-
Language:
English
-
Language:
English
Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Gluster Storage
5.3. Logical Network Tasks
5.3.1. Using the Networks Tab
- Attaching or detaching the networks to clusters and hosts
- Adding and removing permissions for users to access and manage networks
5.3.2. Creating a New Logical Network in Cluster
Create a logical network and define its use in a cluster.
Procedure 5.1. Creating a New Logical Network in a Cluster
- Click the Networks or Clusters tab in tree mode and select a network or cluster.
- Click the Logical Networks tab of the details pane to list the existing logical networks.
- From the Clusters tab, select Logical Networks sub-tab and click Add Network to open the New Logical Network window.
- From the Networks tab, click New to open the New Logical Network window.
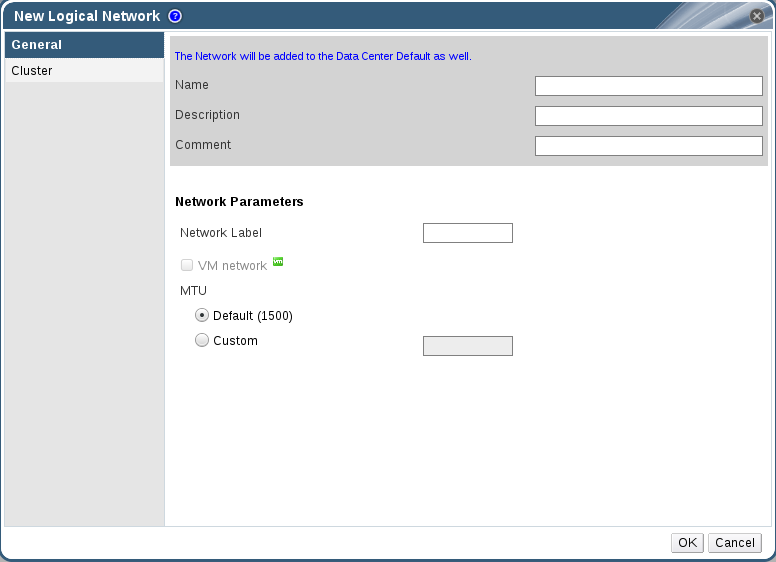
Figure 5.2. New Logical Network
- Enter a Name, Description, and Comment for the logical network.
- From the Cluster tab, select the clusters to which the network will be assigned. You can also specify whether the logical network will be a required network.
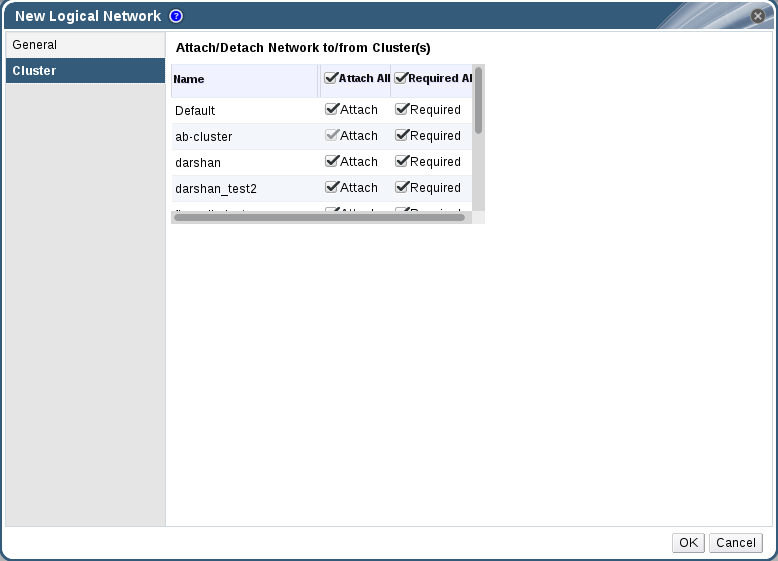
Figure 5.3. New Logical Network - Cluster
- Click OK.
You have defined a logical network as a resource required by a cluster or clusters in the Network. If you entered a label for the logical network, it will be automatically added to all host network interfaces with that label.
5.3.3. Editing a Logical Network
Edit the settings of a logical network.
Procedure 5.2. Editing a Logical Network
- Click Networks tab in tree mode and select a Network.
- Select a logical network and click Edit to open the Edit Logical Network window.
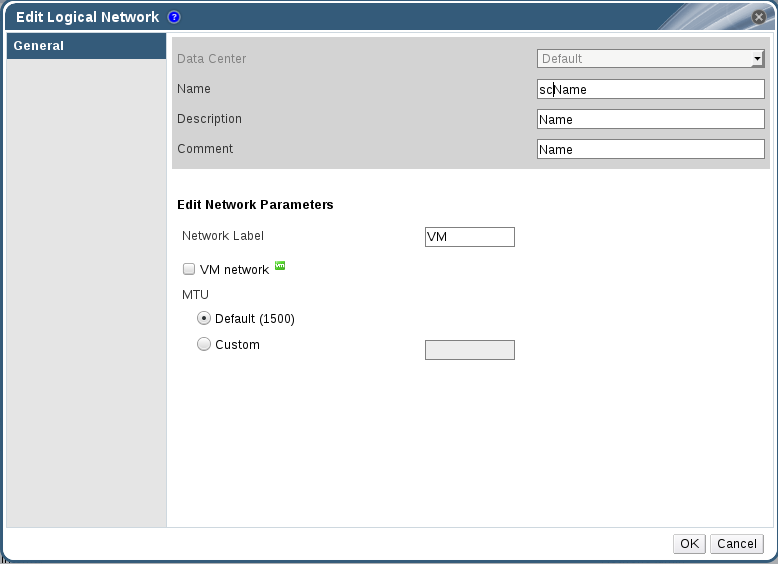
Figure 5.4. New Logical Network - Cluster
- Edit the necessary settings.
- Click OK to save the changes.
You have updated the settings of your logical network.
Note
5.3.4. Explanation of Settings and Controls in the New Logical Network and Edit Logical Network Windows
5.3.4.1. Logical Network General Settings Explained
Table 5.1. New Logical Network and Edit Logical Network Settings
|
Field Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Name
|
The name of the logical network. This text field has a 15-character limit and must be a unique name with any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores.
|
|
Description
|
The description of the logical network. This text field has a 40-character limit.
|
|
Comment
|
A field for adding plain text, human-readable comments regarding the logical network.
|
|
Network Label
|
Allows you to specify a new label for the network or select from existing labels already attached to host network interfaces. If you select an existing label, the logical network will be automatically assigned to all host network interfaces with that label.
|
5.3.4.2. Logical Network Cluster Settings Explained
Table 5.2. New Logical Network Settings
|
Field Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Attach/Detach Network to/from Cluster(s)
|
Allows you to attach or detach the logical network from clusters and specify whether the logical network will be a required network for individual clusters.
Name - the name of the cluster to which the settings will apply. This value cannot be edited.
Attach All - Allows you to attach or detach the logical network to or from all clusters. Alternatively, select or clear the Attach check box next to the name of each cluster to attach or detach the logical network to or from a given cluster.
Required All - Allows you to specify whether the logical network is a required network on all clusters. Alternatively, select or clear the Required check box next to the name of each cluster to specify whether the logical network is a required network for a given cluster.
|
5.3.5. Designate a Specific Traffic Type for a Logical Network with the Manage Networks Window
Specify the traffic type for the logical network to optimize the network traffic flow.
Procedure 5.3. Specifying Traffic Types for Logical Networks
- Click Clusters tab in tree mode and select the cluster in the results list.
- Select the Logical Networks tab in the details pane to list the logical networks assigned to the cluster.
- Click Manage Networks to open the Manage Networks window.

Figure 5.5. Manage Networks Window
- Select appropriate check boxes.
- Click OK to save the changes and close the window.
You have optimized the network traffic flow by assigning a specific type of traffic to be carried on a specific logical network.
5.3.6. Explanation of Settings in the Manage Networks Window
Table 5.3. Manage Networks Settings
|
Field
|
Description/Action
|
|---|---|
|
Assign
|
Assigns the logical network to all hosts in the cluster.
|
|
Required
|
A Network marked "required" must remain operational in order for the hosts associated with it to function properly. If a required network ceases to function, any hosts associated with it become non-operational.
|
|
Gluster Network
| A logical network marked "Gluster Network" carries gluster network traffic. |
5.3.7. Network Labels
Network Label Associations
- When you attach a label to a logical network, that logical network will be automatically associated with any physical host network interfaces with the given label.
- When you attach a label to a physical host network interface, any logical networks with the given label will be automatically associated with that physical host network interface.
- Changing the label attached to a logical network or physical host network interface acts in the same way as removing a label and adding a new label. The association between related logical networks or physical host network interfaces is updated.
Network Labels and Clusters
- When a labeled logical network is added to a cluster and there is a physical host network interface in that cluster with the same label, the logical network is automatically added to that physical host network interface.
- When a labeled logical network is detached from a cluster and there is a physical host network interface in that cluster with the same label, the logical network is automatically detached from that physical host network interface.
Network Labels and Logical Networks With Roles
- When a labeled logical network is assigned to act as a display network or migration network, that logical network is then configured on the physical host network interface using DHCP so that the logical network can be assigned an IP address.

