Chapter 1. Deploying using local storage devices
Deploying OpenShift Container Storage on OpenShift Container Platform using local storage devices provides you with the option to create internal cluster resources. This will result in the internal provisioning of the base services, which helps to make additional storage classes available to applications.
Use this section to deploy OpenShift Container Storage on bare metal infrastructure where OpenShift Container Platform is already installed.
To deploy Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage using local storage, follow these steps:
- Understand the requirements for installing OpenShift Container Storage using local storage devices.
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux based hosts for worker nodes, enable file system access for containers on Red Hat Enterprise Linux based nodes.
NoteSkip this step for Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS).
- Install the Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage Operator.
- Install Local Storage Operator.
- Create OpenShift Container Storage cluster on bare metal.
1.1. Requirements for installing OpenShift Container Storage using local storage devices
- You must upgrade to a latest version of OpenShift Container Platform 4.6 before deploying OpenShift Container Storage 4.6. For information, see Updating OpenShift Container Platform clusters guide.
- The Local Storage Operator version must match the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform version in order to have the Local Storage Operator fully supported with Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage. The Local Storage Operator does not get upgraded when Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform is upgraded.
You must have at least three OpenShift Container Platform worker nodes in the cluster with locally attached storage devices on each of them.
- Each of the three selected nodes must have at least one raw block device available to be used by OpenShift Container Storage.
- The devices you use must be empty; the disks must not include physical volumes (PVs), volume groups (VGs), or logical volumes (LVs) remaining on the disk.
- For minimum starting node requirements, see Resource requirements section in Planning guide.
- To configure OpenShift Container Platform in compact mode, see Configuring a three-node cluster and Delivering a Three-node Architecture for Edge Deployments. [Technology Preview]
1.2. Enabling file system access for containers on Red Hat Enterprise Linux based nodes
Deploying OpenShift Container Storage on an OpenShift Container Platform with worker nodes on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux base in a user provisioned infrastructure (UPI) does not automatically provide container access to the underlying Ceph file system.
This process is not necessary for hosts based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS.
Procedure
Perform the following steps on each node in your cluster.
- Log in to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux based node and open a terminal.
Verify that the node has access to the rhel-7-server-extras-rpms repository.
# subscription-manager repos --list-enabled | grep rhel-7-server
If you do not see both
rhel-7-server-rpmsandrhel-7-server-extras-rpmsin the output, or if there is no output, run the following commands to enable each repository.# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms # subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
Install the required packages.
# yum install -y policycoreutils container-selinux
Persistently enable container use of the Ceph file system in SELinux.
# setsebool -P container_use_cephfs on
1.3. Installing Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage Operator
You can install Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage Operator using the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform Operator Hub. For information about the hardware and software requirements, see Planning your deployment.
Prerequisites
- You must be logged into the OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP) cluster.
- You must have at least three worker nodes in the RHOCP cluster.
When you need to override the cluster-wide default node selector for OpenShift Container Storage, you can use the following command in command line interface to specify a blank node selector for the
openshift-storagenamespace:$ oc annotate namespace openshift-storage openshift.io/node-selector=
-
Taint a node as
infrato ensure only Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage resources are scheduled on that node. This helps you save on subscription costs. For more information, see How to use dedicated worker nodes for Red Hat OpenShift Container Storage chapter in Managing and Allocating Storage Resources guide.
Procedure
- Click Operators → OperatorHub in the left pane of the OpenShift Web Console.
- Use Filter by keyword text box or the filter list to search for OpenShift Container Storage from the list of operators.
- Click OpenShift Container Storage.
- On the OpenShift Container Storage operator page, click Install.
On the Install Operator page, ensure the following options are selected by default::
- Update Channel as stable-4.6
- Installation Mode as A specific namespace on the cluster
-
Installed Namespace as Operator recommended namespace openshift-storage. If Namespace
openshift-storagedoes not exist, it will be created during the operator installation. - Select Enable operator recommended cluster monitoring on this namespace checkbox as this is required for cluster monitoring.
Select Approval Strategy as Automatic or Manual. Approval Strategy is set to Automatic by default.
Approval Strategy as Automatic.
NoteWhen you select the Approval Strategy as Automatic, approval is not required either during fresh installation or when updating to the latest version of OpenShift Container Storage.
- Click Install
- Wait for the install to initiate. This may take up to 20 minutes.
- Click Operators → Installed Operators
-
Ensure the Project is
openshift-storage. By default, the Project isopenshift-storage. - Wait for the Status of OpenShift Container Storage to change to Succeeded.
Approval Strategy as Manual.
NoteWhen you select the Approval Strategy as Manual, approval is required during fresh installation or when updating to the latest version of OpenShift Container Storage.
- Click Install
On the Manual approval required page, you can either click Approve or View Installed Operators in namespace openshift-storage to install the operator.
ImportantBefore you click either of the options, wait for a few minutes on the Manual approval required page until the install plan gets loaded in the window.
ImportantIf you choose to click Approve, you must review the install plan before you proceed.
If you click Approve.
- Wait for a few minutes while the OpenShift Container Storage Operator is getting installed.
- On the Installed operator - ready for use page, click View Operator.
-
Ensure the Project is
openshift-storage. By default, the Project isopenshift-storage. - Click Operators → Installed Operators
- Wait for the Status of OpenShift Container Storage to change to Succeeded.
If you click View Installed Operators in namespace openshift-storage .
- On the Installed Operators page, click ocs-operator.
- On the Subscription Details page, click the Install Plan link.
- On the InstallPlan Details page, click Preview Install Plan.
- Review the install plan and click Approve.
- Wait for the Status of the Components to change from Unknown to either Created or Present.
- Click Operators → Installed Operators
-
Ensure the Project is
openshift-storage. By default, the Project isopenshift-storage. - Wait for the Status of OpenShift Container Storage to change to Succeeded.
Verification steps
- Verify that OpenShift Container Storage Operator shows a green tick indicating successful installation.
-
Click View Installed Operators in namespace openshift-storage link to verify that OpenShift Container Storage Operator shows the Status as
Succeededon the Installed Operators dashboard.
1.4. Installing Local Storage Operator
Use this procedure to install the Local Storage Operator from the Operator Hub before creating OpenShift Container Storage clusters on local storage devices.
Procedure
- Log in to the OpenShift Web Console.
- Click Operators → OperatorHub.
- Search for Local Storage Operator from the list of operators and click on it.
Click Install.
Figure 1.1. Install Operator page
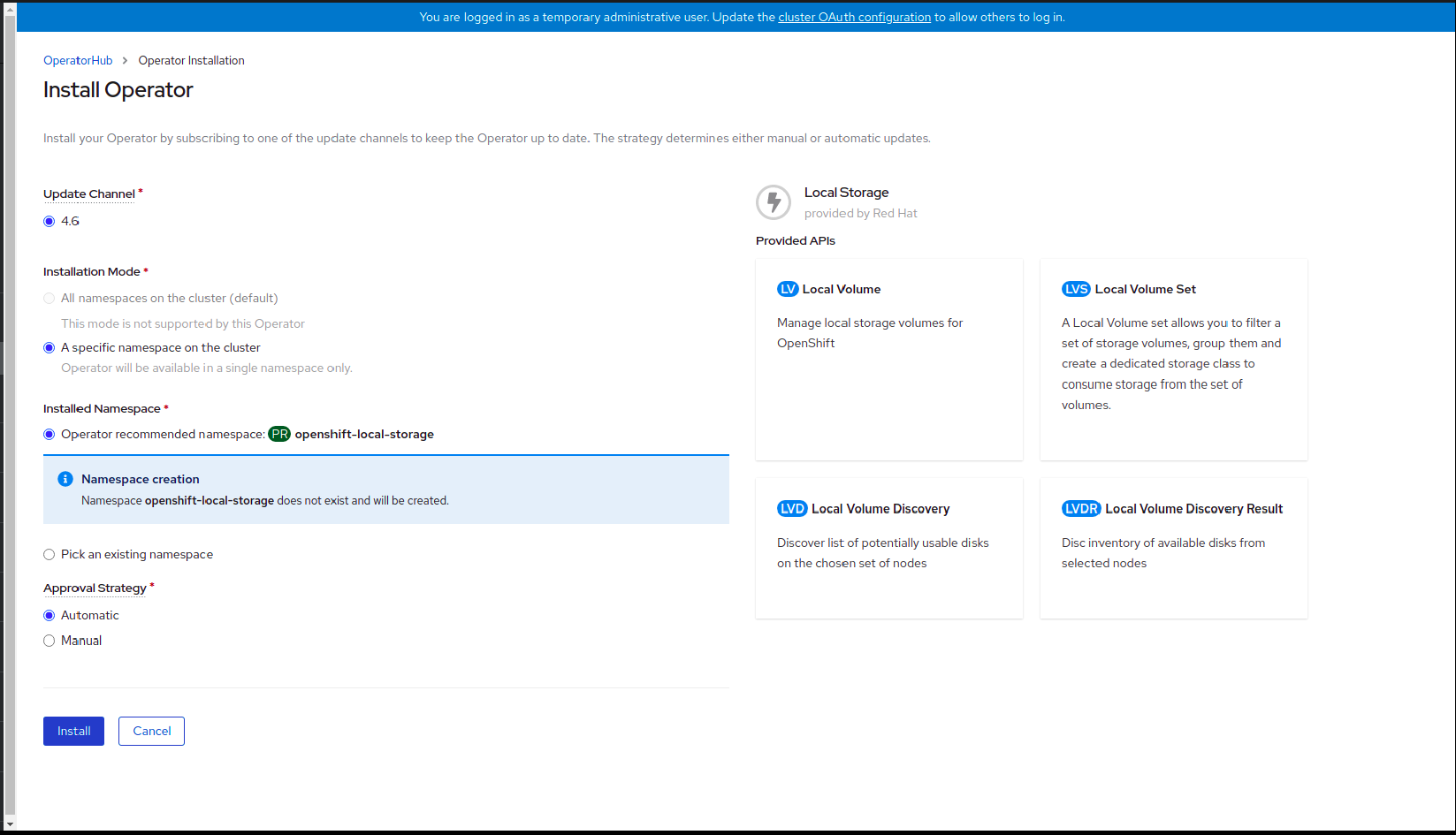
Set the following options on the Install Operator page:
- Update Channel as 4.6
- Installation Mode as A specific namespace on the cluster
- Installed Namespace as Operator recommended namespace openshift-local-storage.
- Approval Strategy as Automatic
- Click Install.
-
Verify that the Local Storage Operator shows the Status as
Succeeded.
1.5. Creating OpenShift Container Storage cluster on bare metal
Use this procedure to create a storage cluster when a storage class does not exist.
If you already have a storage class created, you can directly create a storage cluster as described in Creating a storage cluster on bare metal when a storage class exists.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that all the requirements in the Requirements for installing OpenShift Container Storage using local storage devices section are met.
- You must have a minimum of three worker nodes with the same storage type and size attached to each node (for example, 2TB NVMe hard drive) to use local storage devices on bare metal.
Procedure
- Log into the OpenShift Web Console.
Click Operators → Installed Operators to view all the installed operators.
Ensure that the Project selected is openshift-storage.
Figure 1.2. OpenShift Container Storage Operator page
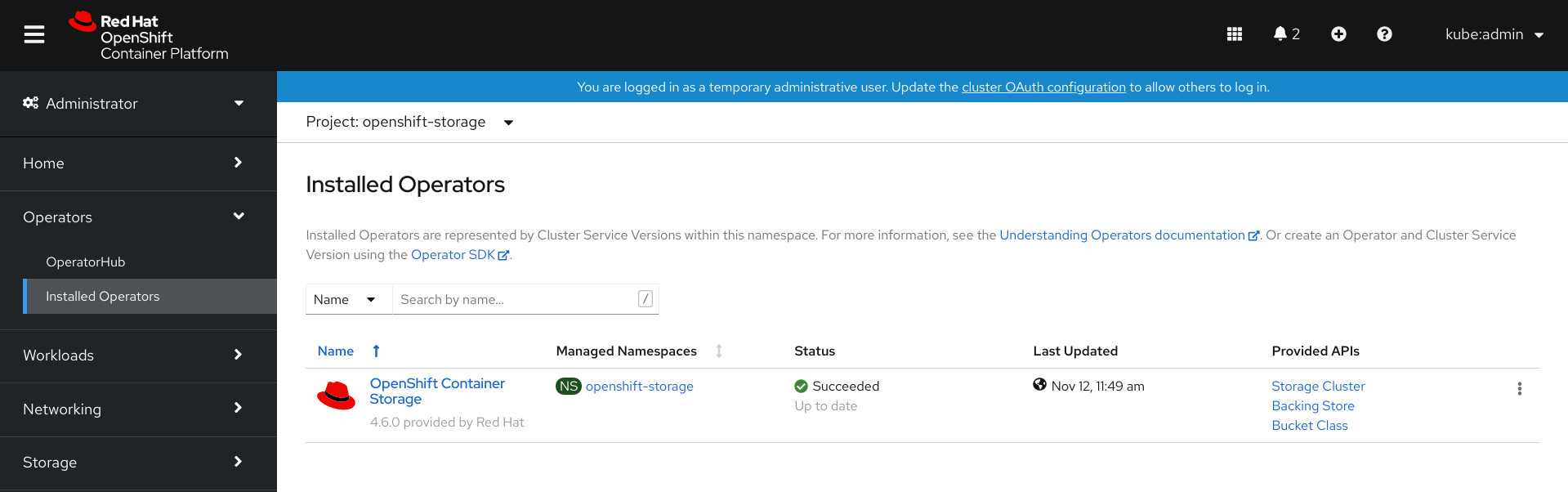
Click OpenShift Container Storage.
Figure 1.3. Details tab of OpenShift Container Storage
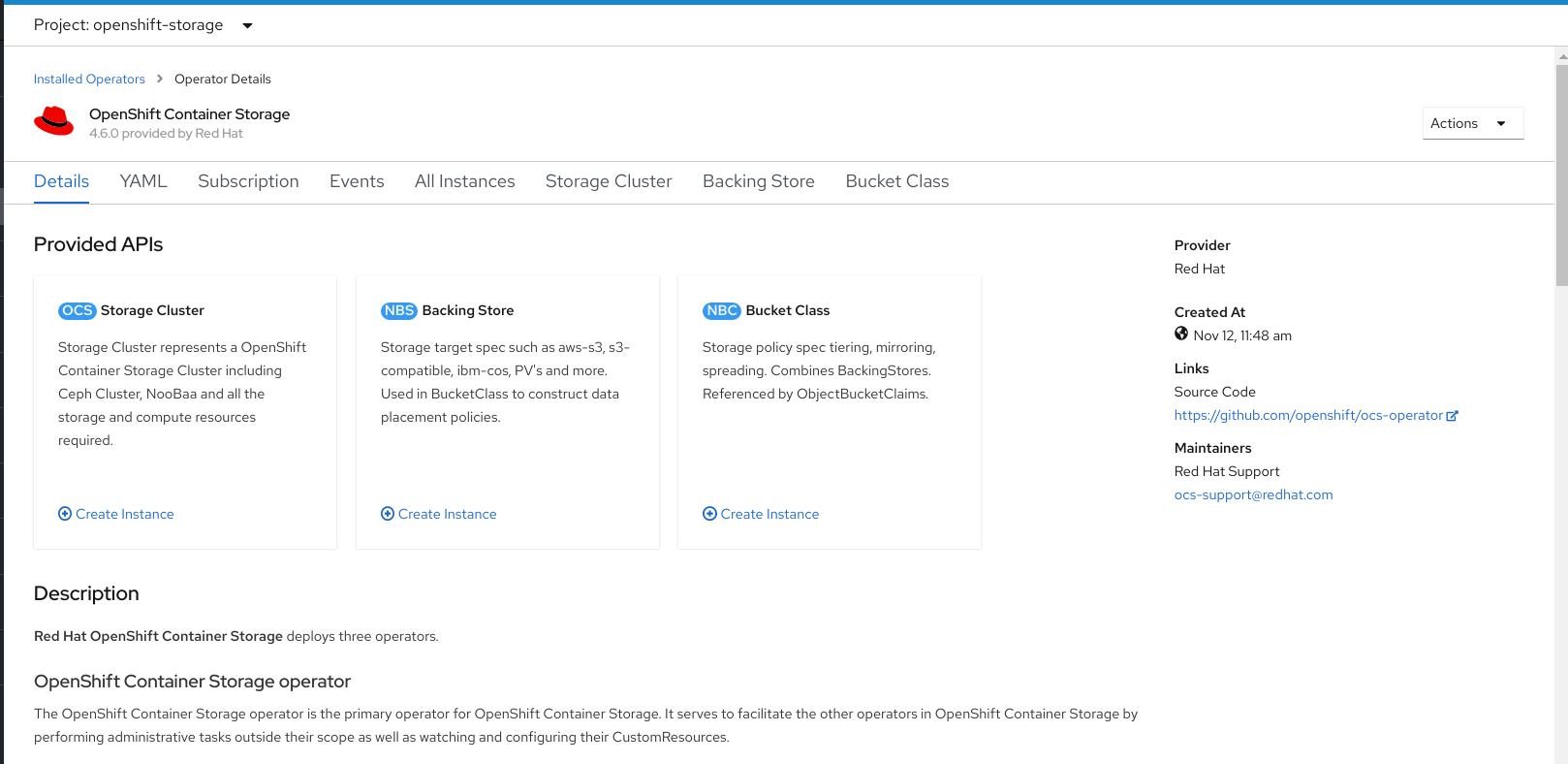
Click Create Instance link of Storage Cluster.
Figure 1.4. Create Storage Cluster page
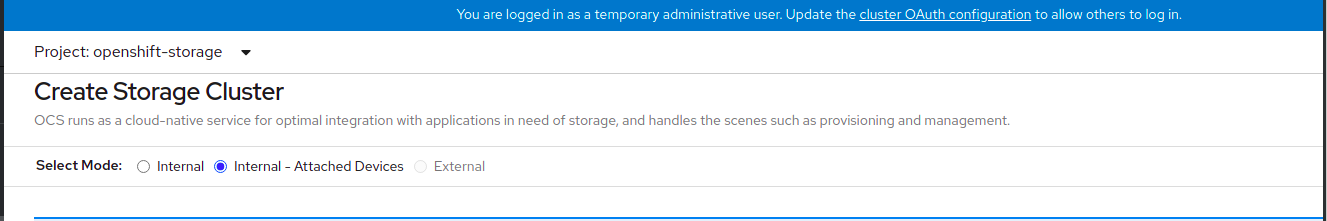
- Select Internal-Attached devices for the Select Mode. By default, Internal is selected.
Create a storage cluster using the wizard that includes disk discovery, storage class creation, and storage cluster creation.
You are prompted to install the Local Storage Operator if it is not already installed. Click Install and install the operator as described in Installing Local Storage Operator.
- Discover disks
You can discover a list of potentially usable disks on the selected nodes. Block disks and partitions that are not in use and available for provisioning persistent volumes (PVs) are discovered.
Figure 1.5. Discovery Disks wizard page
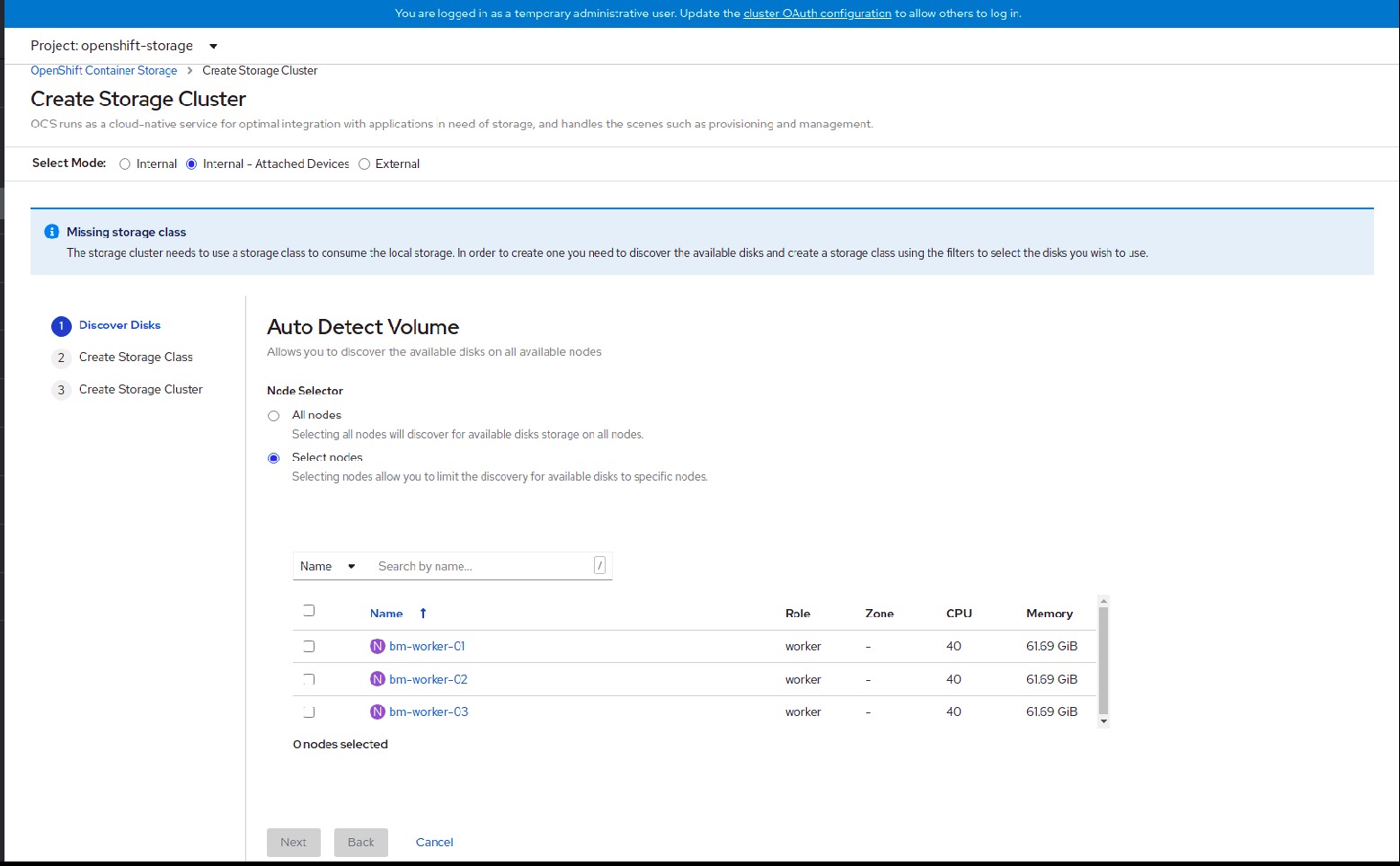
Choose one of the following:
- All nodes to discover disks in all the nodes.
Select nodes to discover disks from a subset of the listed nodes.
To find specific worker nodes in the cluster, you can filter nodes on the basis of Name or Label. Name allows you to search by name of the node and Label allows you to search by selecting the predefined label.
If the nodes selected do not match the OpenShift Container Storage cluster requirement of an aggregated 30 CPUs and 72 GiB of RAM, a minimal cluster will be deployed. For minimum starting node requirements, see Resource requirements section in Planning guide.
NoteIf the nodes to be selected are tainted and not discovered in the wizard, follow the steps provided in the Red Hat Knowledgebase Solution as a workaround.
- Click Next.
- Create Storage Class
You can create a dedicated storage class to consume storage by filtering a set of storage volumes.
Figure 1.6. Create Storage Class wizard page
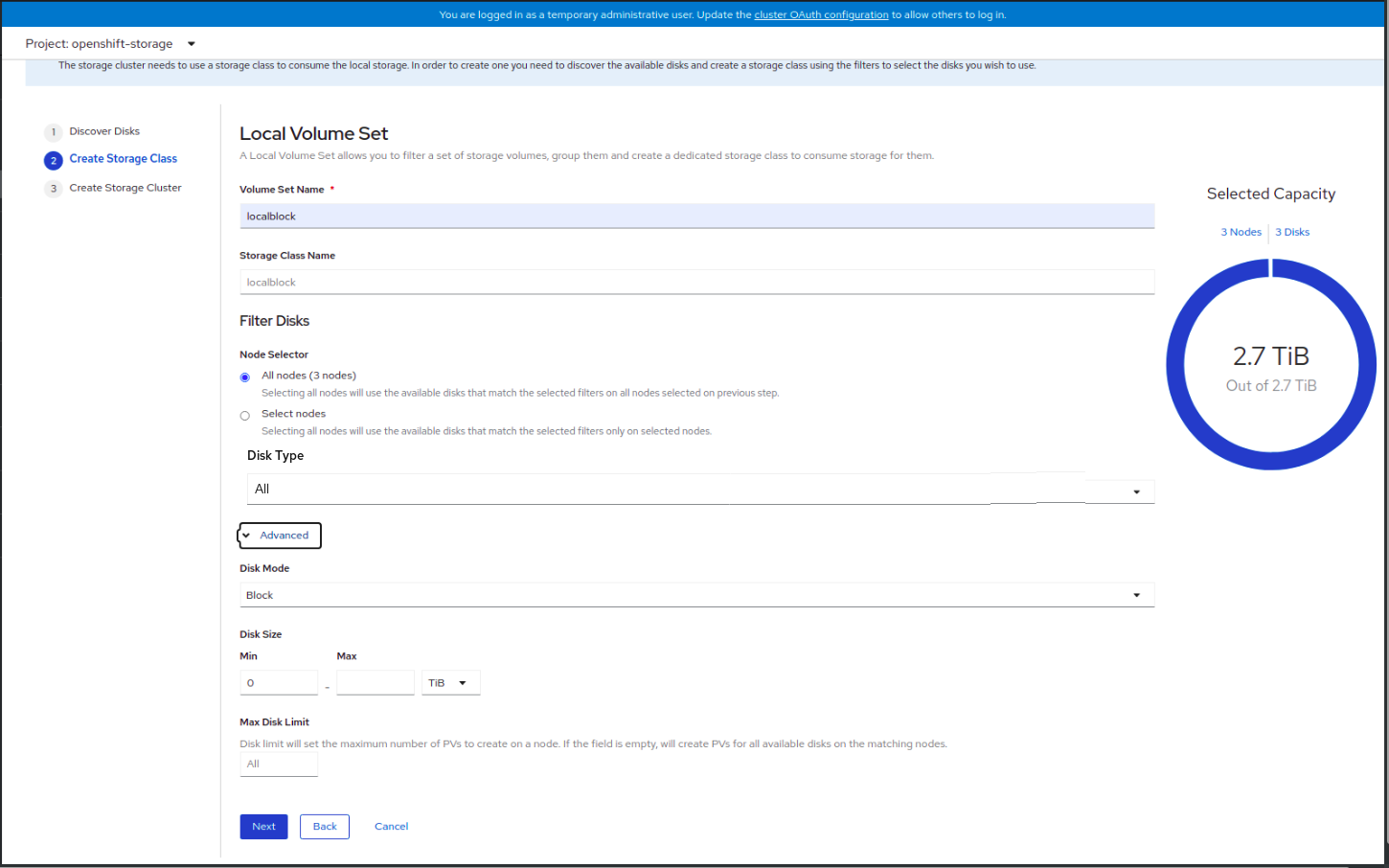
- Enter the Volume Set Name.
- Enter the Storage Class Name. By default, the volume set name appears for the storage class name.
The nodes selected for disk discovery in the earlier step are displayed in the Filter Disks section. Choose one of the following:
- All nodes to select all the nodes for which you discovered the devices.
Select nodes to select a subset of the nodes for which you discovered the devices.
To find specific worker nodes in the cluster, you can filter nodes on the basis of Name or Label. Name allows you to search by name of the node and Label allows you to search by selecting the predefined label.
It is recommended that the worker nodes are spread across three different physical nodes, racks or failure domains for high availability.
NoteEnsure OpenShift Container Storage rack labels are aligned with physical racks in the datacenter to prevent a double node failure at the failure domain level.
Select the required Disk Type. The following options are available:
All
Selects all types of disks present on the nodes. By default, this option is selected.
SSD/NVME
Selects only SSD NVME type of disks.
HDD
Selects only HDD type of disks.
In the Advanced section, you can set the following:
Disk Mode
Block is selected by default.
Disk Size
Minimum and maximum avaialable size of the device that needs to be included.
NoteYou must set a minimum size of 100GB for the device.
Max Disk Limit
This indicates the maximum number of PVs that can be created on a node. If this field is left empty, then PVs are created for all the available disks on the matching nodes.
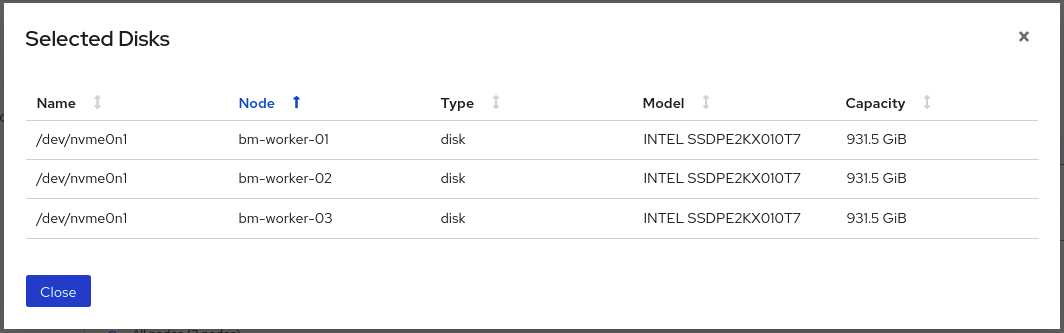
(Optional) You can view the selected capacity of the disks on the selected nodes using the Select Capacity chart.
This chart might take a few minutes to reflect the disks that are discovered in the previous step.
You can click on the Nodes and Disks links on the chart to bring up the list of nodes and disks to view more details.
Figure 1.7. List of selected nodes
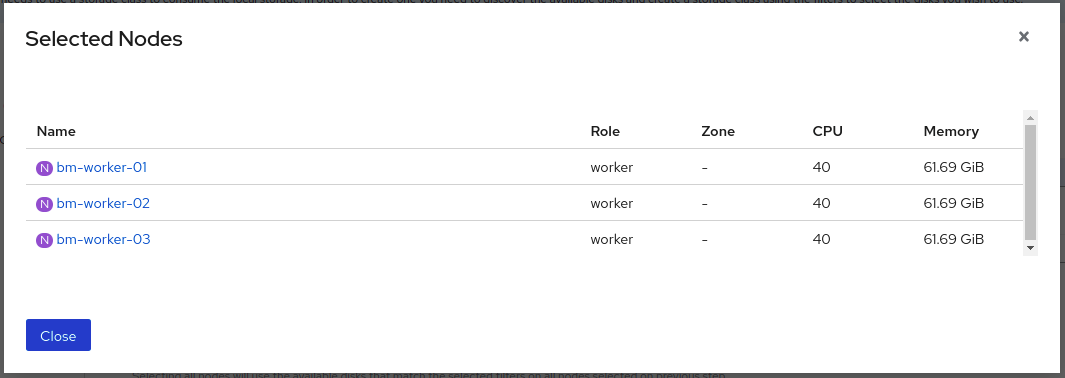
Figure 1.8. List of selected disks
- Click Next.
Click Yes in the message alert to confirm the creation of the storage class.
After the local volume set and storage class are created, it is not possible to go back to the step.
- Create Storage Cluster
Figure 1.9. Create Storage Cluster wizard page
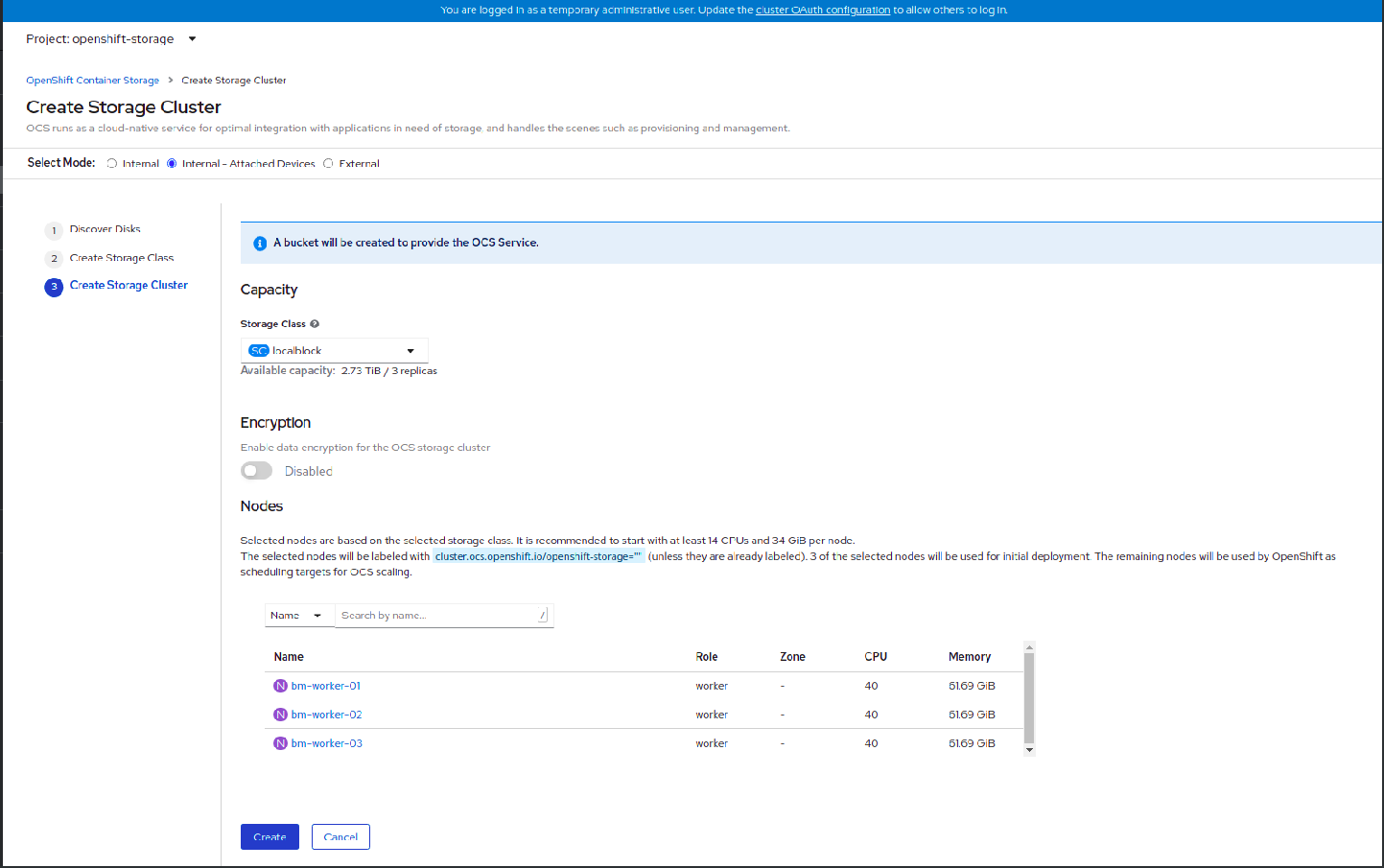
Select the required storage class.
You might need to wait a couple of minutes for the storage nodes corresponding to the selected storage class to get populated.
- (Optional) In the Encryption section, set the toggle to Enabled to enable data encryption on the cluster.
- The nodes corresponding to the storage class are displayed based on the storage class that you selected from the drop down list.
Click Create.
The Create button is enabled only when a minimum of three nodes are selected. A new storage cluster of three volumes will be created with one volume per worker node. The default configuration uses a replication factor of 3.
To expand the capacity of the initial cluster, see Scaling Storage guide.
Verification steps
See Verifying your OpenShift Container Storage installation.
1.6. Creating a storage cluster on bare metal when a storage class exists
You can create a Openshift Container Storage Cluster using the existing storage class that is created through the Local Storage Operator page.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that all the requirements in the Requirements for installing OpenShift Container Storage using local storage devices section are met.
- You must have a minimum of three worker nodes with the same storage type and size attached to each node (for example, 2TB NVMe hard drive) to use local storage devices on bare metal.
- You must have created a storage class that consists of a minimum of three nodes and volume attached to it.
Procedure
- Log into the OpenShift Web Console.
Click Operators → Installed Operators to view all the installed operators.
Ensure that the Project selected is openshift-storage.
Figure 1.10. OpenShift Container Storage Operator page

Click OpenShift Container Storage.
Figure 1.11. Details tab of OpenShift Container Storage

Click Create Instance link of Storage Cluster.
Figure 1.12. Create Storage Cluster page

Select Internal-Attached devices for the Select Mode. By default, Internal is selected.
Figure 1.13. Create Storage Cluster page
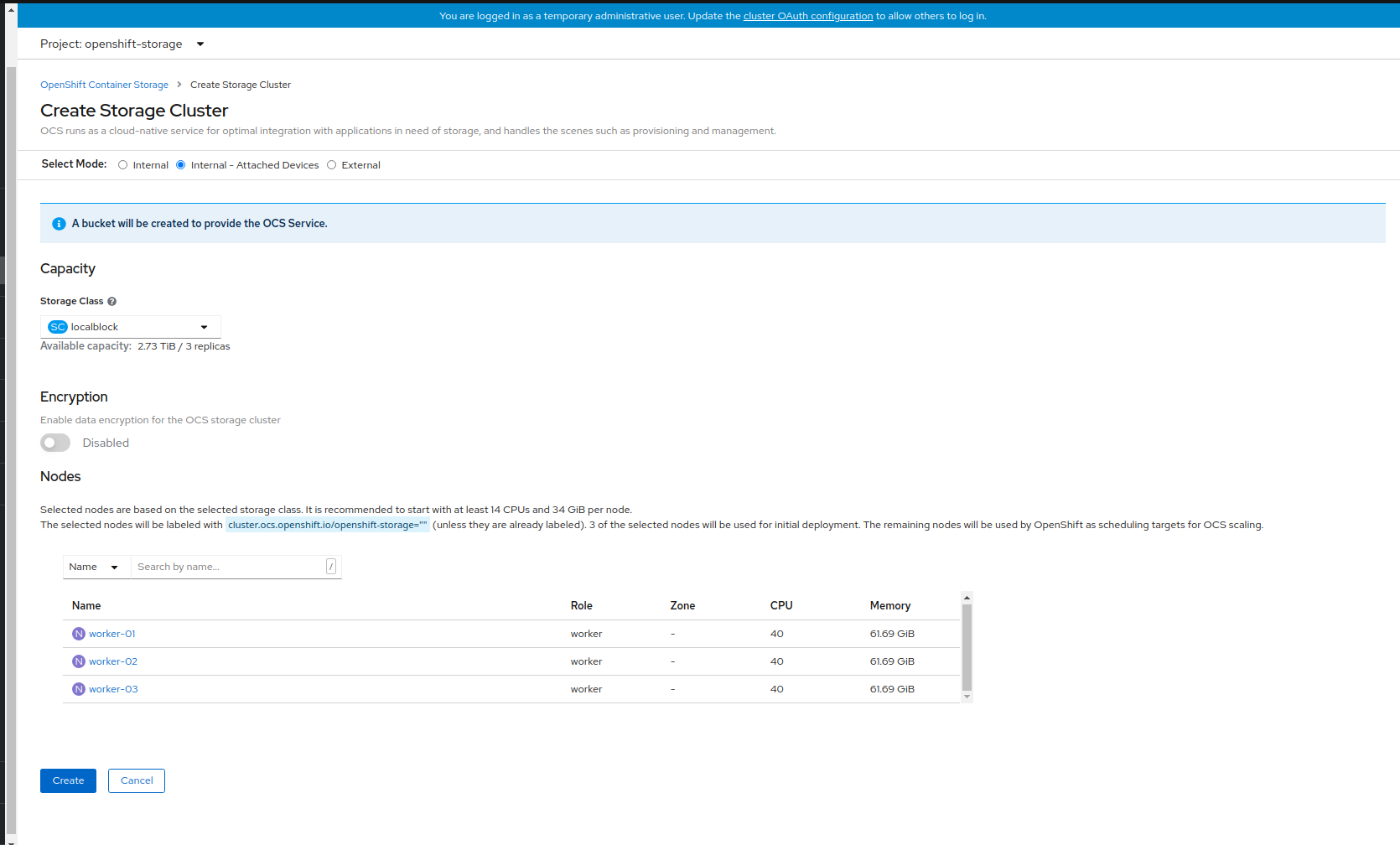
- (Optional) In the Encryption section, set the toggle to Enabled to enable data encryption on the cluster.
The nodes corresponding to the selected storage class are displayed.
The selected nodes are labeled with
cluster.ocs.openshift.io/openshift-storage=’’if they are not already labeled. Three of the selected nodes are used for initial deployment and the remaining nodes are used as the scheduling targets for OpenShift Container Storage scaling.Click Create.
The Create button is enabled only when a minimum of three nodes are selected.
A new storage cluster of three volumes will be created with one volume per worker node. The default configuration uses a replication factor of 3.
To expand the capacity of the initial cluster, see Scaling Storage guide.
Verification steps
See Verifying your OpenShift Container Storage installation.

