Chapter 4. Plug-in Implemented Server Functionality Reference
This chapter contains reference information on Red Hat Directory Server plug-ins.
The configuration for each part of Directory Server plug-in functionality has its own separate entry and set of attributes under the subtree cn=plugins,cn=config.
dn: cn=Telephone Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config objectclass: top objectclass: nsSlapdPlugin objectclass: extensibleObject cn: Telephone Syntax nsslapd-pluginPath: libsyntax-plugin nsslapd-pluginInitfunc: tel_init nsslapd-pluginType: syntax nsslapd-pluginEnabled: on
Some of these attributes are common to all plug-ins while others may be particular to a specific plug-in. Check which attributes are currently being used by a given plug-in by performing an ldapsearch on the cn=config subtree.
All plug-ins are instances of the nsSlapdPlugin object class, which in turn inherits from the extensibleObject object class. For plug-in configuration attributes to be taken into account by the server, both of these object classes (in addition to the top object class) must be present in the entry, as shown in the following example:
dn:cn=ACL Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config objectclass:top objectclass:nsSlapdPlugin objectclass:extensibleObject
4.1. Server Plug-in Functionality Reference
The following tables provide a quick overview of the plug-ins provided with Directory Server, along with their configurable options, configurable arguments, default setting, dependencies, general performance-related information, and further reading. These tables assist in weighing plug-in performance gains and costs and choose the optimal settings for the deployment. The Further Information section cross-references further reading, where this is available.
4.1.1. 7-bit Check Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | NS7bitAtt |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=7-bit check,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Checks certain attributes are 7-bit clean |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
|
List of attributes ( | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| None | Further Information |
4.1.2. ACL Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | acl |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=ACL Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | ACL access check plug-in |
| Type | accesscontrol |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Access control incurs a minimal performance hit. Leave this plug-in enabled since it is the primary means of access control for the server. | Further Information |
4.1.3. ACL Preoperation Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | acl |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=ACL preoperation,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | ACL access check plug-in |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Access control incurs a minimal performance hit. Leave this plug-in enabled since it is the primary means of access control for the server. | Further Information |
4.1.4. Account Policy Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | none |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Defines a policy to lock user accounts after a certain expiration period or inactivity period. |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| A pointer to a configuration entry which contains the global account policy settings. | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| None | Further Information |
4.1.5. Account Usability Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | acctusability |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Account Usability Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Checks the authentication status, or usability, of an account without actually authenticating as the given user |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
4.1.6. AD DN Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | addn |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=addn,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description |
Enables the usage of Active Directory-formatted user names, such as |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
|
| Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
4.1.7. Attribute Uniqueness Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | NSUniqueAttr |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Attribute Uniqueness,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Checks that the values of specified attributes are unique each time a modification occurs on an entry. For example, most sites require that a user ID and email address be unique. |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
|
To check for UID attribute uniqueness in all listed subtrees, enter | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Directory Server provides the UID Uniqueness Plug-in by default. To ensure unique values for other attributes, create instances of the Attribute Uniqueness Plug-in for those attributes. See the "Using the Attribute Uniqueness Plug-in" section in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide for more information about the Attribute Uniqueness Plug-in. The UID Uniqueness Plug-in is off by default due to operation restrictions that need to be addressed before enabling the plug-in in a multi-supplier replication environment. Turning the plug-in on may slow down Directory Server performance. | Further Information |
4.1.8. Auto Membership Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | Auto Membership |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Auto Membership,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Container entry for automember definitions. Automember definitions search new entries and, if they match defined LDAP search filters and regular expression conditions, add the entry to a specified group automatically. |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None for the main plug-in entry. The definition entry must specify an LDAP scope, LDAP filter, default group, and member attribute format. The optional regular expression child entry can specify inclusive and exclusive expressions and a different target group. | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| None. | Further Information |
4.1.9. Binary Syntax Plug-in
Binary syntax is deprecated. Use Octet String syntax instead.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | bin-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Binary Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Syntax for handling binary data. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.10. Bit String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | bitstring-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Bit String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports bit string syntax values and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.11. Bitwise Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | bitwise |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Bitwise Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Matching rule for performing bitwise operations against the LDAP server |
| Type | matchingrule |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.12. Boolean Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | boolean-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Boolean Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports boolean syntax values (TRUE or FALSE) and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.13. Case Exact String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | ces-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Case Exact String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports case-sensitive matching or Directory String, IA5 String, and related syntaxes. This is not a case-exact syntax; this plug-in provides case-sensitive matching rules for different string syntaxes. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.14. Case Ignore String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | directorystring-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Case Ignore String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports case-insensitive matching rules for Directory String, IA5 String, and related syntaxes. This is not a case-insensitive syntax; this plug-in provides case-sensitive matching rules for different string syntaxes. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.15. Chaining Database Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | chaining database |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables back end databases to be linked |
| Type | database |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| There are many performance related tuning parameters involved with the chaining database. See the "Maintaining Database Links" section in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide. | Further Information |
4.1.16. Class of Service Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | cos |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Class of Service,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Allows for sharing of attributes between entries |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| * Type: Database * Named: State Change Plug-in * Named: Views Plug-in | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Leave this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.17. Content Synchronization Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | content-sync-plugin |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Content Synchronization,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description |
Enables support for the |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Retro Changelog Plug-in | Performance-Related Information |
|
If you know which back end or subtree clients access to synchronize data, limit the scope of the | Further Information |
4.1.18. Country String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | countrystring-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Country String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports country naming syntax values and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.19. Delivery Method Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | delivery-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Delivery Method Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports values that are lists of preferred deliver methods and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.20. deref Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | Dereference |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=deref,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | For dereference controls in directory searches |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.21. Distinguished Name Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | dn-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Distinguished Name Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports DN value syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.22. Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in
| Plug-in Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | Distributed Numeric Assignment |
| Configuration Entry DN | cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Distributed Numeric Assignment plugin |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| Dependencies | |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| None | Further Information |
4.1.23. Enhanced Guide Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | enhancedguide-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Enhanced Guide Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for creating complex criteria, based on attributes and filters, to build searches; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.24. Facsimile Telephone Number Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | facsimile-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Facsimile Telephone Number Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for fax numbers; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.25. Fax Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | fax-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Fax Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for storing images of faxed objects; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.26. Generalized Time Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | time-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Generalized Time Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for dealing with dates, times and time zones; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.27. Guide Syntax Plug-in
This syntax is deprecated. Use Enhanced Guide syntax instead.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | guide-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Guide Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Syntax for creating complex criteria, based on attributes and filters, to build searches |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.28. HTTP Client Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | http-client |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=HTTP Client,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | HTTP client plug-in |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Further Information |
4.1.29. Integer Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | int-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Integer Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports integer syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.30. Internationalization Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | orderingrule |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Internationalization Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables internationalized strings to be ordered in the directory |
| Type | matchingrule |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
|
The Internationalization Plug-in has one argument, which must not be modified, which specifies the location of the | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.31. JPEG Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | jpeg-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=JPEG Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for JPEG image data; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.32. ldbm database Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | ldbm-backend |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Implements local databases |
| Type | database |
| Configurable Options | |
| Default Setting | on |
| Configurable Arguments | None |
| Dependencies | * Syntax * matchingRule |
| Performance-Related Information | See Section 4.4, “Database Plug-in Attributes” for further information on database configuration. |
| Further Information | See the "Configuring Directory Databases" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide. |
4.1.33. Linked Attributes Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | Linked Attributes |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Linked Attributes,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description |
Container entry for linked-managed attribute configuration entries. Each configuration entry under the container links one attribute to another, so that when one entry is updated (such as a manager entry), then any entry associated with that entry (such as a custom |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None for the main plug-in entry. Each plug-in instance has three possible attributes: * linkType, which sets the primary attribute for the plug-in to monitor * managedType, which sets the attribute which will be managed dynamically by the plug-in whenever the attribute in linkType is modified * linkScope, which restricts the plug-in activity to a specific subtree within the directory tree | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Any attribute set in linkType must only allow values in a DN format. Any attribute set in managedType must be multi-valued. | Further Information |
4.1.34. Managed Entries Plug-in
| Plug-in Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | Managed Entries |
| Configuration Entry DN | cn=Managed Entries,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Container entry for automatically generated directory entries. Each configuration entry defines a target subtree and a template entry. When a matching entry in the target subtree is created, then the plug-in automatically creates a new, related entry based on the template. |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None for the main plug-in entry. Each plug-in instance has four possible attributes: * originScope, which sets the search base * originFilter, which sets the search base for matching entries * managedScope, which sets the subtree under which to create new managed entries * managedTemplate, which is the template entry used to create the managed entries | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| None | Further Information |
4.1.35. MemberOf Plug-in
| Plug-in Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | memberOf |
| Configuration Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description |
Manages the |
| Type | postoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
|
*
* | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| None | Further Information |
4.1.36. Multi-master Replication Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | replication-multimaster |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Multimaster Replication plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables replication between two current Directory Servers |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| * Named: ldbm database * Named: DES * Named: Class of Service | Performance-Related Information |
| Further Information |
4.1.37. Name and Optional UID Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | nameoptuid-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Name And Optional UID Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules to store and search for a DN with an optional unique ID; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.38. Numeric String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | numstr-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Numeric String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for strings of numbers and spaces; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.39. Octet String Syntax Plug-in
Use the Octet String syntax instead of Binary, which is deprecated.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | octetstring-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Octet String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports octet string syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.40. OID Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | oid-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=OID Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports object identifier (OID) syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.41. PAM Pass Through Auth Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | pam_passthruauth |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=PAM Pass Through Auth,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables pass-through authentication for PAM, meaning that a PAM service can use the Directory Server as its user authentication store. |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Further Information |
4.1.42. Pass Through Authentication Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | passthruauth |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Pass Through Authentication,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables pass-through authentication, the mechanism which allows one directory to consult another to authenticate bind requests. |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| ldap://example.com:389/o=example | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| Pass-through authentication slows down bind requests a little because they have to make an extra hop to the remote server. See the "Using Pass-through Authentication" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide. | Further Information |
4.1.43. Password Storage Schemes
Directory Server implements the password storage schemes as plug-ins. However, the cn=Password Storage Schemes,cn=plugins,cn=config entry itself is just a container, not a plug-in entry. All password storage scheme plug-ins are stored as a subentry of this container.
To display all password storage schemes plug-ins, enter:
# ldapsearch -D "cn=Directory Manager" -W -p 389 -h server.example.com -x \
-b "cn=Password Storage Schemes,cn=plugins,cn=config" -s sub "(objectclass=*)" dnRed Hat recommends not disabling the password scheme plug-ins nor to change the configurations of the plug-ins to prevent unpredictable authentication behavior.
Strong Password Storage Schemes
Red Hat recommends using only the following strong password storage schemes (strongest first):
PBKDF2_SHA256(default)The password-based key derivation function 2 (PBKDF2) was designed to expend resources to counter brute force attacks. PBKDF2 supports a variable number of iterations to apply the hashing algorithm. Higher iterations improve security but require more hardware resources. In Directory Server, the
PBKDF2_SHA256scheme is implemented using 30,000 iterations to apply the SHA256 algorithm. This value is hard-coded and will be increased in future versions of Directory Server without requiring interaction by an administrator.NoteThe network security service (NSS) database in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 does not support PBKDF2. Therefore you cannot use this password scheme in a replication topology with Directory Server 9.
SSHA512The salted secure hashing algorithm (SSHA) implements an enhanced version of the secure hashing algorithm (SHA), that uses a randomly generated salt to increase the security of the hashed password.
SSHA512implements the hashing algorithm using 512 bits.
Weak Password Storage Schemes
Besides the recommended strong password storage schemes, Directory Server supports the following weak schemes for backward compatibility:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
[a]
Directory Server only supports authentication using this scheme. You can no longer use it to encrypt passwords.
[b]
160 bit
| ||
Only continue using a weak scheme over a short time frame, as it increases security risks.
4.1.44. Posix Winsync API Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | posix-winsync-plugin |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Posix Winsync API,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables and configures Windows synchronization for Posix attributes set on Active Directory user and group entries. |
| Type | preoperation |
| Configurable Arguments | * on |
| off * memberUID mapping (groups) * converting and sorting memberUID values in lower case (groups) * memberOf fix-up tasks with sync operations * use Windows 2003 Posix schema | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
4.1.45. Postal Address String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | postaladdress-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Postal Address Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports postal address syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.46. Printable String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | printablestring-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Printable String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and matching rules for alphanumeric and select punctuation strings (for strings which conform to printable strings as defined in RFC 4517). |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.47. Referential Integrity Postoperation Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | referint |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Referential Integrity Postoperation,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables the server to ensure referential integrity |
| Type | postoperation |
| Configurable Options | All configuration and on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
|
When enabled, the post-operation Referential Integrity Plug-in performs integrity updates on the | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
| The Referential Integrity Plug-in should be enabled only on one supplier in a multi-supplier replication environment to avoid conflict resolution loops. When enabling the plug-in on chained servers, be sure to analyze the performance resource and time needs as well as integrity needs; integrity checks can be time consuming and demanding on memory and CPU. All attributes specified must be indexed for both presence and equality. | Further Information |
4.1.48. Retro Changelog Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | retrocl |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description |
Used by LDAP clients for maintaining application compatibility with Directory Server 4.x versions. Maintains a log of all changes occurring in the Directory Server. The retro changelog offers the same functionality as the changelog in the 4.x versions of Directory Server. This plug-in exposes the |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| See Section 4.16, “Retro Changelog Plug-in Attributes” for further information on the two configuration attributes for this plug-in. | Dependencies |
| * Type: Database * Named: Class of Service | Performance-Related Information |
| May slow down Directory Server update performance. | Further Information |
4.1.49. Roles Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | roles |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Roles Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables the use of roles in the Directory Server |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| * Type: Database * Named: State Change Plug-in * Named: Views Plug-in | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.50. RootDN Access Control Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | rootdn-access-control |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=RootDN Access Control,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables and configures access controls to use for the root DN entry. |
| Type | internalpreoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Attributes |
| * rootdn-open-time and rootdn-close-time for time-based access controls * rootdn-days-allowed for day-based access controls * rootdn-allow-host, rootdn-deny-host, rootdn-allow-ip, and rootdn-deny-ip for host-based access controls | Dependencies |
| None | Further Information |
4.1.51. Schema Reload Plug-in
| Plug-in Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | schemareload |
| Configuration Entry DN | cn=Schema Reload,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Task plug-in to reload schema files |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Further Information |
4.1.52. Space Insensitive String Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | none |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Space Insensitive String Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Syntax for handling space-insensitive values |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.53. State Change Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | statechange |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=State Change Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables state-change-notification service |
| Type | postoperation |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Further Information |
4.1.54. Syntax Validation Task Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | none |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Syntax Validation Task,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables syntax validation for attribute values |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Further Information |
4.1.55. Telephone Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | tele-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Telephone Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports telephone number syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.56. Teletex Terminal Identifier Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | teletextermid-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Teletex Terminal Identifier Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports international telephone number syntaxes and related matching rules from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.57. Telex Number Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | telex-syntax |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Telex Number Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for the telex number, country code, and answerback code of a telex terminal; from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.58. URI Syntax Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | none |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=URI Syntax,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Supports syntaxes and related matching rules for unique resource identifiers (URIs), including unique resource locators (URLs); from RFC 4517. |
| Type | syntax |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| None | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. If enabled, Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.1.59. USN Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | USN |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=USN,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Sets an update sequence number (USN) on an entry, for every entry in the directory, whenever there is a modification, including adding and deleting entries and modifying attribute values. |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| off | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| Database | Performance-Related Information |
|
For replication, it is recommended that the | Further Information |
4.1.60. Views Plug-in
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Plug-in ID | views |
| DN of Configuration Entry | cn=Views,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Description | Enables the use of views in the Directory Server databases. |
| Type | object |
| Configurable Options | on |
| off | Default Setting |
| on | Configurable Arguments |
| None | Dependencies |
| * Type: Database * Named: State Change Plug-in | Performance-Related Information |
| Do not modify the configuration of this plug-in. Red Hat recommends leaving this plug-in running at all times. | Further Information |
4.2. List of Attributes Common to All Plug-ins
This list provides a brief attribute description, the entry DN, valid range, default value, syntax, and an example for each attribute.
4.2.1. nsslapdPlugin (Object Class)
Each Directory Server plug-in belongs to the nsslapdPlugin object class.
This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.41
Table 4.1. Required Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| objectClass | Gives the object classes assigned to the entry. |
| cn | Gives the common name of the entry. |
| Identifies the plugin library name (without the library suffix). | |
| Identifies an initialization function of the plugin. | |
| Identifies the type of plugin. | |
| Identifies the plugin ID. | |
| Identifies the version of plugin. | |
| Identifies the vendor of plugin. | |
| Identifies the description of the plugin. | |
| Identifies whether or not the plugin is enabled. | |
| Sets the priority for the plug-in in the execution order. |
4.2.2. nsslapd-logAccess
This attribute enables you to log search operations run by the plug-in to the file set in the nsslapd-accesslog parameter in cn=config.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-logAccess: Off |
4.2.3. nsslapd-logAudit
This attribute enables you to log and audit modifications to the database originated from the plug-in.
Successful modification events are logged in the audit log, if the nsslapd-auditlog-logging-enabled parameter is enabled in cn=config. To log failed modification database operations by a plug-in, enable the nsslapd-auditfaillog-logging-enabled attribute in cn=config.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-logAudit: Off |
4.2.4. nsslapd-pluginDescription
This attribute provides a description of the plug-in.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginDescription: acl access check plug-in |
4.2.5. nsslapd-pluginEnabled
This attribute specifies whether the plug-in is enabled. This attribute can be changed over protocol but will only take effect when the server is next restarted.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginEnabled: on |
4.2.6. nsslapd-pluginId
This attribute specifies the plug-in ID.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid plug-in ID |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginId: chaining database |
4.2.7. nsslapd-pluginInitfunc
This attribute specifies the plug-in function to be initiated.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid plug-in function |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginInitfunc: NS7bitAttr_Init |
4.2.8. nsslapd-pluginPath
This attribute specifies the full path to the plug-in.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid path |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginPath: uid-plugin |
4.2.9. nsslapd-pluginPrecedence
This attribute sets the precedence or priority for the execution order of a plug-in. Precedence defines the execution order of plug-ins, which allows more complex environments or interactions since it can enable a plug-in to wait for a completed operation before being executed. This is more important for pre-operation and post-operation plug-ins.
Plug-ins with a value of 1 have the highest priority and are run first; plug-ins with a value of 99 have the lowest priority. The default is 50.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 1 to 99 |
| Default Value | 50 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginPrecedence: 3 |
4.2.10. nsslapd-pluginType
This attribute specifies the plug-in type. See Section 4.3.5, “nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-type” for further information.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid plug-in type |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginType: preoperation |
4.2.11. nsslapd-pluginVendor
This attribute specifies the vendor of the plug-in.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any approved plug-in vendor |
| Default Value | Red Hat, Inc. |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginVendor: Red Hat, Inc. |
4.2.12. nsslapd-pluginVersion
This attribute specifies the plug-in version.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid plug-in version |
| Default Value | Product version number |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginVersion: 11.3 |
4.3. Attributes Allowed by Certain Plug-ins
4.3.1. nsslapd-dynamic-plugins
Directory Server has dynamic plug-ins that can be enabled without restarting the server. The nsslapd-dynamic-plugins attribute specifies whether the server is configured to allow dynamic plug-ins. By default, dynamic plug-ins are disabled.
Directory Server does not support dynamic plug-ins. Use it only for testing and debugging purposes.
Some plug-ins cannot be configured as dynamic, and they require the server to be restarted.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-dynamic-plugins: on |
4.3.2. nsslapd-pluginConfigArea
Some plug-in entries are container entries, and multiple instances of the plug-in are created beneath this container in cn=plugins,cn=config. However, the cn=plugins,cn=config is not replicated, which means that the plug-in configurations beneath those container entries must be configured manually, in some way, on every Directory Server instance.
The nsslapd-pluginConfigArea attribute points to another container entry, in the main database area, which contains the plug-in instance entries. This container entry can be in a replicated database, which allows the plug-in configuration to be replicated.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid DN |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DN |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginConfigArea: cn=managed entries container,ou=containers,dc=example,dc=com |
4.3.3. nsslapd-pluginLoadNow
This attribute specifies whether to load all of the symbols used by a plug-in immediately (true), as well as all symbols references by those symbols, or to load the symbol the first time it is used (false).
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | true | false |
| Default Value | false |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginLoadNow: false |
4.3.4. nsslapd-pluginLoadGlobal
This attribute specifies whether the symbols in dependent libraries are made visible locally (false) or to the executable and to all shared objects (true).
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plug-in name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | true | false |
| Default Value | false |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginLoadGlobal: false |
4.3.5. nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-type
Multi-valued attribute used to ensure that plug-ins are called by the server in the correct order. Takes a value which corresponds to the type number of a plug-in, contained in the attribute nsslapd-pluginType. See Section 4.2.10, “nsslapd-pluginType” for further information. All plug-ins with a type value which matches one of the values in the following valid range will be started by the server prior to this plug-in. The following postoperation Referential Integrity Plug-in example shows that the database plug-in will be started prior to the postoperation Referential Integrity Plug-in.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=referential integrity postoperation,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | database |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-type: database |
4.3.6. nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-named
Multi-valued attribute used to ensure that plug-ins are called by the server in the correct order. Takes a value which corresponds to the cn value of a plug-in. The plug-in with a cn value matching one of the following values will be started by the server prior to this plug-in. If the plug-in does not exist, the server fails to start. The following postoperation Referential Integrity Plug-in example shows that the Views plug-in is started before Roles. If Views is missing, the server is not going to start.
| Plug-in Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=referential integrity postoperation,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Class of Service |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | * nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-named: Views * nsslapd-pluginId: roles |
4.4. Database Plug-in Attributes
The database plug-in is also organized in an information tree, as shown in Figure 4.1, “Database Plug-in”.
Figure 4.1. Database Plug-in

All plug-in technology used by the database instances is stored in the cn=ldbm database plug-in node. This section presents the additional attribute information for each of the nodes in bold in the cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config information tree.
4.4.1. Database Attributes under cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
This section covers global configuration attributes common to all instances are stored in the cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config tree node.
4.4.1.1. nsslapd-backend-implement
The nsslapd-backend-implement parameter defines the database back end Directory Server uses.
Directory Server currently only supports the Berkeley Database (BDB). Therefore, you cannot set this parameter to a different value.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | bdb |
| Default Value | bdb |
| Syntax | Directory String |
| Example | nsslapd-backend-implement: bdb |
4.4.1.2. nsslapd-backend-opt-level
This parameter can trigger experimental code to improve write performance.
Possible values:
-
0: Disables the parameter. -
1: The replication update vector is not written to the database during the transaction -
2: Changes the order of taking the back end lock and starts the transaction -
4: Moves code out of the transaction.
All parameters can be combined. For example 7 enables all optimisation features.
This parameter is experimental. Never change its value unless you are specifically told to do so by the Red Hat support.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-backend-opt-level: 0 |
4.4.1.3. nsslapd-directory
This attribute specifies absolute path to database instance. If the database instance is manually created then this attribute must be included, something which is set by default (and modifiable) in the Directory Server Console. Once the database instance is created, do not modify this path as any changes risk preventing the server from accessing data.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid absolute path to the database instance |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-directory: /var/lib/dirsrv/slapd-instance/db |
4.4.1.4. nsslapd-exclude-from-export
This attribute contains a space-separated list of names of attributes to exclude from an entry when a database is exported. This mainly is used for some configuration and operational attributes which are specific to a server instance.
Do not remove any of the default values for this attribute, since that may affect server performance.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid attribute |
| Default Value | entrydn entryid dncomp parentid numSubordinates entryusn |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-exclude-from-export: entrydn entryid dncomp parentid numSubordinates entryusn |
4.4.1.5. nsslapd-db-transaction-wait
If you enable the nsslapd-db-transaction-wait parameter, Directory Server does not start the transaction and waits until lock resources are available.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-transaction-wait: off |
4.4.1.6. nsslapd-db-private-import-mem
The nsslapd-db-private-import-mem parameter manages whether or not Directory Server uses private memory for allocation of regions and mutexes for a database import.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-private-import-mem: on |
4.4.1.7. nsslapd-db-deadlock-policy
The nsslapd-db-deadlock-policy parameter sets the libdb library-internal deadlock policy.
Only change this parameter if instructed by Red Hat Support.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 0-9 |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-deadlock-policy: 9 |
4.4.1.8. nsslapd-idl-switch
The nsslapd-idl-switch parameter sets the IDL format Directory Server uses. Note that Red Hat no longer supports the old IDL format.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | new | old |
| Default Value | new |
| Syntax | Directory String |
| Example | nsslapd-idl-switch: new |
4.4.1.9. nsslapd-idlistscanlimit
This performance-related attribute, present by default, specifies the number of entry IDs that are searched during a search operation. Attempting to set a value that is not a number or is too big for a 32-bit signed integer returns an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error message, with additional error information explaining the problem. It is advisable to keep the default value to improve search performance.
For further details, see the corresponding sections in the:
This parameter can be changed while the server is running, and the new value will affect subsequent searches.
The corresponding user-level attribute is nsIDListScanLimit.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 100 to the maximum 32-bit integer value (2147483647) entry IDs |
| Default Value | 4000 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-idlistscanlimit: 4000 |
4.4.1.10. nsslapd-lookthroughlimit
This performance-related attribute specifies the maximum number of entries that the Directory Server will check when examining candidate entries in response to a search request. The Directory Manager DN, however, is, by default, unlimited and overrides any other settings specified here. It is worth noting that binder-based resource limits work for this limit, which means that if a value for the operational attribute nsLookThroughLimit is present in the entry as which a user binds, the default limit will be overridden. Attempting to set a value that is not a number or is too big for a 32-bit signed integer returns an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error message with additional error information explaining the problem.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1 to maximum 32-bit integer in entries (where -1 is unlimited) |
| Default Value | 5000 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-lookthroughlimit: 5000 |
4.4.1.11. nsslapd-mode
This attribute specifies the permissions used for newly created index files.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values |
Any four-digit octal number. However, mode |
| Default Value | 600 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-mode: 0600 |
4.4.1.12. nsslapd-pagedidlistscanlimit
This performance-related attribute specifies the number of entry IDs that are searched, specifically, for a search operation using the simple paged results control.
This attribute works the same as the nsslapd-idlistscanlimit attribute, except that it only applies to searches with the simple paged results control.
If this attribute is not present or is set to zero, then the nsslapd-idlistscanlimit is used to paged searches as well as non-paged searches.
The corresponding user-level attribute is nsPagedIDListScanLimit.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1 to maximum 32-bit integer in entries (where -1 is unlimited) |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-pagedidlistscanlimit: 5000 |
4.4.1.13. nsslapd-pagedlookthroughlimit
This performance-related attribute specifies the maximum number of entries that the Directory Server will check when examining candidate entries for a search which uses the simple paged results control.
This attribute works the same as the nsslapd-lookthroughlimit attribute, except that it only applies to searches with the simple paged results control.
If this attribute is not present or is set to zero, then the nsslapd-lookthroughlimit is used to paged searches as well as non-paged searches.
The corresponding user-level attribute is nsPagedLookThroughLimit.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1 to maximum 32-bit integer in entries (where -1 is unlimited) |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-pagedlookthroughlimit: 25000 |
4.4.1.14. nsslapd-rangelookthroughlimit
This performance-related attribute specifies the maximum number of entries that the Directory Server will check when examining candidate entries in response to a range search request.
Range searches use operators to set a bracket to search for and return an entire subset of entries within the directory. For example, this searches for every entry modified at or after midnight on January 1:
(modifyTimestamp>=20200101010101Z)
The nature of a range search is that it must evaluate every single entry within the directory to see if it is within the range given. Essentially, a range search is always an all IDs search.
For most users, the look-through limit kicks in and prevents range searches from turning into an all IDs search. This improves overall performance and speeds up range search results. However, some clients or administrative users like Directory Manager may not have a look-through limit set. In that case, a range search can take several minutes to complete or even continue indefinitely.
The nsslapd-rangelookthroughlimit attribute sets a separate range look-through limit that applies to all users, including Directory Manager.
This allows clients and administrative users to have high look-through limits while still allowing a reasonable limit to be set on potentially performance-impaired range searches.
Unlike other resource limits, this applies to searches by any user, including the Directory Manager, regular users, and other LDAP clients.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1 to maximum 32-bit integer in entries (where -1 is unlimited) |
| Default Value | 5000 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-rangelookthroughlimit: 5000 |
4.4.1.15. nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test
If you enable the nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test parameter, Directory Server bypasses filter checks when it builds candidate lists during a search. If you set the parameter to verify, Directory Server evaluates the filter against the search candidate entries.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off | verify |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | Directory String |
| Example | nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test: on |
4.4.1.16. nsslapd-search-use-vlv-index
The nsslapd-search-use-vlv-index enables and disables virtual list view (VLV) searches.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | Directory String |
| Example | nsslapd-search-use-vlv-index: on |
4.4.1.17. nsslapd-subtree-rename-switch
Every directory entry is stored as a key in an entry index file. The index key maps the current entry DN to its meta entry in the index. This mapping is done either by the RDN of the entry or by the full DN of the entry.
When a subtree entry is allowed to be renamed (meaning, an entry with children entries, effectively renaming the whole subtree), its entries are stored in the entryrdn.db index, which associates parent and child entries by an assigned ID rather than their DN. If subtree rename operations are not allowed, then the entryrdn.db index is disabled and the entrydn.db index is used, which simply uses full DNs, with the implicit parent-child relationships.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | off | on |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-subtree-rename-switch: on |
4.4.2. Database Attributes under cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
This section covers global configuration attributes common to all instances are stored in the cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config tree node.
4.4.2.1. nsslapd-cache-autosize
This performance tuning-related attribute sets the percentage of free memory that is used in total for the database and entry cache. For example, if the value is set to 10, 10% of the system’s free RAM is used for both caches. If this value is set to a value greater than 0, auto-sizing is enabled for the database and entry cache.
For optimized performance, Red Hat recommends not to disable auto-sizing. However, in certain situations in can be necessary to disable auto-sizing. In this case, set the nsslapd-cache-autosize attribute to 0 and manually set:
-
the database cache in the
nsslapd-dbcachesizeattribute. -
the entry cache in the
nsslapd-cachememsizeattribute.
For further details about auto-sizing, see the corresponding section in the Red Hat Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide.
If the nsslapd-cache-autosize and nsslapd-cache-autosize-split attribute are both set to high values, such as 100, Directory Server fails to start. To fix the problem, set both parameters to more reasonable values. For example:
nsslapd-cache-autosize: 10 nsslapd-cache-autosize-split: 40
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 100. If 0 is set, the default value is used instead. |
| Default Value | 10 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-cache-autosize: 10 |
4.4.2.2. nsslapd-cache-autosize-split
This performance tuning-related attribute sets the percentage of RAM that is used for the database cache. The remaining percentage is used for the entry cache. For example, if the value is set to 40, the database cache uses 40%, and the entry cache the remaining 60% of the free RAM reserved in the nsslapd-cache-autosize attribute.
For further details about auto-sizing, see the corresponding section in the Red Hat Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide.
If the nsslapd-cache-autosize and nsslapd-cache-autosize-split attribute are both set to high values, such as 100, Directory Server fails to start. To fix the problem, set both parameters to more reasonable values. For example:
nsslapd-cache-autosize: 10 nsslapd-cache-autosize-split: 40
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 99. If 0 is set, the default value is used instead. |
| Default Value | 40 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-cache-autosize-split: 40 |
4.4.2.3. nsslapd-db-checkpoint-interval
This sets the amount of time in seconds after which the Directory Server sends a checkpoint entry to the database transaction log. The database transaction log contains a sequential listing of all recent database operations and is used for database recovery only. A checkpoint entry indicates which database operations have been physically written to the directory database. The checkpoint entries are used to determine where in the database transaction log to begin recovery after a system failure. The nsslapd-db-checkpoint-interval attribute is absent from dse.ldif. To change the checkpoint interval, add the attribute to dse.ldif. This attribute can be dynamically modified using ldapmodify. For further information on modifying this attribute, see the "Tuning Directory Server Performance" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
This attribute is provided only for system modification/diagnostics and should be changed only with the guidance of Red Hat Technical Support or Red Hat Consulting. Inconsistent settings of this attribute and other configuration attributes may cause the Directory Server to be unstable.
For more information on database transaction logging, see the "Monitoring Server and Database Activity" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 10 to 300 seconds |
| Default Value | 60 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-checkpoint-interval: 120 |
4.4.2.4. nsslapd-db-circular-logging
This attribute specifies circular logging for the transaction log files. If this attribute is switched off, old transaction log files are not removed and are kept renamed as old log transaction files. Turning circular logging off can severely degrade server performance and, as such, should only be modified with the guidance of Red Hat Technical Support or Red Hat Consulting.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-circular-logging: on |
4.4.2.5. nsslapd-db-compactdb-interval
The nsslapd-db-compactdb-interval attribute defines the interval in seconds when Directory Server compacts the databases and replication changelogs. The compact operation returns the unused pages to the file system and the database file size shrinks. Note that compacting the database is resource-intensive and should not be done too often.
You do not have to restart the server for this setting to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 0 (no compaction) to 2147483647 second |
| Default Value | 2592000 (30 days) |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-compactdb-interval: 2592000 |
4.4.2.6. nsslapd-db-compactdb-time
The nsslapd-db-compactdb-time attribute sets the time of the day when Directory Server compacts all databases and their replication changelogs. The compaction task runs after the compaction interval (nsslapd-db-compactdb-interval) has been exceeded.
You do not have to restart the server for this setting to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | HH:MM. Time is set in 24-hour format |
| Default Value | 23:59 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-compactdb-time: 23:59 |
4.4.2.7. nsslapd-db-debug
This attribute specifies whether additional error information is to be reported to {Directory Server}. To report error information, set the parameter to on. This parameter is meant for troubleshooting; enabling the parameter may slow down the Directory Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-debug: off |
4.4.2.8. nsslapd-db-durable-transactions
This attribute sets whether database transaction log entries are immediately written to the disk. The database transaction log contains a sequential listing of all recent database operations and is used for database recovery only. With durable transactions enabled, every directory change will always be physically recorded in the log file and, therefore, able to be recovered in the event of a system failure. However, the durable transactions feature may also slow the performance of the Directory Server. When durable transactions is disabled, all transactions are logically written to the database transaction log but may not be physically written to disk immediately. If there were a system failure before a directory change was physically written to disk, that change would not be recoverable. The nsslapd-db-durable-transactions attribute is absent from dse.ldif. To disable durable transactions, add the attribute to dse.ldif.
This attribute is provided only for system modification/diagnostics and should be changed only with the guidance of Red Hat Technical Support or Red Hat Consulting. Inconsistent settings of this attribute and other configuration attributes may cause the Directory Server to be unstable.
For more information on database transaction logging, see the "Monitoring Server and Database Activity" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-durable-transactions: on |
4.4.2.9. nsslapd-db-home-directory
To move the database to another physical location for performance reasons, use this parameter to specify the home directory.
This situation will occur only for certain combinations of the database cache size, the size of physical memory, and kernel tuning attributes. In particular, this situation should not occur if the database cache size is less than 100 megabytes.
- The disk is heavily used (more than 1 megabyte per second of data transfer).
- There is a long service time (more than 100ms).
- There is mostly write activity.
If these are all true, use the nsslapd-db-home-directory attribute to specify a subdirectory of a tempfs type filesystem.
The directory referenced by the nsslapd-db-home-directory attribute must be a subdirectory of a filesystem of type tempfs (such as /tmp). However, Directory Server does not create the subdirectory referenced by this attribute. This directory must be created either manually or by using a script. Failure to create the directory referenced by the nsslapd-db-home-directory attribute will result in Directory Server being unable to start.
Also, if there are multiple Directory Servers on the same machine, their nsslapd-db-home-directory attributes must be configured with different directories. Failure to do so will result in the databases for both directories becoming corrupted.
The use of this attribute causes internal Directory Server database files to be moved to the directory referenced by the attribute. It is possible, but unlikely, that the server will no longer start after the files have been moved because not enough memory can be allocated. This is a symptom of an overly large database cache size being configured for the server. If this happens, reduce the size of the database cache size to a value where the server will start again.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values |
Any valid directory name in a tempfs filesystem, such as |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-home-directory: /tmp/slapd-phonebook |
4.4.2.10. nsslapd-db-idl-divisor
This attribute specifies the index block size in terms of the number of blocks per database page. The block size is calculated by dividing the database page size by the value of this attribute. A value of 1 makes the block size exactly equal to the page size. The default value of 0 sets the block size to the page size minus an estimated allowance for internal database overhead. For the majority of installations, the default value should not be changed unless there are specific tuning needs.
Before modifying the value of this attribute, export all databases using the db2ldif script. Once the modification has been made, reload the databases using the ldif2db script.
This parameter should only be used by very advanced users.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 8 |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-idl-divisor: 2 |
4.4.2.11. nsslapd-db-locks
Lock mechanisms in Directory Server control how many copies of Directory Server processes can run at the same time. The nsslapd-db-locks parameter sets the maximum number of locks.
Only set this parameter to a higher value if Directory Server runs out of locks and logs libdb: Lock table is out of available locks error messages. If you set a higher value without a need, this increases the size of the /var/lib/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/db__db.* files without any benefit. For more information about monitoring the logs and determining a realistic value, see the corresponding section in the Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide.
The service must be restarted for changes to this attribute to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 - 2147483647 |
| Default Value | 10000 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-locks: 10000 |
4.4.2.12. nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-enable
Running out of database locks can lead to data corruption. With the nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-enable parameter, you can enable or disable database lock monitoring. If the parameter is enabled, which is the default, Directory Server terminates all searches if the number of active database locks is higher than the percentage threshold configured in nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-threshold. If an issue occurs, the administrator can increase the number of database locks in the nsslapd-db-locks parameter.
Restart the service for changes to this attribute to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-enable: on |
4.4.2.13. nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-pause
If monitoring of database locks is enabled in the nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-enable parameter, nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-pause defines the interval in milliseconds that the monitoring thread sleeps between the checks.
If you set this parameter to a too high value, the server can run out of database locks before the monitoring check happens. However, setting a too low value can slow down the server.
You do not have to restart the server for this setting to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 0 - 2147483647 (value in milliseconds) |
| Default Value | 500 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-pause: 500 |
4.4.2.14. nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-threshold
If monitoring of database locks is enabled in the nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-enable parameter, nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-threshold sets the maximum percentage of used database locks before Directory Server terminates searches to avoid further lock exhaustion.
Restart the service for changes to this attribute to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 70 - 95 |
| Default Value | 90 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-locks-monitoring-threshold: 90 |
4.4.2.15. nsslapd-db-logbuf-size
This attribute specifies the log information buffer size. Log information is stored in memory until the buffer fills up or the transaction commit forces the buffer to be written to disk. Larger buffer sizes can significantly increase throughput in the presence of long running transactions, highly concurrent applications, or transactions producing large amounts of data. The log information buffer size is the transaction log size divided by four.
The nsslapd-db-logbuf-size attribute is only valid if the nsslapd-db-durable-transactions attribute is set to on.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 32K to maximum 32-bit integer (limited to the amount of memory available on the machine) |
| Default Value | 32K |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-logbuf-size: 32K |
4.4.2.16. nsslapd-db-logdirectory
This attribute specifies the path to the directory that contains the database transaction log. The database transaction log contains a sequential listing of all recent database operations. Directory Server uses this information to recover the database after an instance shut down unexpectedly.
By default, the database transaction log is stored in the same directory as the directory database. To update this parameter, you must manually update the /etc/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/dse.ldif file. For details, see the Changing the Transaction Log Directory section in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid path |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-logdirectory: /var/lib/dirsrv/slapd-instance_name/db/ |
4.4.2.17. nsslapd-db-logfile-size
This attribute specifies the maximum size of a single file in the log in bytes. By default, or if the value is set to 0, a maximum size of 10 megabytes is used. The maximum size is an unsigned 4-byte value.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to unsigned 4-byte integer |
| Default Value | 10MB |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-logfile-size: 10 MB |
4.4.2.18. nsslapd-db-page-size
This attribute specifies the size of the pages used to hold items in the database in bytes. The minimum size is 512 bytes, and the maximum size is 64 kilobytes. If the page size is not explicitly set, Directory Server defaults to a page size of 8 kilobytes. Changing this default value can have a significant performance impact. If the page size is too small, it results in extensive page splitting and copying, whereas if the page size is too large it can waste disk space.
Before modifying the value of this attribute, export all databases using the db2ldif script. Once the modification has been made, reload the databases using the ldif2db script.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 512 bytes to 64 kilobytes |
| Default Value | 8KB |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-page-size: 8KB |
4.4.2.19. nsslapd-db-spin-count
This attribute specifies the number of times that test-and-set mutexes should spin without blocking.
Never touch this value unless you are very familiar with the inner workings of Berkeley DB or are specifically told to do so by Red Hat support.
The default value of 0 causes BDB to calculate the actual value by multiplying the number of available CPU cores (as reported by the nproc utility or the sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN) call) by 50. For example, with a processor with 8 logical cores, leaving this attribute set to 0 is equivalent to setting it to 400. It is not possible to turn spinning off entirely - if you want to minimize the amount of times test-and-set mutexes will spin without blocking, set this attribute to 1.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 2147483647 (2^31-1) |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-spin-count: 0 |
4.4.2.20. nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-max-wait
If Section 4.4.2.22, “nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-val” is set, the flushing of transactions is done by a separate thread when the set batch value is reached. However if there are only a few updates, this process might take too long. This parameter controls when transactions should be flushed latest, independently of the batch count. The values is defined in milliseconds.
This parameter is experimental. Never change its value unless you are specifically told to do so by the Red Hat support.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 - 2147483647 (value in milliseconds) |
| Default Value | 50 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-max-wait: 50 |
4.4.2.21. nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-min-wait
If Section 4.4.2.22, “nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-val” is set, the flushing of transactions is done by a separate thread when the set batch value is reached. However if there are only a few updates, this process might take too long. This parameter controls when transactions should be flushed earliest, independently of the batch count. The values is defined in milliseconds.
This parameter is experimental. Never change its value unless you are specifically told to do so by the Red Hat support.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 - 2147483647 (value in milliseconds) |
| Default Value | 50 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-min-wait: 50 |
4.4.2.22. nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-val
This attribute specifies how many transactions will be batched before being committed. This attribute can improve update performance when full transaction durability is not required. This attribute can be dynamically modified using ldapmodify. For further information on modifying this attribute, see the "Tuning Directory Server Performance" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
Setting this value will reduce data consistency and may lead to loss of data. This is because if there is a power outage before the server can flush the batched transactions, those transactions in the batch will be lost.
Do not set this value unless specifically requested to do so by Red Hat support.
If this attribute is not defined or is set to a value of 0, transaction batching will be turned off, and it will be impossible to make remote modifications to this attribute using LDAP. However, setting this attribute to a value greater than 0 causes the server to delay committing transactions until the number of queued transactions is equal to the attribute value. A value greater than 0 also allows modifications to this attribute remotely using LDAP. A value of 1 for this attribute allows modifications to the attribute setting remotely using LDAP, but results in no batching behavior. A value of 1 at server startup is therefore useful for maintaining normal durability while also allowing transaction batching to be turned on and off remotely when required. Remember that the value for this attribute may require modifying the nsslapd-db-logbuf-size attribute to ensure sufficient log buffer size for accommodating the batched transactions.
The nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-val attribute is only valid if the nsslapd-db-durable-transaction attribute is set to on.
For more information on database transaction logging, see the "Monitoring Server and Database Activity" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 30 |
| Default Value | 0 (or turned off) |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-transaction-batch-val: 5 |
4.4.2.23. nsslapd-db-trickle-percentage
This attribute sets that at least the specified percentage of pages in the shared-memory pool are clean by writing dirty pages to their backing files. This is to ensure that a page is always available for reading in new information without having to wait for a write.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 100 |
| Default Value | 40 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-db-trickle-percentage: 40 |
4.4.2.24. nsslapd-db-verbose
This attribute specifies whether to record additional informational and debugging messages when searching the log for checkpoints, doing deadlock detection, and performing recovery. This parameter is meant for troubleshooting, and enabling the parameter may slow down the Directory Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-db-verbose: off |
4.4.2.25. nsslapd-import-cache-autosize
This performance tuning-related attribute automatically sets the size of the import cache (importCache) to be used during the command-line-based import process of LDIF files to the database (the ldif2db operation).
In Directory Server, the import operation can be run as a server task or exclusively on the command-line. In the task mode, the import operation runs as a general Directory Server operation. The nsslapd-import-cache-autosize attribute enables the import cache to be set automatically to a predetermined size when the import operation is run on the command-line. The attribute can also be used by Directory Server during the task mode import for allocating a specified percentage of free memory for import cache.
By default, the nsslapd-import-cache-autosize attribute is enabled and is set to a value of -1. This value autosizes the import cache for the ldif2db operation only, automatically allocating fifty percent (50%) of the free physical memory for the import cache. The percentage value (50%) is hard-coded and cannot be changed.
Setting the attribute value to 50 (nsslapd-import-cache-autosize: 50) has the same effect on performance during an ldif2db operation. However, such a setting will have the same effect on performance when the import operation is run as a Directory Server task. The -1 value autosizes the import cache just for the ldif2db operation and not for any, including import, general Directory Server tasks.
The purpose of a -1 setting is to enable the ldif2db operation to benefit from free physical memory but, at the same time, not compete for valuable memory with the entry cache, which is used for general operations of the Directory Server.
Setting the nsslapd-import-cache-autosize attribute value to 0 turns off the import cache autosizing feature - that is, no autosizing occurs during either mode of the import operation. Instead, Directory Server uses the nsslapd-import-cachesize attribute for import cache size, with a default value of 20000000.
There are three caches in the context of Directory Server: database cache, entry cache, and import cache. The import cache is only used during the import operation. The nsslapd-cache-autosize attribute, which is used for autosizing the entry cache and database cache, is used during the Directory Server operations only and not during the ldif2db command-line operation; the attribute value is the percentage of free physical memory to be allocated for the entry cache and database cache.
If both the autosizing attributes, nsslapd-cache-autosize and nsslapd-import-cache-autosize, are enabled, ensure that their sum is less than 100.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1, 0 (turns import cache autosizing off) to 100 |
| Default Value | -1 (turns import cache autosizing on for ldif2db only and allocates 50% of the free physical memory to import cache) |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-import-cache-autosize: -1 |
4.4.2.26. nsslapd-dbcachesize
This performance tuning-related attribute specifies the database index cache size, in bytes. This is one of the most important values for controlling how much physical RAM the directory server uses.
This is not the entry cache. This is the amount of memory the Berkeley database back end will use to cache the indexes (the .db files) and other files. This value is passed to the Berkeley DB API function set_cachesize. If automatic cache resizing is activated, this attribute is overridden when the server replaces these values with its own guessed values at a later stage of the server startup.
For more technical information on this attribute, see the cache size section of the Berkeley DB reference guide at https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E17076_04/html/programmer_reference/general_am_conf.html#am_conf_cachesize.
Attempting to set a value that is not a number or is too big for a 32-bit signed integer returns an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error message with additional error information explaining the problem.
Do not set the database cache size manually. Red Hat recommends to use the database cache auto-sizing feature for optimized performance. For further see the corresponding section in the Red Hat Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=bdb,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 500 kilobytes to 4 gigabytes for 32-bit platforms and 500 kilobytes to 2^64-1 for 64-bit platforms |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-dbcachesize: 10000000 |
4.4.2.27. nsslapd-dbncache
This attribute can split the LDBM cache into equally sized separate pieces of memory. It is possible to specify caches that are large enough so that they cannot be allocated contiguously on some architectures; for example, some systems limit the amount of memory that may be allocated contiguously by a process. If nsslapd-dbncache is 0 or 1, the cache will be allocated contiguously in memory. If it is greater than 1, the cache will be broken up into ncache, equally sized separate pieces of memory.
To configure a dbcache size larger than 4 gigabytes, add the nsslapd-dbncache attribute to cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config between the nsslapd-dbcachesize and nsslapd-db-logdirectory attribute lines.
Set this value to an integer that is one-quarter (1/4) the amount of memory in gigabytes. For example, for a 12 gigabyte system, set the nsslapd-dbncache value to 3; for an 8 gigabyte system, set it to 2.
This attribute is provided only for system modification/diagnostics and should be changed only with the guidance of Red Hat technical support or Red Hat professional services. Inconsistent settings of this attribute and other configuration attributes may cause the Directory Server to be unstable.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 1 to 4 |
| Default Value | 1 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-dbncache: 1 |
4.4.2.28. nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test
If you enable the nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test parameter, Directory Server bypasses filter checks when it builds candidate lists during a search. If you set the parameter to verify, Directory Server evaluates the filter against the search candidate entries.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off | verify |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | Directory String |
| Example | nsslapd-search-bypass-filter-test: on |
4.4.3. Database Attributes under cn=monitor,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
Global read-only attributes containing database statistics for monitoring activity on the databases are stored in the cn=monitor,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config tree node. For more information on these entries, see the "Monitoring Server and Database Activity" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
dbcachehits
This attribute shows the requested pages found in the database.
dbcachetries
This attribute shows the total cache lookups.
dbcachehitratio
This attribute shows the percentage of requested pages found in the database cache (hits/tries).
dbcachepagein
This attribute shows the pages read into the database cache.
dbcachepageout
This attribute shows the pages written from the database cache to the backing file.
dbcacheroevict
This attribute shows the clean pages forced from the cache.
dbcacherwevict
This attribute shows the dirty pages forced from the cache.
normalizedDNcachetries
Total number of cache lookups since the instance was started.
normalizedDNcachehits
Normalized DNs found within the cache.
normalizedDNcachemisses
Normalized DNs not found within the cache.
normalizedDNcachehitratio
Percentage of the normalized DNs found in the cache.
currentNormalizedDNcachesize
Current size of the normalized DN cache in bytes.
maxNormalizedDNcachesize
Current value of the nsslapd-ndn-cache-max-size parameter. For details how to update this setting, see Section 3.1.1.129, “nsslapd-ndn-cache-max-size”.
currentNormalizedDNcachecount
Number of normalized cached DNs.
4.4.4. Database Attributes under cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
The cn=database_name subtree contains all the configuration data for the user-defined database.
The cn=userRoot subtree is called userRoot by default. However, this is not hard-coded and, given the fact that there are going to be multiple database instances, this name is changed and defined by the user as and when new databases are added. The cn=userRoot database referenced can be any user database.
The following attributes are common to databases, such as cn=userRoot.
4.4.4.1. nsslapd-cachesize
This attribute has been deprecated. To resize the entry cache, use nsslapd-cachememsize.
This performance tuning-related attribute specifies the cache size in terms of the number of entries it can hold. However, this attribute is deprecated in favor of the nsslapd-cachememsize attribute, which sets an absolute allocation of RAM for the entry cache size, as described in Section 4.4.4.2, “nsslapd-cachememsize”.
Attempting to set a value that is not a number or is too big for a 32-bit signed integer (on 32-bit systems) returns an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error message with additional error information explaining the problem.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
The performance counter for this setting goes to the highest 64-bit integer, even on 32-bit systems, but the setting itself is limited on 32-bit systems to the highest 32-bit integer because of how the system addresses memory.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to 232-1 on 32-bit systems or 263-1 on 64-bit systems or -1, which means limitless |
| Default Value | -1 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-cachesize: -1 |
4.4.4.2. nsslapd-cachememsize
This performance tuning-related attribute specifies the size, in bytes, for the available memory space for the entry cache. The simplest method is limiting cache size in terms of memory occupied. Activating automatic cache resizing overrides this attribute, replacing these values with its own guessed values at a later stage of the server startup.
Attempting to set a value that is not a number or is too big for a 32-bit signed integer (on 32-bit systems) returns an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error message with additional error information explaining the problem.
The performance counter for this setting goes to the highest 64-bit integer, even on 32-bit systems, but the setting itself is limited on 32-bit systems to the highest 32-bit integer because of how the system addresses memory.
Do not set the database cache size manually. Red Hat recommends to use the entry cache auto-sizing feature for optimized performance. For further see the corresponding section in the Red Hat Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 500 kilobytes to 264-1 on 64-bit systems |
| Default Value | 209715200 (200 MiB) |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-cachememsize: 209715200 |
4.4.4.3. nsslapd-directory
This attribute specifies the path to the database instance. If it is a relative path, it starts from the path specified by nsslapd-directory in the global database entry cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config. The database instance directory is named after the instance name and located in the global database directory, by default. After the database instance has been created, do not modify this path, because any changes risk preventing the server from accessing data.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid path to the database instance |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-directory: /var/lib/dirsrv/slapd-instance/db/userRoot |
4.4.4.4. nsslapd-dncachememsize
This performance tuning-related attribute specifies the size, in bytes, for the available memory space for the DN cache. The DN cache is similar to the entry cache for a database, only its table stores only the entry ID and the entry DN. This allows faster lookups for rename and moddn operations.
The simplest method is limiting cache size in terms of memory occupied.
Attempting to set a value that is not a number or is too big for a 32-bit signed integer (on 32-bit systems) returns an LDAP_UNWILLING_TO_PERFORM error message with additional error information explaining the problem.
The performance counter for this setting goes to the highest 64-bit integer, even on 32-bit systems, but the setting itself is limited on 32-bit systems to the highest 32-bit integer because of how the system addresses memory.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 500 kilobytes to 232-1 on 32-bit systems and to 264-1 on 64-bit systems |
| Default Value | 10,485,760 (10 megabytes) |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsslapd-dncachememsize: 10485760 |
4.4.4.5. nsslapd-readonly
This attribute specifies read-only mode for a single back-end instance. If this attribute has a value of off, then users have all read, write, and execute permissions allowed by their access permissions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-readonly: off |
4.4.4.6. nsslapd-require-index
When switched to on, this attribute allows one to refuse unindexed searches. This performance-related attribute avoids saturating the server with erroneous searches.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-require-index: off |
4.4.4.7. nsslapd-require-internalop-index
When a plug-in modifies data, it has a write lock on the database. On large databases, if a plug-in then executes an unindexed search, the plug-in can use all database locks and corrupt the database or the server becomes unresponsive. To avoid this problem, you can reject internal unindexed searches by enabling the nsslapd-require-internalop-index parameter.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-require-internalop-index: off |
4.4.4.8. nsslapd-suffix
This attribute specifies the suffix of the database link. This is a single-valued attribute because each database instance can have only one suffix. Previously, it was possible to have more than one suffix on a single database instance, but this is no longer the case. As a result, this attribute is single-valued to enforce the fact that each database instance can only have one suffix entry. Any changes made to this attribute after the entry has been created take effect only after the server containing the database link is restarted.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid DN |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-suffix: o=Example |
4.4.4.9. vlvBase
This attribute sets the base DN for which the browsing or virtual list view (VLV) index is created.
For more information on VLV indexes, see the indexing chapter in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=index_name,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid DN |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | vlvBase: ou=People,dc=example,dc=com |
4.4.4.10. vlvEnabled
The vlvEnabled attribute provides status information about a specific VLV index, and Directory Server sets this attribute at run time. Although vlvEnabled is shown in the configuration, you cannot modify this attribute.
For more information on VLV indexes, see the indexing chapter in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=index_name,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | 0 (disabled) | 1 (enabled) |
| Default Value | 1 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | vlvEnbled: 0 |
4.4.4.11. vlvFilter
The browsing or virtual list view (VLV) index is created by running a search according to a filter and including entries which match that filter in the index. The filter is specified in the vlvFilter attribute.
For more information on VLV indexes, see the indexing chapter in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=index_name,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid LDAP filter |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | vlvFilter: ( |
4.4.4.12. vlvIndex (Object Class)
A browsing index or virtual list view (VLV) index dynamically generates an abbreviated index of entry headers that makes it much faster to visually browse large indexes. A VLV index definition has two parts: one which defines the index and one which defines the search used to identify entries to add to the index. The vlvIndex object class defines the index entry.
This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.42
Table 4.2. Required Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| objectClass | Defines the object classes for the entry. |
| cn | Gives the common name of the entry. |
| Identifies the attribute list that the browsing index (virtual list view index) is sorted on. |
Table 4.3. Allowed Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| Stores the availability of the browsing index. | |
| Contains the count the browsing index is used. |
4.4.4.13. vlvScope
This attribute sets the scope of the search to run for entries in the browsing or virtual list view (VLV) index.
For more information on VLV indexes, see the indexing chapter in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=index_name,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | * 1 (one-level or children search) * 2 (subtree search) |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | vlvScope: 2 |
4.4.4.14. vlvSearch (Object Class)
A browsing index or virtual list view (VLV) index dynamically generates an abbreviated index of entry headers that makes it much faster to visually browse large indexes. A VLV index definition has two parts: one which defines the index and one which defines the search used to identify entries to add to the index. The vlvSearch object class defines the search filter entry.
This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.38
Table 4.4. Required Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| objectClass | Defines the object classes for the entry. |
| Identifies base DN the browsing index is created. | |
| Identifies the scope to define the browsing index. | |
| Identifies the filter string to define the browsing index. |
Table 4.5. Allowed Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| multiLineDescription | Gives a text description of the entry. |
4.4.4.15. vlvSort
This attribute sets the sort order for returned entries in the browsing or virtual list view (VLV) index.
The entry for this attribute is a vlvIndex entry beneath the vlvSearch entry.
For more information on VLV indexes, see the indexing chapter in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=index_name,cn=index_name,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any Directory Server attributes, in a space-separated list |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | vlvSort: cn givenName o ou sn |
4.4.4.16. vlvUses
The vlvUses attribute contains the count the browsing index uses, and Directory Server sets this attribute at run time. Although vlvUses is shown in the configuration, you cannot modify this attribute.
For more information on VLV indexes, see the indexing chapter in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=index_name,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | N/A |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | vlvUses: 800 |
4.4.5. Database Attributes under cn=database,cn=monitor,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
The attributes in this tree node entry are all read-only, database performance counters. All of the values for these attributes are 32-bit integers, except for entrycachehits and entrycachetries.
If the nsslapd-counters attribute in cn=config is set to on, then some of the counters kept by the Directory Server instance increment using 64-bit integers, even on 32-bit machines or with a 32-bit version of Directory Server. For the database monitoring, the entrycachehits and entrycachetries counters use 64-bit integers.
The nsslapd-counters attribute enables 64-bit support for these specific database and server counters. The counters which use 64-bit integers are not configurable; the 64-bit integers are either enabled for all the allowed counters or disabled for all allowed counters.
nsslapd-db-abort-rate
This attribute shows the number of transactions that have been aborted.
nsslapd-db-active-txns
This attribute shows the number of transactions that are currently active.
nsslapd-db-cache-hit
This attribute shows the requested pages found in the cache.
nsslapd-db-cache-try
This attribute shows the total cache lookups.
nsslapd-db-cache-region-wait-rate
This attribute shows the number of times that a thread of control was forced to wait before obtaining the region lock.
nsslapd-db-cache-size-bytes
This attribute shows the total cache size in bytes.
nsslapd-db-clean-pages
This attribute shows the clean pages currently in the cache.
nsslapd-db-commit-rate
This attribute shows the number of transactions that have been committed.
nsslapd-db-deadlock-rate
This attribute shows the number of deadlocks detected.
nsslapd-db-dirty-pages
This attribute shows the dirty pages currently in the cache.
nsslapd-db-hash-buckets
This attribute shows the number of hash buckets in buffer hash table.
nsslapd-db-hash-elements-examine-rate
This attribute shows the total number of hash elements traversed during hash table lookups.
nsslapd-db-hash-search-rate
This attribute shows the total number of buffer hash table lookups.
nsslapd-db-lock-conflicts
This attribute shows the total number of locks not immediately available due to conflicts.
nsslapd-db-lock-region-wait-rate
This attribute shows the number of times that a thread of control was forced to wait before obtaining the region lock.
nsslapd-db-lock-request-rate
This attribute shows the total number of locks requested.
nsslapd-db-lockers
This attribute shows the number of current lockers.
nsslapd-db-log-bytes-since-checkpoint
This attribute shows the number of bytes written to this log since the last checkpoint.
nsslapd-db-log-region-wait-rate
This attribute shows the number of times that a thread of control was forced to wait before obtaining the region lock.
nsslapd-db-log-write-rate
This attribute shows the number of megabytes and bytes written to this log.
nsslapd-db-longest-chain-length
This attribute shows the longest chain ever encountered in buffer hash table lookups.
nsslapd-db-page-create-rate
This attribute shows the pages created in the cache.
nsslapd-db-page-read-rate
This attribute shows the pages read into the cache.
nsslapd-db-page-ro-evict-rate
This attribute shows the clean pages forced from the cache.
nsslapd-db-page-rw-evict-rate
This attribute shows the dirty pages forced from the cache.
nsslapd-db-page-trickle-rate
This attribute shows the dirty pages written using the memp_trickle interface.
nsslapd-db-page-write-rate
This attribute shows the pages read into the cache.
nsslapd-db-pages-in-use
This attribute shows all pages, clean or dirty, currently in use.
nsslapd-db-txn-region-wait-rate
This attribute shows the number of times that a thread of control was force to wait before obtaining the region lock.
currentdncachecount
This attribute shows the number of DNs currently present in the DN cache.
currentdncachesize
This attribute shows the total size, in bytes, of DNs currently present in the DN cache.
maxdncachesize
This attribute shows the maximum size, in bytes, of DNs that can be maintained in the database DN cache.
4.4.6. Database Attributes under cn=monitor,cn=userRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
The attributes in this tree node entry are all read-only, database performance counters.
If the nsslapd-counters attribute in cn=config is set to on, then some of the counters kept by the Directory Server instance increment using 64-bit integers, even on 32-bit machines or with a 32-bit version of Directory Server. For database monitoring, the entrycachehits and entrycachetries counters use 64-bit integers.
The nsslapd-counters attribute enables 64-bit support for these specific database and server counters. The counters which use 64-bit integers are not configurable; the 64-bit integers are either enabled for all the allowed counters or disabled for all allowed counters.
dbfilename-number
This attribute gives the name of the file and provides a sequential integer identifier (starting at 0) for the file. All associated statistics for the file are given this same numerical identifier.
dbfilecachehit-number
This attribute gives the number of times that a search requiring data from this file was performed and that the data were successfully obtained from the cache. The number in this attributes name corresponds to the one in dbfilename.
dbfilecachemiss-number
This attribute gives the number of times that a search requiring data from this file was performed and that the data could not be obtained from the cache. The number in this attributes name corresponds to the one in dbfilename.
dbfilepagein-number
This attribute gives the number of pages brought to the cache from this file. The number in this attributes name corresponds to the one in dbfilename.
dbfilepageout-number
This attribute gives the number of pages for this file written from cache to disk. The number in this attributes name corresponds to the one in dbfilename.
currentDNcachecount
Number of cached DNs.
currentDNcachesize
Current size of the DN cache in bytes.
DNcachehitratio
Percentage of the DNs found in the cache.
DNcachehits
DNs found within the cache.
DNcachemisses
DNs not found within the cache.
DNcachetries
Total number of cache lookups since the instance was started.
maxDNcachesize
Current value of the nsslapd-ndn-cache-max-size parameter. For details how to update this setting, see Section 3.1.1.129, “nsslapd-ndn-cache-max-size”.
4.4.7. Database Attributes under cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
The set of default indexes is stored here. Default indexes are configured per back end in order to optimize Directory Server functionality for the majority of setup scenarios. All indexes, except system-essential ones, can be removed, but care should be taken so as not to cause unnecessary disruptions. For further information on indexes, see the "Managing Indexes" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
4.4.7.1. cn
This attribute provides the name of the attribute to index.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid index cn |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | cn: aci |
4.4.7.2. nsIndex
This object class defines an index in the back end database. This object is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.44
Table 4.6. Required Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| objectClass | Defines the object classes for the entry. |
| cn | Gives the common name of the entry. |
| Identify whether or not the index is a system defined index. |
Table 4.7. Allowed Attributes
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| description | Gives a text description of the entry. |
| Identifies the index type. | |
| Identifies the matching rule. |
4.4.7.3. nsIndexType
This optional, multi-valued attribute specifies the type of index for Directory Server operations and takes the values of the attributes to be indexed. Each required index type has to be entered on a separate line.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | * pres = presence index * eq = equality index * approx = approximate index * sub = substring index * matching rule = international index * index browse = browsing index |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsIndexType: eq |
4.4.7.4. nsMatchingRule
This optional, multi-valued attribute specifies the ordering matching rule name or OID used to match values and to generate index keys for the attribute. This is most commonly used to ensure that equality and range searches work correctly for languages other than English (7-bit ASCII).
This is also used to allow range searches to work correctly for integer syntax attributes that do not specify an ordering matching rule in their schema definition. uidNumber and gidNumber are two commonly used attributes that fall into this category.
For example, for a uidNumber that uses integer syntax, the rule attribute could be nsMatchingRule: integerOrderingMatch.
Any change to this attribute will not take effect until the change is saved and the index is rebuilt using db2index, which is described in more detail in the "Managing Indexes" chapter of the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide).
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid collation order object identifier (OID) |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsMatchingRule: 2.16.840.1.113730.3.3.2.3.1 (For Bulgarian) |
4.4.7.5. nsSystemIndex
This mandatory attribute specifies whether the index is a system index, an index which is vital for Directory Server operations. If this attribute has a value of true, then it is system-essential. System indexes should not be removed, as this will seriously disrupt server functionality.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | true | false |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nssystemindex: true |
4.4.8. Database Attributes under cn=index,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
In addition to the set of default indexes that are stored under cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config, custom indexes can be created for user-defined back end instances; these are stored under cn=index,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config. Each indexed attribute represents a subentry under the cn=config information tree nodes, as shown in the following diagram:
Figure 4.2. Indexed Attribute Representing a Subentry
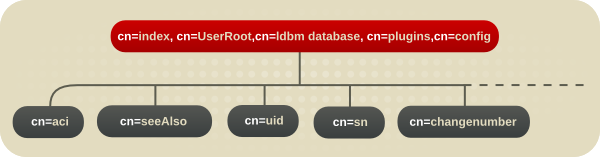
For example, the index file for the aci attribute under o=UserRoot appears in the Directory Server as follows:
dn:cn=aci,cn=index,cn=UserRoot,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config objectclass:top objectclass:nsIndex cn:aci nsSystemIndex:true nsIndexType:pres
These entries share all of the indexing attributes listed for the default indexes in Section 4.4.7, “Database Attributes under cn=default indexes,cn=config,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config”. For further information about indexes, see the "Managing Indexes" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
4.4.8.1. nsIndexIDListScanLimit
This multi-valued parameter defines a search limit for certain indices or to use no ID list. For further information, see the corresponding section in the Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_name,cn=index,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | See the corresponding section in the Directory Server Performance Tuning Guide. |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsIndexIDListScanLimit: limit=0 type=eq values=inetorgperson |
4.4.8.2. nsSubStrBegin
By default, for a search to be indexed, the search string must be at least three characters long, without counting any wildcard characters. For example, the string abc would be an indexed search while ab* would not be. Indexed searches are significantly faster than unindexed searches, so changing the minimum length of the search key is helpful to increase the number of indexed searches.
This substring length can be edited based on the position of any wildcard characters. The nsSubStrBegin attribute sets the required number of characters for an indexed search for the beginning of a search string, before the wildcard. For example:
abc*
If the value of this attribute is changed, then the index must be regenerated using db2index.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_name,cn=index,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any integer |
| Default Value | 3 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsSubStrBegin: 2 |
4.4.8.3. nsSubStrEnd
By default, for a search to be indexed, the search string must be at least three characters long, without counting any wildcard characters. For example, the string abc would be an indexed search while ab* would not be. Indexed searches are significantly faster than unindexed searches, so changing the minimum length of the search key is helpful to increase the number of indexed searches.
This substring length can be edited based on the position of any wildcard characters. The nsSubStrEnd attribute sets the required number of characters for an indexed search for the end of a search string, after the wildcard. For example:
*xyz
If the value of this attribute is changed, then the index must be regenerated using db2index.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_name,cn=index,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any integer |
| Default Value | 3 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsSubStrEnd: 2 |
4.4.8.4. nsSubStrMiddle
By default, for a search to be indexed, the search string must be at least three characters long, without counting any wildcard characters. For example, the string abc would be an indexed search while ab* would not be. Indexed searches are significantly faster than unindexed searches, so changing the minimum length of the search key is helpful to increase the number of indexed searches.
This substring length can be edited based on the position of any wildcard characters. The nsSubStrMiddle attribute sets the required number of characters for an indexed search where a wildcard is used in the middle of a search string. For example:
ab*z
If the value of this attribute is changed, then the index must be regenerated using db2index.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_name,cn=index,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any integer |
| Default Value | 3 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsSubStrMiddle: 3 |
4.4.9. Database Attributes under cn=attributeName,cn=encrypted attributes,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config
The nsAttributeEncryption object class allows selective encryption of attributes within a database. Extremely sensitive information such as credit card numbers and government identification numbers may not be protected enough by routine access control measures. Normally, these attribute values are stored in CLEAR within the database; encrypting them while they are stored adds another layer of protection. This object class has one attribute, nsEncryptionAlgorithm, which sets the encryption cipher used per attribute. Each encrypted attribute represents a subentry under the above cn=config information tree nodes, as shown in the following diagram:
Figure 4.3. Encrypted Attributes under the cn=config Node

For example, the database encryption file for the userPassword attribute under o=UserRoot appears in the Directory Server as follows:
dn:cn=userPassword,cn=encrypted attributes,o=UserRoot,cn=ldbm database, cn=plugins,cn=config objectclass:top objectclass:nsAttributeEncryption cn:userPassword nsEncryptionAlgorithm:AES
To configure database encryption, see the "Database Encryption" section of the "Configuring Directory Databases" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide. For more information about indexes, see the "Managing Indexes" chapter in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
4.4.9.1. nsAttributeEncryption (Object Class)
This object class is used for core configuration entries which identify and encrypt selected attributes within a Directory Server database.
This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.316
Table 4.8. Required Attributes
| objectClass | Defines the object classes for the entry. |
| cn | Specifies the attribute being encrypted using its common name. |
| The encryption cipher used. |
4.4.9.2. nsEncryptionAlgorithm
nsEncryptionAlgorithm selects the cipher used by nsAttributeEncryption. The algorithm can be set per encrypted attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attributeName,cn=encrypted attributes,cn=database_name,cn=ldbm database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | The following are supported ciphers: * Advanced Encryption Standard Block Cipher (AES) * Triple Data Encryption Standard Block Cipher (3DES) |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsEncryptionAlgorithm: AES |
4.5. Database Link Plug-in Attributes (Chaining Attributes)
The database link plug-in attributes are also organized in an information tree, as shown in the following diagram:
Figure 4.4. Database Link Plug-in
All plug-in technology used by the database link instances is stored in the cn=chaining database plug-in node. This section presents the additional attribute information for the three nodes marked in bold in the cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config information tree in Figure 4.4, “Database Link Plug-in”.
4.5.1. Database Link Attributes under cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config
This section covers global configuration attributes common to all instances are stored in the cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config tree node.
4.5.1.1. nsActiveChainingComponents
This attribute lists the components using chaining. A component is any functional unit in the server. The value of this attribute overrides the value in the global configuration attribute. To disable chaining on a particular database instance, use the value None. This attribute also allows the components used to chain to be altered. By default, no components are allowed to chain, which explains why this attribute will probably not appear in a list of cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=config attributes, as LDAP considers empty attributes to be non-existent.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid component entry |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsActiveChainingComponents: cn=uid uniqueness,cn=plugins,cn=config |
4.5.1.2. nsMaxResponseDelay
This error detection, performance-related attribute specifies the maximum amount of time it can take a remote server to respond to an LDAP operation request made by a database link before an error is suspected. Once this delay period has been met, the database link tests the connection with the remote server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid delay period in seconds |
| Default Value | 60 seconds |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsMaxResponseDelay: 60 |
4.5.1.3. nsMaxTestResponseDelay
This error detection, performance-related attribute specifies the duration of the test issued by the database link to check whether the remote server is responding. If a response from the remote server is not returned before this period has passed, the database link assumes the remote server is down, and the connection is not used for subsequent operations.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid delay period in seconds |
| Default Value | 15 seconds |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsMaxTestResponseDelay: 15 |
4.5.1.4. nsTransmittedControls
This attribute, which can be both a global (and thus dynamic) configuration or an instance (that is, cn=database link instance, cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config) configuration attribute, allows the controls the database link forwards to be altered. The following controls are forwarded by default by the database link:
- Managed DSA (OID: 2.16.840.1.113730.3.4.2)
- Virtual list view (VLV) (OID: 2.16.840.1.113730.3.4.9)
- Server side sorting (OID: 1.2.840.113556.1.4.473)
- Loop detection (OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.1466.29539.12)
Other controls, such as dereferencing and simple paged results for searches, can be added to the list of controls to forward.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid OID or the above listed controls forwarded by the database link |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsTransmittedControls: 1.2.840.113556.1.4.473 |
4.5.2. Database Link Attributes under cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config
Default instance configuration attributes for instances are housed in the cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config tree node.
4.5.2.1. nsAbandonedSearchCheckInterval
This attribute shows the number of seconds that pass before the server checks for abandoned operations.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647) seconds |
| Default Value | 1 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsAbandonedSearchCheckInterval: 10 |
4.5.2.2. nsBindConnectionsLimit
This attribute shows the maximum number of TCP connections the database link establishes with the remote server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to 50 connections |
| Default Value | 3 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsBindConnectionsLimit: 3 |
4.5.2.3. nsBindRetryLimit
Contrary to what the name suggests, this attribute does not specify the number of times a database link retries to bind with the remote server but the number of times it tries to bind with the remote server. A value of 1 here indicates that the database link only attempts to bind once.
Retries only occur for connection failures and not for other types of errors, such as invalid bind DNs or bad passwords.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 5 |
| Default Value | 3 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsBindRetryLimit: 3 |
4.5.2.4. nsBindTimeout
This attribute shows the amount of time before the bind attempt times out. There is no real valid range for this attribute, except reasonable patience limits.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to 60 seconds |
| Default Value | 15 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsBindTimeout: 15 |
4.5.2.5. nsCheckLocalACI
Reserved for advanced use only. This attribute controls whether ACIs are evaluated on the database link as well as the remote data server. Changes to this attribute only take effect once the server has been restarted.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsCheckLocalACI: on |
4.5.2.6. nsConcurrentBindLimit
This attribute shows the maximum number of concurrent bind operations per TCP connection.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to 25 binds |
| Default Value | 10 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsConcurrentBindLimit: 10 |
4.5.2.7. nsConcurrentOperationsLimit
This attribute specifies the maximum number of concurrent operations allowed.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to 50 operations |
| Default Value | 2 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsConcurrentOperationsLimit: 5 |
4.5.2.8. nsConnectionLife
This attribute specifies connection lifetime. Connections between the database link and the remote server can be kept open for an unspecified time or closed after a specific period of time. It is faster to keep the connections open, but it uses more resources. When the value is 0 and a list of failover servers is provided in the nsFarmServerURL attribute, the main server is never contacted after failover to the alternate server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 to limitless seconds (where 0 means forever) |
| Default Value | 0 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsConnectionLife: 0 |
4.5.2.9. nsOperationConnectionsLimit
This attribute shows the maximum number of LDAP connections the database link establishes with the remote server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to n connections |
| Default Value | 20 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsOperationConnectionsLimit: 10 |
4.5.2.10. nsProxiedAuthorization
Reserved for advanced use only. If you disable proxied authorization, binds for chained operations are executed as the user set in the nsMultiplexorBindDn attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsProxiedAuthorization: on |
4.5.2.11. nsReferralOnScopedSearch
This attribute controls whether referrals are returned by scoped searches. This attribute can be used to optimize the directory because returning referrals in response to scoped searches is more efficient. A referral is returned to all the configured farm servers.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsReferralOnScopedSearch: off |
4.5.2.12. nsSizeLimit
This attribute shows the default size limit for the database link in bytes.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1 (no limit) to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647) entries |
| Default Value | 2000 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsSizeLimit: 2000 |
4.5.2.13. nsTimeLimit
This attribute shows the default search time limit for the database link.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=default instance config,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | -1 to maximum 32-bit integer (2147483647) seconds |
| Default Value | 3600 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsTimeLimit: 3600 |
4.5.3. Database Link Attributes under cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config
This information node stores the attributes concerning the server containing the data. A farm server is a server which contains data on databases. This attribute can contain optional servers for failover, separated by spaces. For cascading chaining, this URL can point to another database link.
4.5.3.1. nsBindMechanism
This attribute sets a bind mechanism for the farm server to connect to the remote server. A farm server is a server containing data in one or more databases. This attribute configures the connection type, either standard, TLS, or SASL.
-
empty. This performs simple authentication and requires the
nsMultiplexorBindDnandnsMultiplexorCredentialsattributes to give the bind information. EXTERNAL. This uses an TLS certificate to authenticate the farm server to the remote server. Either the farm server URL must be set to the secure URL (
ldaps) or thensUseStartTLSattribute must be set toon.Additionally, the remote server must be configured to map the farm server’s certificate to its bind identity. Certificate mapping is described in the Administration Guide.
-
DIGEST-MD5. This uses SASL with DIGEST-MD5 encryption. As with simple authentication, this requires the
nsMultiplexorBindDnandnsMultiplexorCredentialsattributes to give the bind information. GSSAPI. This uses Kerberos-based authentication over SASL. The farm server must be connected over the standard port, meaning the URL has
ldap, because the Directory Server does not support SASL/GS-API over TLS.The farm server must be configured with a Kerberos keytab, and the remote server must have a defined SASL mapping for the farm server’s bind identity. Setting up Kerberos keytabs and SASL mappings is described in the Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | * empty * EXTERNAL * DIGEST-MD5 * GSSAPI |
| Default Value | empty |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsBindMechanism: GSSAPI |
4.5.3.2. nsFarmServerURL
This attribute gives the LDAP URL of the remote server. A farm server is a server containing data in one or more databases. This attribute can contain optional servers for failover, separated by spaces. If using cascading changing, this URL can point to another database link.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid remote server LDAP URL |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsFarmServerURL: ldap://farm1.example.com farm2.example.com:389 farm3.example.com:1389/ |
4.5.3.3. nsMultiplexorBindDN
This attribute gives the DN of the administrative entry used to communicate with the remote server. The multiplexor is the server that contains the database link and communicates with the farm server. This bind DN cannot be the Directory Manager, and, if this attribute is not specified, the database link binds as anonymous.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | |
| Default Value | DN of the multiplexor |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsMultiplexerBindDN: cn=proxy manager |
4.5.3.4. nsMultiplexorCredentials
Password for the administrative user, given in plain text. If no password is provided, it means that users can bind as anonymous. The password is encrypted in the configuration file. The example below is what is shown, not what is typed.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid password, which will then be encrypted using the DES reversible password encryption schema |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsMultiplexerCredentials: {DES} 9Eko69APCJfF |
4.5.3.5. nshoplimit
This attribute specifies the maximum number of times a database is allowed to chain; that is, the number of times a request can be forwarded from one database link to another.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to an appropriate upper limit for the deployment |
| Default Value | 10 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | nsHopLimit: 3 |
4.5.3.6. nsUseStartTLS
This attribute sets whether to use Start TLS to initiate a secure, encrypted connection over an insecure port. This attribute can be used if the nsBindMechanism attribute is set to EXTERNAL but the farm server URL set to the standard URL (ldap) or if the nsBindMechanism attribute is left empty.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=database_link_name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | off | on |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsUseStartTLS: on |
4.5.4. Database Link Attributes under cn=monitor,cn=database instance name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config
Attributes used for monitoring activity on the instances are stored in the cn=monitor,cn=database instance name,cn=chaining database,cn=plugins,cn=config information tree.
nsAddCount
This attribute gives the number of add operations received.
nsDeleteCount
This attribute gives the number of delete operations received.
nsModifyCount
This attribute gives the number of modify operations received.
nsRenameCount
This attribute gives the number of rename operations received.
nsSearchBaseCount
This attribute gives the number of base level searches received.
nsSearchOneLevelCount
This attribute gives the number of one-level searches received.
nsSearchSubtreeCount
This attribute gives the number of subtree searches received.
nsAbandonCount
This attribute gives the number of abandon operations received.
nsBindCount
This attribute gives the number of bind requests received.
nsUnbindCount
This attribute gives the number of unbinds received.
nsCompareCount
This attribute gives the number of compare operations received.
nsOperationConnectionCount
This attribute gives the number of open connections for normal operations.
nsOpenBindConnectionCount
This attribute gives the number of open connections for bind operations.
4.6. PAM Pass Through Auth Plug-in Attributes
Local PAM configurations on Unix systems can leverage an external authentication store for LDAP users. This is a form of pass-through authentication which allows the Directory Server to use the externally-stored user credentials for directory access.
PAM pass-through authentication is configured in child entries beneath the PAM Pass Through Auth Plug-in container entry. All of the possible configuration attributes for PAM authentication (defined in the 60pam-plugin.ldif schema file) are available to a child entry; the child entry must be an instance of the PAM configuration object class.
Example 4.1. Example PAM Pass Through Auth Configuration Entries
dn: cn=PAM Pass Through Auth,cn=plugins,cn=config objectClass: top objectClass: nsSlapdPlugin objectClass: extensibleObject objectClass: pamConfig cn: PAM Pass Through Auth nsslapd-pluginPath: libpam-passthru-plugin nsslapd-pluginInitfunc: pam_passthruauth_init nsslapd-pluginType: preoperationnsslapd-pluginEnabled: onnsslapd-pluginLoadGlobal: true nsslapd-plugin-depends-on-type: database nsslapd-pluginId: pam_passthruauth nsslapd-pluginVersion: 9.0.0 nsslapd-pluginVendor: Red Hat nsslapd-pluginDescription: PAM pass through authentication plugin dn: cn=Example PAM Config,cn=PAM Pass Through Auth,cn=plugins,cn=config objectClass: top objectClass: nsSlapdPlugin objectClass: extensibleObject objectClass: pamConfig cn: Example PAM Config pamMissingSuffix: ALLOWpamExcludeSuffix: cn=configpamIDMapMethod: RDN ou=people,dc=example,dc=compamIDMapMethod: ENTRY ou=engineering,dc=example,dc=compamIDAttr: customPamUidpamFilter: (manager=uid=bjensen,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com)pamFallback: FALSEpamSecure: TRUEpamService: ldapserver
The PAM configuration, at a minimum, must define a mapping method (a way to identify what the PAM user ID is from the Directory Server entry), the PAM server to use, and whether to use a secure connection to the service.
pamIDMapMethod: RDN pamSecure: FALSE pamService: ldapserver
The configuration can be expanded for special settings, such as to exclude or specifically include subtrees or to map a specific attribute value to the PAM user ID.
4.6.1. pamConfig (Object Class)
This object class is used to define the PAM configuration to interact with the directory service. This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.318
Allowed Attributes
4.6.2. pamExcludeSuffix
This attribute specifies a suffix to exclude from PAM authentication.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2068 |
| Syntax | DN |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Multi-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.3. pamFallback
Sets whether to fallback to regular LDAP authentication if PAM authentication fails.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2072 |
| Syntax | Boolean |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Single-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.4. pamFilter
Sets an LDAP filter to use to identify specific entries within the included suffixes for which to use PAM pass-through authentication. If not set, all entries within the suffix are targeted by the configuration entry.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2131 |
| Syntax | Boolean |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Single-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.5. pamIDAttr
This attribute contains the attribute name which is used to hold the PAM user ID.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2071 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Multi-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.6. pamIDMapMethod
Gives the method to use to map the LDAP bind DN to a PAM identity.
Directory Server user account inactivation is only validated using the ENTRY mapping method. With RDN or DN, a Directory Server user whose account is inactivated can still bind to the server successfully.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2070 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Single-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.7. pamIncludeSuffix
This attribute sets a suffix to include for PAM authentication.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2067 |
| Syntax | DN |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Multi-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.8. pamMissingSuffix
Identifies how to handle missing include or exclude suffixes. The options are ERROR (which causes the bind operation to fail); ALLOW, which logs an error but allows the operation to proceed; and IGNORE, which allows the operation and does not log any errors.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2069 |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Single-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.9. pamSecure
Requires secure TLS connection for PAM authentication.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2073 |
| Syntax | Boolean |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Single-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.6.10. pamService
Contains the service name to pass to PAM. This assumes that the service specified has a configuration file in the /etc/pam.d/ directory.
The pam_fprintd.so module cannot be in the configuration file referenced by the pamService attribute of the PAM Pass-Through Authentication Plug-in configuration. Using the PAM pam_fprintd.so module causes the Directory Server to hit the max file descriptor limit and can cause the Directory Server process to abort.
The pam_fprintd.so module cannot be in the configuration file referenced by the pamService attribute of the PAM Pass-Through Authentication Plug-in configuration. Using the PAM fprintd module causes the Directory Server to hit the max file descriptor limit and can cause the Directory Server process to abort.
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2074 |
| Syntax | IA5String |
| Multi- or Single-Valued | Single-valued |
| Defined in | Directory Server |
4.7. Account Policy Plug-in Attributes
Account policies can be set that automatically lock an account after a certain amount of time has elapsed. This can be used to create temporary accounts that are only valid for a preset amount of time or to lock users which have been inactive for a certain amount of time.
The Account Policy Plug-in itself only accept on argument, which points to a plug-in configuration entry.
dn: cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config ... nsslapd-pluginarg0: cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config
The account policy configuration entry defines, for the entire server, what attributes to use for account policies. Most of the configuration defines attributes to use to evaluate account policies and expiration times, but the configuration also defines what object class to use to identify subtree-level account policy definitions.
dn: cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config objectClass: top objectClass: extensibleObject cn: config ... attributes for evaluating accounts ... alwaysRecordLogin: yes stateattrname: lastLoginTime altstateattrname: createTimestamp ... attributes for account policy entries ... specattrname: acctPolicySubentry limitattrname: accountInactivityLimit
One the plug-in is configured globally, account policy entries can be created within the user subtrees, and then these policies can be applied to users and to roles through classes of service.
Example 4.2. Account Policy Definition
dn: cn=AccountPolicy,dc=example,dc=com objectClass: top objectClass: ldapsubentry objectClass: extensibleObject objectClass: accountpolicy # 86400 seconds per day * 30 days = 2592000 seconds accountInactivityLimit: 2592000 cn: AccountPolicy
Any entry, both individual users and roles or CoS templates, can be an account policy subentry. Every account policy subentry has its creation and login times tracked against any expiration policy.
Example 4.3. User Account with Account Policy
dn: uid=scarter,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com ... lastLoginTime: 20060527001051Z acctPolicySubentry: cn=AccountPolicy,dc=example,dc=com
4.7.1. altstateattrname
Account expiration policies are based on some timed criteria for the account. For example, for an inactivity policy, the primary criteria may be the last login time, lastLoginTime. However, there may be instances where that attribute does not exist on an entry, such as a user who never logged into his account. The altstateattrname attribute provides a backup attribute for the server to reference to evaluate the expiration time.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any time-based entry attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | altstateattrname: createTimeStamp |
4.7.2. alwaysRecordLogin
By default, only entries which have an account policy directly applied to them — meaning, entries with the acctPolicySubentry attribute — have their login times tracked. If account policies are applied through classes of service or roles, then the acctPolicySubentry attribute is on the template or container entry, not the user entries themselves.
The alwaysRecordLogin attribute sets that every entry records its last login time. This allows CoS and roles to be used to apply account policies.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | yes | no |
| Default Value | no |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | alwaysRecordLogin: no |
4.7.3. alwaysRecordLoginAttr
The Account Policy plug-in uses the attribute name set in the alwaysRecordLoginAttr parameter to store the time of the last successful login in this attribute in the user’s directory entry. For further information, see the corresponding section in the Directory Server Administration Guide.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid attribute name |
| Default Value | stateAttrName |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | alwaysRecordLoginAttr: lastLoginTime |
4.7.4. limitattrname
The account policy entry in the user directory defines the time limit for the account lockout policy. This time limit can be set in any time-based attribute, and a policy entry could have multiple time-based attributes in ti. The attribute within the policy to use for the account inactivation limit is defined in the limitattrname attribute in the Account Policy Plug-in, and it is applied globally to all account policies.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any time-based entry attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | limitattrname: accountInactivityLimit |
4.7.5. specattrname
There are really two configuration entries for an account policy: the global settings in the plug-in configuration entry and then yser- or subtree-level settings in an entry within the user directory. An account policy can be set directly on a user entry or it can be set as part of a CoS or role configuration. The way that the plug-in identifies which entries are account policy configuration entries is by identifying a specific attribute on the entry which flags it as an account policy. This attribute in the plug-in configuration is is specattrname; its will usually be set to acctPolicySubentry.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any time-based entry attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | specattrname: acctPolicySubentry |
4.7.6. stateattrname
Account expiration policies are based on some timed criteria for the account. For example, for an inactivity policy, the primary criteria may be the last login time, lastLoginTime. The primary time attribute used to evaluate an account policy is set in the stateattrname attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=config,cn=Account Policy Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any time-based entry attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | stateattrname: lastLoginTime |
4.8. AD DN Plug-in Attributes
The AD DN plug-in supports multiple domain configurations. Create one configuration entry for each domain. For details, see the corresponding section in the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide.
4.8.1. cn
Sets the domain name of the configuration entry. The plug-in uses the domain name from the authenticating user name to select the corresponding configuration entry.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=domain_name,cn=addn,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Entry | Any string |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | cn: example.com |
4.8.2. addn_base
Sets the base DN under which Directory Server searches the user’s DN.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=domain_name,cn=addn,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Entry | Any valid DN |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | addn_base: ou=People,dc=example,dc=com |
4.8.3. addn_filter
Sets the search filter. Directory Server replaces the %s variable automatically with the non-domain part of the authenticating user. For example, if the user name in the bind is user_name@example.com, the filter searches the corresponding DN which is (&(objectClass=account)(uid=user_name)).
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=domain_name,cn=addn,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Entry | Any valid DN |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | addn_filter: (&(objectClass=account)(uid=%s)) |
4.9. Auto Membership Plug-in Attributes
Automembership essentially allows a static group to act like a dynamic group. Different automembership definitions create searches that are automatically run on all new directory entries. The automembership rules search for and identify matching entries — much like the dynamic search filters — and then explicitly add those entries as members to the specified static group.
The Auto Membership Plug-in itself is a container entry. Each automember definition is a child of the Auto Membership Plug-in. The automember definition defines the LDAP search base and filter to identify entries and a default group to add them to.
dn: cn=Hostgroups,cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config objectclass: autoMemberDefinition cn: Hostgroups autoMemberScope: dc=example,dc=com autoMemberFilter: objectclass=ipHost autoMemberDefaultGroup: cn=systems,cn=hostgroups,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com autoMemberGroupingAttr: member:dn
Each automember definition can have its own child entry that defines additional conditions for assigning the entry to group. Regular expressions can be used to include or exclude entries and assign them to specific groups based on those conditions.
dn: cn=webservers,cn=Hostgroups,cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config objectclass: autoMemberRegexRule description: Group for webservers cn: webservers autoMemberTargetGroup: cn=webservers,cn=hostgroups,dc=example,dc=com autoMemberInclusiveRegex: fqdn=^www\.web[0-9]+\.example\.com
If the entry matches the main definition and not any of the regular expression conditions, then it uses the group in the main definition. If it matches a regular expression condition, then it is added to the regular expression condition group.
4.9.1. autoMemberDefaultGroup
This attribute sets a default or fallback group to add the entry to as a member. If only the definition entry is used, then this is the group to which all matching entries are added. If regular expression conditions are used, then this group is used as a fallback if an entry which matches the LDAP search filter do not match any of the regular expressions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any existing Directory Server group |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Single |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberDefaultGroup: cn=hostgroups,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com |
4.9.2. autoMemberDefinition (Object Class)
This attribute identifies the entry as an automember definition. This entry must be a child of the Auto Membership Plug-in, cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config.
Allowed Attributes
- autoMemberScope
- autoMemberFilter
- autoMemberDefaultGroup
- autoMemberGroupingAttr
4.9.3. autoMemberExclusiveRegex
This attribute sets a single regular expression to use to identify entries to exclude. If an entry matches the exclusion condition, then it is not included in the group. Multiple regular expressions could be used, and if an entry matches any one of those expressions, it is excluded in the group.
The format of the expression is a Perl-compatible regular expression (PCRE). For more information on PCRE patterns, see the pcresyntax(3) man page.
Exclude conditions are evaluated first and take precedence over include conditions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any regular expression |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Multi-valued |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberExclusiveRegex: fqdn=^www\.web[0-9]+\.example\.com |
4.9.4. autoMemberFilter
This attribute sets a standard LDAP search filter to use to search for matching entries.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid LDAP search filter |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Single |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberFilter:objectclass=ntUser |
4.9.5. autoMemberGroupingAttr
This attribute gives the name of the member attribute in the group entry and the attribute in the object entry that supplies the member attribute value, in the format group_member_attr:entry_attr.
This structures how the Automembership Plug-in adds a member to the group, depending on the group configuration. For example, for a groupOfUniqueNames user group, each member is added as a uniqueMember attribute. The value of uniqueMember is the DN of the user entry. In essence, each group member is identified by the attribute-value pair of uniqueMember: user_entry_DN. The member entry format, then, is uniqueMember:dn.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Single |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberGroupingAttr: member:dn |
4.9.6. autoMemberInclusiveRegex
This attribute sets a single regular expression to use to identify entries to include. Multiple regular expressions could be used, and if an entry matches any one of those expressions, it is included in the group (assuming it does not match an exclude expression).
The format of the expression is a Perl-compatible regular expression (PCRE). For more information on PCRE patterns, see the pcresyntax(3) man page.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any regular expression |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Multi-valued |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberInclusiveRegex: fqdn=^www\.web[0-9]+\.example\.com |
4.9.7. autoMemberProcessModifyOps
By default, the Directory Server invokes the Automembership plug-in for add and modify operations. With this setting, the plug-in changes groups when you add a group entry to a user or modify a group entry of a user. If you set the autoMemberProcessModifyOps to off, Directory Server only invokes the Automembership plug-in when you add a group entry to a user. In this case, if an administrator changes a user entry, and that entry impactes what Automembership groups the user belongs to, the plug-in does not remove the user from the old group and only adds the new group. To update the old group, you must then manually run a fix-up task.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | on |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Single |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberProcessModifyOps: on |
4.9.8. autoMemberRegexRule (Object Class)
This attribute identifies the entry as a regular expression rule. This entry must be a child of an automember definition (objectclass: autoMemberDefinition).
Allowed Attributes
- autoMemberInclusiveRegex
- autoMemberExclusiveRegex
- autoMemberTargetGroup
4.9.9. autoMemberScope
This attribute sets the subtree DN to search for entries. This is the search base.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server subtree |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Single |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberScope: dc=example,dc=com |
4.9.10. autoMemberTargetGroup
This attribute sets which group to add the entry to as a member, if it meets the regular expression conditions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Auto Membership Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server group |
| Default Value | None |
| Single- or Multi-Valued | Single |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | autoMemberTargetGroup: cn=webservers,cn=hostgroups,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com |
4.10. Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in Attributes
The Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in manages ranges of numbers and assigns unique numbers within that range to entries. By breaking number assignments into ranges, the Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in allows multiple servers to assign numbers without conflict. The plug-in also manages the ranges assigned to servers, so that if one instance runs through its range quickly, it can request additional ranges from the other servers.
Distributed numeric assignment can be configured to work with single attribute types or multiple attribute types, and is only applied to specific suffixes and specific entries within the subtree.
Distributed numeric assignment is handled per-attribute and is only applied to specific suffixes and specific entries within the subtree.
4.10.1. dnaPluginConfig (Object Class)
This object class is used for entries which configure the DNA Plug-in and numeric ranges to assign to entries.
This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.324
Allowed Attributes
- dnaType
- dnaPrefix
- dnaNextValue
- dnaMaxValue
- dnaInterval
- dnaMagicRegen
- dnaFilter
- dnaScope
- dnaSharedCfgDN
- dnaThreshold
- dnaNextRange
- dnaRangeRequestTimeout
- cn
4.10.2. dnaFilter
This attribute sets an LDAP filter to use to search for and identify the entries to which to apply the distributed numeric assignment range.
The dnaFilter attribute is required to set up distributed numeric assignment for an attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid LDAP filter |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | dnaFilter: (objectclass=person) |
4.10.3. dnaInterval
This attribute sets an interval to use to increment through numbers in a range. Essentially, this skips numbers at a predefined rate. If the interval is 3 and the first number in the range is 1, the next number used in the range is 4, then 7, then 10, incrementing by three for every new number assignment.
In a replication environment, the dnaInterval enables multiple servers to share the same range. However, when you configure different servers that share the same range, set the dnaInterval and dnaNextVal parameters accordingly so that the different servers do not generate the same values. You must also consider this if you add new servers to the replication topology.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any integer |
| Default Value | 1 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | dnaInterval: 1 |
4.10.4. dnaMagicRegen
This attribute sets a user-defined value that instructs the plug-in to assign a new value for the entry. The magic value can be used to assign new unique numbers to existing entries or as a standard setting when adding new entries.
The magic entry should be outside of the defined range for the server so that it cannot be triggered by accident. Note that this attribute does not have to be a number when used on a DirectoryString or other character type. However, in most cases the DNA plug-in is used on attributes which only accept integer values, and in such cases the dnamagicregen value must also be an integer.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any string |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | dnaMagicRegen: -1 |
4.10.5. dnaMaxValue
This attribute sets the maximum value that can be assigned for the range. The default is -1, which is the same as setting the highest 64-bit integer.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer on 32-bit systems and to the maximum 64-bit integer on 64-bit systems; -1 is unlimited |
| Default Value | -1 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | dnaMaxValue: 1000 |
4.10.6. dnaNextRange
This attribute defines the next range to use when the current range is exhausted. This value is automatically set when range is transferred between servers, but it can also be manually set to add a range to a server if range requests are not used.
The dnaNextRange attribute should be set explicitly only if a separate, specific range has to be assigned to other servers. Any range set in the dnaNextRange attribute must be unique from the available range for the other servers to avoid duplication. If there is no request from the other servers and the server where dnaNextRange is set explicitly has reached its set dnaMaxValue, the next set of values (part of the dnaNextRange) is allocated from this deck.
The dnaNextRange allocation is also limited by the dnaThreshold attribute that is set in the DNA configuration. Any range allocated to another server for dnaNextRange cannot violate the threshold for the server, even if the range is available on the deck of dnaNextRange.
If the dnaNextRange attribute is handled internally if it is not set explicitly. When it is handled automatically, the dnaMaxValue attribute serves as upper limit for the next range.
The attribute sets the range in the format lower_range-upper_range.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer on 32-bit systems and to the maximum 64-bit integer on 64-bit systems for the lower and upper ranges |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | dnaNextRange: 100-500 |
4.10.7. dnaNextValue
This attribute gives the next available number which can be assigned. After being initially set in the configuration entry, this attribute is managed by the Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in.
The dnaNextValue attribute is required to set up distributed numeric assignment for an attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer on 32-bit systems and to the maximum 64-bit integer on 64-bit systems |
| Default Value | -1 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | dnaNextValue: 1 |
4.10.8. dnaPrefix
This attribute defines a prefix that can be prepended to the generated number values for the attribute. For example, to generate a user ID such as user1000, the dnaPrefix setting would be user.
dnaPrefix can hold any kind of string. However, some possible values for dnaType (such as uidNumber and gidNumber) require only integer values. To use a prefix string, consider using a custom attribute for dnaType which allows strings.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any string |
| Default Value | None |
| Example | dnaPrefix: id |
4.10.9. dnaRangeRequestTimeout
One potential situation with the Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in is that one server begins to run out of numbers to assign. The dnaThreshold attribute sets a threshold of available numbers in the range, so that the server can request an additional range from the other servers before it is unable to perform number assignments.
The dnaRangeRequestTimeout attribute sets a timeout period, in seconds, for range requests so that the server does not stall waiting on a new range from one server and can request a range from a new server.
For range requests to be performed, the dnaSharedCfgDN attribute must be set.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer on 32-bit systems and to the maximum 64-bit integer on 64-bit systems |
| Default Value | 10 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | dnaRangeRequestTimeout: 15 |
4.10.10. dnaScope
This attribute sets the base DN to search for entries to which to apply the distributed numeric assignment. This is analogous to the base DN in an ldapsearch.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server entry |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | dnaScope: ou=people,dc=example,dc=com |
4.10.11. dnaSharedCfgDN
This attribute defines a shared identity that the servers can use to transfer ranges to one another. This entry is replicated between servers and is managed by the plug-in to let the other servers know what ranges are available. This attribute must be set for range transfers to be enabled.
The shared configuration entry must be configured in the replicated subtree, so that the entry can be replicated to the servers. For example, if the ou=People,dc=example,dc=com subtree is replicated, then the configuration entry must be in that subtree, such as ou=UID Number Ranges, ou=People,dc=example,dc=com.
The entry identified by this setting must be manually created by the administrator. The server will automatically contain a sub-entry beneath it to transfer ranges.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any DN |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DN |
| Example | dnaSharedCfgDN: cn=range transfer user,cn=config |
4.10.12. dnaThreshold
One potential situation with the Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in is that one server begins to run out of numbers to assign, which can cause problems. The Distributed Numeric Assignment Plug-in allows the server to request a new range from the available ranges on other servers.
So that the server can recognize when it is reaching the end of its assigned range, the dnaThreshold attribute sets a threshold of remaining available numbers in the range. When the server hits the threshold, it sends a request for a new range.
For range requests to be performed, the dnaSharedCfgDN attribute must be set.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 1 to the maximum 32-bit integer on 32-bit systems and to the maximum 64-bit integer on 64-bit systems |
| Default Value | 100 |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | dnaThreshold: 100 |
4.10.13. dnaType
This attribute sets which attributes have unique numbers being generated for them. In this case, whenever the attribute is added to the entry with the magic number, an assigned value is automatically supplied.
This attribute is required to set a distributed numeric assignment for an attribute.
If the dnaPrefix attribute is set, then the prefix value is prepended to whatever value is generated by dnaType. The dnaPrefix value can be any kind of string, but some reasonable values for dnaType (such as uidNumber and gidNumber) require only integer values. To use a prefix string, consider using a custom attribute for dnaType which allows strings.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Example | dnaType: uidNumber |
4.10.14. dnaSharedConfig (Object Class)
This object class is used to configure the shared configuration entry that is replicated between suppliers that are all using the same DNA Plug-in configuration for numeric assignements.
This object class is defined in Directory Server.
Superior Class
top
OID
2.16.840.1.113730.3.2.325
Allowed Attributes
- dnaHostname
- dnaPortNum
- dnaSecurePortNum
- dnaRemainingValues
4.10.15. dnaHostname
This attribute identifies the host name of a server in a shared range, as part of the DNA range configuration for that specific host in multi-supplier replication. Available ranges are tracked by host and the range information is replicated among all suppliers so that if any supplier runs low on available numbers, it can use the host information to contact another supplier and request an new range.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Valid Range | Any valid host name |
| Default Value | None |
| Example | dnahostname: ldap1.example.com |
4.10.16. dnaPortNum
This attribute gives the standard port number to use to connect to the host identified in dnaHostname.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Valid Range | 0 to 65535 |
| Default Value | 389 |
| Example | dnaPortNum: 389 |
4.10.17. dnaRemainingValues
This attribute contains the number of values that are remaining and available to a server to assign to entries.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | dnaHostname=host_name+dnaPortNum=port_number,ou=ranges,dc=example,dc=com |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Valid Range | Any integer |
| Default Value | None |
| Example | dnaRemainingValues: 1000 |
4.10.18. dnaRemoteBindCred
Specifies the Replication Manager’s password. If you set a bind method in the dnaRemoteBindMethod attribute that requires authentication, additionally set the dnaRemoteBindDN and dnaRemoteBindCred parameter for every server in the replication deployment in the plug-in configuration entry under the cn=config entry.
Set the parameter in plain text. The value is automatically AES-encrypted before it is stored.
A server restart is required for the change to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Syntax | DirectoryString {AES} encrypted_password |
| Valid Values | Any valid AES-encrypted password. |
| Default Value | |
| Example | dnaRemoteBindCred: {AES-TUhNR0NTcUdTSWIzRFFFRkRUQm1NRVVHQ1NxR1NJYjNEUUVGRERBNEJDUmxObUk0WXpjM1l5MHdaVE5rTXpZNA0KTnkxaE9XSmhORGRoT0MwMk1ESmpNV014TUFBQ0FRSUNBU0F3Q2dZSUtvWklodmNOQWdjd0hRWUpZSVpJQVdVRA0KQkFFcUJCQk5KbUFDUWFOMHlITWdsUVp3QjBJOQ==}bBR3On6cBmw0DdhcRx826g== |
4.10.19. dnaRemoteBindDN
Specifies the Replication Manager DN. If you set a bind method in the dnaRemoteBindMethod attribute that requires authentication, additionally set the dnaRemoteBindDN and dnaRemoteBindCred parameter for every server in the replication deployment in the plug-in configuration under the cn=config entry.
A server restart is required for the change to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=DNA_config_entry,cn=Distributed Numeric Assignment Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Valid Values | Any valid Replication Manager DN. |
| Default Value | |
| Example | dnaRemoteBindDN: cn=replication manager,cn=config |
4.10.20. dnaRemoteBindMethod
Specifies the remote bind method. If you set a bind method in this attribute that requires authentication, additionally set the dnaRemoteBindDN and dnaRemoteBindCred parameter for every server in the replication deployment in the plug-in configuration entry under the cn=config entry.
A server restart is required for the change to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | dnaHostname=host_name+dnaPortNum=port_number,ou=ranges,dc=example,dc=com |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Valid Values |
|
| Default Value | |
| Example | dnaRemoteBindMethod: SIMPLE |
4.10.21. dnaRemoteConnProtocol
Specifies the remote connection protocol.
A server restart is required for the change to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | dnaHostname=host_name+dnaPortNum=port_number,ou=ranges,dc=example,dc=com |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Valid Values |
|
| Default Value | |
| Example | dnaRemoteConnProtocol: LDAP |
4.10.22. dnaSecurePortNum
This attribute gives the secure (TLS) port number to use to connect to the host identified in dnaHostname.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | dnaHostname=host_name+dnaPortNum=port_number,ou=ranges,dc=example,dc=com |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Valid Range | 0 to 65535 |
| Default Value | 636 |
| Example | dnaSecurePortNum: 636 |
4.11. Linked Attributes Plug-in Attributes
Many times, entries have inherent relationships to each other (such as managers and employees, document entries and their authors, or special groups and group members). While attributes exist that reflect these relationships, these attributes have to be added and updated on each entry manually. That can lead to a whimsically inconsistent set of directory data, where these entry relationships are unclear, outdated, or missing.
The Linked Attributes Plug-in allows one attribute, set in one entry, to update another attribute in another entry automatically. The first attribute has a DN value, which points to the entry to update; the second entry attribute also has a DN value which is a back-pointer to the first entry. The link attribute which is set by users and the dynamically-updated "managed" attribute in the affected entries are both defined by administrators in the Linked Attributes Plug-in instance.
Conceptually, this is similar to the way that the MemberOf Plug-in uses the member attribute in group entries to set memberOf attribute in user entries. Only with the Linked Attributes Plug-in, all of the link/managed attributes are user-defined and there can be multiple instances of the plug-in, each reflecting different link-managed relationships.
There are a couple of caveats for linking attributes:
- Both the link attribute and the managed attribute must have DNs as values. The DN in the link attribute points to the entry to add the managed attribute to. The managed attribute contains the linked entry DN as its value.
- The managed attribute must be multi-valued. Otherwise, if multiple link attributes point to the same managed entry, the managed attribute value would not be updated accurately.
4.11.1. linkScope
This restricts the scope of the plug-in, so it operates only in a specific subtree or suffix. If no scope is given, then the plug-in will update any part of the directory tree.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plugin_instance,cn=Linked Attributes,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any DN |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DN |
| Example | linkScope: ou=People,dc=example,dc=com |
4.11.2. linkType
This sets the user-managed attribute. This attribute is modified and maintained by users, and then when this attribute value changes, the linked attribute is automatically updated in the targeted entries.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plugin_instance,cn=Linked Attributes,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | linkType: directReport |
4.11.3. managedType
This sets the managed, or plug-in maintained, attribute. This attribute is managed dynamically by the Linked Attributes Plug-in instance. Whenever a change is made to the managed attribute, then the plug-in updates all of the linked attributes on the targeted entries.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=plugin_instance,cn=Linked Attributes,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server attribute |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DN |
| Example | managedType: manager |
4.12. Managed Entries Plug-in Attributes
In some unique circumstances, it is useful to have an entry created automatically when another entry is created. For example, this can be part of Posix integration by creating a specific group entry when a new user is created. Each instance of the Managed Entries Plug-in identifies two areas:
- The scope of the plug-in, meaning the subtree and the search filter to use to identify entries which require a corresponding managed entry
- A template entry that defines what the managed entry should look like
4.12.1. managedBase
This attribute sets the subtree under which to create the managed entries. This can be any entry in the directory tree.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=instance_name,cn=Managed Entries Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any Directory Server subtree |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | managedBase: ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com |
4.12.2. managedTemplate
This attribute identifies the template entry to use to create the managed entry. This entry can be located anywhere in the directory tree; however, it is recommended that this entry is in a replicated suffix so that all suppliers and consumers in replication are using the same template.
The attributes used to create the managed entry template are described in the Red Hat Directory Server Configuration, Command, and File Reference.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=instance_name,cn=Managed Entries Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values |
Any Directory Server entry of the |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | managedTemplate: cn=My Template,ou=Templates,dc=example,dc=com |
4.12.3. originFilter
This attribute sets the search filter to use to search for and identify the entries within the subtree which require a managed entry. The filter allows the managed entries behavior to be limited to a specific type of entry or subset of entries. The syntax is the same as a regular search filter.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=instance_name,cn=Managed Entries Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid LDAP filter |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | originFilter: objectclass=posixAccount |
4.12.4. originScope
This attribute sets the scope of the search to use to see which entries the plug-in monitors. If a new entry is created within the scope subtree, then the Managed Entries Plug-in creates a new managed entry that corresponds to it.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=instance_name,cn=Managed Entries Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any Directory Server subtree |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | originScope: ou=people,dc=example,dc=com |
4.13. MemberOf Plug-in Attributes
Group membership is defined within group entries using attributes such as member. Searching for the member attribute makes it easy to list all of the members for the group. However, group membership is not reflected in the member’s user entry, so it is impossible to tell to what groups a person belongs by looking at the user’s entry.
The MemberOf Plug-in synchronizes the group membership in group members with the members' individual directory entries by identifying changes to a specific member attribute (such as member) in the group entry and then working back to write the membership changes over to a specific attribute in the members' user entries.
4.13.1. cn
Sets the name of the plug-in instance.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid string |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | cn: Example MemberOf Plugin Instance |
4.13.2. memberOfAllBackends
This attribute specifies whether to search the local suffix for user entries or all available suffixes. This can be desirable in directory trees where users may be distributed across multiple databases so that group membership is evaluated comprehensively and consistently.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | memberOfAllBackends: on |
4.13.3. memberOfAttr
This attribute specifies the attribute in the user entry for the Directory Server to manage to reflect group membership. The MemberOf Plug-in generates the value of the attribute specified here in the directory entry for the member. There is a separate attribute for every group to which the user belongs.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server attribute |
| Default Value | memberOf |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | memberOfAttr: memberOf |
4.13.4. memberOfAutoAddOC
To enable the memberOf plug-in to add the memberOf attribute to a user, the user object must contain an object class that allows this attribute. If an entry does not have an object class that allows the memberOf attribute then the memberOf plugin will automatically add the object class listed in the memberOfAutoAddOC parameter.
This setting does not require restarting the server to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any Directory Server object class |
| Default Value | nsMemberOf |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | memberOfAutoAddOC: nsMemberOf |
4.13.5. memberOfEntryScope
If you configured several back ends or multiple-nested suffixes, the multi-valued memberOfEntryScope parameter enables you to set what suffixes the MemberOf plug-in works on. If the parameter is not set, the plug-in works on all suffixes. The value set in the memberOfEntryScopeExcludeSubtree parameter has a higher priority than values set in memberOfEntryScope.
For further details, see the corresponding section in the Directory Server Administration Guide.
This setting does not require restarting the server to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server entry DN. |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | memberOfEntryScope: ou=people,dc=example,dc=com |
4.13.6. memberOfEntryScopeExcludeSubtree
If you configured several back ends or multiple-nested suffixes, the multi-valued memberOfEntryScopeExcludeSubtree parameter enables you to set what suffixes the MemberOf plug-in excludes. The value set in the memberOfEntryScopeExcludeSubtree parameter has a higher priority than values set in memberOfEntryScope. If the scopes set in both parameters overlap, the MemberOf plug-in only works on the non-overlapping directory entries.
For further details, see the corresponding section in the Directory Server Administration Guide.
This setting does not require restarting the server to take effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server entry DN. |
| Default Value | |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | memberOfEntryScopeExcludeSubtree: ou=sample,dc=example,dc=com |
4.13.7. memberOfGroupAttr
This attribute specifies the attribute in the group entry to use to identify the DNs of group members. By default, this is the member attribute, but it can be any membership-related attribute that contains a DN value, such as uniquemember or member.
Any attribute can be used for the memberOfGroupAttr value, but the MemberOf Plug-in only works if the value of the target attribute contains the DN of the member entry. For example, the member attribute contains the DN of the member’s user entry:
member: uid=jsmith,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
Some member-related attributes do not contain a DN, like the memberURL attribute. That attribute will not work as a value for memberOfGroupAttr. The memberURL value is a URL, and a non-DN value cannot work with the MemberOf Plug-in.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=MemberOf Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any Directory Server attribute |
| Default Value | member |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | memberOfGroupAttr: member |
4.14. Attribute Uniqueness Plug-in Attributes
The Attribute Uniqueness plug-in ensures that the value of an attribute is unique across the directory or subtree.
4.14.1. cn
Sets the name of the Attribute Uniqueness plug-in configuration record. You can use any string, but Red Hat recommends naming the configuration record attribute_name Attribute Uniqueness.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_uniqueness_configuration_record_name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid string |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | cn: mail Attribute Uniqueness |
4.14.2. uniqueness-attribute-name
Sets the name of the attribute whose values must be unique. This attribute is multi-valued.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_uniqueness_configuration_record_name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid attribute name |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | uniqueness-attribute-name: mail |
4.14.3. uniqueness-subtrees
Sets the DN under which the plug-in checks for uniqueness of the attribute’s value. This attribute is multi-valued.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_uniqueness_configuration_record_name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid subtree DN |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | uniqueness-subtrees: ou=Sales,dc=example,dc=com |
4.14.4. uniqueness-across-all-subtrees
If enabled (on), the plug-in checks that the attribute is unique across all subtrees set. If you set the attribute to off, uniqueness is only enforced within the subtree of the updated entry.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_uniqueness_configuration_record_name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on | off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | uniqueness-across-all-subtrees: off |
4.14.5. uniqueness-top-entry-oc
Directory Server searches this object class in the parent entry of the updated object. If it was not found, the search continues at the next higher level entry up to the root of the directory tree. If the object class was found, Directory Server verifies that the value of the attribute set in uniqueness-attribute-name is unique in this subtree.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_uniqueness_configuration_record_name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid object class |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | uniqueness-top-entry-oc: nsContainer |
4.14.6. uniqueness-subtree-entries-oc
Optionally, when using the uniqueness-top-entry-oc parameter, you can configure that the Attribute Uniqueness plug-in only verifies if an attribute is unique, if the entry contains the object class set in this parameter.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=attribute_uniqueness_configuration_record_name,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid object class |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | uniqueness-subtree-entries-oc: inetOrgPerson |
4.15. Posix Winsync API Plug-in Attributes
By default, Posix-related attributes are not synchronized between Active Directory and Red Hat Directory Server. On Linux systems, system users and groups are identified as Posix entries, and LDAP Posix attributes contain that required information. However, when Windows users are synced over, they have ntUser and ntGroup attributes automatically added which identify them as Windows accounts, but no Posix attributes are synced over (even if they exist on the Active Directory entry) and no Posix attributes are added on the Directory Server side.
The Posix Winsync API Plug-in synchronizes POSIX attributes between Active Directory and Directory Server entries.
All POSIX attributes (such as uidNumber, gidNumber, and homeDirectory) are synchronized between Active Directory and Directory Server entries. However, if a new POSIX entry or POSIX attributes are added to an existing entry in the Directory Server, only the POSIX attributes are synchronized over to the Active Directory corresponding entry. The POSIX object class (posixAccount for users and posixGroup for groups) is not added to the Active Directory entry.
This plug-in is disabled by default and must be enabled before any Posix attributes will be synchronized from the Active Directory entry to the Directory Server entry.
4.15.1. posixWinsyncCreateMemberOfTask
This attribute sets whether to run the memberOf fix-up task immediately after a sync run in order to update group memberships for synced users. This is disabled by default because the memberOf fix-up task can be resource-intensive and cause performance issues if it is run too frequently.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Posix Winsync API Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | true | false |
| Default Value | false |
| Example | posixWinsyncCreateMemberOfTask: false |
4.15.2. posixWinsyncLowerCaseUID
This attribute sets whether to store (and, if necessary, convert) the UID value in the memberUID attribute in lower case.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Posix Winsync API Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | true | false |
| Default Value | false |
| Example | posixWinsyncLowerCaseUID: false |
4.15.3. posixWinsyncMapMemberUID
This attribute sets whether to map the memberUID attribute in an Active Directory group to the uniqueMember attribute in a Directory Server group.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Posix Winsync API Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | true | false |
| Default Value | true |
| Example | posixWinsyncMapMemberUID: false |
4.15.4. posixWinsyncMapNestedGrouping
The posixWinsyncMapNestedGrouping parameter manages if nested groups are updated when memberUID attributes in an Active Directory POSIX group change. Updating nested groups is supported up a depth of five levels.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Posix Winsync API Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | true | false |
| Default Value | false |
| Example | posixWinsyncMapNestedGrouping: false |
4.15.5. posixWinsyncMsSFUSchema
This attribute sets whether to the older Microsoft System Services for Unix 3.0 (msSFU30) schema when syncing Posix attributes from Active Directory. By default, the Posix Winsync API Plug-in uses Posix schema for modern Active Directory servers: 2005, 2008, and later versions. There are slight differences between the modern Active Directory Posix schema and the Posix schema used by Windows Server 2003 and older Windows servers. If an Active Directory domain is using the older-style schema, then the older-style schema can be used instead.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Posix Winsync API Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | true | false |
| Default Value | false |
| Example | posixWinsyncMsSFUSchema: true |
4.16. Retro Changelog Plug-in Attributes
Two different types of changelogs are maintained by Directory Server. The first type, referred to as simply a changelog, is used by multi-supplier replication, and the second changelog, a plug-in referred to as the retro changelog, is intended for use by LDAP clients for maintaining application compatibility with Directory Server 4.x versions.
This Retro Changelog Plug-in is used to record modifications made to a supplier server. When the supplier server’s directory is modified, an entry is written to the Retro Changelog that contains both of the following:
- A number that uniquely identifies the modification. This number is sequential with respect to other entries in the changelog.
- The modification action; that is, exactly how the directory was modified.
It is through the Retro Changelog Plug-in that the changes performed to the Directory Server are accessed using searches to cn=changelog suffix.
4.16.1. isReplicated
This optional attribute sets a flag to indicate on a change in the changelog whether the change is newly made on that server or whether it was replicated over from another server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| OID | 2.16.840.1.113730.3.1.2085 |
| Entry DN | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | true | false |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | Boolean |
| Example | isReplicated: true |
4.16.2. nsslapd-attribute
This attribute explicitly specifies another Directory Server attribute which must be included in the retro changelog entries.
Many operational attributes and other types of attributes are commonly excluded from the retro changelog, but these attributes may need to be present for a third-party application to use the changelog data. This is done by listing the attribute in the retro changelog plug-in configuration using the nsslapd-attribute parameter.
It is also possible to specify an optional alias for the specified attribute within the nsslapd-attribute value.
nsslapd-attribute: attribute:alias
Using an alias for the attribute can help avoid conflicts with other attributes in an external server or application which may use the retro changelog records.
Setting the value of the nsslapd-attribute attribute to isReplicated is a way of indicating, in the retro changelog entry itself, whether the modification was done on the local server (that is, whether the change is an original change) or whether the change was replicated over to the server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid directory attribute (standard or custom) |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-attribute: nsUniqueId: uniqueID |
4.16.3. nsslapd-changelogdir
This attribute specifies the name of the directory in which the changelog database is created the first time the plug-in is run. By default, the database is stored with all the other databases under /var/lib/dirsrv/slapd-instance/changelogdb.
For performance reasons, store this database on a different physical disk.
The server has to be restarted for changes to this attribute to go into effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid path to the directory |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-changelogdir: /var/lib/dirsrv/slapd-instance/changelogdb |
4.16.4. nsslapd-changelogmaxage (Max Changelog Age)
This attribute specifies the maximum age of any entry in the changelog. The changelog contains a record for each directory modification and is used when synchronizing consumer servers. Each record contains a timestamp. Any record with a timestamp that is older than the value specified in this attribute is removed. If nsslapd-changelogmaxage attribute is absent, there is no age limit on changelog records.
Expired changelog records will not be removed if there is an agreement that has fallen behind further than the maximum age.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | 0 (meaning that entries are not removed according to their age) to the maximum 32 bit integer value (2147483647) |
| Default Value | 7d |
| Syntax | DirectoryString Integer AgeID
AgeID is |
| Example | nsslapd-changelogmaxage: 30d |
4.16.5. nsslapd-exclude-attrs
The nsslapd-exclude-attrs parameter stores an attribute name to exclude from the retro changelog database. To exclude multiple attributes, add one nsslapd-exclude-attrs parameter for each attribute to exclude.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid attribute name |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-exclude-attrs: example |
4.16.6. nsslapd-exclude-suffix
The nsslapd-exclude-suffix parameter stores a suffix to exclude from the retro changelog database. You can add the parameter multiple times to exclude multiple suffixes.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=Retro Changelog Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | Any valid attribute name |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | nsslapd-exclude-suffix: ou=demo,dc=example,dc=com |
4.17. RootDN Access Control Plug-in Attributes
The root DN, cn=Directory Manager, is a special user entry that is defined outside the normal user database. Normal access control rules are not applied to the root DN, but because of the powerful nature of the root user, it can be beneficial to apply some kind of access control rules to the root user.
The RootDN Access Control Plug-in sets normal access controls — host and IP address restrictions, time-of-day restrictions, and day of week restrictions — on the root user.
This plug-in is disabled by default.
4.17.1. rootdn-allow-host
This sets what hosts, by fully-qualified domain name, the root user is allowed to use to access the Directory Server. Any hosts not listed are implicitly denied.
Wild cards are allowed.
This attribute can be used multiple times to specify multiple hosts, domains, or subdomains.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=RootDN Access Control Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid host name or domain, including asterisks (*) for wildcards |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | rootdn-allow-host: *.example.com |
4.17.2. rootdn-allow-ip
This sets what IP addresses, either IPv4 or IPv6, for machines the root user is allowed to use to access the Directory Server. Any IP addresses not listed are implicitly denied.
Wild cards are allowed.
This attribute can be used multiple times to specify multiple addresses, domains, or subnets.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=RootDN Access Control Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid IPv4 or IPv6 address, including asterisks (*) for wildcards |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | rootdn-allow-ip: 192.168.. |
4.17.3. rootdn-close-time
This sets part of a time period or range when the root user is allowed to access the Directory Server. This sets when the time-based access ends, when the root user is no longer allowed to access the Directory Server.
This is used in conjunction with the rootdn-open-time attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=RootDN Access Control Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid time, in a 24-hour format |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | rootdn-close-time: 1700 |
4.17.4. rootdn-days-allowed
This gives a comma-separated list of what days the root user is allowed to use to access the Directory Server. Any days listed are implicitly denied. This can be used with rootdn-close-time and rootdn-open-time to combine time-based access and days-of-week or it can be used by itself (with all hours allowed on allowed days).
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=RootDN Access Control Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | * Sun * Mon * Tue * Wed * Thu * Fri * Sat |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | rootdn-days-allowed: Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri |
4.17.5. rootdn-deny-ip
This sets what IP addresses, either IPv4 or IPv6, for machines the root user is not allowed to use to access the Directory Server. Any IP addresses not listed are implicitly allowed.
Deny rules supercede allow rules, so if an IP address is listed in both the rootdn-allow-ip and rootdn-deny-ip attributes, it is denied access.
Wild cards are allowed.
This attribute can be used multiple times to specify multiple addresses, domains, or subnets.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=RootDN Access Control Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid IPv4 or IPv6 address, including asterisks (*) for wildcards |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | DirectoryString |
| Example | rootdn-deny-ip: 192.168.0.0 |
4.17.6. rootdn-open-time
This sets part of a time period or range when the root user is allowed to access the Directory Server. This sets when the time-based access begins.
This is used in conjunction with the rootdn-close-time attribute.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=RootDN Access Control Plugin,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Range | Any valid time, in a 24-hour format |
| Default Value | None |
| Syntax | Integer |
| Example | rootdn-open-time: 0800 |
4.18. Referential Integrity Plug-in Attributes
Referential Integrity ensures that when you perform update or remove operations to an entry in the the directory, the server also updates information for entries that reference removed/updated one. For example, if a user’s entry is removed from the directory and Referential Integrity is enabled, the server also removes the user from any groups where the user is a member.
4.18.1. nsslapd-pluginAllowReplUpdates
Referential Integrity can be a very resource demanding procedure. So if you configured multi-supplier replication the Referential Integrity plug-in will ignore replicated updates by default. However, sometimes it is not possible to enable the Referential Integrity plug-in, or the plug-in is not available.
For example, one of your suppliers in the replication topology is Active Directory (see chapter Windows Synchronization for more details) that does not support Referential Integrity. In cases like this you can allow the Referential Integrity plug-in on another supplier to process replicated updates using nsslapd-pluginAllowReplUpdates attribute.
Only one supplier must have the nsslapd-pluginAllowReplUpdates attribute value on in multi-supplier replication topology. Otherwise, it can lead to replication errors, and requires a full initialization to fix the problem. On the other hand, the Referential Integrity plug-in must be enabled on all supplies where possible.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Entry DN | cn=referential integrity postoperation,cn=plugins,cn=config |
| Valid Values | on/off |
| Default Value | off |
| Syntax | Boolean |
| Example | nsslapd-pluginAllowReplUpdates: on |

