-
Language:
English
-
Language:
English
Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Fuse
Chapter 2. Design and develop an API definition with Apicurito
You can use Apicurito to design and develop a REST API definition that complies with the OpenAPI 2.0 specification.
Prerequisites
- You created an OpenShift project.
- You added the Apicurito service to your OpenShift project.
2.1. Creating a REST API definition
The following steps describe how to create a REST API definition.
- You can access the Apicurito user interface from Fuse Online or Fuse on OpenShift.
- For Fuse on OpenShift only, Apicurito is stateless which means that it does not save your work between OpenShift sessions. You need to save the API to your local file system between sessions.
About the example
The Task Management API example simulates a simple API that sales consultants might use to track the tasks that they need to do when interacting with customer contacts. Example "to-do" tasks might be "create an account for a new contact" or "place an order for an existing contact". To implement the Task Management API example, you create two paths - one for tasks and one for a specific task. You then define operations to create a task, retrieve a task by its ID, and delete a task by its ID.
Prerequisites
-
You know the endpoints for the API that you want to create. For the Task Management API example, there are two endpoints:
/todoand/todo/{id}. - For Fuse on OpenShift only, you created an OpenShift project and you added the Apicurito service to your OpenShift project.
Procedure
If you are using Fuse Online, skip to step 2.
If you are using Fuse on OpenShift:
- Log in to your OpenShift web console and then open the project that contains Apicurito.
In the list of applications, click the URL for Apicurito, for example
https://apicurito-myproject.192.168.64.43.nip.io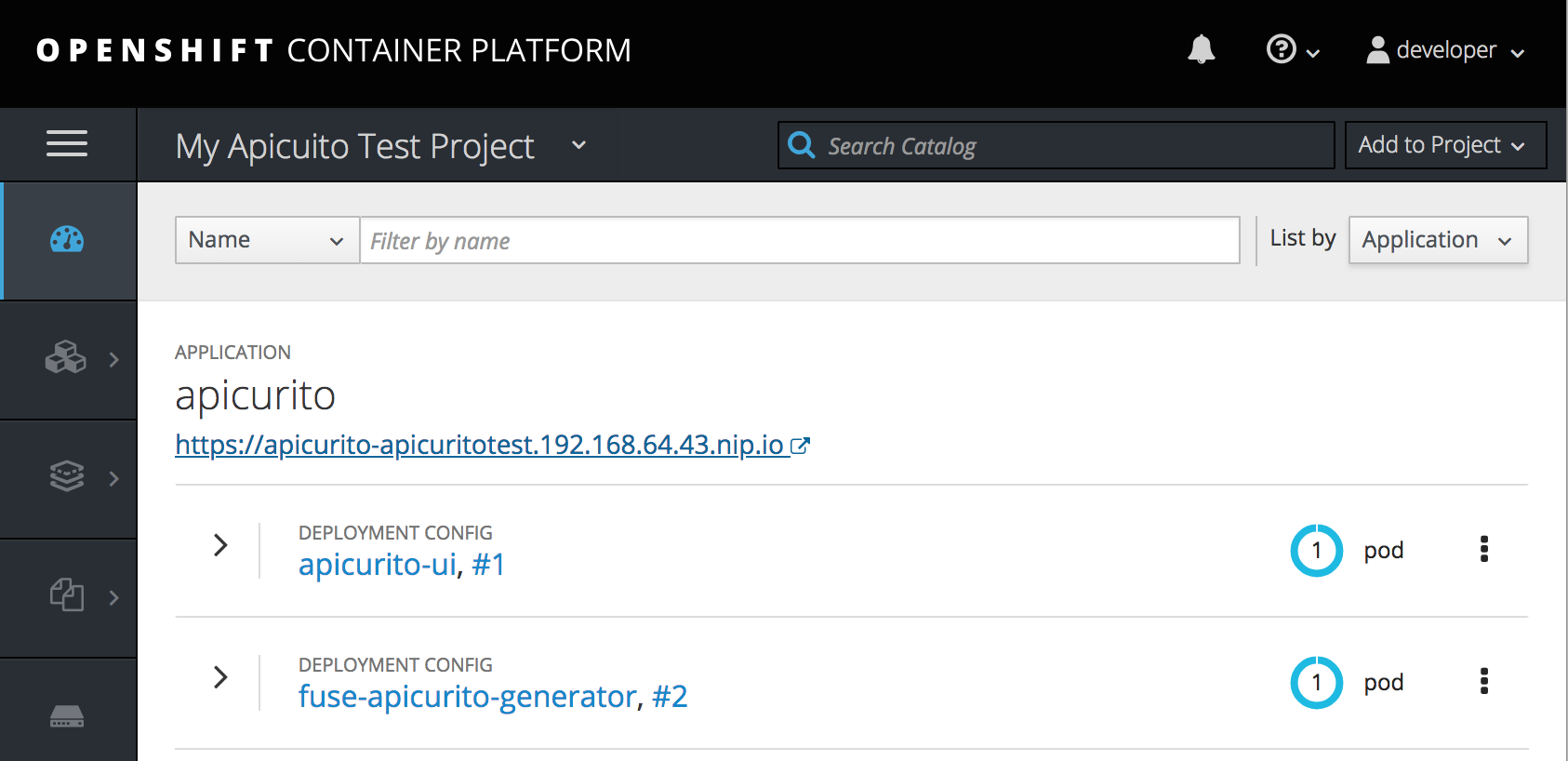
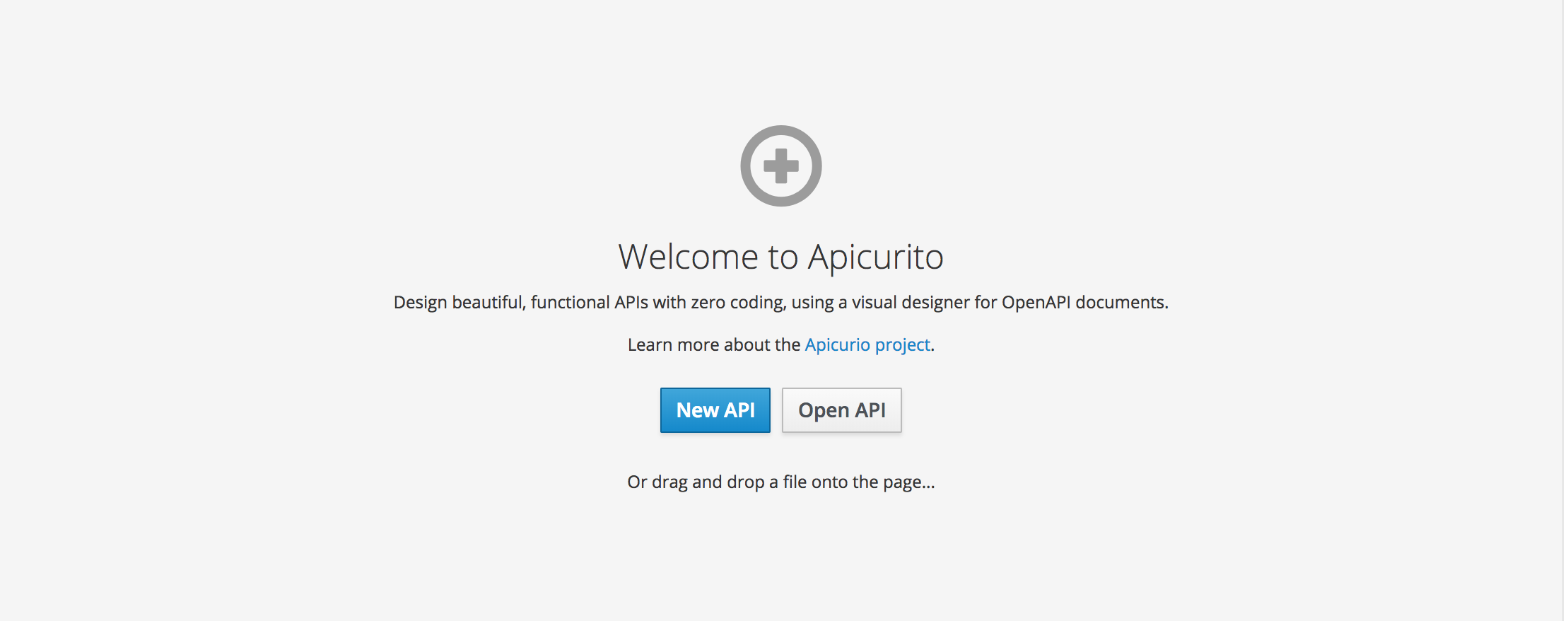
A new browser window or tab opens for Apicurito:
 Note
NoteBecause Apicurito is a “light” version of the Apicurio Studio open source project, "Apicurio" shows in the Apicurito interface.
- Click New API. A new API page opens.
To change the API name:
-
Hover the cursor over the name and then click the edit icon (
 ) that appears.
) that appears.
- Edit the name. For example, type Task API.
- Confirm the name change.
-
Hover the cursor over the name and then click the edit icon (
Optionally:
- Add your contact information (name, email address, and URL).
- Select a license.
- Define tags.
- Define a security scheme.
- Specify security requirements.
Define a relative path to each individual endpoint of the API. The field name must begin with a slash (/).
For the Task Management API example, create two paths:
-
A path for tasks:
/todo A path for a specific task by ID:
/todo/{id}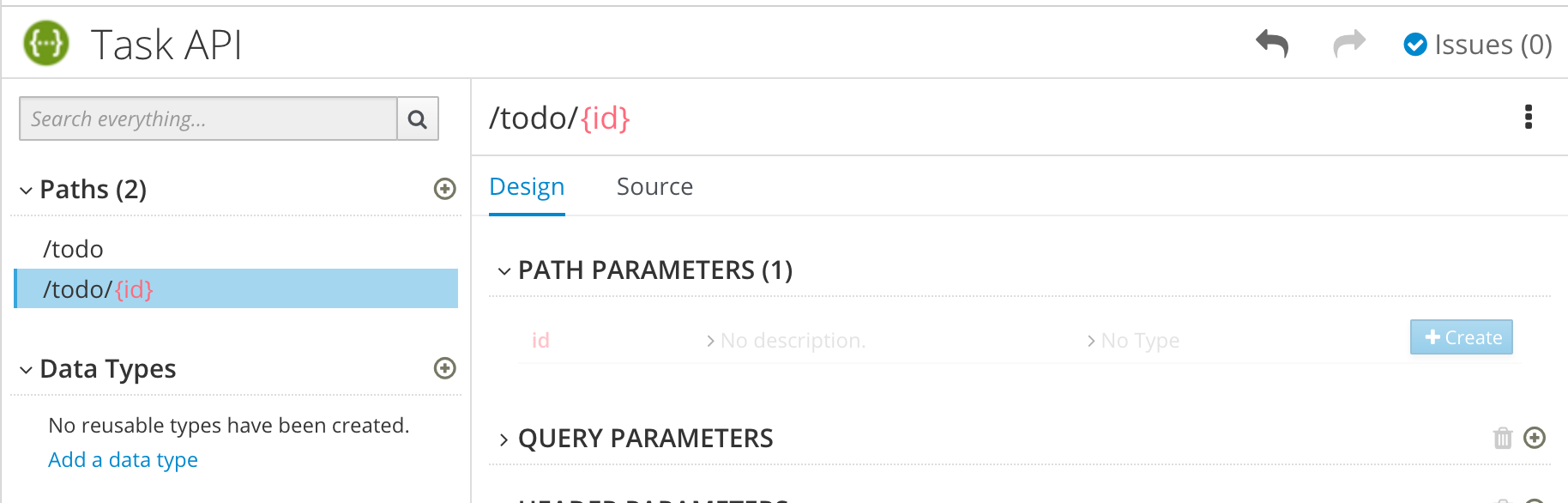
-
A path for tasks:
Specify the type of any path parameters.
For the example
idparameter:In the Paths list, click
/todo/{id}.The id parameter appears in the PATH PARAMETERS section.
- Click Create.
- For the description, type: The ID of the task to find.
For the type, select integer as 32-Bit integer.

In the Data Types section, define reusable types for the API.
- Click Add a data type.
- In the Add Data Type dialog, type a name. For the Task Management API example, type Todo.
Optionally, you can provide an example from which Apicurito creates the data type’s schema. You can then edit the generated schema.
For the Task Management API example, start with the following JSON example:
{ "id": 1, "task": "my task", "completed": false }- Optionally, you can choose to create a REST Resource with the data type.
Click Save. If you provided an example, Apicurito generates a schema from the example:

- Optionally, you can add edit the schema properties and add new ones.
For the Task Management API example, create another data type named Task with one property named task of type string.

For each path, define operations (GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, OPTIONS, HEAD, or PATCH).
For the Task Management API example, define the operations as described in the following table:
Table 2.1. Task Management API oeprations
Path Operation Description Request Response /todoPOST
Create a new task.
Request Body type: Task
Status Code: 201
Description: Task created
Response Body: Todo type
/todo/{id}GET
Get a task by ID.
Not applicable
Status Code: 200
Description: Task found for ID
Response Body: Todo type
/todo/{id}DELETE
Delete a task by ID.
Not applicable
Status Code: 200
Description: Task deleted
Status Code: 400
Description: Task not deleted
- Resolve any issues, as described in Section 2.2, “Resolving issues in Apicurito”.
For Fuse on OpenShift only, save your API specification by clicking Save As and then select JSON or YAML format.
The JSON or YAML file is downloaded to your local download folder. The default filename is
openapi-specwith the appropriate file extension.
Additional resources
- For information about the OpenAPI 2.0 Specification, go to: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/2.0.md
2.2. Resolving issues in Apicurito
When you create and edit an API, Apicurito identifies issues that you must resolve with an exclamation (!) icon.
Prerequisites
- Open an API in Apicurito.
Procedure
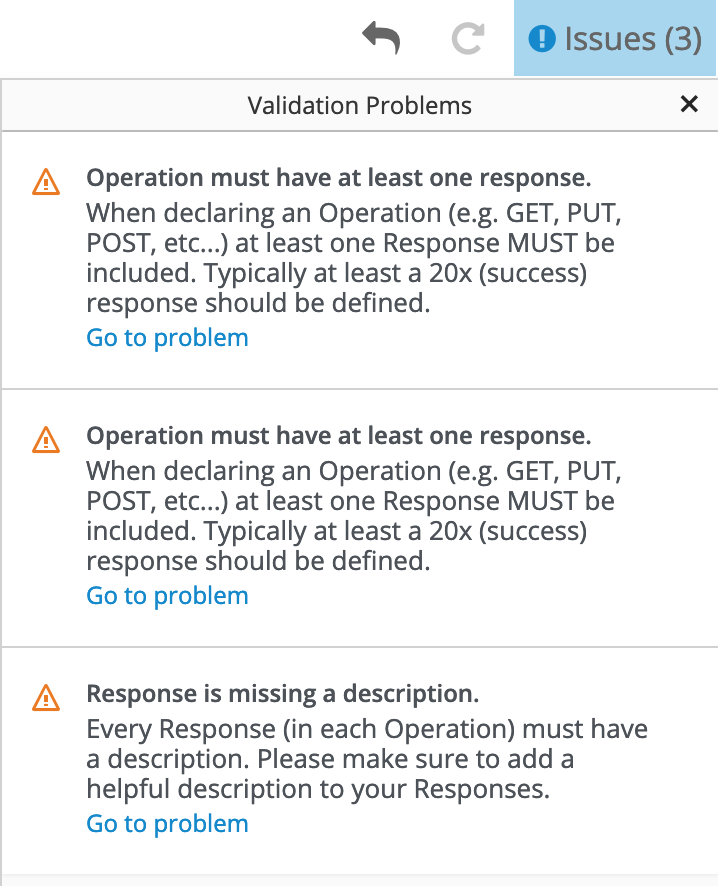
Find an issue indicated by an exclamation (!) icon. For example:

Click the exclamation icon to view a description of the issue. For example:
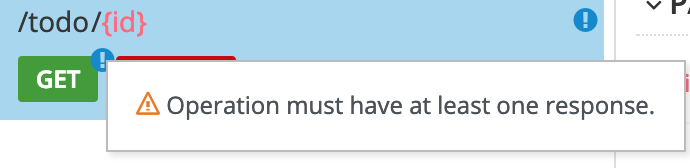
Based on the information provided by the issue description, navigate to the location of the issue and fix it.
For example, open the GET operation and then add a response.
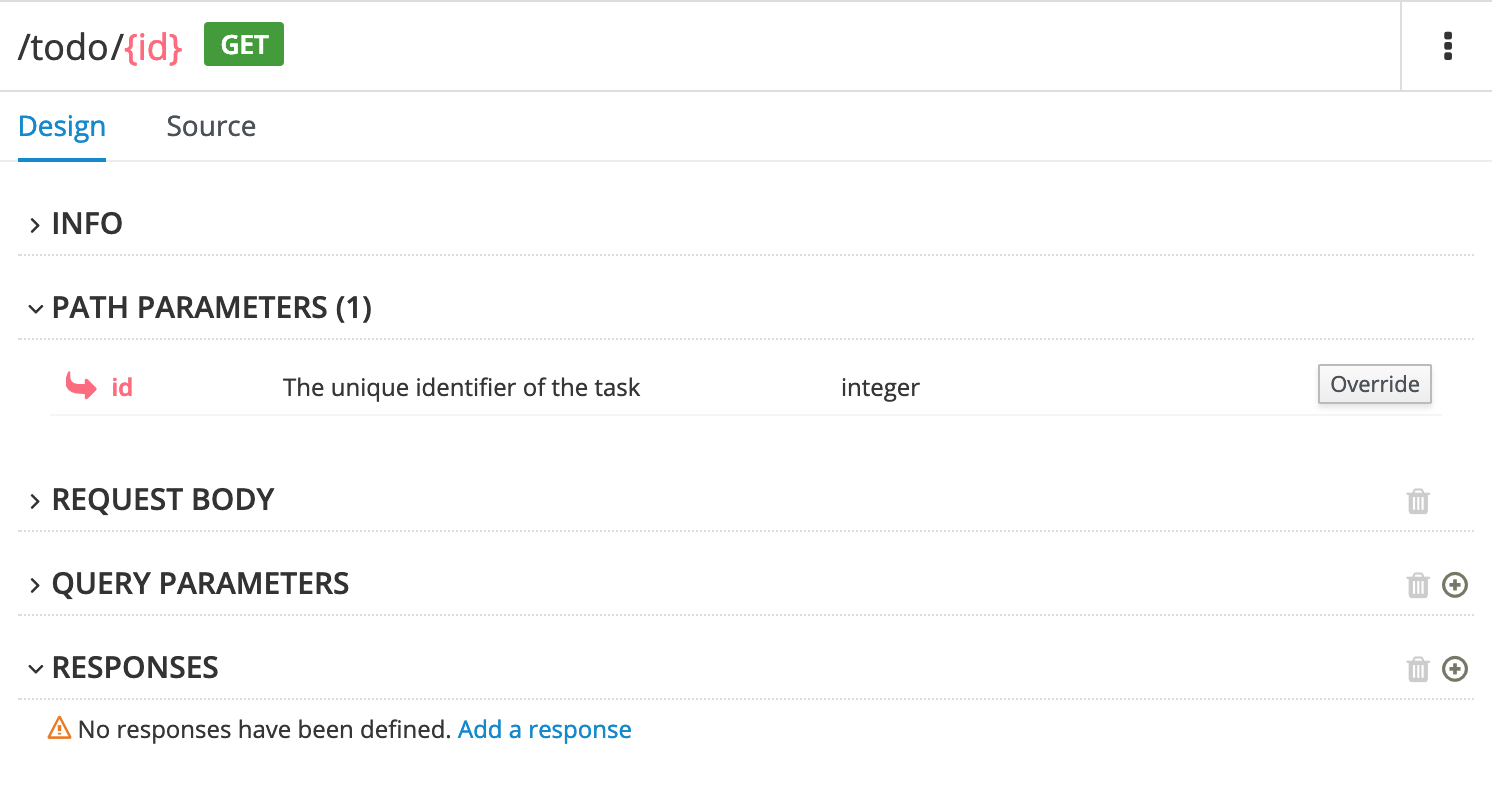
After you add a description, the issue is resolved and the exclamation icon disappears:
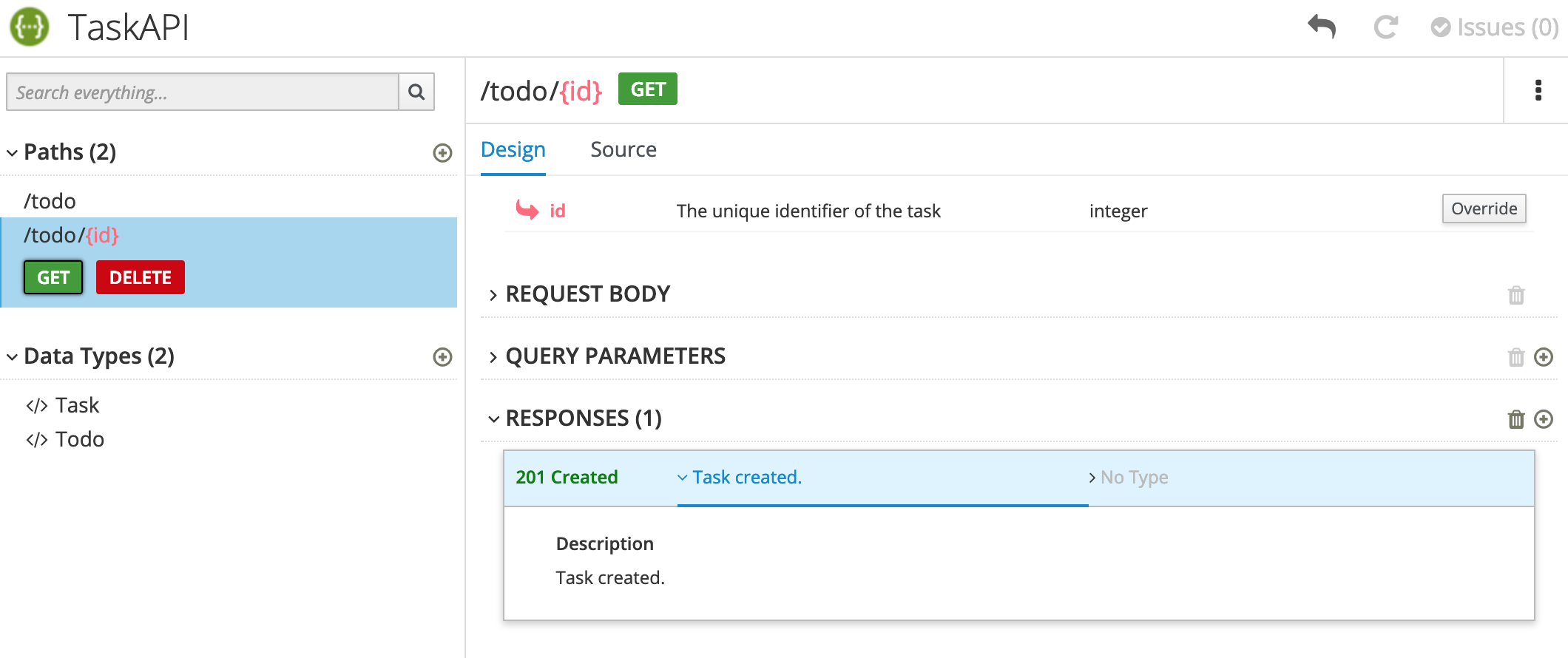
For a summary of all issues:
Click the Issues link in the upper right corner.

Click Go to a problem for a specific issue to go to the location of the issue so that you can resolve it.