Red Hat Training
A Red Hat training course is available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
46.2.2.3. Configuring the Target Type
When a kernel crash is captured, the core dump can be either stored as a file in a local file system, written directly to a device, or sent over a network using the NFS (Network File System) or SSH (Secure Shell) protocol. To change this, click the Edit Location button, and select a location type as described below.
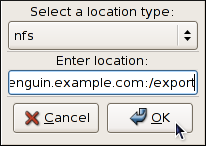
Figure 46.3. The Edit Location dialog
To save the dump to the local file system, select file from the pulldown list. Optionally, if you wish to write the file to a different partition, select ext3 or ext2 from the pulldown list according to the file system you are using, and enter a valid device name to the Enter location field. Note that after clicking OK, you can then customize the destination directory by changing the value in the Path field at the bottom.
To write the dump directly to a device, select raw from the pulldown list, and enter a valid device name (for example,
/dev/sdb1). When you are done, click OK to confirm your choice.
To store the dump to a remote machine using the NFS protocol, select nfs from the pulldown list, and enter a valid target in the hostname:directory form (for example,
penguin.example.com:/export). Clicking the OK button will confirm your changes. Finally, edit the value of the Path field to customize the destination directory (for instance, cores).
To store the dump to a remote machine using the SSH protocol, select ssh from the pulldown list, and enter a valid username and hostname in the username@hostname form (for example,
john@penguin.example.com). Clicking the OK button will confirm your changes. Finally, edit the value of the Path field to customize the destination directory (for instance, /export/cores).
Refer to Chapter 20, OpenSSH for information on how to configure an SSH server, and how to set up a key-based authentication.

