-
Language:
English
-
Language:
English
Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Fuse
Chapter 3. Connecting to applications that you want to integrate
When you create an integration you add a connection to each application that you want to integrate. The following topics provide details for creating connections and adding them to integrations:
- Section 3.1, “Overview of creating connections”
- Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”
- Section 3.3, “Connecting to Amazon S3”
- Section 3.4, “Connecting to AMQ”
- Section 3.5, “Connecting to AMQP”
- Section 3.6, “Connecting to Dropbox”
- Section 3.7, “Connecting to an FTP or SFTP server”
- Section 3.8, “Connecting to HTTP and HTTPS endpoints”
- Section 3.9, “Connecting to MQTT”
- Section 3.10, “Connecting to REST APIs”
- Section 3.11, “Connecting to Salesforce”
- Section 3.12, “Connecting to Slack”
- Section 3.13, “Connecting to SQL databases”
- Section 3.14, “Connecting to Twitter”
3.1. Overview of creating connections
You must create a connection to each application that you want to integrate. The procedure for creating a connection varies for each application. The following topics provide an overview of the workflow:
3.1.1. About creating connections
To create a connection, you select the connector for the application that you want to connect to and respond to prompts to configure the connection to that application. The configuration details that you need to provide vary for each application. After configuring the connection, you give it a name that helps you distinguish it from any other connections to the same application. Optionally, you can specify a description of the connection.
You can use the same connector to create any number of connections to that application. For example, you might use the AMQ connector to create three different connections. Each AMQ connection could specify a different broker.
For examples, see:
3.1.2. Obtaining authorization to access applications
In an integration, you might want to connect to an application that uses the OAuth protocol to authenticate access requests. To do this, you must register your installation of Ignite for access to that application. Registration authorizes all connections from your Ignite installation to a given application. For example, if you register your Ignite installation with Salesforce, all connections from your Ignite installation to Salesforce use the same client ID and the same client secret.
In each Ignite environment, for each application that uses OAuth, only one registration of Ignite as a client is required. This registration lets you create multiple connections and each connection can use different user credentials.
For information about using custom connectors that let you access applications that use the OAuth protocol, see Section 3.1.5, “Creating connections from custom connectors”.
For details, see the following topics:
3.1.2.1. General procedure for obtaining authorization
To integrate applications that use OAuth, you must register with that application before you can create a connection to the application. For example, after you register your installation of Ignite as an application that can access Salesforce, then you can create a Salesforce connection.
While the specific steps vary for each OAuth application that you want to connect to, registration always provides your installation of Ignite with a client ID and a client secret. Some applications use other labels for the client ID and client secret. For example, Salesforce generates a consumer key and a consumer secret.
For some OAuth applications, Ignite provides an entry in its Settings page that makes it easy to register with the application. To see which applications this applies to, in the left panel of Ignite, click Settings.
For an application that has an entry in the Ignite Settings page, to register Ignite with that application, the main steps are:
- In the Ignite OAuth Application Management page, in the entry for the application with which you want to register Ignite, click Register to display the Client ID and Client Secret fields.
-
Near the top of the OAuth Application Management page, where you see
During registration, enter this callback URL:, copy that URL to the clipboard. - In another browser tab, go to the web site for the application that you want to register with and perform the steps required to obtain a client ID and secret. One of these steps requires you to enter the callback URL for your installation of Ignite. Paste the URL that you copied to the clipboard in the second step.
- On your Ignite installation Settings page, paste the client ID and client secret and save the settings.
For examples, see
For an example of registering with an application that does not have an entry in the Ignite Settings page, see: Section 3.6.1, “Register Ignite as a Dropbox client”.
3.1.2.2. About connection validation
After obtaining authorization for Ignite to access an application that uses OAuth, you can create one or more connections to that application. When you create a connection to an OAuth application, Ignite validates it to confirm that authorization is in place. At any time, you can validate the connection again to ensure that authorization is still in place.
Some OAuth applications grant access tokens that have an expiration data. If the access token expires, you can reconnect to the application to obtain a new acess token.
To validate a connection that uses OAuth or to obtain a new access token for an OAuth application:
- In the left panel, click Connections.
- Click the connection you want to validate or for which you want to obtain a new access token.
- In the connection’s details page, click Validate or click Reconnect.
If validation or reconnection fails, then check with the application/service provider to determine if the application’s OAuth keys, IDs, tokens, or secrets are still valid. It is possible that an item has expired or been revoked.
If you find that an OAuth item is invalid, has expired, or been revoked, obtain new values and paste them into the Ignite settings for the application. See the instructions in this guide for registering the application whose connection did not validate. With the updated settings in place, follow the instructions above to try to validate the updated connection. If validation is successful, and there is a running integration that is using this connection, republish the integration. To republish an integration, stop it and restart it.
If validation fails and reconnection fails but everything appears to be valid at the service provider, then try reregistering your Ignite environment with the application and then recreate the connection. Ignite validates the connection when you recreate it. If you recreate the connection, and there is an integration that is using the connection, then you must edit the integration to delete the old connection and add the new connection. If the integration is running, then you must stop it and restart it.
3.1.3. About adding connections to integrations
When you add a connection to an integration, Ignite displays a list of the actions that the connection can perform when it connects to the application. You must select exactly one action. In a running integration, each connection performs only the action you choose. For example, when you add a Twitter connection as an integration’s start connection, you might choose the Mention action, which monitors Twitter for tweets that mention your Twitter handle.
Selection of some actions prompts you to specify one or more parameters. For example, if you add a Salesforce connection to an integration and choose the On create action then you must indicate the type of object whose creation you are interested in, such as a lead or a contact.
3.1.4. Viewing and editing connection information
After you create a connection, Ignite assigns an internal identifier to the connection. This identifier does not change. You can change the connection’s name, description, or configuration values and Ignite recognizes it as the same connection.
There are two ways to view and edit information about a connection:
- In the left panel, click Connections and then click any connection to view its details.
- In the left panel, click Integrations and then click any integration to view its details. In the Integration Summary page, in the flow diagram of the integration, click a connection icon to view that connection’s details.
On the Connection Details page, for the connection you want to edit, click
 next to a field to edit that field. Or, for some connections, below the configuration fields, click Edit to change configuration values. If you change any values, be sure to click Save.
next to a field to edit that field. Or, for some connections, below the configuration fields, click Edit to change configuration values. If you change any values, be sure to click Save.
If you update a connection that is used in an integration that is running, you must republish the integration by stopping it and publishing it again.
For connections to applications that use the OAuth protocol to authorize access, you cannot change the login credentials that the connection uses. To connect to the application and use different login credentials, you must create a new connection.
3.1.5. Creating connections from custom connectors
After you upload an extension that defines a custom connector, the custom connector is available for use. You use custom connectors to create connections in the same way that you use Ignite-provided connectors to create connections.
A custom connector might be for an application that uses the OAuth protocol. Before you create a connection from this kind of connector, you must register your installation of Ignite for access to the application that the connector is for. You do this in the interface for the application that the connector is for. The details for how to register your installation of Ignite vary for each application.
For example, suppose the custom connector is for creating connections to Yammer. You would need to register your installation of Ignite by creating a new application within Yammer. Registration provides a Yammer client ID for Ignite and a Yammer client secret value for Ignite A connection from your Ignite installation to Yammer must provide these two values.
Note that an application might use different names for these values, such as consumer ID or consumer secret.
After you register your installation of Ignite, you can create a connection to the application. When you configure the connection, there should be parameters for entering the client ID and the client secret. If these parameters are not available, you need to talk with the extension developer and ask for an updated extension that lets you specify the client ID and client secret.
For more information, see Section 3.1, “Overview of creating connections”.
3.2. Specifying connection input or output types
To process data from the start connection through the finish connection, sometimes you need to specify input/output types when you configure a connection’s action. Type specifications let Ignite alert you when a data mapping step is required. A data mapping step ensures that the next integration step can process the data it receives.
After you configure an Amazon S3, AMQ, AMQP, Dropbox, or FTP/SFTP connection, Ignite prompts you to specify input and/or output data types as follows:
In the Select Type field, if the data type does not need to be known, accept Type specification not required and then, at the bottom, click Done. You do not need to follow the rest of these instructions.
Otherwise, select one of the following as the schema type:
-
JSON schema is a document that describes the structure of JSON data. The document’s media type is
application/schema+json. -
JSON instance is a document that contains JSON data. The document’s media type is
application/json. -
XML schema is a document that describes the structure of XML data. The document’s file extension is
.xsd. -
XML instance is a document that contains XML data. The document’s file extension is
.xml.
-
JSON schema is a document that describes the structure of JSON data. The document’s media type is
-
In the Definition input box, paste a definition that conforms to the schema type you selected. For example, if you select JSON schema then you would paste the content of a JSON schema file, which has a media type of
application/schema+json. In the Data Type Name field, enter a name that you choose for the data type. For example, suppose you are specifying a JSON schema for vendors. You can specify
Vendoras the data type name.You will see this data type name when you are creating or editing an integration that uses the connection for which you are specifying this type. Ignite displays the type name in the integration visualization panel and in the data mapper.
- In the Data Type Description field, provide information that helps you distinguish this type. This description appears in the data mapper when you hover over the step that processes this type.
- Click Done.
3.3. Connecting to Amazon S3
In an integration, to retrieve data from an Amazon S3 bucket or copy data into an Amazon S3 bucket, you create an Amazon S3 connection. You then add that Amazon S3 connection to an integration. For details, see:
3.3.1. Prerequisites for creating an Amazon S3 connection
To create an Amazon S3 connection, you must know the following:
Amazon S3 access key ID that is associated with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) account that created, or will create, the bucket that you want the connection to access.
You can create a connection that accesses a bucket that does not yet exist. In this case, when the integration starts running then it use the AWS account associated with this access key ID to try to create the bucket.
- Amazon S3 secret access key that is associated with the AWS account that created or will try to create (when the integration starts running) the bucket that you want the connection to access.
Name of the bucket that you want to access or its Amazon Resource Name (ARN).
If the bucket you specify does not yet exist then the connection tries to create a bucket with the name that you specify. Because S3 allows a bucket to be used as a URL that can be accessed publicly, the bucket name that you specify must be globally unique. Also, it must meet S3 bucket naming requirements.
If the bucket you specify does not exist in the AWS account that is associated with the Amazon S3 access key ID, but it does exist in another AWS account, then the connection does not create the bucket and an integration that uses this connection cannot start running.
- Region in which the bucket is located or the region in which you want the connection to create the bucket.
A user with the login credentials for the AWS account that created or will create the bucket obtains the Amazon S3 keys as follows:
- Go to https://aws.amazon.com/s3/.
- Sign in to the console with the AWS account that created the bucket that you want to access or with the account that you want the connection to use to create the bucket.
- In the console, in the upper right, click the down arrow next to the user name and click My Security Credentials.
- Expand Access Keys and click Create New Access Keys.
- Follow the prompts to obtain the keys.
3.3.2. Create an Amazon S3 connection
To create an Amazon S3 connection:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display Ignite connectors.
- Click the Amazon S3 connector.
- In the Access Key field, enter the Amazon S3 access key ID, provided by AWS, for the AWS account that created the bucket that you want this connection to access. If the bucket you want the connection to access does not already exist then when Ignite tries to start running the integration, it uses the AWS account associated with this access key to create the bucket. However, if the bucket already exists in some other AWS account, then the connection cannot create the bucket and the integration cannot start.
- In the Bucket Name or Amazon Resource Name field, enter the name of the bucket that you want this connection to access or enter the bucket’s ARN. If the bucket does not already exist in either the AWS account being used or in any other AWS account, then the connection creates it. For details about bucket name requirements, see Section 3.3.1, “Prerequisites for creating an Amazon S3 connection”.
- In the Region field, select the AWS region in which the bucket resides. If the connection creates the bucket, then it creates it in the selected region.
- In the Secret Key field, enter the Amazon S3 secret access key, provided by AWS, for the account that created, or will create, the bucket that you want this connection to access.
- Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether or not validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the configuration details as needed and try again.
- When validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
Obtain S3 Data. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample S3 connection that obtains data from the northeast bucket. - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that Obtain S3 Data is now available.
3.3.3. Adding an Amazon S3 connection to an integration
You must create an Amazon S3 connection before you can add an Amazon S3 connection to an integration. If you did not already create an Amazon S3 connection, see Section 3.3.1, “Prerequisites for creating an Amazon S3 connection”.
The procedure for adding an Amazon S3 connection to an integration varies according to whether you want to use the S3 connection to start the integration, finish the integration, or access data in the middle of the integration. See the following topics:
3.3.3.1. Starting an integration by obtaining data from Amazon S3
To start an integration by obtaining data from an Amazon S3 bucket, add an Amazon S3 connection as the start connection:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the Amazon S3 connection that you want to use to start the integration.
On the Choose an Action page, click one of these actions:
Get Object to obtain a file from the bucket that the connection accesses. To configure this action:
- In the File Name field, enter the name of the file that you want to obtain.
- To obtain a file and then delete it from the bucket, select Delete After Read.
Poll an Amazon S3 Bucket to periodically obtain files from the bucket that the connection accesses. To configure this action:
- In the Delay field, accept the default of 500 milliseconds as the time that elapses between polls. Or, to specify a different polling interval, enter a number and select its time unit.
In the Maximum Objects to Retrieve field, enter the largest number of files that one poll operation can obtain. The default is 10.
To have no limit on the number of files that can be obtained, specify
0or a negative integer. When Maximum Objects to Retrieve is unlimited, the poll action obtains all files in the bucket.If the bucket contains more than the specified maximum number of files then the action obtains the files that were most recently modified or created.
- In the Prefix field, optionally specify a regular expression that evaluates to a string. If you specify a prefix then this action retrieves a file only when its name starts with that string.
- Indicate whether you want to Obtain files and then delete them from the bucket.
- Click Done to specify the action’s output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.3.3.2. Finishing an integration by adding data to Amazon S3
To finish an integration by copying data to Amazon S3, add an Amazon S3 connection as the finish connection:
- Start creating the integration.
- Add and configure the start connection.
- On the Choose a Finish Connection page, click the Amazon S3 connection that you want to use to finish the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Copy Object action to copy one or more objects into the bucket that the connection accesses. The integration obtains the objects to be added to the bucket from the previous integration step(s).
- Click Next to specify the action’s input type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.3.3.3. Adding data to Amazon S3 in the middle of an integration
In the middle of an integration, to add data to Amazon S3, add an Amazon S3 connection between the start and finish connections:
- Add the start and finish connections.
- In the left panel, hover over the plus sign that is in the location where you want to add the Amazon S3 connection.
- In the popup, click Add a Connection.
- Click the Amazon S3 connection that you want to use as a middle connection in the integration.
- Click the Copy Object action. The integration obtains the objects to be added to the bucket from the previous integration step(s).
- Click Next to specify the action’s input type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.4. Connecting to AMQ
In an integration, you can obtain messages from an ApacheMQ (AMQ) broker or publish messages to an AMQ broker. AMQ uses the OpenWire protocol for communication between clients and message brokers. To communicate with the following broker types, use the AMQ connector to create a connection to the broker of interest:
- Apache ActiveMQ broker that does not support AMQP
- AMQ 6 broker
To communicate with one of the following broker types, use the AMQP connector to create a connection to the broker of interest:
- Apache ActiveMQ broker that supports AMQP
- Apache ActiveMQ Artemis
- AMQ 7 broker
- EnMasse, which is an open source messaging platform
See Section 3.5, “Connecting to AMQP”.
To use the AMQ connector, see:
3.4.1. Create an AMQ connection
To create an AMQ connection:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display connectors.
- Click the AMQ connector.
Configure the connection by entering:
-
In the Broker URL field, enter the location that you want to send data to or obtain data from, for example,
tcp://localhost:61616. - In the User Name field, enter the user name for the account that you want to use to access this broker.
- In the Password field, enter the password for the account that you want to use to access this broker.
- In the Client ID field, enter the ID that allows connections to close and reopen without missing messages. The destination type must be a topic.
- If this connection will be used in a development environment, you can save some time by disabling Check Certificates. Disabling the checking of certificates is a convenience for development environments. For secure production environments, always enable Check Certificates.
- In the Broker Certificate field, paste the broker’s PEM certificate text. This is required except when you disable checking the certificates.
- In the Client Certificate field, paste the client’s PEM certificate text. Content in this field is always optional.
-
In the Broker URL field, enter the location that you want to send data to or obtain data from, for example,
- Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the configuration details as needed and try again.
- If validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, you might enter
AMQ 1. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample AMQ connection that uses a provided broker. - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that AMQ 1 is now available.
3.4.2. Adding an AMQ connection to an integration
You must create an AMQ connection before you can add it to an integration. If you did not already create an AMQ connection, see Section 3.4.1, “Create an AMQ connection”.
The procedure for adding an AMQ connection to an integration varies according to whether you want to use the AMQ connection to start the integration, finish the integration, or publish messages in the middle of an integration. See the following topics:
3.4.2.1. Starting an integration based on receiving AMQ messages
To trigger execution of an integration based on receiving a message from an AMQ broker, add an AMQ connection as the start connection:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the AMQ connection that you want to use to start the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Subscribe for messages action to receive messages from the queue or topic you specify.
To configure the action:
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to receive data from.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- In the Durable Subscription ID field, to allow connections to close and reopen without missing messages, enter the durable subscription ID. The destination type must be a topic.
- In the Message Selector field, if you want to receive only data that satisfies a particular condition, enter a filter expression.
- Click Next to specify the action’s output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.4.2.2. Finishing an integration by publishing AMQ messages
To finish an integration by publishing messages to an AMQ broker, add an AMQ connection as the finish connection:
- Start creating the integration by adding and configuring the start connection.
- On the Choose a Finish Connection page, click the AMQ connection that you want to use to finish the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Publish messages action to publish messages to the queue or topic you specify.
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to send messages to.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- Select Persistent to guarantee message delivery even if a connection fails.
- Click Next to specify the action’s input/output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.4.2.3. Publishing AMQ messages in the middle of an integration
In the middle of an integration, to publish messages to an AMQ broker, add an AMQ connection between the start and finish connections. You must be creating or editing an integration. The integratation’s start and finish connections must have already been added.
To add an AMQ connection as a middle connection:
- In the integration visualization panel on the left, click the plus sign that is in the location where you want to add the connection.
- Click Add a connection.
- On the Choose a Connection page, click the AMQ connection that you want the integration to use after the start connection and before the finish connection.
On the Choose an Action page, select one of the following actions:
Publish messages action to publish messages to the queue or topic you specify. To configure this action:
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to send messages to.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- Select Persistent to guarantee message delivery even if a connection fails.
Request response using messages to send messages to the JMS destination you specify and receive a response. To configure this action:
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to send messages to.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- In the Message Selector field, if you want to receive only responses that satisfy a particular condition, enter a filter expression.
- In the Named Reply To field, enter the name of a queue or topic. The destination sends its response to this queue or topic.
- Select Persistent to guarantee message delivery even if a connection fails.
- In the Response Time Out field, specify the number of milliseconds that this connection waits for a response message before throwing a runtime exception. The default is 5000 milliseconds (5 seconds).
- Click Next to specify the action’s input type and then the action’s output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.5. Connecting to AMQP
In an integration, you can obtain messages from or publish messages to an Advanced Message Queue Protocol (AMQP) broker. AMQP defines communication between clients and message brokers. To communicate with the following broker types, use the AMQP connector to create a connection to the broker of interest:
- Apache ActiveMQ broker that supports AMQP
- Apache ActiveMQ Artemis
- AMQ 7 broker
- EnMasse, which is an open source messaging platform
To communicate with one of the following broker types, use the AMQ connector to create a connection to the broker of interest:
- Apache ActiveMQ broker that does not support AMQP
- AMQ 6 broker
See Section 3.4, “Connecting to AMQ”.
It is possible to use the AMQP connector to create a connection to an Apache ActiveMQ broker that does not support AMQP or to an AMQ 6 broker. Doing this requires transport configuration in the broker. For information about configuring the broker, see Red Hat JBoss A-MQ Managing and Monitoring Brokers, Adding Client Connection Points. For information about the configuration values to specify, see Red Hat JBoss A-MQ Connection Reference, Advanced Message Queueing Protocol (AMQP).
To use the AMQP connector, see:
3.5.1. Create an AMQP connection
To create an AMQP connection:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display connectors.
- Click the AMQP connector.
Configure the connection by entering:
- In the Connection URI field, enter the location you want to send data to or obtain data from.
- In the User Name field, enter the user name for the account that you want to use to access this broker.
- In the Password field, enter the password for the account that you want to use to access this broker.
- In the Client ID field, enter the ID that allows connections to close and reopen without missing messages. The destination type must be a topic.
- If this connection will be used in a development environment, you can save some time by disabling Check Certificates. Disabling the checking of certificates is a convenience for development environments. For secure production environments, always enable Check Certificates.
- In the Broker Certificate field, paste the broker’s PEM certificate text. This is required except when disable checking the certificates.
- In the Client Certificate field, paste the client’s PEM certificate text. Content in this field is always optional.
- Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the configuration details as needed and try again.
- If validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, you might enter
AMQP 1. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample AMQP connection - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that AMQP 1 is now available.
3.5.2. Adding an AMQP connection to an integration
You must create an AMQP connection before you can add an AMQP connection to an integration. If you did not already create an AMQP connection, see Section 3.5.1, “Create an AMQP connection”.
The procedure for adding an AMQP connection to an integration varies according to whether you want to use the connection to start an integration, finish an integration, or publish messages in the middle of an integration. See the following topics:
3.5.2.1. Starting an integration based on receiving AMQP messages
To trigger execution of an integration based on receiving messages from an AMQP broker, add an AMQP connection as the start connection:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the AMQP connection that you want to use to start the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Subscribe for messages action to receive messages from the queue or topic you specify.
To configure the action:
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to receive data from.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- In the Durable Subscription ID field, to allow connections to close and reopen without missing messages, enter the durable subscription ID. The destination type must be a topic.
- In the Message Selector field, if you want to receive only data that satisfies a particular condition, enter a filter expression.
- Click Next to specify the action’s output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.5.2.2. Finishing an integration by publishing AMQP messages
To finish an integration by publishing messages to an AMQP broker, add an AMQP connection as the finish connection. You must be creating or editing an integration. You must have already added the start connection. Follow these instructions:
- On the Choose a Finish Connection page, click the AMQP connection that you want to use to finish the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click Publish messages to publish messages to the queue or topic you specify.
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to send messages to.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- Select Persistent to guarantee message delivery even if a connection fails.
- Click Next to specify the action’s input and output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.5.2.3. Publishing messages to AMQP in the middle of an integration
In the middle of an integration, to publish messages to an AMQP broker, add an AMQP connection between the start and finish connections. You must be creating or editing an integration. You must have already added the start and finish connections to the integration. Follow these instructions:
- In the integration visualization panel on the left, click the plus sign in the location where you want to add the connection.
- Click Add a connection.
- On the Choose a Connection page, click the AMQP connection that you want the integration to use after the start connection and before the finish connection.
On the Choose an Action page, select one of the following actions:
Publish messages to publish messages to the queue or topic you specify. To configure this action:
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to send messages to.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- Select Persistent to guarantee message delivery even if a connection fails.
Request response using messages to send messages to the JMS destination you specify and receive a response. To configure this action:
- In the Destination Name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to send messages to.
- For the Destination Type, accept Queue or select Topic.
- In the Message Selector field, if you want to receive only responses that satisfy a particular condition, enter a filter expression.
- In the Named Reply To field, enter the name of a queue or topic. The destination sends its response to this queue or topic.
- Select Persistent to guarantee message delivery even if a connection fails.
- In the Response Time Out field, specify the number of milliseconds that this connection waits for a response message before throwing a runtime exception. The default is 5000 milliseconds (5 seconds).
- Click Next to specify the action’s input and output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.6. Connecting to Dropbox
In an integration, you can download files from Dropbox or upload files to Dropbox. The following topics provide the details:
3.6.1. Register Ignite as a Dropbox client
You must register your installation of Ignite as an application that can access Dropbox. This lets you create any number of integrations that connect to Dropbox. In other words, you need to register a particular installation of Ignite with Dropbox only once.
In each Ignite environment, there can be only one registration of Ignite as a Dropbox client. However, while each Dropbox connection uses the same registration, it can use different user credentials.
Perform these steps:
In Ignite:
- In the left panel, click Settings.
-
Near the top of the page, in the sentence that starts with
During registration, enter this callback URL:, copy the URL at the end of that sentence to the clipboard. For example, the URL is something like this:https://app-proj9128.7b63.fuse-ignite.openshiftapps.com/api/v1/credentials/callback.
In another browser tab, go to
https://www.dropbox.comand do the following:- Sign in to the Dropbox account that has the data that you want to access in an integration.
- After signing in, go to https://www.dropbox.com/developers/apps.
- Click Create App.
- Select Dropbox API.
- Choose whether Ignite can access a single folder or all of the folders and files.
-
Specify a name for your Dropbox app. For example, you might specify
Ignite Access From Aslan LLC. The name you specify must be unique in the set of Dropbox app names. - Check the box to indicate that you agree to Dropbox API terms and conditions.
- Click Create App.
- In the Dropbox Settings page for your new app, in the input field for OAuth2 Redirect URIs, paste your Ignite URL, which you copied to the clipboard at the beginning of this procedure.
- Click Add.
Your installation of Ignite is now registered as a Dropbox client, which means that Ignite can access content in the Dropbox account that you signed into.
3.6.2. Create a Dropbox connection
A connection to Dropbox requires registration of Ignite as an application that can access Dropbox. If you did not already register Ignite, see Section 3.6.1, “Register Ignite as a Dropbox client”.
Follow the instructions below to create a Dropbox connection. You can use the same Dropbox connection in multiple integrations.
To create a Dropbox connection:
In a new browser tab, go to
https://www.dropbox.comand do the following:- Sign in to the Dropbox account in which you created the app that registers access from your Ignite installation.
- Go to https://www.dropbox.com/developers/apps.
- Click the Ignite app to display its settings.
In another browser tab, in Ignite, do the following:
- In the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display the available connectors.
- Click the Dropbox connector.
Go back to the Dropbox settings display for your app and do the following:
- Scroll down to see Generated Access Token.
- Click Generate.
- Copy the generated access token to the clipboard.
- Back in Ignite, in the Configure Connection page, in the Access Token field, paste the generated access token.
- In the Client Identifier field, enter the name that you specified when you created the Dropbox app.
- Click Validate. Ignite displays a message that indicates whether it can validate this connection. If validation fails, try again and be sure to enter the correct values.
- When validation is successful, in the upper right, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
Dropbox Connect 1. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample Dropbox connection that can access all content in our company Dropbox account. - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that Dropbox Connect 1 is now available.
3.6.3. Adding a Dropbox connection to an integration
You must create a Dropbox connection before you can add a Dropbox connection to an integration. If you did not already create a Dropbox connection, see Section 3.6.2, “Create a Dropbox connection”.
You must be creating an integration or updating an integration to add a connection to that integration. If you need to, see Section 5.2, “Procedure for creating an integration” or Section 7.10, “Updating integrations”.
The procedure for adding a Dropbox connection to an integration varies according to whether you want to use the connection to start an integration, finish an integration, or access Dropbox in the middle of an integration. See the following topics:
3.6.3.1. Starting an integration by obtaining files from Dropbox
To start an integration by downloading files from Dropbox, add a Dropbox connection as the start connection:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the Dropbox connection that you want to use to start the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Download from Dropbox action to obtain one or more files from the Dropbox account that this connection accesses.
- To configure the action, in the Folder or file name path to download field, specify the filename path for the content that you want the integration to obtain. In this release, you can download only a single file.
- Click Next to specify the action’s output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.6.3.2. Finishing an integration by adding files to Dropbox
To finish an integration by uploading files to Dropbox, add a Dropbox connection as the finish connection:
- Start creating the integration, add and configure the start connection.
- On the Choose a Finish Connection page, click the Dropbox connection that you want to use to finish the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Upload a file to Dropbox action to add the current integration data to the Dropbox account that this connection accesses.
- In the Remote Path field, enter the local filename path for file that you want to upload. Dropbox stores the file with the same path and name. In this release, you can upload only a single file.
For the Upload mode,
- Select Add to upload a file only when a file with the same name is not already in the same Dropbox folder. If a file with the same name is already in the same Dropbox folder, then the file is not uploaded and the integration continues. This is the behavior regardless of whether the content in the file you are trying to upload has been updated.
- Select Force to ensure that the file is uploaded even if a file with the same name is present in the same Dropbox folder. Dropbox overwrites the file that it already has with the file that you are uploading.
- Click Next to specify the action’s input type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.6.3.3. Accessing Dropbox in the middle of an integration
To download or upload Dropbox files in the middle of an integration, add a Dropbox connection between the start and finish connections. You must be creating or editing an integration. You must add the start and finish connections first. Follow these instructions:
- In the integration visualization panel on the left, hover over the plus sign that is in the location where you want to add a Dropbox connection.
- In the popup, click Add a connection.
- On the Choose a Connection page, click the Dropbox connection that you want the integration to use.
On the Choose an Action page, select one of the following actions:
Upload a file to Dropbox to add the current integration data to the Dropbox account that this connection accesses. To configure this action:
- In the Remote Path field, specify the local path and file name of the file you want to upload. Dropbox stores the file with the same path and name. In this release, you can upload only a single file.
For the Upload mode,
- Select Add to upload a file only when a file with the same name is not already in the same Dropbox folder. If a file with the same name is already in the same Dropbox folder, then the file is not uploaded and the integration continues. This is the behavior regardless of whether the content in the file you are trying to upload has been updated.
- Select Force to ensure that the file is uploaded even if a file with the same name is present in the same Dropbox folder. Dropbox overwrites the file that it already has with the file that you are uploading.
- Download from Dropbox to obtain one file from the Dropbox account that this connection accesses. To configure this action, in the Folder or filename path to download field, enter the Dropbox filename path of the file you want to obtain. In this release, you can download only a single file.
- Click Next to specify the action’s input and output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.7. Connecting to an FTP or SFTP server
In an integration, you can connect to an FTP or SFTP server to download or upload files by creating an FTP or SFTP connection. You can then add this connection to any number of integrations. The following topics provide details:
3.7.1. Creating an FTP or SFTP connection
To create a connection to an FTP server or an SFTP server:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display Ignite connectors.
To create a connection that uses File Transfer Protocol, click the FTP connector.
Or, to create a connection that uses Secure File Transfer Protocol, click the SFTP connector.
Configure the connection.
For an FTP connection:
-
Host is the only parameter that you must specify. Enter the host name of the server that you want to connect to. For example, if the name of your FTP host is
FTP.WEST, then you would enter exactly that,FTP.WEST. Do not specify the protocol, for example, you should not specify something like this:ftp://FTP.WEST. -
Port is required and has a default value of
21. This is the port that the FTP server is listening on. - All other parameters are either not required or have default values. The defaults are suitable for most integrations. Descriptions of these parameters are after this procedure.
-
Host is the only parameter that you must specify. Enter the host name of the server that you want to connect to. For example, if the name of your FTP host is
For an SFTP connection, there must be values for these parameters:
-
Host is the host name of the SFTP server that you want to connect to. For example, if the name of your SFTP host is
SFTP.EAST, then you would enter exactly that,SFTP.EAST. Do not specify the protocol, for example, you should not specify something like this:sftp://SFTP.EAST. -
Port has a default of
22. This is the port that the SFTP server is listening on. - User name of the account that you want to use to access the SFTP server.
- Password that is associated with that user name.
- All other parameters have default values. The defaults are suitable for most integrations. Descriptions of these parameters are after this procedure.
-
Host is the host name of the SFTP server that you want to connect to. For example, if the name of your SFTP host is
- Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether or not validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the configuration details as needed and try again.
- When validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
XLight FTP Server. - In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection.
- In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that XLight FTP Server is now available.
Descriptions of other parameters
- Connect timeout defaults to 10000 milliseconds and indicates a maximum wait of 10 seconds to establish the connection. If 10 seconds elapse without a connection then Ignite waits for the number of milliseconds defined by Reconnect delay and then tries to reconnect.
- Reconnect delay defaults to 1000 milliseconds and indicates the wait time before trying to reconnect again.
- Maximum reconnect attempts defaults to 3. Ignite tries as many as 3 times to establish a connection.
- Binary file transfer mode is used by default. Select No for ASCII transfer mode.
- Passive connection mode defaults to Yes, which is usually the preferred mode. In passive mode, the client opens communication channels with the server as a way to avoid firewall issues. If you select No then active mode is used.
- Disconnect from the server after use defaults to No. The connection remains established after it performs the action. Select Yes if you want to disconnect from the server after the connection performs the upload or download.
- Data timeout defaults to 30000 milliseconds and indicates the maximum length of time that Ignite waits for a reply.
3.7.2. Adding an FTP or SFTP connection to an integration
After you create an FTP connection or an SFTP connection, you can add it to any number of integrations. See the following topics:
3.7.2.1. Obtaining files from an FTP or SFTP server
To trigger integration execution when an FTP or SFTP connection finds the file(s) you are interested in, you must add an FTP or SFTP connection as an integration’s start connection.
To add an FTP or SFTP connection as a start connection:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the FTP or SFTP connection that you want to use to poll an FTP or SFTP server.
- On the Choose an Action page, click Download.
- In the File name expression field, if you are interested in a single file, then enter an Apache Camel Simple language expression that resolves to a file name. You cannot specify a regular expression. The connection polls (periodically checks) the server for this file and downloads it when it is found. Leave this field blank if you want to download more than one file.
- In the FTP directory field, enter the absolute or relative path of the server directory to poll. The connection watches this directory for any content and downloads all files when it finds any content.
- In the Milliseconds before polling starts field, accept the default of 1000 milliseconds or change the number of milliseconds.
- In the Milliseconds before the next poll field, accept the default of 500 milliseconds or change the number of milliseconds. This is the interval between polls.
- In the Delete after download field, accept the default of No or select Yes to download the file(s) and then delete it(them) from the server.
- Click Next to specify the action’s output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.7.2.2. Uploading files to an FTP or SFTP server
To finish an integration by uploading files to an FTP or SFTP server, you add an FTP or SFTP connection as the finish connection. You can also upload files to an FTP or SFTP server in the middle of an integration. To do this, you add an FTP or SFTP connection as a middle connection.
To add an FTP or SFTP connection that uploads files:
- Start creating the integration.
- Add and configure the start connection.
On the Choose a Finish Connection page, do one of the following:
- To finish an integration by uploading files, click the FTP or SFTP connection that you want to use.
- To upload files in the middle of an integration, click the connection you want to use to finish the integration. Configure that connection. When the finish connection is part of the integration, in the left panel, hover over the plus sign where you want to add an FTP or SFTP connection and click Add a connection. Click the FTP or SFTP connection that you want to use to upload files in the middle of an integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click Upload.
- In the File name expression field, if you want to upload only one particular file, then enter an Apache Camel Simple language expression that resolves to a file name. This is the name of the file that the action uploads to the server. You cannot specify a regular expression. To upload more than one file, leave this field blank.
- In the FTP directory field, enter the absolute or relative name of a server directory. If the File name expression field contains an expression, then the connection stores the specified file in this directory. If the File name expression field is blank, then the connection uploads to this directory all files that were received from the previous integration step.
In the If file exists field, indicate the behavior when you are uploading a file that has the same path and name as a file that is on the server. Accept the default, Override, to overwrite the file that is on the server with the file that you are uploading. Or, select one of the following:
- Append adds the content in the file being uploaded to the file that is on the server.
-
Fail throws
GenericFileOperationException. The integration does not enter an error state. - Ignore does not upload the file. The integration continues running under the assumption that everything is okay.
- Move renames one of the files.
- TryRename uploads the file with a temporary name and renames the file to the desired name. This operation does not check for the existence of a file with the desired name, which makes the operation faster on most servers than when existence checks are done.
- In the Temporary file prefix while copying field, specify a string. The connection prepends this string to the name of a file while it is being uploaded. This enables the connection to write to a temporary file on the server and then rename that temporary file to have the correct name. This is useful for reducing locks when uploading very large files.
- In the Temporary file name while copying field, specify a string. The connection renames a file being uploaded to have this name while it is being uploaded. This enables the connection to write to a temporary file on the server and then rename that temporary file to have the correct name. This is useful for reducing locks when uploading very large files.
- Click Next to specify the action’s input type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.8. Connecting to HTTP and HTTPS endpoints
In an integration, you can connect to HTTP and HTTPS endpoints to execute the GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE, or PATCH method. To do this, create an HTTP or HTTPS connection and then add it to an integration. The following topics provide details:
3.8.1. Create a connection to an HTTP or HTTPS endpoint
To create a connection to an HTTP or HTTPS endpoint:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display Ignite connectors.
- If you want to use Hyper Text Transfer Protocol to connect to the endpoint, then click the HTTP connector. If you want to use Secure Hyper Text Transfer protocol, then click the HTTPS connector.
-
In the Base URL field, enter the endpoint path. For example,
www.mycompany.com/sales. - Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether validation is successful. If validation fails, revise specification of the base URL and try again.
- If validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
HTTPS My Company Sales. - In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection.
- In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that HTTPS My Company Sales is now available.
3.8.2. Add an HTTP or HTTPS connection to an integration
After you create an HTTP or HTTPS connection, you can use it in any number of integrations as follows:
- To start an integration by periodically invoking an HTTP or HTTPS endpoint, add an HTTP or HTTPS connection as the integration’s start connection.
- To finish an integration by invoking an HTTP or HTTPS endpoint once, add an HTTP or HTTPS connection as the integration’s finish connection.
- In the middle of an integration, to invoke an HTTP or HTTPS endpoint once, add an HTTP or HTTPS connection after the start connection and before the finish connection.
If you are creating an integration, Ignite prompts you to choose and configure the start connection, and then choose and configure the finish connection. To add a middle connection, hover over the plus sign in the left panel at the location where you want to add the connection, and select Add a connection.
In all of these situations, Ignite displays the available connections. To add an HTTP or HTTPS connection:
- Click the HTTP or HTTPS connection that you want to add to the integration.
Select the action that you want the connection to perform:
- If you are adding a start connection, then Periodic invoke URL is the only available action. This action invokes the endpoint at intervals that you specify and triggers the integration if the endpoint returns any data.
- If you are adding a finish or middle connection, then Invoke URL is the only available action. This action invokes the endpoint once.
- In the URL Path field, specify the location of the endpoint that you want to invoke.
In the HTTP Method field, select the method that you want the connection to perform. The default method is
GET.-
GETobtains the content at the URL path. -
PUTreplaces the content at the URL path with the integration data. -
POSTstores the integration data at the URL path to create new content. -
DELETEremoves content at the URL path. -
HEADobtains metadata about the content at the URL path. -
OPTIONSobtains communication option settings at the URL path. -
TRACEobtains information for testing and diagnostic purposes. -
PATCHpartially updates the content at the URL path according to the integration data.
-
- If you are adding a start connection, which periodically invokes the URL, then in the Period field, accept the default interval of 1 second or specify a number and its unit (milliseconds, seconds, minutes, or hours) to indicate how long to wait between invocations.
- Click Done to specify the action’s input or output type. See Section 3.2, “Specifying connection input or output types”.
3.9. Connecting to MQTT
MQ Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a lightweight, machine-to-machine, internet of things, connectivity protocol. In an integration, you can obtain messages from or publish messages to an MQTT broker. To do this, create a connection to the MQTT broker of interest and then add that connection to an integration. Details are in the following topics:
3.9.1. Create a connection to an MQTT broker
To create an MQTT connection:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display connectors.
- Click the MQTT connector.
To configure the connection:
- In the MQTT broker URL field, enter the location of the MQTT broker that you want to send data to or obtain data from. This is the only required field.
- In the User Name field, optionally enter the user name for the MQTT account whose credentials you want to use to access the broker.
- In the Password field, if you specified a user name, then specify the password associated with that account.
- In the Client ID field, optionally enter the ID that allows connections to close and reopen without missing messages. The connection must subscribe to or publish to a topic.
- Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the input parameters and try again.
- If validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, you might enter
MQTT West. - In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection.
- In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that MQTT West now available.
3.9.2. Adding an MQTT connection to an integration
You must create an MQTT connection before you can add it to an integration. If you did not already create an MQTT connection, see Section 3.9.1, “Create a connection to an MQTT broker”.
The procedure for adding an MQTT connection to an integration varies according to whether you want to use the MQTT connection to obtain a message or publish a message. See the following topics:
3.9.2.1. Obtain a message from an MQTT broker
To trigger execution of an integration based on receiving a message from an MQTT broker, add an MQTT connection as the start connection. When you publish the integration, the MQTT connection continuously watches for messages on the MQTT queue or topic that you specify. When the connection finds a message, it passes it to the next step in the integration. An MQTT connection handles one message at a time.
To start an integration when a message from an MQTT broker is found:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the MQTT connection that you want to use to start the integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click the Subscribe action to receive messages from the queue or topic you specify.
- In the MQTT queue/topic name field, enter the name of the queue or topic to subscribe to in order to receive data.
- Click Done to add the start connection.
3.9.2.2. Publishing a message to an MQTT broker
In an integration, you can publish a message to an MQTT broker to finish an integration. To do this, add an MQTT connection as the integration’s finish connection. To publish a message to an MQTT broker in the middle of integration, add an MQTT connection to an integration after the start connection and before the finish connection.
To add an MQTT connection that publishes a message:
- Start creating the integration.
- Add and configure the start connection.
On the Choose a Finish Connection page, do one of the following:
- To finish an integration by publishing a message, click the MQTT connection that you want to use.
- To publish a message in the middle of an integration, click the connection you want to use to finish the integration. Configure that connection. When the finish connection is part of the integration, in the left panel, hover over the plus sign where you want to add an MQTT connection and click Add a connection. Click the MQTT connection that you want to use to publish a message in the middle of an integration.
- On the Choose an Action page, click Publish.
- In the MQTT queue/topic name field, specify the name of he queue or topic to publish the message to.
- Click Done to add the connection to the integration.
3.10. Connecting to REST APIs
In an integration, to connect to a REST API, you must have created a connector for that API by uploading a Swagger specification that describes the API. See Section 4.1, “Adding REST API client connectors”.
When a connector for the REST API you want to connect to is available in Ignite, the steps for connecting to that REST API are:
3.10.1. Register Ignite as an API client
Before Ignite creates an API client connector, it prompts you to indicate the API’s security requirements. For APIs that use OAuth, when Ignite creates the connector it also adds an entry for the API to the Ignite Settings page. This is where you provide the API client ID and the API client secret that authorize Ignite to access the API.
If the API you want to connect to does not use OAuth, skip this section and see Section 3.10.2, “Create an API client connection”.
To register Ignite as an authorized API client:
In Ignite:
- In the left panel, click Settings.
-
Near the top of the OAuth Application Management page, where you see
During registration, enter this callback URL:, copy that URL to the clipboard. - Look for the name of the API you want to connect to and click its Register button to display its client ID and client secret fields.
- In another browser window, you must register Ignite as an OAuth client of the API you want to connect to. The exact steps for doing this vary for each API service. Typically, the API service provides an OAuth custom application setting page. Go to that page.
On that page:
- Provide the Ignite callback URL, which you copied at the beginning of this procedure.
- Obtain the client ID and client secret that the API service assigns to your installation of Ignite.
- In the Ignite Settings page, in the entry for the API service you are registering with, paste the assigned client ID and the client secret.
- Click Save.
3.10.2. Create an API client connection
To create a connection to a REST API:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display available connectors.
- Click the connector for the API that you want to create a connection for.
- Respond to prompts for additional information. The definition of the API determines what Ignite prompts for. For example, for an API that uses HTTP Basic Authorization, Ignite prompts for the user name and password to use to access the API. For an API that uses OAuth, Ignite displays a button for you to click so that Ignite can verify its registration credentials for connecting to the API.
- In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections.
- In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection.
- In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available.
3.10.3. Add an API client connection to an integration
Before you can add an API connection to an integration, you must create a connection to that API. See Section 3.10.2, “Create an API client connection”.
In this release, in an integration, a connection to an API can be the finish connection or a middle connection. It cannot be the start connection. The instructions below assume that Ignite is prompting you to select a finish connection or a connection that is not the start connection.
To add an API connection to an integraton:
- On the page that displays available connections, click the API connection that you want to add to the integration.
- Click the action that you want the connection to perform. The actions that are available are based on the resource operations specified in the Swagger file that was uploaded to Ignite and that describes the API you are connecting to.
- Depending on the action you select, enter any parameters that Ignite prompts for.
- Click Done.
3.11. Connecting to Salesforce
To connect to Salesforce in an integration, see the following topics:
3.11.1. Register Ignite as a Salesforce client
You must register your installation of Ignite as an application that can access Salesforce. This lets you create any number of integrations that connect to Salesforce. In other words, you need to register a particular installation of Ignite with Salesforce only once.
In each Ignite environment, there can be only one registration of Ignite as a Salesforce client. However, while each Salesforce connection uses the same registration, it can use different user credentials.
Perform these steps to register Ignite as a Salesforce client:
In Ignite:
- In the left panel, click Settings.
-
Near the top of the OAuth Application Management page, where you see
During registration, enter this callback URL:, copy that URL to the clipboard. - To the right of the Salesforce entry, click Register to display the Client ID and Client Secret fields.
In another browser tab, log in to your Salesforce account and follow the steps below to create a connected app. These instructions assume that you are using the Salesforce Classic user interface. To switch from the Salesforce Lightning Experience interface, click your profile icon and select Switch to Salesforce Classic. For additional information, see the Salesforce documentation for Create a Connected App.
- In Salesforce, in the upper right, click Setup.
- In the left panel, select Build > Create > Apps.
- Scroll down to Connected Apps and click New.
- Enter the required information and then select Enable OAuth Settings.
-
In the Callback URL field, paste your Ignite URL, which you copied at the beginning of this procedure. For example:
https://app-proj9128.7b63.fuse-ignite.openshiftapps.com/api/v1/credentials/callback. For OAuth Scopes, add:
- Access and manage your data
- Allow access to your unique identifier
- Perform requests on your behalf at any time
- Select Include ID token and then Include Standard Claims.
- Scroll down and click Save.
-
Scroll up to see that Salesforce indicates a short wait:
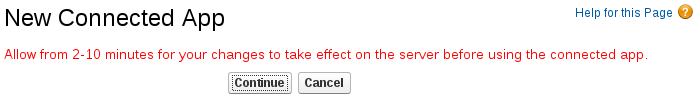
- Click Continue.
- Copy the consumer key that Salesforce provides.
- Return to your Ignite installation Settings page and paste the Salesforce-provided consumer key into the Salesforce Client ID field.
- Back in Salesforce, copy the consumer secret that Salesforce provides.
- Return to your Ignite installation Settings page and paste the Salesforce-provided consumer secret into the Salesforce Client Secret field.
- Click Save and then click Ok.
3.11.2. Create a Salesforce connection
A connection to Salesforce requires registration of Ignite as an application that can access Salesforce.
Be sure to wait 2 - 10 minutes after registering your Ignite installation as a Salesforce client before you try to create a Salesforce connection. After you create a Salesforce connection, you can use it in multiple integrations.
To create a Salesforce connection:
- In the left panel, click Connections to display available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display the available connectors. A connector is a template for creating one or more connections.
- Click the Salesforce connector.
Click Connect Salesforce to display a Salesforce authorization page. You might need to log in to Salesforce before you see the authorization page.
NoteThe following error indicates that Salesforce does not have the correct Ignite callback URL:
error=redirect_uri_mismatch&error_description=redirect_uri%20must%20match%20configurationIf you get this error message, then in Salesforce, ensure that the Ignite callback URL is specified according to the instructions in Section 3.11.1, “Register Ignite as a Salesforce client”.
- Click Allow to return to Ignite.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
SF Connect 1. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample Salesforce connection that uses my Salesforce login credentials. - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that SF Connect 1 is now available.
3.11.3. Adding a Salesforce connection to an integration
You must create a Salesforce connection before you can add a Salesforce connection to an integration. If you did not already create a Salesforce connection, see Section 3.11.2, “Create a Salesforce connection”.
You must be creating an integration or updating an integration to add a connection to that integration. If you need to, see Section 5.2, “Procedure for creating an integration” or Section 7.10, “Updating integrations”.
The instructions below assume that Ignite is prompting you to select a start connection, a finish connection or a middle connection.
To add a Salesforce connection to an integraton:
- On the page that displays available connections, click the Salesforce connection that you want to add to the integration. When the integration uses the connection you select to connect to Salesforce, Ignite uses the credentials defined in that connection.
- Click the action that you want the selected connection to perform. Each Salesforce connection that you add to an integration performs only the action you choose.
- Specify the Salesforce object that the action operates on, for example, it might be a contact, lead or price book entry. Click in the Object field to select from a list of Salesforce objects or enter the name of the object.
- Click Done to add the connection to the integration.
3.12. Connecting to Slack
In an integration, you can connect to an instance of Slack and deliver a message to a particular user or to a channel. For example, this is useful when an integration downloads a file from an FTP server and processes it in some way. You can finish an integration by notifying a Slack channel or user that the process was successful.
To connect to Slack in an integration, create a Slack connection. You can then add that same connection to any number of integrations. Details are in the following topics:
3.12.1. Create a Slack connection
To create a connection to an instance of Slack:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display Ignite connectors.
- Click the Slack connector.
- In the Slack webhook URL field, enter the webhook URL of the Slack instance to send messages to. This is the only required parameter.
Optionally, enter values for additional parameters:
- In the Sending user name for messages field, enter the user name that the bot has when it sends messages to Slack.
- In the Message avatar emoji field, specify the emoji that the bot uses as the message avatar when it sends a message.
- In the Message avatar icon URL field, specify the URL of the avatar that the bot uses when it sends messages to Slack.
If you specify an emoji and an icon URL, then the integration uses the icon URL.
- Click Validate. Ignite immediately tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the connection configuration values and try again.
- If validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
Slack for Company Sales. - In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection.
- In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that Slack for Company Sales is now available.
3.12.2. Adding a Slack connection to an integration
In an integration, to send a message to a Slack channel or user, first create a Slack connection. You can then add that connection to any number of integrations as a finish connection or as a middle connection. It does not make sense to add a Slack connection that starts an integration because you must map the message content from a previous step to a Slack connection field. In other words, a data mapping step must be in the integration just before the Slack connection.
To add a Slack connection to an integration, you must be creating or editing an integration. If you are creating an integration, then Ignite might be prompting you to choose a finish connection. To add a middle connection, hover over the plus sign in the left panel in the location where you want to add the connection and select Add a connection.
To add a Slack connection:
- Click the Slack connection that you want to add to the integration.
Select the action that you want the connection to perform.
- Click User name to send a message to one user. To configure this action, in the User name field, specify the name of the user to send the message to.
- Click Channel to publish a message on a channel. To configure this action, in the Channel field, specify the channel to publish the message to. The integration sends the integration data in a message to that channel.
- Click Next to add the connection to the integration.
- After you add all connections to the integration, add a data mapping step just before the Slack connection. In the mapping step, map a string from a previous step to the Slack message field. This string should contain the message that you want to send to the Slack user or channel. See Section 5.3.1, “Add a data mapping step”.
3.13. Connecting to SQL databases
In an integration, you can connect to any of the following types of SQL databases:
- Apache Derby
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
You create a connection to the database that you want to access in an integration and then you add that connection to an integration.
To connect to other types of databases, you must upload a JDBC driver for that database.
See the following topics for details:
3.13.1. Create a database connection
You create a separate connection for each database that you want to connect to in an integration. You can use the same connection in multiple integrations.
A database connection operates on a database table that you specify or invokes a stored procedure that you specify. The database table or the stored procedure must exist when an integration connects to the database.
To create a database connection:
- Ensure that the JDBC driver for the database that you want to connect to is on your classpath. If you uploaded a JDBC driver library extension to connect to a proprietary database, then the upload process puts the driver on your classpath. See Section 4.2.4, “Creating JDBC driver library extensions”.
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display Ignite connectors.
- Click the Database connector.
Configure the connection by entering:
- In the Password field, enter the password associated with the user account you want to use to access the database.
-
In the Schema field, enter the name of the schema for the database. If the connection URL specifies the schema, ensure that this field indicates the same schema as the connection URL. For example, enter
sampledb. -
In the Connection URL field, enter the JDBC URL for the database that you want to connect to. For example, enter
jdbc:postgresql://ignite-db1234/sampledb. - In the Username field, enter the name of the account that you want to use to access the database. Ensure that the specified password and user name are for the same account.
- Click Validate. Ignite tries to validate the connection and displays a message that indicates whether validation is successful. If validation fails, revise the configuration details as needed and try again.
- If validation is successful, click Next.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
PostgreSQL DB 1. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample PostgreSQL connection that uses my login credentials. - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that PostgreSQL DB 1 is available.
3.13.2. Add a database connection to an integration
You must create a database connection before you can add a database connection to an integration. If you did not already create the database connection, see Section 3.13.1, “Create a database connection”.
See the instructions for where in the integration you want to access the database:
3.13.2.1. Starting an integration by accessing a database
To start an integration by accessing a database:
- In the Ignite panel on the left, click Integrations.
- Click Create Integration.
- On the Choose a Start Connection page, click the database connection that you want to use to start an integration.
On the Choose an Action page, click one of the following:
- Periodic SQL Invocation obtains data by periodically invoking the SQL query you specify.
- Periodic Stored Procedure obtains data by periodically invoking the stored procedure you specify or select.
If you selected Periodic SQL Invocation, in the Query field, enter a SQL
SELECTstatement to obtain one or more records. For example:SELECT * from my_db_table. The database table that contains the data you want must already exist.If you selected Periodic Stored Procedure, in the Stored Procedure field, select or enter the stored procedure to invoke to obtain the data of interest. The stored procedure you specify must already exist. The database administrator should have created any stored procedures you need to use in an integration.
-
In the Period field, enter an integer and indicate whether the unit is minutes, hours, or days. For example, if you specify
5 minutesthen the connection invokes the specified query or stored procedure every five minutes. - Click Done.
Ignite tries to validate the connection, which includes checking that a specified SQL query is syntactically correct and confirming that the query or stored procedure target data exists. If verfication is successful then Ignite adds the start connection to the integration. If verification fails then Ignite displays a message about the problem. Update your input as needed and try again.
3.13.2.2. Accessing a database in the middle or to complete an integration
To finish an integration by accessing a database, add a database connection as the finish connection. To access a database in the middle of an integration, add a database connection between the start and finish connections. The instructions below assume that you are on the Ignite Choose a Finish Connection page or the Choose a Connection page.
To add a database connection:
- Click the database connection for the database you want to access.
On the Choose an Action page, click one of the following:
- Invoke SQL operates on data by executing the SQL statement you specify.
- Invoke Stored Procedure operates on data by invoking the stored procedure you specify or select.
If you selected Invoke SQL, in the SQL Statement field:
For a middle connection, enter a SQL
SELECTstatement that obtains one record or enter a SQLINSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEstatement that operates on one or more records. The database table that contains the data must already exist.In this release, when a database connection is a middle connection, a
SELECTstatement can obtain only one record. You should define theSELECTstatement so that it obtains one record.-
For a finish connection, enter a SQL
INSERT,UPDATEorDELETEstatement to operate on one or more records.
If you selected Invoke Stored Procedure, in the Stored Procedure field, select or enter the name of the stored procedure to invoke to operate on the data of interest. The stored procedure you specify must already exist. The database administrator should have created any stored procedures you need to use in an integration.
- See the information below about specifying placeholder parameters in queries.
- Click Done.
Ignite tries to validate the connection, which includes checking that a specified SQL query is syntactically correct and confirming that the query or stored procedure target data exists. If verfication is successful then Ignite adds the connection to the integration. If verification fails then Ignite displays a message about the problem. Update your input as needed and try again.
Specifying parameters in queries
When you access a database in the middle of an integration or to complete an integration, you can specify placeholder parameters in the SQL query or there can be placeholders in the stored procedure. For example:
INSERT INTO TODO(task, completed) VALUES(:#param_1, :#param_2) DELETE FROM TODO WHERE task LIKE :#param_3
To specify the values of these placeholders, add a data mapping step to your integration before the database connection. In the data mapping step, map the appropriate source data fields to the target data fields, for example, map source data to the :#param_1, :#param_2, and :#param_3 target fields. See Section 5.3.1, “Add a data mapping step”.
3.13.3. Connecting to proprietary databases
To connect to a proprietary SQL database, the main tasks that must be accomplished are as follows:
- A developer creates a library extension that contains the JDBC driver for the database that you want to access in an integration. See Section 4.2.4, “Creating JDBC driver library extensions”.
-
The developer provides a
.jarfile that contains the library extension. -
You upload that
.jarfile to Ignite. See Section 4.2.2, “Making custom features available”. - You create a connection to your database by selecting the Ignite Database connector and specifying the connection URL for your database. See Section 3.13.1, “Create a database connection”.
- In an integration, you add the connection to your database. See Section 3.13.2, “Add a database connection to an integration”.
3.14. Connecting to Twitter
To connect to Twitter in an integration, see the following topics:
3.14.1. Register Ignite as a Twitter client
You must register your installation of Ignite as an application that can access Twitter. This lets you create any number of integrations that connect to Twitter. In other words, you need to register a particular installation of Ignite with Twitter only once.
In each Ignite environment, there can be only one registration of Ignite as a Twitter client. However, while each Twitter connection uses the same registration, it can use different user credentials.
Perform these steps:
In Ignite:
- In the left panel, click Settings.
-
Near the top of the OAuth Application Management page, where you see
During registration, enter this callback URL:, copy the URL at the end of the sentence to the clipboard. - To the right of the Twitter entry, click Register to display the Client ID and Client Secret fields.
In another browser tab, go to the Twitter Application Management web site at https://apps.twitter.com and do the following:
-
Confirm that the URL is
apps.twitter.comand not justtwitter.com. - If you are not already logged in to the Twitter Application Management site, log in.
- Click Create New App.
- In the Name field, enter a name for your new app. This name must be unique among all names of apps registered with Twitter.
- In the Description field, enter helpful information. Twitter requires some input in this field.
-
In the Website field, paste the URL that you copied at the beginning of this procedure and remove
api/v1/credentials/callbackfrom the end of the URL. -
In the Callback URL field, paste the URL again. It should be something like this:
https://app-proj9128.7b63.fuse-ignite.openshiftapps.com/api/v1/credentials/callback. - Click Yes to agree to the Twitter developer agreement.
- Click Create your Twitter application.
- Click the Keys and Access Tokens tab.
- Copy the Consumer Key.
-
Confirm that the URL is
- On your Ignite installation Settings page, paste the Twitter consumer key into the Twitter Client ID field.
- On the Twitter Keys and Access Tokens tab, copy the Consumer Secret and paste it into the Ignite Twitter Client Secret field.
- Click Save and then click Ok.
3.14.2. Create a Twitter connection
A connection to Twitter requires registration of Ignite as an application that can access Twitter. If you did not already register Ignite, see Section 3.14.1, “Register Ignite as a Twitter client”.
After you create a Twitter connection, you can use it in multiple integrations.
To create a Twitter connection:
- In Ignite, in the left panel, click Connections to display any available connections.
- In the upper right, click Create Connection to display the available connectors. A connector is a template that you use to create one or more connections.
- Click the Twitter connector.
- Click Connect Twitter to display a Twitter authorization page. You might need to log in to Twitter before you see the authorization page.
- Click Authorize app to return to Ignite.
-
In the Connection Name field, enter your choice of a name that helps you distinguish this connection from any other connections. For example, enter
Twitter Connect 1. -
In the Description field, optionally enter any information that is helpful to know about this connection. For example, enter
Sample Twitter connection that uses my Twitter login credentials. - In the upper right, click Create to see that the connection you created is now available. If you entered the example name, you would see that Twitter Connect 1 is now available.
3.14.3. Adding a Twitter connection to an integration
You must create a Twitter connection before you can add a Twitter connection to an integration. If you did not already create a Twitter connection, see Section 3.14.2, “Create a Twitter connection”.
You must be creating an integration or updating an integration to add a connection to that integration. If you need to, see Section 5.2, “Procedure for creating an integration” or Section 7.10, “Updating integrations”.
The instructions below assume that Ignite is prompting you to select a start connection, a finish connection or a middle connection.
To add a Twitter connection to an integraton:
- On the page that displays available connections, click the Twitter connection that you want to add to the integration. When the integration uses the selected connection to connect to Twitter, Ignite uses the credentials defined in that connection.
- Click the action that you want the selected connection to perform. Each Twitter connection that you add to an integration performs only the action you choose.
- Optionally, enter the configuration information that Ignite prompts for. For example, the Search action prompts you to specify how often to search and keywords to search for.
- Click Done to add the connection to the integration.

