks is prepopulated. You can add the probes with the default data or further customize the values and then add them. For example, to add a Readiness probe that checks if your container is ready to handle requests:
- Click Add Readiness Probe, to see a form containing the parameters for the probe.
- Click the Type drop-down list to select the request type you want to add. For example, in this case, select Container Command to select the command that will be executed inside the container.
-
In the Command field, add an argument
cat, similarly, you can add multiple arguments for the check, for example, add another argument/tmp/healthy. Retain or modify the default values for the other parameters as required.
NoteThe
Timeoutvalue must be lower than thePeriodvalue. TheTimeoutdefault value is1. ThePerioddefault value is10.- Click the check mark at the bottom of the form. The Readiness Probe Added message is displayed.
- Click Add to add the health check. You are redirected to the Topology view and the container is restarted.
- In the side panel, verify that the probes have been added by clicking on the deployed pod under the Pods section.
- In the Pod Details page, click the listed container in the Containers section.
-
In the Container Details page, verify that the Readiness probe - Exec Command
cat/tmp/healthyhas been added to the container.
11.5. Editing health checks using the Developer perspective
You can use the Topology view to edit health checks added to your application, modify them, or add more health checks.
Prerequisites:
- You have switched to the Developer perspective in the web console.
- You have created and deployed an application on OpenShift Dedicated using the Developer perspective.
- You have added health checks to your application.
Procedure
- In the Topology view, right-click your application and select Edit Health Checks. Alternatively, in the side panel, click the Actions drop-down list and select Edit Health Checks.
In the Edit Health Checks page:
- To remove a previously added health probe, click the Remove icon adjoining it.
To edit the parameters of an existing probe:
- Click the Edit Probe link next to a previously added probe to see the parameters for the probe.
- Modify the parameters as required, and click the check mark to save your changes.
To add a new health probe, in addition to existing health checks, click the add probe links. For example, to add a Liveness probe that checks if your container is running:
- Click Add Liveness Probe, to see a form containing the parameters for the probe.
Edit the probe parameters as required.
NoteThe
Timeoutvalue must be lower than thePeriodvalue. TheTimeoutdefault value is1. ThePerioddefault value is10.- Click the check mark at the bottom of the form. The Liveness Probe Added message is displayed.
- Click Save to save your modifications and add the additional probes to your container. You are redirected to the Topology view.
- In the side panel, verify that the probes have been added by clicking on the deployed pod under the Pods section.
- In the Pod Details page, click the listed container in the Containers section.
-
In the Container Details page, verify that the Liveness probe -
HTTP Get 10.129.4.65:8080/has been added to the container, in addition to the earlier existing probes.
11.6. Monitoring health check failures using the Developer perspective
In case an application health check fails, you can use the Topology view to monitor these health check violations.
Prerequisites:
- You have switched to the Developer perspective in the web console.
- You have created and deployed an application on OpenShift Dedicated using the Developer perspective.
- You have added health checks to your application.
Procedure
- In the Topology view, click on the application node to see the side panel.
- Click the Observe tab to see the health check failures in the Events (Warning) section.
- Click the down arrow adjoining Events (Warning) to see the details of the health check failure.
Additional resources
- For details on adding health checks while creating and deploying an application, see Advanced Options in the Creating applications using the Developer perspective section.
Chapter 12. Editing applications
You can edit the configuration and the source code of the application you create using the Topology view.
12.1. Prerequisites
- You have created and deployed an application on OpenShift Dedicated using the Developer perspective.
- You have logged in to the web console and have switched to the Developer perspective.
12.2. Editing the source code of an application using the Developer perspective
You can use the Topology view in the Developer perspective to edit the source code of your application.
Procedure
In the Topology view, click the Edit Source code icon, displayed at the bottom-right of the deployed application, to access your source code and modify it.
NoteThis feature is available only when you create applications using the From Git, From Catalog, and the From Dockerfile options.
12.3. Editing the application configuration using the Developer perspective
You can use the Topology view in the Developer perspective to edit the configuration of your application.
Currently, only configurations of applications created by using the From Git, Container Image, From Catalog, or From Dockerfile options in the Add workflow of the Developer perspective can be edited. Configurations of applications created by using the CLI or the YAML option from the Add workflow cannot be edited.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have created an application using the From Git, Container Image, From Catalog, or From Dockerfile options in the Add workflow.
Procedure
After you have created an application and it is displayed in the Topology view, right-click the application to see the edit options available.
Figure 12.1. Edit application

- Click Edit application-name to see the Add workflow you used to create the application. The form is pre-populated with the values you had added while creating the application.
Edit the necessary values for the application.
NoteYou cannot edit the Name field in the General section, the CI/CD pipelines, or the Create a route to the application field in the Advanced Options section.
Click Save to restart the build and deploy a new image.
Figure 12.2. Edit and redeploy application

Chapter 13. Working with quotas
A resource quota, defined by a ResourceQuota object, provides constraints that limit aggregate resource consumption per project. It can limit the quantity of objects that can be created in a project by type, as well as the total amount of compute resources and storage that may be consumed by resources in that project.
An object quota count places a defined quota on all standard namespaced resource types. When using a resource quota, an object is charged against the quota if it exists in server storage. These types of quotas are useful to protect against exhaustion of storage resources.
This guide describes how resource quotas work and how developers can work with and view them.
13.1. Viewing a quota
You can view usage statistics related to any hard limits defined in a project’s quota by navigating in the web console to the project’s Quota page.
You can also use the CLI to view quota details.
Procedure
Get the list of quotas defined in the project. For example, for a project called
demoproject:$ oc get quota -n demoproject
Example output
NAME AGE besteffort 11m compute-resources 2m core-object-counts 29m
Describe the quota you are interested in, for example the
core-object-countsquota:$ oc describe quota core-object-counts -n demoproject
Example output
Name: core-object-counts Namespace: demoproject Resource Used Hard -------- ---- ---- configmaps 3 10 persistentvolumeclaims 0 4 replicationcontrollers 3 20 secrets 9 10 services 2 10
13.2. Resources managed by quotas
The following describes the set of compute resources and object types that can be managed by a quota.
A pod is in a terminal state if status.phase in (Failed, Succeeded) is true.
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The sum of CPU requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of memory requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of CPU requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of memory requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The sum of CPU limits across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The sum of memory limits across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The sum of storage requests across all persistent volume claims in any state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The total number of persistent volume claims that can exist in the project. |
|
| The sum of storage requests across all persistent volume claims in any state that have a matching storage class, cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The total number of persistent volume claims with a matching storage class that can exist in the project. |
|
|
The sum of local ephemeral storage requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
|
The sum of ephemeral storage requests across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
|
| The sum of ephemeral storage limits across all pods in a non-terminal state cannot exceed this value. |
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The total number of pods in a non-terminal state that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of ReplicationControllers that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of resource quotas that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of services that can exist in the project. |
|
|
The total number of services of type |
|
|
The total number of services of type |
|
| The total number of secrets that can exist in the project. |
|
|
The total number of |
|
| The total number of persistent volume claims that can exist in the project. |
|
| The total number of imagestreams that can exist in the project. |
13.3. Quota scopes
Each quota can have an associated set of scopes. A quota only measures usage for a resource if it matches the intersection of enumerated scopes.
Adding a scope to a quota restricts the set of resources to which that quota can apply. Specifying a resource outside of the allowed set results in a validation error.
| Scope | Description |
|
|
Match pods that have best effort quality of service for either |
|
|
Match pods that do not have best effort quality of service for |
A BestEffort scope restricts a quota to limiting the following resources:
-
pods
A NotBestEffort scope restricts a quota to tracking the following resources:
-
pods -
memory -
requests.memory -
limits.memory -
cpu -
requests.cpu -
limits.cpu
13.4. Quota enforcement
After a resource quota for a project is first created, the project restricts the ability to create any new resources that may violate a quota constraint until it has calculated updated usage statistics.
After a quota is created and usage statistics are updated, the project accepts the creation of new content. When you create or modify resources, your quota usage is incremented immediately upon the request to create or modify the resource.
When you delete a resource, your quota use is decremented during the next full recalculation of quota statistics for the project. A configurable amount of time determines how long it takes to reduce quota usage statistics to their current observed system value.
If project modifications exceed a quota usage limit, the server denies the action, and an appropriate error message is returned to the user explaining the quota constraint violated, and what their currently observed usage statistics are in the system.
13.5. Requests versus limits
When allocating compute resources, each container might specify a request and a limit value each for CPU, memory, and ephemeral storage. Quotas can restrict any of these values.
If the quota has a value specified for requests.cpu or requests.memory, then it requires that every incoming container make an explicit request for those resources. If the quota has a value specified for limits.cpu or limits.memory, then it requires that every incoming container specify an explicit limit for those resources.
Chapter 14. Pruning objects to reclaim resources
Over time, API objects created in OpenShift Dedicated can accumulate in the cluster’s etcd data store through normal user operations, such as when building and deploying applications.
A user with the dedicated-admin role can periodically prune older versions of objects from the cluster that are no longer required. For example, by pruning images you can delete older images and layers that are no longer in use, but are still taking up disk space.
14.1. Basic pruning operations
The CLI groups prune operations under a common parent command:
$ oc adm prune <object_type> <options>
This specifies:
-
The
<object_type>to perform the action on, such asgroups,builds,deployments, orimages. -
The
<options>supported to prune that object type.
14.2. Pruning groups
To prune groups records from an external provider, administrators can run the following command:
$ oc adm prune groups \
--sync-config=path/to/sync/config [<options>]| Options | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicate that pruning should occur, instead of performing a dry-run. |
|
| Path to the group blacklist file. |
|
| Path to the group whitelist file. |
|
| Path to the synchronization configuration file. |
Procedure
To see the groups that the prune command deletes, run the following command:
$ oc adm prune groups --sync-config=ldap-sync-config.yaml
To perform the prune operation, add the
--confirmflag:$ oc adm prune groups --sync-config=ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm
14.3. Pruning deployment resources
You can prune resources associated with deployments that are no longer required by the system, due to age and status.
The following command prunes replication controllers associated with DeploymentConfig objects:
$ oc adm prune deployments [<options>]
To also prune replica sets associated with Deployment objects, use the --replica-sets flag. This flag is currently a Technology Preview feature.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicate that pruning should occur, instead of performing a dry-run. |
|
|
Per the |
|
|
Per the |
|
|
Do not prune any replication controller that is younger than |
|
|
Prune all replication controllers that no longer have a |
Procedure
To see what a pruning operation would delete, run the following command:
$ oc adm prune deployments --orphans --keep-complete=5 --keep-failed=1 \ --keep-younger-than=60mTo actually perform the prune operation, add the
--confirmflag:$ oc adm prune deployments --orphans --keep-complete=5 --keep-failed=1 \ --keep-younger-than=60m --confirm
14.4. Pruning builds
To prune builds that are no longer required by the system due to age and status, administrators can run the following command:
$ oc adm prune builds [<options>]
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicate that pruning should occur, instead of performing a dry-run. |
|
| Prune all builds whose build configuration no longer exists, status is complete, failed, error, or canceled. |
|
|
Per build configuration, keep the last |
|
|
Per build configuration, keep the last |
|
|
Do not prune any object that is younger than |
Procedure
To see what a pruning operation would delete, run the following command:
$ oc adm prune builds --orphans --keep-complete=5 --keep-failed=1 \ --keep-younger-than=60mTo actually perform the prune operation, add the
--confirmflag:$ oc adm prune builds --orphans --keep-complete=5 --keep-failed=1 \ --keep-younger-than=60m --confirm
Developers can enable automatic build pruning by modifying their build configuration.
14.5. Automatically pruning images
Images from the OpenShift image registry that are no longer required by the system due to age, status, or exceed limits are automatically pruned. Cluster administrators can configure the Pruning Custom Resource, or suspend it.
Prerequisites
-
You have access to an OpenShift Dedicated cluster using an account with
dedicated-adminpermissions. -
Install the
ocCLI.
Procedure
-
Verify that the object named
imagepruners.imageregistry.operator.openshift.io/clustercontains the followingspecandstatusfields:
spec: schedule: 0 0 * * * 1 suspend: false 2 keepTagRevisions: 3 3 keepYoungerThanDuration: 60m 4 keepYoungerThan: 3600000000000 5 resources: {} 6 affinity: {} 7 nodeSelector: {} 8 tolerations: [] 9 successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 3 10 failedJobsHistoryLimit: 3 11 status: observedGeneration: 2 12 conditions: 13 - type: Available status: "True" lastTransitionTime: 2019-10-09T03:13:45 reason: Ready message: "Periodic image pruner has been created." - type: Scheduled status: "True" lastTransitionTime: 2019-10-09T03:13:45 reason: Scheduled message: "Image pruner job has been scheduled." - type: Failed staus: "False" lastTransitionTime: 2019-10-09T03:13:45 reason: Succeeded message: "Most recent image pruning job succeeded."
- 1
schedule:CronJobformatted schedule. This is an optional field, default is daily at midnight.- 2
suspend: If set totrue, theCronJobrunning pruning is suspended. This is an optional field, default isfalse. The initial value on new clusters isfalse.- 3
keepTagRevisions: The number of revisions per tag to keep. This is an optional field, default is3. The initial value is3.- 4
keepYoungerThanDuration: Retain images younger than this duration. This is an optional field. If a value is not specified, eitherkeepYoungerThanor the default value60m(60 minutes) is used.- 5
keepYoungerThan: Deprecated. The same askeepYoungerThanDuration, but the duration is specified as an integer in nanoseconds. This is an optional field. WhenkeepYoungerThanDurationis set, this field is ignored.- 6
resources: Standard pod resource requests and limits. This is an optional field.- 7
affinity: Standard pod affinity. This is an optional field.- 8
nodeSelector: Standard pod node selector. This is an optional field.- 9
tolerations: Standard pod tolerations. This is an optional field.- 10
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: The maximum number of successful jobs to retain. Must be>= 1to ensure metrics are reported. This is an optional field, default is3. The initial value is3.- 11
failedJobsHistoryLimit: The maximum number of failed jobs to retain. Must be>= 1to ensure metrics are reported. This is an optional field, default is3. The initial value is3.- 12
observedGeneration: The generation observed by the Operator.- 13
conditions: The standard condition objects with the following types:-
Available: Indicates if the pruning job has been created. Reasons can be Ready or Error. -
Scheduled: Indicates if the next pruning job has been scheduled. Reasons can be Scheduled, Suspended, or Error. -
Failed: Indicates if the most recent pruning job failed.
-
The Image Registry Operator’s behavior for managing the pruner is orthogonal to the managementState specified on the Image Registry Operator’s ClusterOperator object. If the Image Registry Operator is not in the Managed state, the image pruner can still be configured and managed by the Pruning Custom Resource.
However, the managementState of the Image Registry Operator alters the behavior of the deployed image pruner job:
-
Managed: the--prune-registryflag for the image pruner is set totrue. -
Removed: the--prune-registryflag for the image pruner is set tofalse, meaning it only prunes image metatdata in etcd.
14.6. Pruning cron jobs
Cron jobs can perform pruning of successful jobs, but might not properly handle failed jobs. Therefore, the cluster administrator should perform regular cleanup of jobs manually. They should also restrict the access to cron jobs to a small group of trusted users and set appropriate quota to prevent the cron job from creating too many jobs and pods.
Additional resources
Chapter 15. Idling applications
Cluster administrators can idle applications to reduce resource consumption. This is useful when the cluster is deployed on a public cloud where cost is related to resource consumption.
If any scalable resources are not in use, OpenShift Dedicated discovers and idles them by scaling their replicas to 0. The next time network traffic is directed to the resources, the resources are unidled by scaling up the replicas, and normal operation continues.
Applications are made of services, as well as other scalable resources, such as deployment configs. The action of idling an application involves idling all associated resources.
15.1. Idling applications
Idling an application involves finding the scalable resources (deployment configurations, replication controllers, and others) associated with a service. Idling an application finds the service and marks it as idled, scaling down the resources to zero replicas.
You can use the oc idle command to idle a single service, or use the --resource-names-file option to idle multiple services.
15.1.1. Idling a single service
Procedure
To idle a single service, run:
$ oc idle <service>
15.1.2. Idling multiple services
Idling multiple services is helpful if an application spans across a set of services within a project, or when idling multiple services in conjunction with a script to idle multiple applications in bulk within the same project.
Procedure
- Create a file containing a list of the services, each on their own line.
Idle the services using the
--resource-names-fileoption:$ oc idle --resource-names-file <filename>
The idle command is limited to a single project. For idling applications across a cluster, run the idle command for each project individually.
15.2. Unidling applications
Application services become active again when they receive network traffic and are scaled back up their previous state. This includes both traffic to the services and traffic passing through routes.
Applications can also be manually unidled by scaling up the resources.
Procedure
To scale up a DeploymentConfig, run:
$ oc scale --replicas=1 dc <dc_name>
Automatic unidling by a router is currently only supported by the default HAProxy router.
Chapter 16. Deleting applications
You can delete applications created in your project.
16.1. Deleting applications using the Developer perspective
You can delete an application and all of its associated components using the Topology view in the Developer perspective:
- Click the application you want to delete to see the side panel with the resource details of the application.
- Click the Actions drop-down menu displayed on the upper right of the panel, and select Delete Application to see a confirmation dialog box.
- Enter the name of the application and click Delete to delete it.
You can also right-click the application you want to delete and click Delete Application to delete it.
Chapter 17. Using the Red Hat Marketplace
The Red Hat Marketplace is an open cloud marketplace that makes it easy to discover and access certified software for container-based environments that run on public clouds and on-premises.
17.1. Red Hat Marketplace features
Cluster administrators can use the Red Hat Marketplace to manage software on OpenShift Dedicated, give developers self-service access to deploy application instances, and correlate application usage against a quota.
17.1.1. Connect OpenShift Dedicated clusters to the Marketplace
Cluster administrators can install a common set of applications on OpenShift Dedicated clusters that connect to the Marketplace. They can also use the Marketplace to track cluster usage against subscriptions or quotas. Users that they add by using the Marketplace have their product usage tracked and billed to their organization.
During the cluster connection process, a Marketplace Operator is installed that updates the image registry secret, manages the catalog, and reports application usage.
17.1.2. Install applications
Cluster administrators can install Marketplace applications from within OperatorHub in OpenShift Dedicated, or from the Marketplace web application.
You can access installed applications from the web console by clicking Operators > Installed Operators.
17.1.3. Deploy applications from different perspectives
You can deploy Marketplace applications from the web console’s Administrator and Developer perspectives.
The Developer perspective
Developers can access newly installed capabilities by using the Developer perspective.
For example, after a database Operator is installed, a developer can create an instance from the catalog within their project. Database usage is aggregated and reported to the cluster administrator.
This perspective does not include Operator installation and application usage tracking.
The Administrator perspective
Cluster administrators can access Operator installation and application usage information from the Administrator perspective.
They can also launch application instances by browsing custom resource definitions (CRDs) in the Installed Operators list.
Legal Notice
Copyright © 2024 Red Hat, Inc.
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of Joyent. Red Hat Software Collections is not formally related to or endorsed by the official Joyent Node.js open source or commercial project.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.