Web console
Read more to learn how to use console components.
Abstract
Chapter 1. Web console
Learn how to access the console for your Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management console and learn how to use console components.
1.1. Accessing your console
From the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform web console, you can access the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console. You can also access the console from your terminal after installation. See all the options for accessing your console.
1.1.1. From the OpenShift Container Platform web console
- For OpenShift Container Platform 4.8 and later, you can launch Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management from the perspective switcher near the navigation menu.
- For earlier versions of OpenShift Container Platform, you can click the Application launcher in the header and choose the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes option.
You can also access the console from the left-hand navigation.
- Click Networking > Routes
-
From the Project menu, select the namespace where Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes is installed. The default namespace is
open-cluster-management. -
Click the
multicloud-consoleURL from theLocationcolumn.
1.1.2. From the Red Hat OpenShift CLI:
-
While logged in to Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform and after you install Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes, run the following command to find the route. Here,
<namespace-from-install>is the namespace where you installed the product:
oc get routes -n <namespace-from-install>
-
Find the
open-cluster-managementname and theHost/Portcolumns to get your URL.
Learn more about the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console, see Web console.
1.2. Console overview
Learn more about console components that you can use to view, manage, or customize your console.
See the following image of the Navigation from the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console, which is described in more detail later in each section. See that the navigation represents major production function.
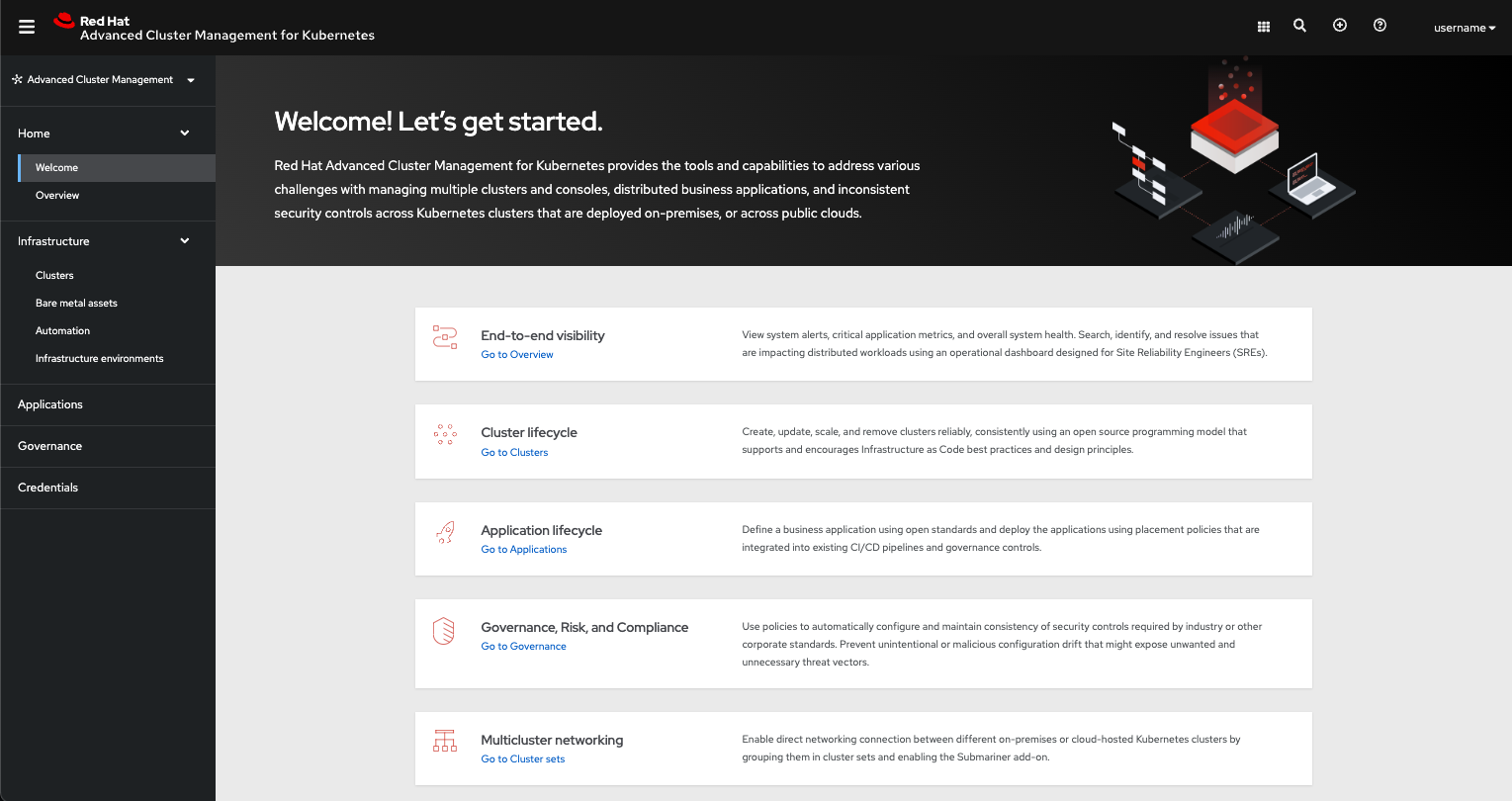
Note: Visual Web Terminal is removed as of this release and Infrastructure environments is an additional tab from Infrastructure.
1.2.1. Console components
To learn about Search, see Search in the console
1.2.2. Home
From the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes Home page, you get more information about the product and you can access header features, as well as the pages for the major components of the product.
Access the Welcome page and the Overview, which gives you visibility into your clusters.
You can view the following information about your clusters on the Overview dashboard:
- Metric data from your managed clusters by selecting the Grafana link
- Cluster, node, and pod counts across all clusters and for each provider
- Cluster status
- Cluster compliance
- Pod status
Additionally, you can view many clickable elements on the dashboard open a search for related resources. Click on a provider card to view information for clusters from a single provider.
- Select Grafana to access the Grafana dashboard.
- Click Add provider connections to access the Clusters page.
1.2.3. Infrastructure
From Clusters, you can create new clusters or import existing clusters. From Bare metal assets, you can create and import assets. From Automation, you can create an Ansible template.
For more information about managing clusters, see Managing your clusters with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes.
Additionally, see specific information on these cluster types at Creating and modifying bare metal assets and Configuring Ansible Tower tasks to run on managed clusters.
1.2.4. Applications
Click Create application to edit a .yaml file and create your application. Click Overview and Advanced configuration to view the information of each application. For more information about application resources, see Managing applications.
1.2.5. Governance
Use the Governance dashboard to create and manage policies and policy controllers. Click Create policy to edit a .yaml file and create your application. For more information, see Governance.
1.2.6. Credentials
View your credentials and click Add credential to select and add new cloud provider credentials.
1.3. Search in the console
For Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes, search provides visibility into your Kubernetes resources across all of your clusters. Search indexes the Kubernetes resources and the relationships to other resources. You can create a searchcustomization custom resource (CR) to define the storage settings for search persistence if you want to change the storage class and storage size.
1.3.1. Search components
The search architecture is composed of the following components:
-
Collector: Watches the Kubernetes resources and creates an index. The
search-collectorcomputes relationships for resources within the managed cluster. -
Aggregator: Receives data from the collector and writes to a database. The
search-aggregatorwatches resources in the hub cluster, computes multicluster relationships, and tracks the activity from connected collectors. - Search API: Provides access to the data in the search index and enforces role-based access control.
Search is enabled by default. Search is also enabled when you provision or manually import a managed cluster. If you want to disable search on your managed cluster, see Modifying the klusterlet add-ons settings of your cluster for more information.
1.3.2. Search customization
When you install Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management, the product is configured to persist the data in-memory to a file system. The StatefulSet search-redisgraph deploys the Redisgraph pod, which mounts the persistent volume named persist. If your cluster has a defined default storage class, the search component creates a Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) of 10Gi on the default storage class. If a default storage class does not exist in your cluster, search saves the index in an empty directory (emptyDir).
You can customize the storage settings for search by creating the searchcustomization CR. Search customization is namespace-scoped and located where search is installed in the hub cluster. View the following example of the search customization CR:
apiVersion: search.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1 kind: SearchCustomization metadata: name: searchcustomization namespace: open-cluster-management spec: persistence: true storageClass: gp2 storageSize: 12Gi
Run the following command to view search customization CRD:
oc get crd searchcustomizations.search.open-cluster-management.io -o yaml
You can disable persistence by updating the persistence flag to false in the customization CR, which turns off saving search index to the file system. A status for persistence can be retrieved from the search operator (searchoperator) CR. Run the following command to view search operator CR: oc get searchoperator searchoperator -o yaml.
1.3.2.1. Options to increase the redisgraph memory
Redisgraph is an in-memory database that needs linear growth of memory as the number of objects are cached. A Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management cluster with many managed clusters, or with a large number of Kubernetes objects require limit memory updates for the redisgraph pod (search-redisgraph-0).
By default, the redisgraph pod (search-redisgraph-0) is deployed with a memory limit of 4Gi. If you are managing larger clusters, you might need to increase this limit by editing the redisgraph_resource.limit_memory for the searchoperator in the hub cluster namespace. For example, you can update the limit to 8Gi with the following command:
oc patch searchoperator searchoperator --type='merge' -p '{"spec":{"redisgraph_resource":{"limit_memory":"8Gi"}}}'
After the change is made, the search-redisgraph pod automatically restarts with the updated configuration.
1.3.3. Queries in the console
You can type any text value in the Search box and results include anything with that value from any property, such as a name or namespace. Users are unable to search for values that contain an empty space.
For more specific search results, include the property selector in your search. You can combine related values for the property, for a more precise scope of your search. For example, search for cluster:dev red to receive results that match the string "red" in the dev cluster.
View the following steps to make queries with search:
- Click Search in the navigation menu.
Type a word in the Search box, then Search finds your resources that contain that value.
- As you search for resources, you receive other resources that are related to your original search result, which help you visualize how the resources interact with other resources in the system.
- Search returns and lists each cluster with the resource that you search. For resources in the hub cluster, the cluster name is displayed as local-cluster.
-
Your search results are grouped by
kind, and each resourcekindis grouped in a table. Your search options depend on your cluster objects. You can refine your results with specific labels. Search is case-sensitive when you query labels. See the following examples: name, namespace, status, and other resource fields. Auto-complete provides suggestions to refine your search. See the following example:
-
Search for a single field, such as
kind:podto find all pod resources. -
Search for multiple fields, such as
kind:pod namespace:defaultto find the pods in the default namespace.
-
Search for a single field, such as
Notes:
-
You can also search with conditions by using characters, such as
>, >=, <, <=, !=. When you search for more than one property selector with multiple values, the search returns either of the values that were queried. View the following examples:
-
When you search for
kind:pod name:a, any pod namedais returned. -
When you search for
kind:pod name:a,b, any pod namedaorbare returned. -
Search for
kind:pod status:!Runningto find all pod resources where the status is notRunning. -
Search for
kind:pod restarts:>1to find all pods that restarted at least twice.
-
When you search for
- If you want to save your search, click the Save search icon.
1.3.3.1. Query ArgoCD applications
When you search for an ArgoCD application, you are directed to the Applications page. Complete the following steps to access the ArgoCD application from the Search page:
- Log in to your Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub cluster.
- From the console header, select the Search icon.
-
Filter your query with the following values:
kind:applicationandapigroup:argoproj.io - Select an application to view. The Application page displays an overview of information for the application.
Learn more about the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console, see Web console.

