Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Chapter 13. KVM Para-virtualized Drivers
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.8 and newer
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.3 and newer
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
Important
- Windows XP (32-bit only)
- Windows Server 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit versions)
- Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit versions)
- Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit versions)
13.1. Installing the KVM Windows para-virtualized drivers
- hosting the installation files on a network accessible to the guest,
- using a virtualized CD-ROM device of the driver installation disk .iso file, or
- using a virtualized floppy device to install the drivers during boot time (for Windows guests).
Download the drivers
The virtio-win package contains the para-virtualized block and network drivers for all supported Windows guests.If the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Supplementary channel entitlements are not enabled for the system, the download will not be available. Enable the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Supplementary channel to access the virtio-win package.Download the virtio-win package with theyumcommand.# yum install virtio-win
The drivers are also available on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Supplementary disc or from Microsoft (windowsservercatalog.com). Note that the Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization Hypervisor and Red Hat Enterprise Linux are created on the same code base so the drivers for the same version (for example, 5.5) are supported for both environments.The virtio-win package installs a CD-ROM image,virtio-win.iso, in the/usr/share/virtio-win/directory.Install the para-virtualized drivers
It is recommended to install the drivers on the guest before attaching or modifying a device to use the para-virtualized drivers.For block devices storing root file systems or other block devices required for booting the guest, the drivers must be installed before the device is modified. If the drivers are not installed on the guest and the driver is set to the virtio driver the guest will not boot.
This procedure covers installing the para-virtualized drivers with a virtualized CD-ROM after Windows is installed.
virt-manager to mount a CD-ROM image for a Windows guest” to add a CD-ROM image with virt-manager and then install the drivers.
Procedure 13.1. Using virt-manager to mount a CD-ROM image for a Windows guest
Open virt-manager and the guest
Openvirt-manager, select your guest from the list by double clicking the guest name.Open the hardware tab
Click the Add Hardware button in the Hardware tab.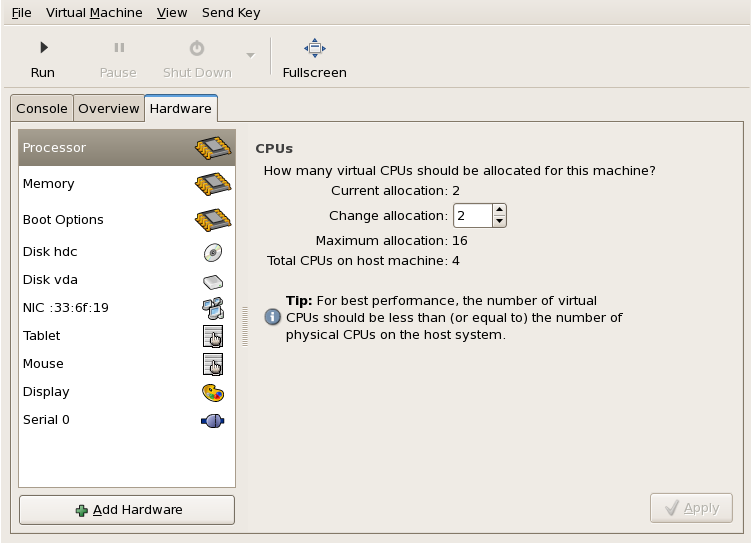
Select the device type
This opens a wizard for adding the new device. Select Storage from the dropdown menu. Click the Forward button to proceed.
Click the Forward button to proceed.Select the ISO file
Choose the File (disk image) option and set the file location of the para-virtualized drivers .iso image file. The location file is named/usr/share/virtio-win/virtio-win.iso.If the drivers are stored on a physical CD-ROM, use the Normal Disk Partition option.Set the Device type to IDE cdrom and click Forward to proceed.
Disc assigned
The disk has been assigned and is available for the guest once the guest is started. Click Finish to close the wizard or back if you made a mistake.
Reboot
Reboot or start the guest to add the new device. Virtualized IDE devices require a restart before they can be recognized by guests.
Procedure 13.2. Windows installation
Open My Computer
On the Windows guest, open My Computer and select the CD-ROM drive.
Select the correct installation files
There are four files available on the disc. Select the drivers you require for your guest's architecture:- the para-virtualized block device driver (
RHEV-Block.msifor 32-bit guests orRHEV-Block64.msifor 64-bit guests), - the para-virtualized network device driver (
RHEV-Network.msifor 32-bit guests orRHEV-Block64.msifor 64-bit guests), - or both the block and network device drivers.
Double click the installation files to install the drivers.Install the block device driver
Start the block device driver installation
Double clickRHEV-Block.msiorRHEV-Block64.msi.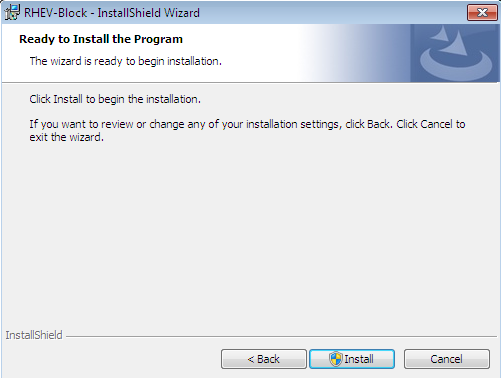 Press Next to continue.
Press Next to continue.Confirm the exception
Windows may prompt for a security exception. Press Yes if it is correct.
Press Yes if it is correct.Finish
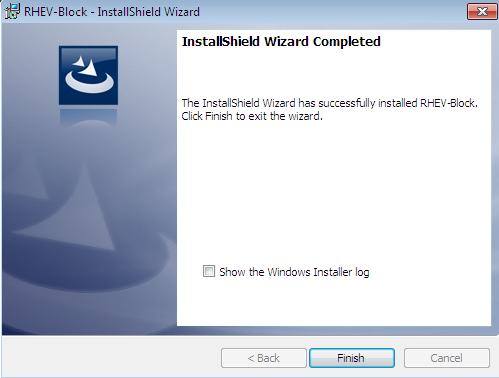 Press Finish to complete the installation.
Press Finish to complete the installation.
Install the network device driver
Start the network device driver installation
Double clickRHEV-Network.msiorRHEV-Network64.msi.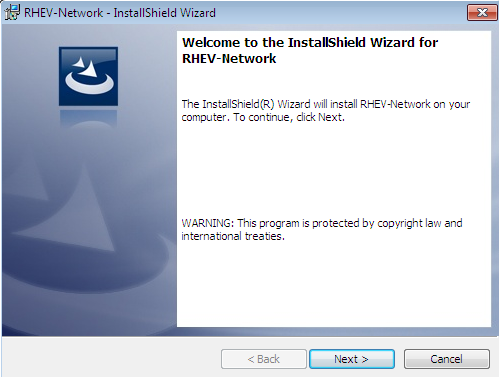 Press Next to continue.
Press Next to continue.Performance setting
This screen configures advanced TCP settings for the network driver. TCP timestamps and TCP window scaling can be enabled or disabled. The default is, 1, for window scaling to be enabled.TCP window scaling is covered by IETF RFC 1323. The RFC defines a method of increasing the receive window size to a size greater than the default maximum of 65,535 bytes up to a new maximum of 1 gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes). TCP window scaling allows networks to transfer at closer to theoretical network bandwidth limits. Larger receive windows may not be supported by some networking hardware or operating systems.TCP timestamps are also defined by IETF RFC 1323. TCP timestamps are used to better calculate Return Travel Time estimates by embedding timing information is embedded in packets. TCP timestamps help the system to adapt to changing traffic levels and avoid congestion issues on busy networks.Value Action 0 Disable TCP timestamps and window scaling. 1 Enable TCP window scaling. 2 Enable TCP timestamps. 3 Enable TCP timestamps and window scaling. 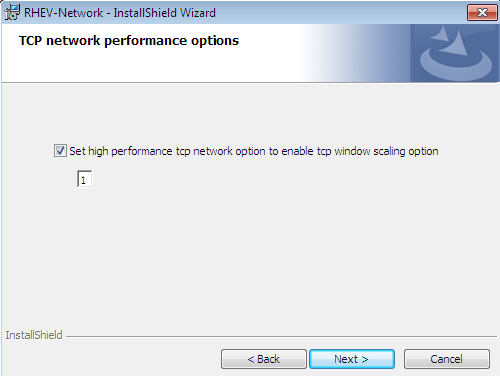 Press Next to continue.
Press Next to continue.Confirm the exception
Windows may prompt for a security exception. Press Yes if it is correct.
Press Yes if it is correct.Finish
 Press Finish to complete the installation.
Press Finish to complete the installation.
Reboot
Reboot the guest to complete the driver installation.

