MicroShift is Developer Preview software only. For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Developer Preview software, see Developer Preview Support Scope.
Chapter 2. Architecture
Learn the specifics of Red Hat build of MicroShift architecture including design intent, how it differs from OpenShift Kubernetes Engine, and API compatibility.
2.1. Architectural design
Red Hat build of MicroShift is a single-node container orchestration runtime designed to extend the benefits of using containers for running applications to low-resource edge environments. Because Red Hat build of MicroShift is primarily a platform for deploying applications, only the APIs and features essential to operating in edge and small form factor computing environments are included.
For example, Red Hat build of MicroShift contains only the following Kubernetes cluster capabilities:
- Networking
- Ingress
- Storage
- Helm
Red Hat build of MicroShift also provides the following Kubernetes functions:
- Orchestration
- Security
To optimize your deployments, use Red Hat build of MicroShift with a compatible operating system, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) for Edge. Using Red Hat build of MicroShift and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) for Edge together forms Red Hat Device Edge. Virtual machines are handled by the operating system in Red Hat build of MicroShift deployments.
Figure 2.1. Red Hat build of MicroShift as part of Red Hat Device Edge.

The following operational differences from OpenShift Kubernetes Engine can help you understand where Red Hat build of MicroShift can be deployed:
2.2. Key differences from OpenShift Kubernetes Engine
- Devices with Red Hat build of MicroShift installed are self-managing
- Compatible with RPM-OStree-based systems
- Uses only the APIs needed for essential functions, such as security and runtime controls
-
Enables a subset of commands from the OpenShift CLI (
oc) tool - Does not support workload high availability (HA) or horizontal scalability with the addition of worker nodes
Figure 2.2. Red Hat build of MicroShift differences from OpenShift Kubernetes Engine.
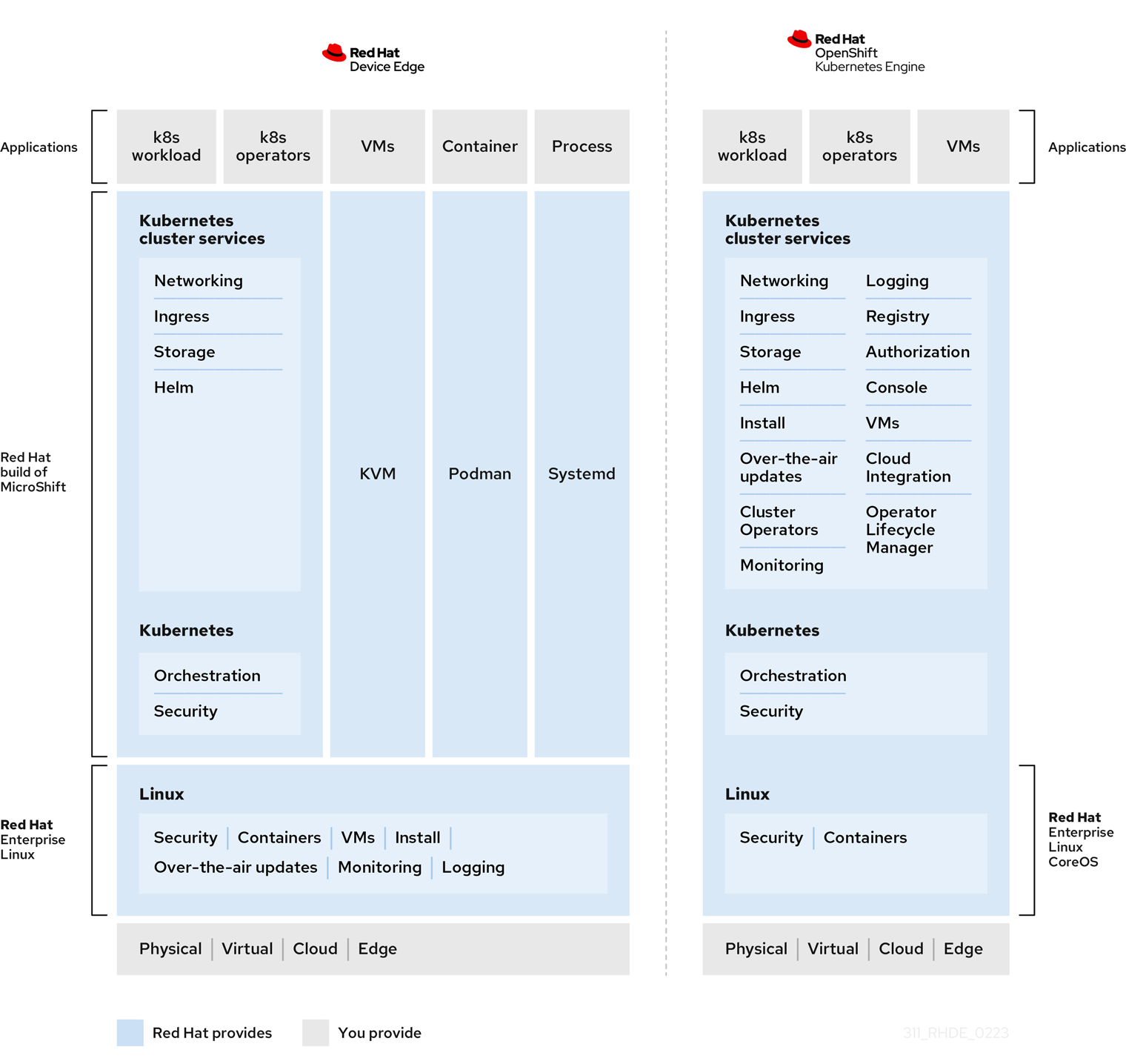
Figure 2 shows that OpenShift Kubernetes Engine has the same cluster capabilities as Red Hat build of MicroShift, and adds the following:
- Install
- Over-the-air updates
- Cluster Operators
- Operator Lifecycle Manager
- Monitoring
- Logging
- Registry
- Authorization
- Console
- Cloud Integration
- Virtual Machines (VMs) through OpenShift Virtualization
In OpenShift Kubernetes Engine and other OpenShift Container Platform deployments, all of the components from the operating system through the cluster capabilities work as one comprehensive unit, with full cluster services for a multi-node Kubernetes workload. With Red Hat build of MicroShift, functions such as over-the-air-updates, monitoring, and logging, are performed by the operating system.
2.3. Red Hat build of MicroShift OpenShift APIs
In addition to standard Kubernetes APIs, Red Hat build of MicroShift includes a small subset of the APIs supported by OpenShift Container Platform.
| API | API group |
|---|---|
| route.openshift.io/v1 | |
| security.openshift.io/v1 |
2.4. Red Hat build of MicroShift Kubernetes APIs
The Kubernetes API is fully accessible within Red Hat build of MicroShift and can be managed with the kubectl command-line tool or the OpenShift Container Platform CLI tool (oc). The oc binary is compatible with kubectl and offers a set of features that can be used with Red Hat build of MicroShift. Installing both tools to use with Red Hat build of MicroShift can help you access all of the resources you need to work with your deployments.

