Chapter 3. ODBC compatibility
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard database access method developed by the SQL Access group in 1992. ODBC, just like JDBC in Java, allows consistent client access regardless of which database management system (DBMS) is handling the data. ODBC uses a driver to translate the application’s data queries into commands that the DBMS understands. For this to work, both the application and the DBMS must be ODBC-compliant – that is, the application must be capable of issuing ODBC commands and the DBMS must be capable of responding to them.
Data Virtualization can provide ODBC access to deployed VDBs in the Data Virtualization runtime through PostgreSQL’s ODBC driver. This is possible because Data Virtualization has a PostgreSQL server emulation layer accessible via socket clients.
By default, ODBC is enabled and running on on port 35432.
The pg emulation is not complete. The intention of the ODBC access is to provide non-JDBC connectivity to issue Data Virtualization queries - not pgsql queries. Although you can use many PostgreSQL constructs, the default behavior for queries matches Data Virtualization’s expectations. See System Properties for optional properties that further emulate pgsql handling.
Handling names with underscore ("") in ODBC. By default Data Virtualization does not have a default like escape character. Depending upon the ODBC client however there may be an expectation that backslash is used by default - which is the behavior of PostgreSQL. This may cause metadata queries to be issued against objects with "" in their name to return no or incorrect results. You may globally emulate the behavior of PostgreSQL by setting the org.teiid.backslashDefaultMatchEscape system property to true. To alter the property just for the current session then have your ODBC client issue select cast(teiid_session_set('backslashDefaultMatchEscape', true) as boolean) statement before any other statement.
Postgres ODBC drivers 9.5 and later do not require this special property as the client will use an E escaped literal instead.
Compatibility was last ensured with the 9.6 Postgres ODBC driver. You are encouraged to use later client versions when needed and report any issues to the community.
3.1. Known Limitations:
- Updateable cursors are not supported. You will receive parsing errors containing the pg system column ctid if this feature is not disabled.
- LO support is not available. LOBs will be returned as string or bytea as appropriate using the transport max lob size setting.
- The Data Virtualization object type will map to the PostgreSQL UNKNOWN type, which cannot be serialized by the ODBC layer. Cast/Convert should be used to provide a type hint when appropriate - for example teiid_session_set returns an object value. "SELECT teiid_session_set('x', 'y')" will fail, but "SELECT cast(teiid_session_set('x', 'y') as string)" will succeed.
- Multi-dimensional arrays are not supported.
3.2. Installation
Before an application can use ODBC, you must first install the ODBC driver on same machine that the application is running on and then create a Data Source Name (DSN) that represents a connection profile for your Data Virtualization VDB.
3.3. Configuration
By default, clients use plain text password authentication in Data Virtualization for pg/ODBC interfaces. If the client/server are not configured to use SSL or GSS authentication, the password will be sent in plain text over the network.
For a windows client, see the Configuring the Data Source Name.
See also DSN Less Connection.
3.3.1. Connection Settings
All the available pg driver connection options with their descriptions that can be used are defined here https://odbc.postgresql.org/docs/config.html. When using these properties on the connection string, their property names are defined here https://odbc.postgresql.org/docs/config-opt.html.
However Data Virtualization does not honor all properties, and some, such as Updatable Cursors, will cause query failures.
Table 3.1. Primary ODBC Settings For Data Virtualization
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Updateable Cursors & Row Versioning | Should not be used. |
| Use serverside prepare & Parse Statements & Disallow Premature | It is recommended that "Use serverside prepare" is enabled and "Parse Statements"/"Disallow Premature" are disabled |
| SSL mode | May be needed if you are connecting to a secured pg transport port. |
| Use Declare/Fetch cursors & Fetch Max Count | Should be used to better manage resources when large result sets are used |
Logging/debug settings can be utilized as needed.
Settings that manipulate datatypes, metadata, or optimizations such as "Show SystemTables", "True is -1", "Backend genetic optimizer", "Bytea as LongVarBinary", "Bools as Char", etc. are ignored by the Data Virtualization server and have no client side effect. If there is a need for these or any other settings to have a defined affect, please open an issue with the product/project.
Any other setting that does have a client side affect, such as "LF <→ CR/LF conversion", may be used if desired but there is currently no server side usage of the setting.
3.3.1.1. Data Virtualization Connection Settings
Most Data Virtualization specific connection properties do not map to ODBC client connection settings. If you find yourself in this situation and cannot use post connection SET statements, then the VDB itself may take default connection properties for ODBC. Use VDB properties of the form connection.XXX to control things like partial results mode, result set caching, etc.
The application name may be set by some clients. If not, you may use a SET statement - "SET application_name name" - to set the name even after the connection is made.
3.4. Configuring the Data Source Name (DSN)
See Data Virtualization compatible options for a description of the available client configuration options.
3.4.1. Windows Installation
Once you have installed the ODBC Driver Client software on your workstation, you have to configure it to connect to a Data Virtualization Runtime. Note that the following instructions are specific to the Microsoft Windows Platform.
To do this, you must have logged into the workstation with administrative rights, and you need to use the Control Panel’s Data Sources (ODBC) applet to add a new data source name.
Each data source name you configure can only access one VDB within a Data Virtualization System. To make more than one VDB available, you need to configure more than one data source name.
Follow the below steps in creating a data source name (DSN)
- From the Start menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
- The Control Panel displays. Double click Administrative Tools.
- Then Double-click Data Sources (ODBC).
- The ODBC Data Source Administrator applet displays. Click the tab associated with the type of DSN you want to add.
- The Create New Data Source dialog box displays. In the Select a driver for which you want to set up a data source table, select PostgreSQL Unicode.
- Click Finish
The PostgreSQL ODBC DSN Setup dialog box displays.
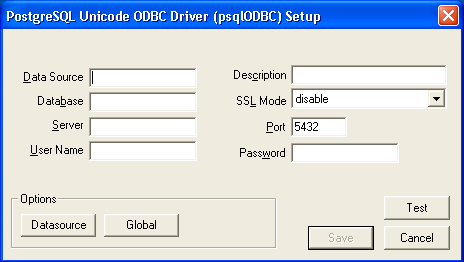
In the Data Source Name edit box, type the name you want to assign to this data source. In the Database edit box, type the name of the virtual database you want to access through this data source. In the Server edit box, type the host name or IP address of your Data Virtualization runtime. If connecting via a firewall or NAT address, the firewall address or NAT address should be entered. In the Port edit box, type the port number to which the Data Virtualization System listens for ODBC requests. By default, Data Virtualization listens for ODBC requests on port 35432 In the User Name and Password edit boxes, supply the user name and password for the Data Virtualization runtime access. Provide any description about the data source in the Description field.
Click on the Datasource button, you will see this below figure. Configure options as shown.
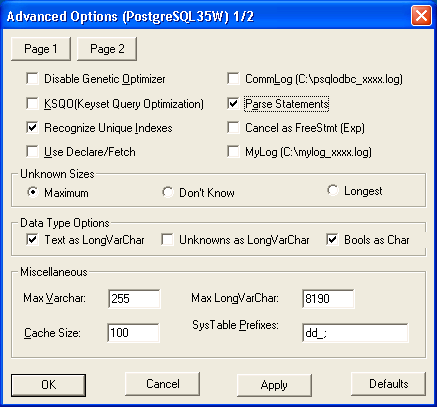
Click on "page2" and make sure the options are selected as shown

- Click "save" and you can optionally click "test" to validate your connection if the Data Virtualization is running. You have configured a Data Virtualization’s virtual database as a data source for your ODBC applications. Now you can use applications such as Excel, Access to query the data in the VDB
3.4.2. Other *nix Platform Installations
Before you can access Data Virtualization using ODBC on any *nix platforms, you need to either install a ODBC driver manager or verify that one already exists. As the ODBC Driver manager Data Virtualization recommends unixODBC. If you are working with RedHat Linux or Fedora you can check the graphical "yum" installer to search, find and install unixODBC. Otherwise you can download the unixODBC manager here. To install, simply untar the contents of the file to a temporary location and execute the following commands as super user.
./configure make make install
Check unixODBC website site for more information, if you run into any issues during the installation.
Now, to verify that PostgreSQL driver installed correctly from earlier step, execute the following command
odbcinst -q -d
That should show you all the ODBC drivers installed in your system. Now it is time to create a DSN. Edit "/etc/odbc.ini" file and add the following
[<DSN name>] Driver = /usr/lib/psqlodbc.so Description = PostgreSQL Data Source Servername = <Data Virtualization Host name or ip> Port = 35432 Protocol = 7.4-1 UserName = <user-name> Password = <password> Database = <vdb-name> ReadOnly = no ServerType = Postgres ConnSettings = UseServerSidePrepare=1 Debug=0 Fetch = 10000 # enable below when dealing large resultsets to enable cursoring #UseDeclareFetch=1
Note that you need "sudo" permissions to edit the "/etc/odbc.ini" file. For all the available configurable options that you can use in defining a DSN can be found here on postgreSQL ODBC page.
Once you are done with defining the DSN, you can verify your DSN using the following command
isql <DSN-name> [<user-name> <password>] < commands.sql
where "commands.sql" file contains the SQL commands you would like to execute. You can also omit the commands.sql file, then you will be provided with a interactive shell.
You can also use languages like Perl, Python, C/C++ with ODBC ports to Postgres, or if they have direct Postgres connection modules you can use them too to connect Data Virtualization and issue queries an retrieve results.
3.5. DSN Less Connection
You can also connect to Data Virtualization VDB using ODBC with out explicitly creating a DSN. However, in these scenarios your application needs, what is called as "DSN less connection string". The below is a sample connection string
For Windows:
ODBC;DRIVER={PostgreSQL Unicode};DATABASE=<vdb-name>;SERVER=<host-name>;PORT=<port>;Uid=<username>;Pwd=<password>;c4=0;c8=1;For *nix:
ODBC;DRIVER={PostgreSQL};DATABASE=<vdb-name>;SERVER=<host-name>;PORT=<port>;Uid=<username>;Pwd=<password>;c4=0;c8=1;See the available Data Virtualization connection options.
3.6. Configuring Connection Properties with ODBC
When working with ODBC connection, the user can set the connection properties Driver Connection#URL Connection Properties that are available in Data Virtualization by executing the command like below.
SET <property-name> TO <property-value>
for example to turn on the result set caching you can issue
SET resultSetCacheMode TO 'true'
Another option is to set this as VDB property in the vdb file as
CREATE DATABASE vdb OPTIONS ("connection.partialResultsMode" true);
