Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
1.6. Gerenciador de Volume Lógico de Cluster
O Cluster Logical Volume Manager ( CLVM ), ( Gerenciador de Volume Lógico de Cluster ) fornece uma versão ampla de cluster de LVM2. O CLVM fornece a mesma capacidade de LVM2 num único nó, mas faz a disponibilidade dos volumes de todos os nós num cluster Red Hat. Os volumes lógicos criados com o CLVM, tornam disponíveis os volumes lógicos para todos os nós em um cluster.
The key component in CLVM is
clvmd. clvmd is a daemon that provides clustering extensions to the standard LVM2 tool set and allows LVM2 commands to manage shared storage. clvmd runs in each cluster node and distributes LVM metadata updates in a cluster, thereby presenting each cluster node with the same view of the logical volumes (refer to Figura 1.14, “CLVM Overview”). Logical volumes created with CLVM on shared storage are visible to all nodes that have access to the shared storage. CLVM allows a user to configure logical volumes on shared storage by locking access to physical storage while a logical volume is being configured. CLVM uses the lock-management service provided by the cluster infrastructure (refer to Seção 1.3, “Cluster Infrastructure”).
Nota
Armazenamento compartilhado para uso no Red Hat Cluster Suite, requer que você esteja executando o daemon do gerenciador do volume lógico do cluster (
clvmd) ou os agentes do Gerenciamento de Volume Lógico de Alta Disponibilidade (HA-LVM). Se você não conseguir usar o daemon do clvmd ou o HA-LVM por motivos operacionais ou porque você não possui os direitos corretos, não use o single-instance LVM no disco compartilhado, pois isto pode danificar os dados. Caso tenha qualquer dúvida, entre em contato com o representante de serviços da Red Hat.
Nota
O uso do CLVM requer pequenas mudanças de acordo com o
/etc/lvm/lvm.conf para bloqueamento de um cluster amplo.
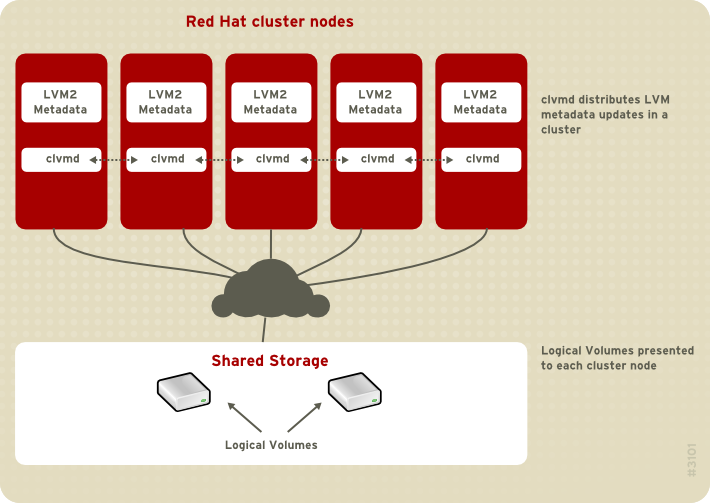
Figura 1.14. CLVM Overview
You can configure CLVM using the same commands as LVM2, using the LVM graphical user interface (refer to Figura 1.15, “LVM Graphical User Interface”), or using the storage configuration function of the Conga cluster configuration graphical user interface (refer to Figura 1.16, “Conga LVM Graphical User Interface”) . Figura 1.17, “Creating Logical Volumes” shows the basic concept of creating logical volumes from Linux partitions and shows the commands used to create logical volumes.
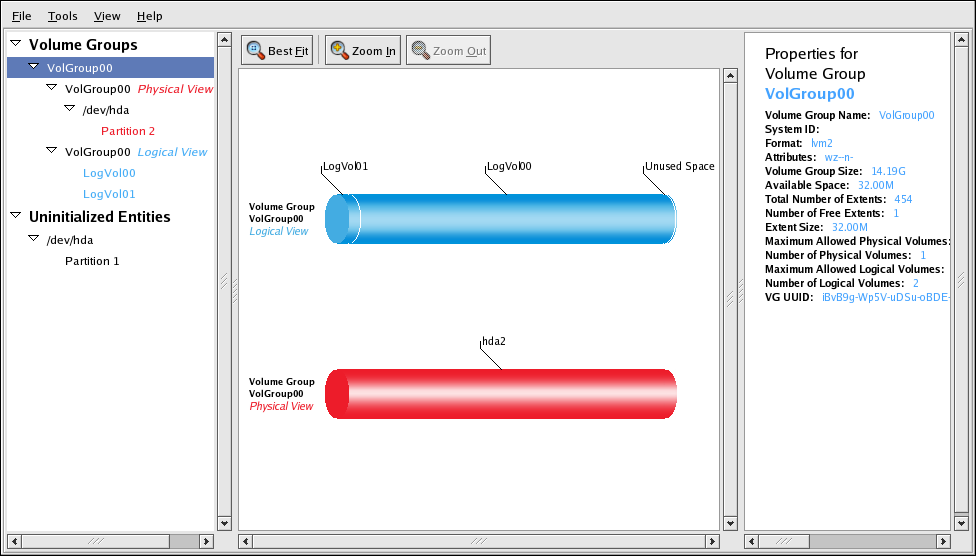
Figura 1.15. LVM Graphical User Interface
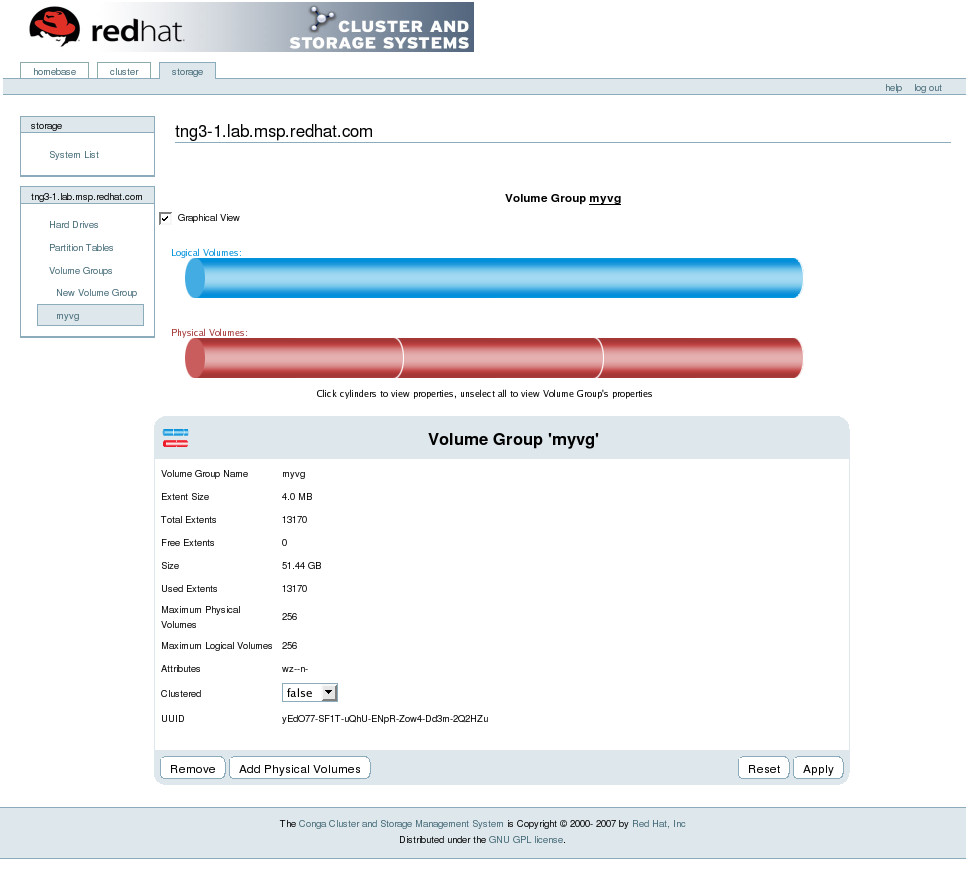
Figura 1.16. Conga LVM Graphical User Interface
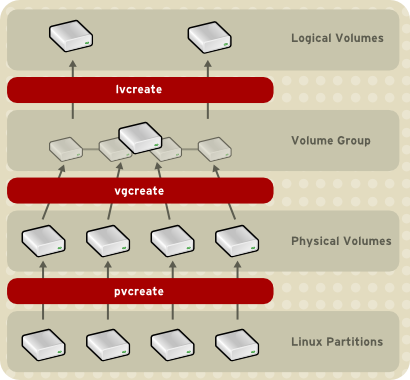
Figura 1.17. Creating Logical Volumes

