Visual Studio Code Extension Guide
Identify and resolve migration issues by analyzing your applications with the Migration Toolkit for Applications extension for Visual Studio Code.
Abstract
Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code, documentation, and web properties. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Because of the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be implemented gradually over several upcoming releases. For more details, see our CTO Chris Wright’s message.
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. About the MTA extension for Microsoft Visual Studio Code
You can migrate and modernize applications by using the Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA) extension for Microsoft Visual Studio Code.
The MTA extension analyzes your projects using customizable rulesets, marks issues in the source code, provides guidance to fix the issues, and offers automatic code replacement, if possible.
The MTA extension is also compatible with Visual Studio Codespaces, the Microsoft cloud-hosted development environment.
1.2. About the Migration Toolkit for Applications
What is the Migration Toolkit for Applications?
Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA) accelerates large-scale application modernization efforts across hybrid cloud environments on Red Hat OpenShift. This solution provides insight throughout the adoption process, at both the portfolio and application levels: inventory, assess, analyze, and manage applications for faster migration to OpenShift via the user interface.
MTA uses an extensive questionaire as the the basis for assessing your applications, enabling you to estimate the difficulty, time, and other resources needed to prepare an application for containerization. You can use the results of an assessment as the basis for discussions between stakeholders to determine which applications are good candidates for containerization, which require significant work first, and which are not suitable for containerization.
MTA analyzes applications by applying one or more rulesets to each application considered to determine which specific lines of that application must be modified before it can be modernized.
MTA examines application artifacts, including project source directories and application archives, and then produces an HTML report highlighting areas needing changes. MTA supports many migration paths including the following:
- Upgrading to the latest release of Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform
- Migrating from Oracle WebLogic or IBM WebSphere Application Server to Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform
- Containerizing applications and making them cloud-ready
- Migrating from Java Spring Boot to Quarkus
- Upgrading from OpenJDK 8 to OpenJDK 11
- Upgrading from OpenJDK 11 to OpenJDK 17
- Migrating EAP Java applicatons to Azure App Service
- Migrating Spring Boot Java applications to Azure App Service
For more information about use cases and migration paths, see the MTA for developers web page.
How does the Migration Toolkit for Applications simplify migration?
The Migration Toolkit for Applications looks for common resources and known trouble spots when migrating applications. It provides a high-level view of the technologies used by the application.
MTA generates a detailed report evaluating a migration or modernization path. This report can help you to estimate the effort required for large-scale projects and to reduce the work involved.
Chapter 2. Installing the MTA extension for Visual Studio Code
You can install the MTA extension for Visual Studio Code (VS Code).
Prerequisites
Java Development Kit (JDK) installed. MTA supports the following JDKs:
- OpenJDK 11
- Oracle JDK 11
- 8 GB RAM
-
macOS installation: the value of
maxprocmust be2048or greater.
Procedure
Set the environmental variable
JAVA_HOME:$ export JAVA_HOME=jdk11
- In VS Code, click the Extensions icon on the Activity bar to open the Extensions view.
-
Enter
Migration Toolkit for Applicationsin the Search field. Select the Migration Toolkit for Applications extension and click Install.
The MTA extension icon (
 ) is displayed on the Activity bar.
) is displayed on the Activity bar.
Chapter 3. Analyzing your projects with the MTA extension
You can analyze your projects with the MTA extension by creating a run configuration and running an analysis.
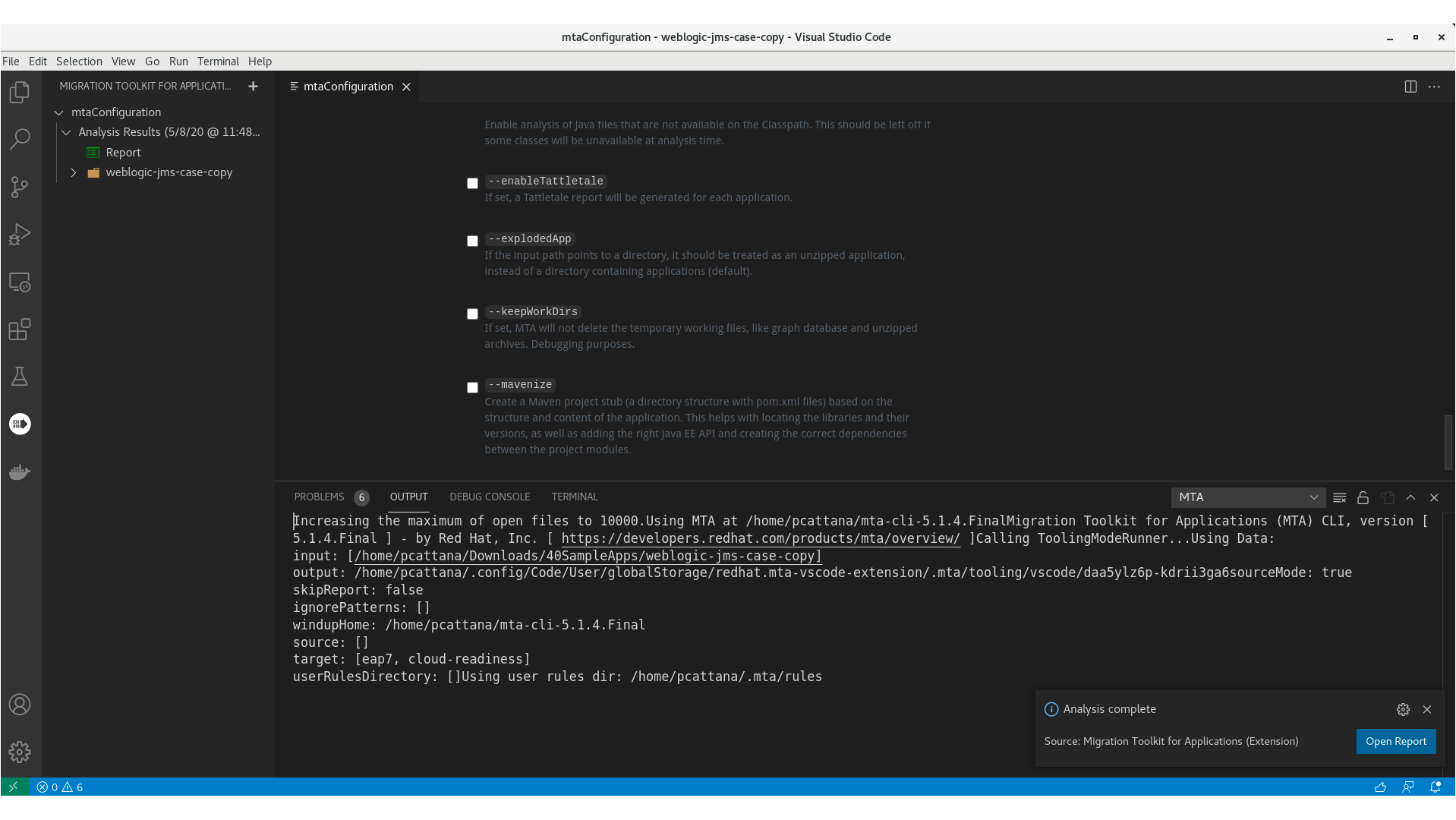
3.1. MTA extension interface
The interface of the Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA) extension is designed to make it easier for you to find information and perform actions:
- In the left pane, you can see a directory tree named Analysis Results with a report icon at its top. You can click the icon to open the MTA report in your browser. Beneath the report icon are the other elements of the tree: the applications analyzed by MTA, the rulesets used, and the issues discovered by the analysis.
- In the upper right pane, you can configure an analysis.
- In the lower right pane, you can see the settings of the configuration, including source, target, and advanced options. You can view the progress of an analysis in this pane. When the analysis is completed, you can click the Open Report button to open the MTA report, which describes any issues you need to address before you migrate or modernize your application. For more information, see Reviewing the reports in the CLI Guide.
Figure 3.1. MTA extension interface
3.2. Configuring a run configuration
You can configure multiple run configurations to run against each project you import to VS Code.
Prerequisites
-
windup-cliexecutable installed. You can download thewindup-cliexecutable from mta download.
Procedure
-
In Extensions view, click the Migration Toolkit for Applications icon (
 ) on the Activity bar.
) on the Activity bar.
- Click the + (plus sign) next to Migration Toolkit for Applications to add a run configuration.
Complete the following configuration fields:
- Name: Enter a meaningful name for the analysis configuration or accept the default.
-
cli: Enter the path to the cli executable. For example:
$HOME/mta-cli-6.0.1.GA-redhat/bin/windup-cli. Input: Set to the path of the project that you have open within your IDE by clicking Add and doing one of the following:
- Enter the input file or directory and press Enter.
- Click Open File Explorer and select the directory.
- Target: Select one or more target migration paths.
Right-click the run configuration and select Run.
When the analysis is completed, you can click the Open Report button to open the MTA report, which describes any issues you need to address before you migrate or modernize your application. For more information, see Reviewing the reports in the CLI Guide.
Chapter 4. Reviewing and resolving migration issues
You can review and resolve migration issues identified by the MTA extension in the left pane.
4.1. Reviewing issues
You can use the MTA extension icons to prioritize issues based on their severity. You can also see which issues have a Quick Fix automatic code replacement.
Procedure
- Select a run configuration directory on the left pane.
- Expand its folders to view the Hints generated for each application file.
- Select a hint to view the source code.
- Right-click a hint and select View Details to view the Rule ID and other information.
Prioritize issues based on the following icons, which are displayed next to each hint:
-
 : The issue must be fixed for a successful migration.
: The issue must be fixed for a successful migration.
-
 : The issue might need to be addressed during migration.
: The issue might need to be addressed during migration.
-
 : The issue is optional to fix for migration. This icon is also used to indicate any Quick Fixes available for an issue.
: The issue is optional to fix for migration. This icon is also used to indicate any Quick Fixes available for an issue.
-
4.2. Resolving issues
You can resolve issues by doing one of the following:
- Using a Quick Fix automatic code replacement
- Editing the code of a file with a hint
You can keep track of resolved issues by using the Delete or Mark as Complete options. Files marked deleted or completed will be analyzed again the next time you analyze a project that contains them.
4.2.1. Using a Quick Fix
You can use a Quick Fix automatic code replacement to save time and ensure consistency in resolving repetitive issues.
Procedure
-
In the left pane, right-click an issue that has the Quick Fix icon (
 ) and select Preview Quick Fix.
) and select Preview Quick Fix.
- To accept the suggested fix, right-click the issue again and select Apply Quick Fix.
- Optional: Right-click the issue and select Mark as Complete or Delete.
4.2.2. Editing the code of a file
You can edit the file of a project imported to VS Code.
Procedure
- In the left pane, right-click an issue and select Open Code.
- Make any changes needed to the code and save the file.
- Optional: Right-click the issue and select Mark as Complete or Delete.

