Chapter 2. Cluster lifecycle architecture
There are two main types of clusters: hub clusters and managed clusters.
The hub cluster is the main cluster with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes installed on it. You can create, manage and monitor other Kubernetes clusters with the hub cluster.
The managed clusters are Kubernetes clusters that are managed by the hub cluster. You can create some clusters by using the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub cluster, while you can also import existing clusters to be managed by the hub cluster.
The following diagram shows the components that are installed with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for cluster management:
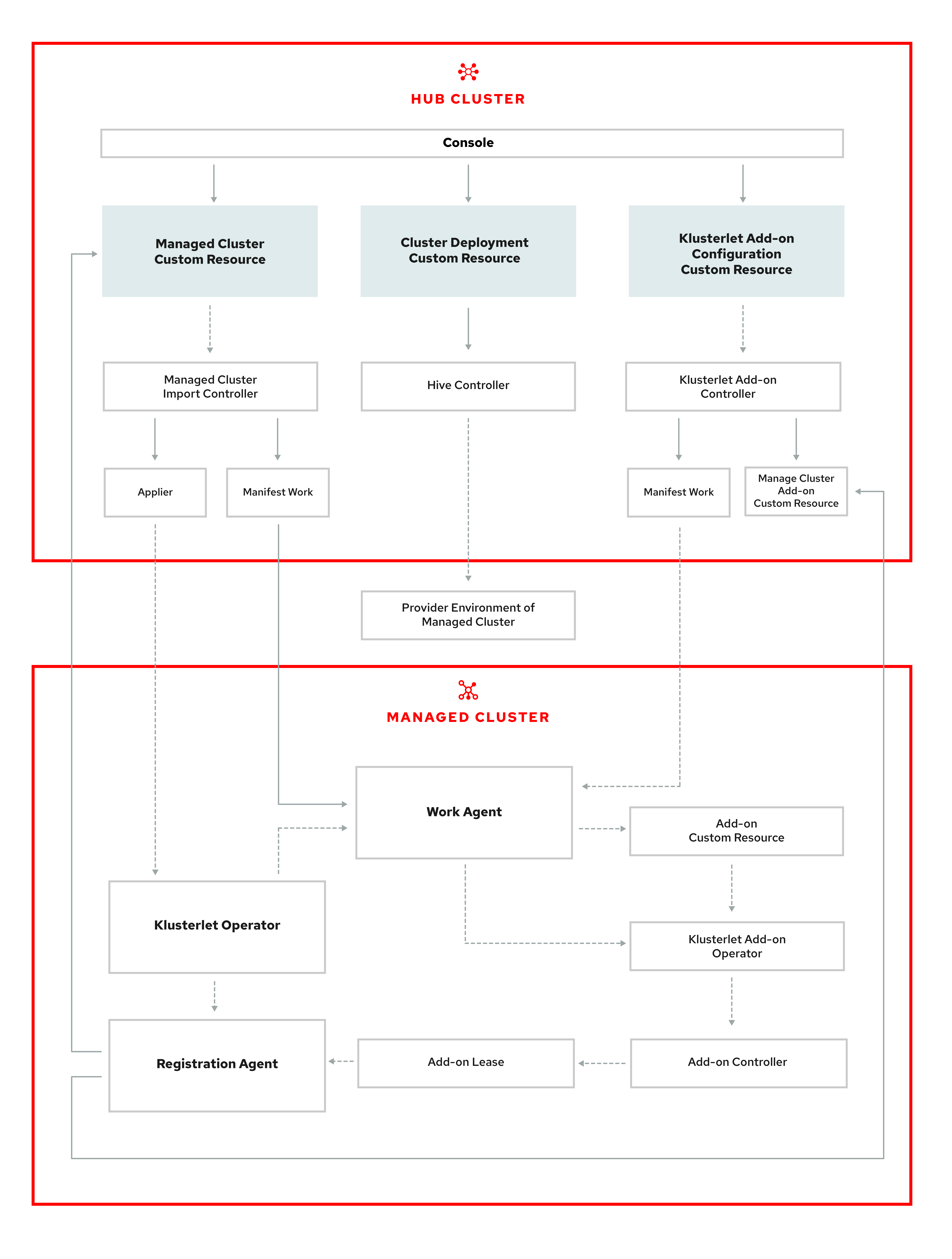
The components of the cluster lifecycle management architecture include the following items:
Components on the hub cluster:
- Console: Provides a web-based interface to manage the cluster lifecycle of the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management managed clusters.
- Hive Controller: Provisions the clusters that you create with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management. The Hive Controller also detaches and destroys managed clusters that were created by Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management.
- Managed Cluster Import Controller: Deploys the klusterlet operator to the managed clusters.
- Klusterlet Add-on Controller: Deploys the klusterlet add-on operator to managed clusters.
Components on the managed cluster:
- Klusterlet Operator: Deploys the registration and work controllers on the managed cluster.
- Registration Agent: Registers the managed cluster with the hub cluster.
- Work Agent: Applies the manifest work to the managed cluster.
- Klusterlet Add-on Operator: Deploys the add-on components.

