Chapter 6. Configuring IPoIB
By default, InfiniBand does not use the internet protocol (IP) for communication. However, IP over InfiniBand (IPoIB) provides an IP network emulation layer on top of InfiniBand remote direct memory access (RDMA) networks. This allows existing unmodified applications to transmit data over InfiniBand networks, but the performance is lower than if the application would use RDMA natively.
The Mellanox devices, starting from ConnectX-4 and above, on RHEL 8 and later use Enhanced IPoIB mode by default (datagram only). Connected mode is not supported on these devices.
6.1. The IPoIB communication modes
An IPoIB device is configurable in either Datagram or Connected mode. The difference is the type of queue pair the IPoIB layer attempts to open with the machine at the other end of the communication:
In the
Datagrammode, the system opens an unreliable, disconnected queue pair.This mode does not support packages larger than Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of the InfiniBand link layer. During transmission of data, the IPoIB layer adds a 4-byte IPoIB header on top of the IP packet. As a result, the IPoIB MTU is 4 bytes less than the InfiniBand link-layer MTU. As
2048is a common InfiniBand link-layer MTU, the common IPoIB device MTU inDatagrammode is2044.In the
Connectedmode, the system opens a reliable, connected queue pair.This mode allows messages larger than the InfiniBand link-layer MTU. The host adapter handles packet segmentation and reassembly. As a result, in the
Connectedmode, the messages sent from Infiniband adapters have no size limits. However, there are limited IP packets due to thedatafield and TCP/IPheaderfield. For this reason, the IPoIB MTU in theConnectedmode is65520bytes.The
Connectedmode has a higher performance but consumes more kernel memory.
Though a system is configured to use the Connected mode, a system still sends multicast traffic using the Datagram mode because InfiniBand switches and fabric cannot pass multicast traffic in the Connected mode. Also, when the host is not configured to use the Connected mode, the system falls back to the Datagram mode.
While running an application that sends multicast data up to MTU on the interface, configures the interface in Datagram mode or configure the application to cap the send size of a packet that will fit in datagram-sized packets.
6.2. Understanding IPoIB hardware addresses
IPoIB devices have a 20 byte hardware address that consists of the following parts:
- The first 4 bytes are flags and queue pair numbers
The next 8 bytes are the subnet prefix
The default subnet prefix is
0xfe:80:00:00:00:00:00:00. After the device connects to the subnet manager, the device changes this prefix to match with the configured subnet manager.- The last 8 bytes are the Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) of the InfiniBand port that attaches to the IPoIB device
As the first 12 bytes can change, do not use them in the udev device manager rules.
6.3. Configuring an IPoIB connection using nmcli commands
The nmcli command-line utility controls the NetworkManager and reports network status using CLI.
Prerequisites
- An InfiniBand device is installed on the server
- The corresponding kernel module is loaded
Procedure
Create the InfiniBand connection to use the
mlx4_ib0interface in theConnectedtransport mode and the maximum MTU of65520bytes:# nmcli connection add type infiniband con-name mlx4_ib0 ifname mlx4_ib0 transport-mode Connected mtu 65520You can also set
0x8002as aP_Keyinterface of themlx4_ib0connection:# nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 infiniband.p-key 0x8002To configure the IPv4 settings set a static IPv4 address, network mask, default gateway, and DNS server of the
mlx4_ib0connection:# nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv4.addresses 192.0.2.1/24 # nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv4.gateway 192.0.2.254 # nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv4.dns 192.0.2.253 # nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv4.method manual
To configure the IPv6 settings set a static IPv6 address, network mask, default gateway, and DNS server of the
mlx4_ib0connection:# nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv6.addresses 2001:db8:1::1/32 # nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv6.gateway 2001:db8:1::fffe # nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv6.dns 2001:db8:1::fffd # nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 ipv6.method manual
To activate the
mlx4_ib0connection:# nmcli connection up mlx4_ib0
6.4. Configuring an IPoIB connection by using the network RHEL System Role
You can use the network RHEL System Role to remotely create NetworkManager connection profiles for IP over InfiniBand (IPoIB) devices. For example, remotely add an InfiniBand connection for the mlx4_ib0 interface with the following settings by running an Ansible Playbook:
-
An IPoIB device -
mlx4_ib0.8002 -
A partition key
p_key-0x8002 -
A static
IPv4address -192.0.2.1with a/24subnet mask -
A static
IPv6address -2001:db8:1::1with a/64subnet mask
Perform this procedure on the Ansible control node.
Prerequisites
- You have prepared the control node and the managed nodes
- You logged in to the control node as a user who can run playbooks on the managed nodes.
-
The account you use to connect to the managed nodes has
sudopermissions on them. - The managed nodes or groups of managed nodes on which you want to run this playbook are listed in the Ansible inventory file.
-
An InfiniBand device named
mlx4_ib0is installed in the managed nodes. - The managed nodes use NetworkManager to configure the network.
Procedure
Create a playbook file, for example
~/IPoIB.yml, with the following content:--- - name: Configure the network hosts: managed-node-01.example.com tasks: - name: Configure IPoIB include_role: name: rhel-system-roles.network vars: network_connections: # InfiniBand connection mlx4_ib0 - name: mlx4_ib0 interface_name: mlx4_ib0 type: infiniband # IPoIB device mlx4_ib0.8002 on top of mlx4_ib0 - name: mlx4_ib0.8002 type: infiniband autoconnect: yes infiniband: p_key: 0x8002 transport_mode: datagram parent: mlx4_ib0 ip: address: - 192.0.2.1/24 - 2001:db8:1::1/64 state: upIf you set a
p_keyparameter as in this example, do not set aninterface_nameparameter on the IPoIB device.Validate the playbook syntax:
# ansible-playbook ~/IPoIB.yml --syntax-checkNote that this command only validates the syntax and does not protect against a wrong but valid configuration.
Run the playbook:
# ansible-playbook ~/IPoIB.yml
Verification
On the
managed-node-01.example.comhost, display the IP settings of themlx4_ib0.8002device:# ip address show mlx4_ib0.8002 ... inet 192.0.2.1/24 brd 192.0.2.255 scope global noprefixroute ib0.8002 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 2001:db8:1::1/64 scope link tentative noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Display the partition key (P_Key) of the
mlx4_ib0.8002device:# cat /sys/class/net/mlx4_ib0.8002/pkey 0x8002Display the mode of the
mlx4_ib0.8002device:# cat /sys/class/net/mlx4_ib0.8002/mode datagram
Additional resources
-
/usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.network/README.mdfile
6.5. Configuring an IPoIB connection using nm-connection-editor
The nmcli-connection-editor application configures and manages network connections stored by NetworkManager using the management console.
Prerequisites
- An InfiniBand device is installed on the server.
- Corresponding kernel module is loaded
-
The
nm-connection-editorpackage is installed.
Procedure
Enter the command:
$ nm-connection-editor- Click the + button to add a new connection.
-
Select the
InfiniBandconnection type and click Create. On the
InfiniBandtab:- Change the connection name if you want to.
- Select the transport mode.
- Select the device.
- Set an MTU if needed.
-
On the
IPv4 Settingstab, configure the IPv4 settings. For example, set a static IPv4 address, network mask, default gateway, and DNS server:
-
On the
IPv6 Settingstab, configure the IPv6 settings. For example, set a static IPv6 address, network mask, default gateway, and DNS server: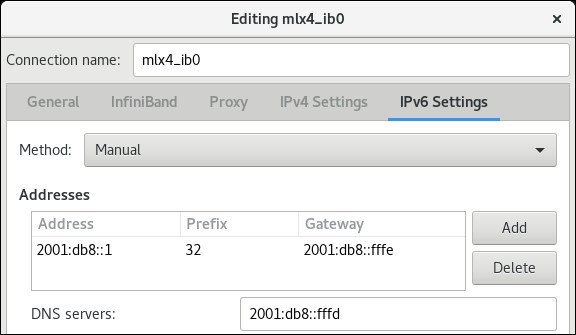
- Click Save to save the team connection.
-
Close
nm-connection-editor. You can set a
P_Keyinterface. As this setting is not available innm-connection-editor, you must set this parameter on the command line.For example, to set
0x8002asP_Keyinterface of themlx4_ib0connection:# nmcli connection modify mlx4_ib0 infiniband.p-key 0x8002

