-
Language:
English
-
Language:
English
Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Gluster Storage
Chapter 10. Managing Multilevel Administration
Red Hat Storage Console supports multilevel administration. That is, users can be assigned a variety of permissions for specific objects using a number of default roles. This section describes how to set up user roles that control levels of permissions for different objects and actions in your storage environment. Customized roles can also be created and assigned to users.
Red Hat Storage Console relies on directory services for user authentication. The providers of directory services currently supported for use with the Red Hat Storage Console are Identity (IdM), Active Directory, and Red Hat Directory Server (RHDS).
Note
Users are not created in Red Hat Storage, but in the Directory Services domain. Red Hat Storage Console can be configured to use multiple Directory Services domains. See the Red Hat Storage Console Installation Guide for more information.
10.1. Configuring Roles
Roles are predefined sets of privileges that can be configured from Red Hat Storage Console, providing access and management permissions to different levels of resources in the cluster. Permissions enable users to perform actions on objects.
With multilevel administration, any permissions that apply to a container object also apply to all individual objects within that container. For example, when a server administrator role is assigned to a user on a specific server, the user gains permissions to perform any of the available operations, but only on the assigned server. However, if the administrator role is assigned to a user on a cluster, the user gains permissions to perform operations on all servers within the cluster.
10.1.1. Roles
There is one type of role in Red Hat Storage Console, which is the
administrator role. This role allows access to the Administration Portal for managing server resources. For example, if a user has an administrator role on a cluster, they can manage all servers in the cluster using the Administration Portal.
The default roles cannot be removed from the Red Hat Storage, and their privileges cannot be modified. However, you can clone them and then customize the new roles as required.
10.1.2. Creating Custom Roles
In addition to the default roles, you can set up custom roles that permit actions on objects, such as servers and clusters, and assign privileges to specific entities. Use roles to create a granular model of permissions to suit the needs of the enterprise or a group or set of users. Use the Configure option to work with roles. You can create a New role, or Edit, Clone or Remove an existing role. In each case, the appropriate dialog box displays.
Once the role is set up, you can assign the role to users as required.
Procedure 10.1. Creating a New Role
- On the header bar of the Red Hat Storage Console menu, click Configure. The Configure dialog box displays. The dialog box includes a list of Administrator roles, and any custom roles.
- Click New. The New Role dialog box displays.
- Enter the Name and Description of the new role. This name will display in the list of roles.
- Select Admin as the Account Type. If Admin is selected, this role displays with the administrator icon in the list.
- Use the Expand All or Collapse All buttons to view more or fewer of the permissions for the listed objects in the Check Boxes to Allow Action list. You can also expand or collapse the options for each object.
- For each of the objects, select or deselect the actions you wish to permit/deny for the role you are setting up.
- Click OK to apply the changes you have made. The new role displays on the list of roles.
10.1.3. Editing Roles
While you cannot make changes to the default roles, you may need to change the permissions, names or descriptions of custom roles. To edit custom roles, use the Edit button on the Configure dialog box.
Procedure 10.2. Editing a Role
- On the header bar of the Red Hat Storage Console menu, click Configure. The Configure dialog box displays. The dialog box below shows the list of administrator roles.
- Click Edit. The Edit Role dialog box displays.
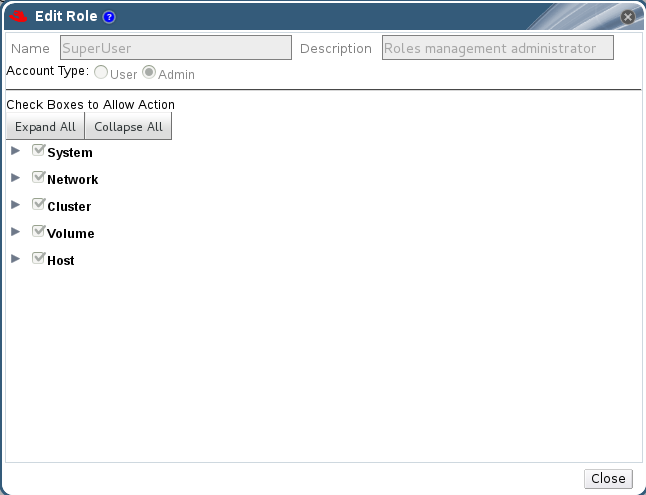
Figure 10.1. The Edit Role Dialog Box
- If necessary, edit the Name and Description of the role. This name will display in the list of roles.
- Use the Expand All or Collapse All buttons to view more or fewer of the permissions for the listed objects. You can also expand or collapse the options for each object.
- For each of the objects, select or deselect the actions you wish to permit/deny for the role you are editing.
- Click OK to apply the changes you have made.
10.1.4. Copying Roles
You can create a new role by cloning an existing default or custom role, and changing the permissions set as required. Use the Copy button on the Configure dialog box.
Procedure 10.3. Copying a Role
- On the header bar of the Red Hat Storage Console, click Configure. The Configure dialog box displays. The dialog box includes a list of default roles, and any custom roles that exist on the Red Hat Storage Console.
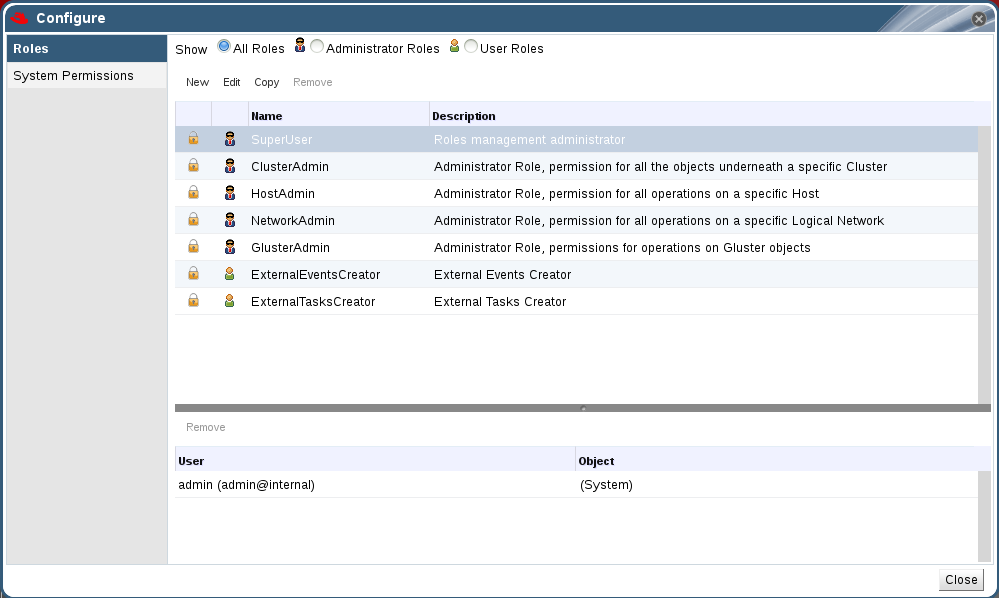
Figure 10.2. The Configure Dialog Box
- Click Copy. The Copy Role dialog box displays.
- Change the Name and Description of the new role. This name will display in the list of roles.
- Use the Expand All or Collapse All buttons to view more or fewer of the permissions for the listed objects. You can also expand or collapse the options for each object.
- For each of the objects, select or deselect the actions you wish to permit/deny for the role you are editing.
- Click Close to apply the changes you have made.

