Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
1.6. Cluster Logical Volume Manager
Il Cluster Logical Volume Manager (CLVM) fornisce una versione cluster-wide di LVM2. CLVM fornisce le stesse caratteristiche di LVM2 su di un nodo singolo, rendendo i volumi disponibili su tutti i nodi in un cluster di Red Hat. I volumi logici creati con CLVM, rende gli stessi disponibili a tutti i nodi presenti in un cluster.
The key component in CLVM is
clvmd. clvmd is a daemon that provides clustering extensions to the standard LVM2 tool set and allows LVM2 commands to manage shared storage. clvmd runs in each cluster node and distributes LVM metadata updates in a cluster, thereby presenting each cluster node with the same view of the logical volumes (refer to Figura 1.14, «CLVM Overview»). Logical volumes created with CLVM on shared storage are visible to all nodes that have access to the shared storage. CLVM allows a user to configure logical volumes on shared storage by locking access to physical storage while a logical volume is being configured. CLVM uses the lock-management service provided by the cluster infrastructure (refer to Sezione 1.3, «Cluster Infrastructure»).
Nota
Lo storage condiviso con Red Hat Cluster Suite necessita di una esecuzione del cluster logical volume manager daemon (
clvmd) o degli High Availability Logical Volume Management agent (HA-LVM). Se non siete in grado di utilizzare il demone clvmd o HA-LVM per ragioni operative, o perchè non siete in possesso degli entitlement corretti, è consigliato non usare il single-instance LVM sul disco condiviso, poichè tale utilizzo potrebbe risultare in una corruzione dei dati. Per qualsiasi problema si prega di consultare un rappresentante per la gestione dei servizi di Red Hat.
Nota
L'utilizzo di CLVM richiede piccole modifiche di
/etc/lvm/lvm.conf per il cluster-wide locking.

Figura 1.14. CLVM Overview
You can configure CLVM using the same commands as LVM2, using the LVM graphical user interface (refer to Figura 1.15, «LVM Graphical User Interface»), or using the storage configuration function of the Conga cluster configuration graphical user interface (refer to Figura 1.16, «Conga LVM Graphical User Interface») . Figura 1.17, «Creating Logical Volumes» shows the basic concept of creating logical volumes from Linux partitions and shows the commands used to create logical volumes.
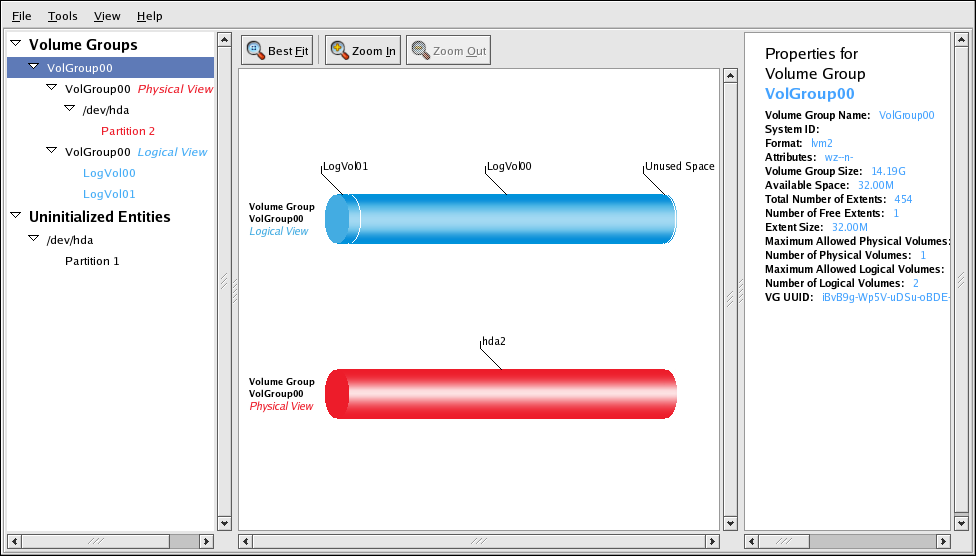
Figura 1.15. LVM Graphical User Interface
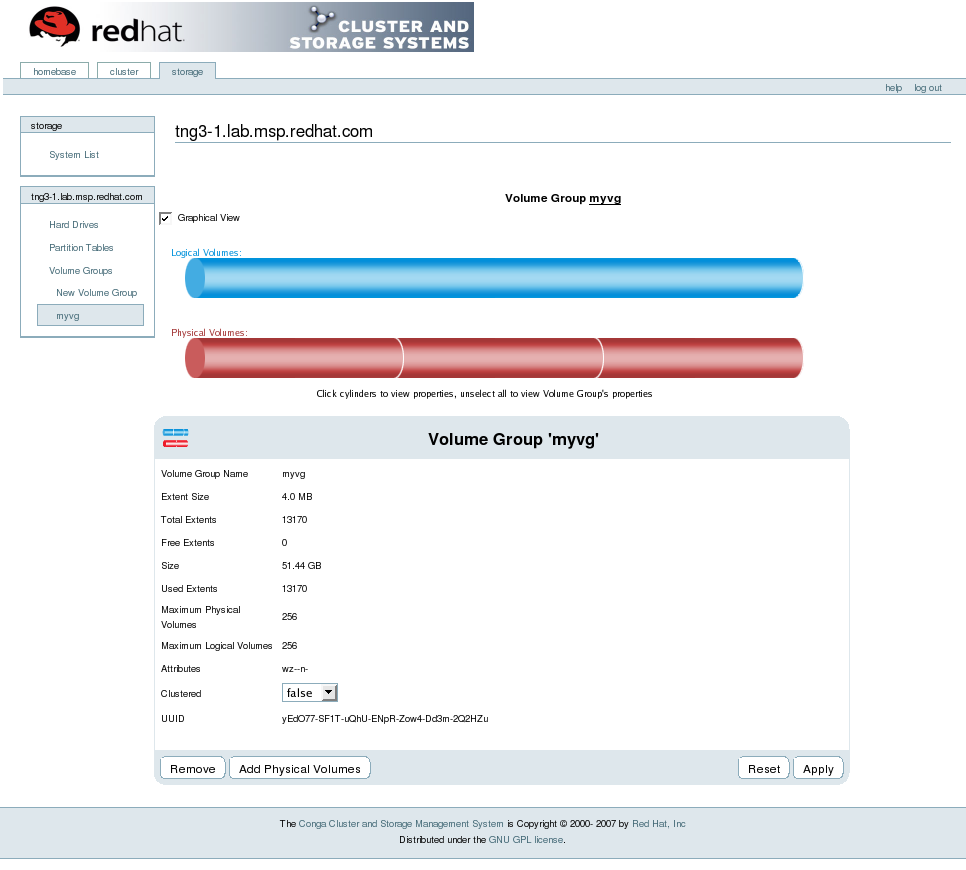
Figura 1.16. Conga LVM Graphical User Interface
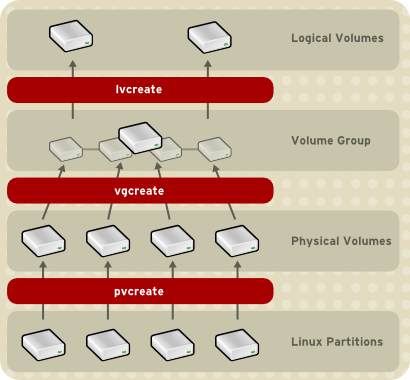
Figura 1.17. Creating Logical Volumes

