Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for RHEL 8
Managing and monitoring security updates
Update RHEL 8 system security to prevent attackers from exploiting known flaws
Abstract
Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code, documentation, and web properties. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Because of the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be implemented gradually over several upcoming releases. For more details, see our CTO Chris Wright’s message.
Providing feedback on Red Hat documentation
We appreciate your feedback on our documentation. Let us know how we can improve it.
Submitting feedback through Jira (account required)
- Log in to the Jira website.
- Click Create in the top navigation bar.
- Enter a descriptive title in the Summary field.
- Enter your suggestion for improvement in the Description field. Include links to the relevant parts of the documentation.
- Click Create at the bottom of the dialogue.
Chapter 1. Identifying security updates
Keeping enterprise systems secure from current and future threats requires regular security updates. Red Hat Product Security provides the guidance you need to confidently deploy and maintain enterprise solutions.
1.1. What are security advisories?
Red Hat Security Advisories (RHSA) document the information about security flaws being fixed in Red Hat products and services.
Each RHSA includes the following information:
- Severity
- Type and status
- Affected products
- Summary of fixed issues
- Links to the tickets about the problem. Note that not all tickets are public.
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) numbers and links with additional details, such as attack complexity.
Red Hat Customer Portal provides a list of Red Hat Security Advisories published by Red Hat. You can display details of a specific advisory by navigating to the advisory’s ID from the list of Red Hat Security Advisories.
Figure 1.1. List of security advisories
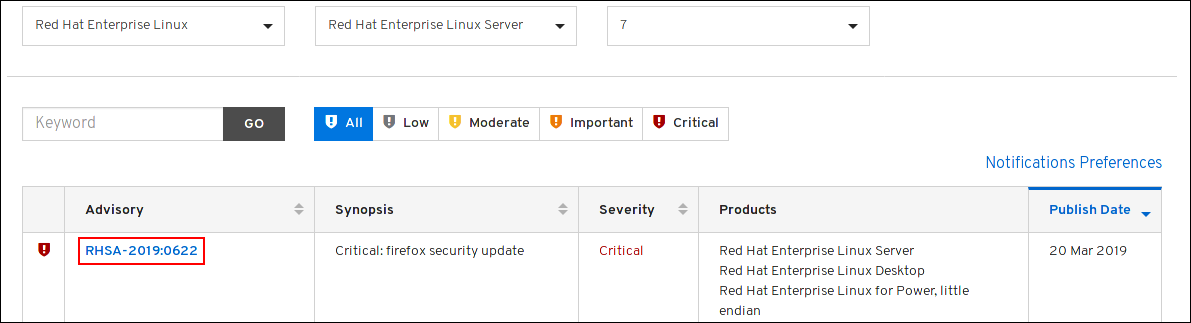
Optionally, you can also filter the results by specific product, variant, version, and architecture. For example, to display only advisories for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, you can set the following filters:
- Product: Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Variant: All Variants
- Version: 8
- Optionally, select a minor version, such as 8.2.
1.2. Displaying security updates that are not installed on a host
You can list all available security updates for your system by using the yum utility.
Prerequisite
- A Red Hat subscription attached to the host.
Procedure
List all available security updates which have not been installed on the host:
#
yum updateinfo list updates security... RHSA-2019:0997 Important/Sec. platform-python-3.6.8-2.el8_0.x86_64 RHSA-2019:0997 Important/Sec. python3-libs-3.6.8-2.el8_0.x86_64 RHSA-2019:0990 Moderate/Sec. systemd-239-13.el8_0.3.x86_64 ...
1.3. Displaying security updates that are installed on a host
You can list installed security updates for your system by using the yum utility.
Procedure
List all security updates which are installed on the host:
#
yum updateinfo list security --installed... RHSA-2019:1234 Important/Sec. libssh2-1.8.0-7.module+el8+2833+c7d6d092 RHSA-2019:4567 Important/Sec. python3-libs-3.6.7.1.el8.x86_64 RHSA-2019:8901 Important/Sec. python3-libs-3.6.8-1.el8.x86_64 ...If multiple updates of a single package are installed,
yumlists all advisories for the package. In the previous example, two security updates for thepython3-libspackage have been installed since the system installation.
1.4. Displaying a specific advisory by using yum
You can use the yum utility to display a specific advisory information that is available for an update.
Prerequisites
- A Red Hat subscription attached to the host.
-
You have a security advisory
Update ID. See identifying the security advisory updates. - The update provided by the advisory is not installed.
Procedure
Display a specific advisory:
#
yum updateinfo info <Update ID>==================================================================== Important: python3 security update ==================================================================== Update ID: RHSA-2019:0997 Type: security Updated: 2019-05-07 05:41:52 Bugs: 1688543 - CVE-2019-9636 python: Information Disclosure due to urlsplit improper NFKC normalization CVEs: CVE-2019-9636 Description: ...Replace the Update ID with the required advisory. For example,
# yum updateinfo info <RHSA-2019:0997>.
Chapter 2. Installing security updates
2.1. Installing all available security updates
To keep the security of your system up to date, you can install all currently available security updates using the yum utility.
Prerequisite
- A Red Hat subscription attached to the host.
Procedure
Install security updates using
yumutility:#
yum update --securityNoteThe
--securityparameter is important. Without it,yum updateinstalls all updates, including bug fixes and enhancements.Confirm and start the installation by pressing y:
... Transaction Summary =========================================== Upgrade ... Packages Total download size: ... M Is this ok [y/d/N]: yOptional: list processes that require a manual restart of the system after installing the updated packages:
#
yum needs-restarting1107 : /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n 1199 : -bashNoteThis command lists only processes that require a restart, and not services. That is, you cannot restart processes listed using the
systemctlutility. For example, thebashprocess in the output is terminated when the user that owns this process logs out.
2.2. Installing a security update provided by a specific advisory
In certain situations, you might want to install only specific updates. For example, if a specific service can be updated without scheduling a downtime, you can install security updates for only this service, and install the remaining security updates later.
Prerequisites
- A Red Hat subscription attached to the host.
- You have the ID of the security advisory that you want to update. For more information, see identifying the security advisory updates.
Procedure
Install a specific advisory:
#
yum update --advisory=<Update_ID>Replace <Update_ID> with the ID of the security advisory that you want to update. For example:
# yum update --advisory=RHSA-2019:0997ImportantYou can update to apply a specific advisory with a minimal version change by using the
yum upgrade-minimal --advisory=<Update_ID>command.Confirm and start the installation by pressing
y:... Transaction Summary =========================================== Upgrade ... Packages Total download size: ... M Is this ok [y/d/N]: yOptional: List the processes that require a manual restart of the system after installing the updated packages:
#
yum needs-restarting1107 : /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -n 1199 : -bashNoteThis command lists only processes that require a restart, and not services. This means that you cannot restart all processes listed by using the
systemctlutility. For example, thebashprocess in the output is terminated when the user that owns this process logs out.
2.3. Installing security updates automatically
You can configure your system so that it automatically downloads and installs all security updates.
Prerequisites
- A Red Hat subscription attached to the host.
-
The
dnf-automaticpackage is installed.
Procedure
In the
/etc/dnf/automatic.conffile, under the[commands]section, make sure theupgrade_typeoption is set to eitherdefaultorsecurity:[commands] # What kind of upgrade to perform: # default = all available upgrades # security = only the security upgrades upgrade_type = security
Enable and start the
systemdtimer unit:# systemctl enable --now dnf-automatic-install.timer
Verification
Verify that the timer is enabled:
# systemctl status dnf-automatic-install.timer
Additional resources
-
dnf-automatic(8)man page
2.4. Additional resources
- See practices of securing workstations and servers in Security Hardening document.
- Security-Enhanced Linux documentation.

